Home>Events & Info>Opera>What Is The Difference Between A Musical And An Opera


Opera
What Is The Difference Between A Musical And An Opera
Published: January 6, 2024
Discover the key distinctions between a musical and an opera, exploring the genre, vocal styles, and narrative structures. Understand the essence of opera and its significance in the world of performing arts.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Music has the incredible power to touch our souls and evoke a wide range of emotions. It has been used as a storytelling medium for centuries, bringing stories to life through melody and lyrics. Two popular forms of musical theater that showcase this power are musicals and operas. While both involve music and performance, there are distinct differences between the two. In this article, we will explore the nuances of musicals and operas, shedding light on their unique characteristics and what sets them apart.
A musical, also known as a musical theater or a musical comedy, is a form of theatrical performance that combines spoken dialogue, acting, singing, and dance. It is characterized by a strong emphasis on storytelling through music and lyrics. Musicals often include a wide range of musical styles, including pop, rock, jazz, and classical music. The songs in a musical serve as a means of advancing the plot, expressing the characters’ emotions, and providing memorable moments for the audience.
On the other hand, an opera is a form of musical theater that originated in Italy in the late 16th century. It is a theatrical work entirely sung from start to finish, with little or no spoken dialogue. Operas are typically accompanied by an orchestra and feature elaborate sets, costumes, and staging. The music in an opera is composed specifically for the production and is often performed in an operatic vocal style, characterized by its richness, power, and control.
Now that we have a general understanding of what musicals and operas are, let’s delve deeper into the specific elements and characteristics that define each form. By exploring their vocal styles, narrative structures, production and performance aspects, and their popularity and audience reach, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the difference between musicals and operas.
Definition of a Musical
A musical is a form of theatrical performance that combines elements of spoken dialogue, music, singing, and dance to tell a story. Musicals have been a popular form of entertainment for centuries, captivating audiences with their vibrant characters, catchy songs, and engaging narratives. What sets musicals apart from other forms of theater is their seamless integration of music and lyrics into the storytelling process.
The music in a musical serves multiple purposes. It helps to advance the plot by expressing the characters’ thoughts, emotions, and motivations in a way that words alone cannot. The songs also provide memorable moments, often serving as showstoppers that leave a lasting impression on the audience. Additionally, the music in a musical sets the tone and enhances the overall atmosphere of the production, creating a more immersive experience.
Musicals often feature a wide range of musical styles, allowing for diversity and versatility in the storytelling. From lively tap numbers and catchy show tunes to emotional ballads and powerful ensemble pieces, musicals incorporate various genres of music to cater to different moods and themes within the narrative. This eclectic mix of musical styles adds depth and dimension to the storytelling, appealing to a broad spectrum of audiences.
In addition to the music, another defining element of musicals is the use of dance. Choreographed dance sequences are commonly featured in musicals, adding an extra layer of visual excitement and artistic expression to the performance. Dance numbers can vary from energetic ensemble routines to intimate duets, showcasing the talent and skill of the performers while enhancing the overall spectacle of the production.
While original musicals are created specifically for the stage, there are also adaptations of popular works such as books, movies, or historical events. These adaptations bring the familiar stories to life through music and performance, offering a fresh perspective and adding a new dimension to the source material.
In summary, a musical is a dynamic form of theatrical performance that combines spoken dialogue, music, singing, and dance to create a captivating and entertaining storytelling experience. With its diverse musical styles, memorable songs, and engaging choreography, the musical genre continues to captivate audiences around the world.
Definition of an Opera
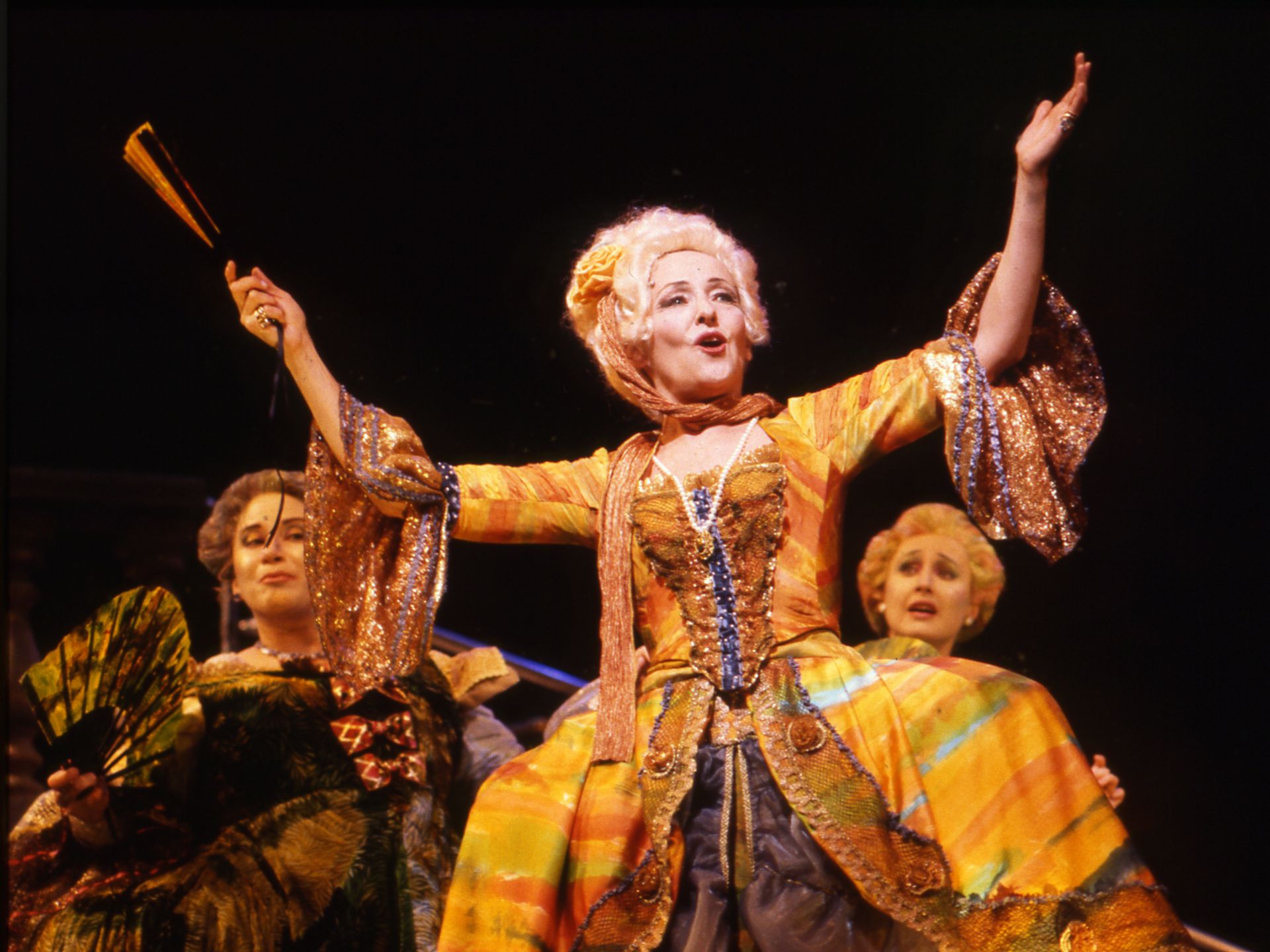
An opera is a form of musical theater that originated in Italy in the late 16th century. It is a theatrical work in which the entire story is sung from beginning to end, with little or no spoken dialogue. Operas are known for their grandiose and dramatic nature, incorporating elaborate sets, costumes, and staging to bring the story to life.
One of the distinguishing features of an opera is its use of operatic vocal style. Operatic singing is characterized by its richness, power, and control. Singers in opera, known as opera singers or operatic vocalists, undergo extensive vocal training to master the techniques necessary to perform in this demanding genre. The vocal range and flexibility required in opera allow the performers to convey intense emotions and deliver powerful performances that can resonate with the audience on a profound level.
Another notable aspect of opera is its focus on classical music. The music in an opera is typically composed specifically for the production, with the composer crafting melodies, harmonies, and orchestrations that align closely with the narrative and the emotions it seeks to evoke. The music in opera often includes arias, which are solo songs that highlight the character’s emotions, as well as ensembles and choruses that bring together multiple voices to create depth and complexity.
Alongside the music, opera places a strong emphasis on the visual aspects of the performance. Elaborate sets, costumes, and staging are integral to opera productions, creating a visually stunning and immersive experience for the audience. From lavish period costumes to intricately designed stage sets, every aspect of the visual presentation in opera contributes to the overall storytelling and aesthetic appeal.
Operas encompass a wide range of genres, from tragic and dramatic operas like “Carmen” and “La Traviata” to comedic operas like “The Marriage of Figaro” and “The Barber of Seville.” The variety in opera allows for exploration of diverse themes, emotions, and storytelling styles, ensuring there is something for every taste and preference.
Over the centuries, opera has evolved and adapted, incorporating contemporary elements and pushing the boundaries of traditional opera conventions. Today, opera continues to be performed in opera houses and theaters around the world, captivating audiences with its powerful music, captivating storytelling, and stunning visual spectacle.
In summary, an opera is a form of musical theater characterized by its sung dialogue, operatic vocal style, classical music compositions, and emphasis on visual spectacle. With its rich history and enduring popularity, opera remains an art form that continues to inspire and enchant audiences.
Musical Elements
Musicals are a complex art form that combines various elements to create a captivating and cohesive theatrical experience. From music and lyrics to storytelling and choreography, each element plays a crucial role in the overall impact of a musical performance.
The music in a musical is the backbone of the production. Composers create melodies and harmonies that not only complement the storyline but also evoke the intended emotions. The music in a musical spans a wide range of genres, from energetic show tunes and catchy pop-inspired numbers to heartfelt ballads and stirring ensemble pieces. These songs serve as a means of expressing the characters’ thoughts, emotions, and motivations while advancing the storyline.
The lyrics in a musical are as important as the music itself. Lyricists craft words that not only fit seamlessly with the melodies but also convey the emotions and messages of the characters. Clever wordplay, memorable phrases, and powerful storytelling through lyrics enrich the narrative and create moments that resonate with the audience long after the performance ends.
Storytelling is another integral element of a musical. The plot of a musical is often developed through a combination of spoken dialogue and the songs. The dialogue provides context, while the songs delve deeper into the characters’ thoughts, inner conflicts, and relationships. The narrative structure in musicals can vary, ranging from linear stories to non-linear narratives that utilize flashbacks or multiple perspectives. The cohesive combination of dialogue and song creates a unique storytelling experience that engages the audience both emotionally and intellectually.
In addition to the music and storytelling, choreography plays a significant role in many musicals. Dance numbers are carefully choreographed to enhance the energy, emotions, and visual impact of a performance. From large-scale ensemble dances to intimate duets, the choreography adds layers of expression and excitement, elevating the overall theatrical experience.
Visual elements such as costumes, sets, lighting, and special effects also contribute to the overall impact of a musical. The costumes help to establish the time period, setting, and character identities, creating a visually captivating ensemble on stage. Sets provide the backdrop for the story, transporting the audience to different locations and creating a sense of atmosphere. Lighting and special effects are used to enhance dramatic moments, create mood changes, and highlight key moments in the performance.
Collaboration is crucial in bringing all these musical elements together. The creative team, including the director, music director, choreographer, set designer, and lighting designer, work in tandem to ensure that each element harmoniously supports the overarching vision of the musical. The performers, both actors and musicians, bring the music, lyrics, and choreography to life through their talent and interpretation, creating a truly immersive and unforgettable experience for the audience.
In essence, the combination of music, lyrics, storytelling, choreography, and visual elements in musicals results in a vibrant and multi-dimensional art form that not only entertains but also communicates profound emotions and messages. The careful integration and harmony of these elements contribute to the unique and enduring appeal of musicals.
Vocal Styles
Vocal performance is a key component of both musicals and operas, but the vocal styles employed in each differ significantly. While musicals showcase a variety of contemporary vocal styles, operas emphasize classical operatic singing techniques. These contrasting vocal styles contribute to the unique character and atmosphere of each genre.
In musicals, the vocal styles can vary depending on the genre, time period, and character requirements. The songs in musicals often reflect popular music styles such as pop, rock, jazz, or even country. The vocal performances in musicals are characterized by a more contemporary and natural style of singing. The singers aim to connect with the audience through emotive and expressive vocals that convey the emotions and intentions of the characters. The emphasis in musical theater is on clear diction, proper microphone technique, and compelling storytelling through song.
In contrast, operas demand a more specialized vocal technique known as operatic singing. Operatic vocalists undergo rigorous training to develop their voices and master the technical aspects of the genre. The singers in opera possess a wide vocal range, enabling them to sing demanding arias and intricate melodic lines. Operatic singing requires a considerable amount of breath control, vocal projection, and resonance. The performers aim to convey intense emotions, showcase the beauty and power of their voices, and bring the characters to life on stage. The operatic vocal style is characterized by a clarity of enunciation, an evenness of tone, and a strong ability to sustain long phrases.
While musicals emphasize the use of amplification systems and microphones to enhance the sound, opera predominantly relies on natural, unamplified vocal projection. In opera houses, the acoustics are designed to allow the singers’ voices to carry throughout the venue without the need for amplification.
Both musicals and operas require skilled performers who can communicate the depth of emotions through their voices. However, the vocal techniques and styles employed are distinct, catering to the specific requirements and traditions of each genre.
It’s worth noting that in recent years, certain musicals have incorporated operatic elements or blended genres, resulting in a fusion of vocal styles. This crossover has enriched the musical theater landscape, bringing different vocal techniques and colors to the forefront and captivating audiences with the diversity of vocal performances.
Overall, while musicals showcase a more contemporary singing style that connects with a broader audience, opera relies on the centuries-old tradition of operatic singing, with its emphasis on vocal range, power, and control. The contrasting vocal styles add depth and nuance to the storytelling and musical experience in both genres.
Narrative Structure
The narrative structure is a fundamental element in both musicals and operas, shaping the way the story unfolds and the audience engages with the characters and plot. While both genres utilize storytelling techniques, their narrative structures differ in significant ways.
In musicals, the narrative structure often follows a linear progression, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. The storyline is conveyed through a combination of spoken dialogue and musical numbers. The songs in musicals serve as a means of advancing the plot, expressing the characters’ thoughts and emotions, and providing pivotal moments of character development. The narrative in a musical can be driven by a central conflict, character arcs, or thematic exploration. The storylines in musicals can range from lighter, comedic fare to more dramatic and emotionally intense narratives.
Alternatively, operas tend to employ a more episodic or non-linear narrative structure. Traditionally, operas consist of multiple acts divided into scenes, with each scene focused on a particular interaction or event. The progression of the story may not always be linear, as operas may include flashbacks, time jumps, or multiple storylines intertwining. The emphasis in opera is often placed on the emotional journey and exploration of themes rather than a linear plot. The arias, ensemble pieces, and choruses in opera serve as moments of introspection, reflection, or commentary on the events unfolding on stage.
The narrative structure in both musicals and operas is supported by the lyrics and music. In musicals, the songs are often integrated into the storyline, with characters expressing their thoughts and emotions through song. The lyrics provide additional context and depth to the narrative, enhancing the audience’s connection to the characters and their journey. In opera, the libretto, or the text of the opera, is crafted to align with the musical composition, ensuring that the themes and emotions are conveyed through both the vocal and instrumental elements.
It’s important to note that there are variations within each genre, and contemporary works may blur the lines between traditional narrative structures. Some modern musicals incorporate non-linear storytelling techniques, while certain operas embrace a more straightforward, linear plot. The evolving nature of both genres allows for experimentation and innovation, pushing the boundaries of narrative structure in musical theater.
In summary, while musicals tend to follow a linear narrative structure with a clear progression of events, operas often utilize episodic or non-linear storytelling techniques. The integration of music and lyrics enhances the narrative in both genres, allowing audiences to form deep emotional connections with the characters and themes explored on stage.
Production and Performance
The production and performance aspects of musicals and operas are crucial in bringing the stories to life on stage. From the casting and staging to the technical elements and orchestration, the production and performance contribute to the overall impact and success of both genres.
In musicals, the production process begins with the casting of performers who possess the acting, singing, and dancing abilities necessary for the roles. Once the cast is assembled, rehearsals commence, during which the actors work closely with the director, choreographer, and musical director to develop their characters, perfect their performances, and learn the choreography and vocal arrangements.
The staging of a musical involves the design and creation of sets, costumes, lighting, and special effects. Set designers and scenic artists collaborate to construct the physical environments that transport the audience to different locations within the story. Costume designers work closely with the creative team to develop outfits that not only reflect the characters’ personalities and time period but also allow for ease of movement during performances. Lighting designers use a combination of techniques and effects to enhance mood, highlight key moments, and create visual interest throughout the production.
In terms of music, musicals often require a live orchestra or band to perform the music alongside the actors. Musical directors conduct and manage the musicians, ensuring that the music aligns seamlessly with the performances on stage. Sound technicians also play a vital role in balancing the actors’ vocals with the music and ensuring that the sound is clear and well-balanced throughout the venue.
Operas, on the other hand, require a significant investment in terms of production. Due to the complex vocal and musical requirements, opera houses often have larger stages, detailed set designs, and grand costumes to accommodate the scale and visual spectacle of the performances. The technical aspects of opera productions, such as set changes, intricate lighting designs, and complex scene transitions, require meticulous planning and coordination.
Performing in an opera demands a high level of vocal skill and endurance from the singers. The operatic vocalists undergo extensive training to develop their voices and techniques, enabling them to master the demanding music and perform with power and precision. The performers in operas must convey intense emotions and project their voices without the aid of microphones, utilizing vocal training techniques to ensure clarity and projection throughout the performance.
Both musicals and operas require performers with a range of talent, from lead actors and vocalists to ensemble members and dancers. The collaboration and synergy among the cast and crew are essential for creating a cohesive and engaging performance that captivates the audience.
Ultimately, the production and performance aspects of both musicals and operas work together to create a dynamic and captivating theatrical experience. The careful coordination of casting, staging, technical elements, and musical accompaniment ensures that the stories are brought to life with precision, passion, and professionalism.
Popularity and Audience
Musicals and operas have both garnered significant popularity and have captivated diverse audiences throughout history. While they share a common love for music and performance, their appeal and audience demographics can vary.
Musicals have enjoyed widespread popularity across different cultures and generations. Their versatility in incorporating various musical styles, relatable storytelling, and memorable songs has contributed to their broad appeal. Musicals have often found success on Broadway and in regional theaters, as well as through film adaptations and touring productions. The accessibility of musicals, both in terms of their relatable themes and their integration into popular culture, has helped them attract a wide range of audience members, from theater enthusiasts to casual viewers.
One of the reasons for the enduring popularity of musicals is their ability to resonate with audiences on an emotional level. The power of music and the universal themes explored in musicals—such as love, hope, dreams, and overcoming adversity—strike a chord with people of all ages and backgrounds. Additionally, the visual spectacle, choreography, and energetic performances often contribute to a highly entertaining and immersive experience that appeals to a broad audience.
Opera, on the other hand, has a more specific and dedicated following. Opera attracts those who appreciate the classical music traditions, complex vocal techniques, and the grandeur of the operatic style. Opera houses and theaters are renowned for their prestigious productions, and opera festivals draw audiences from around the world. The appreciation of opera often requires a deeper understanding and familiarity with the art form, as well as an appreciation for the intricacies of the vocal performances and the significance of the historical repertoire.
Despite its more niche appeal, opera has evolved and embraced new ideas and innovations to expand its audience base. Opera companies have introduced modern interpretations, translations, and adaptations to make the art form more accessible to a wider audience. Many opera houses also offer educational programs, outreach initiatives, and accessible ticketing options to encourage new and diverse audiences to experience the beauty and power of opera.
It is worth noting that there is considerable overlap in the audience base between musicals and operas. Many theater enthusiasts appreciate and enjoy both genres, recognizing the unique qualities and artistic merits of each. Additionally, the crossover between musicals and operas, where elements of both are combined or reimagined, further blurs the lines and attracts a broader spectrum of viewers.
Ultimately, the popularity of musicals and operas depends on a multitude of factors, including cultural context, the availability of productions, and the preferences and tastes of the audience. Both genres continue to bring joy, entertainment, and artistic expression to people around the world, with their enduring appeal and ability to transport audiences into captivating musical worlds.
Conclusion
In the world of musical theater, both musicals and operas hold a significant place, captivating audiences with their unique storytelling through music and performance. While they share the common foundation of utilizing music and vocals to convey emotions and advance narratives, musicals and operas have distinct characteristics that set them apart.
Musicals thrive on their ability to blend various musical genres, employing contemporary vocal styles and captivating choreographed dance sequences. With relatable stories, catchy songs, and dynamic staging, musicals appeal to a broad audience, creating a vibrant and engaging theatrical experience.
On the other hand, operas immerse audiences in the world of classical music and operatic vocal techniques. With their emphasis on arias, operas showcase the beauty and power of the human voice, accompanied by intricate orchestration and grand staging. The dedicated following of opera appreciates the richness and depth of the genre, as well as its historical significance.
While musicals and operas have their own unique qualities, it’s important to recognize that the boundaries between the two can sometimes blur. Contemporary productions may incorporate elements from both genres, resulting in fusion works that offer a richer and more diverse experience to audiences.
Regardless of the specific genre, both musicals and operas have made a lasting impact on the world of theater and continue to draw people in with their brilliant performances, inventive storytelling, and captivating music. Their enduring popularity speaks to the universal appeal of music and the power it holds to connect with our emotions and ignite our imagination.
Whether we find ourselves tapping our feet to a show-stopping musical number or sitting in awe of the soaring opera vocals, there is no denying the magic and transformative power of these art forms. Both musicals and operas have the ability to transport us to different worlds, evoke deep emotions, and create lasting memories.
So, whether you find yourself drawn to the joy and spectacle of a musical or the grandeur and emotional intensity of an opera, one thing is clear: the world of musical theater is a vast and captivating realm that continues to captivate and enchant audiences around the globe.