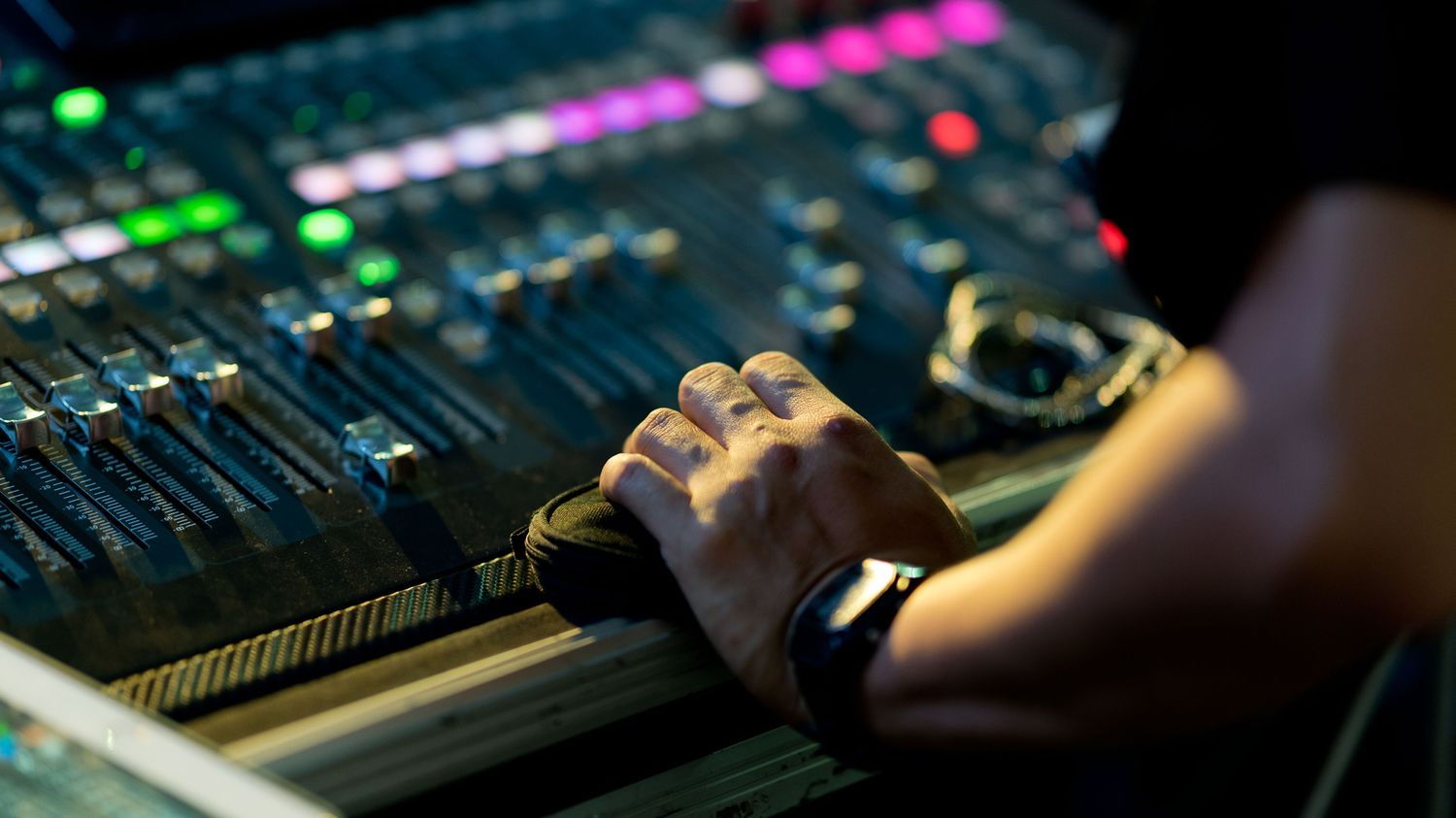
Home>Production & Technology>Sound Engineer>What Is It Like Being A Sound Engineer


Sound Engineer
What Is It Like Being A Sound Engineer
Published: March 7, 2024
Discover the world of sound engineering and gain insights into the unique experiences and challenges faced by sound engineers. Learn what it takes to thrive in this dynamic and creative profession.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Being a sound engineer is an exhilarating journey into the heart of music and audio production. It's a profession that seamlessly blends technical expertise with artistic creativity, offering a unique and fulfilling career path for those passionate about music and sound. Sound engineers play a pivotal role in the music and entertainment industry, shaping the way we experience and enjoy audio content across various platforms.
From recording studios to live concerts, sound engineers are the unsung heroes behind the scenes, meticulously crafting the perfect sonic landscape for audiences to immerse themselves in. Their expertise extends beyond simply operating equipment; they are the architects of sound, sculpting and refining audio to achieve the desired emotional impact and sonic clarity.
In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted world of sound engineering, exploring the education and training required, the diverse job responsibilities, the dynamic work environment, as well as the challenges and rewards that come with this profession. We will also uncover the essential skills and qualities that define a successful sound engineer, along with the myriad of career opportunities available in this ever-evolving field.
Join us on this captivating journey as we unravel the intricacies of being a sound engineer, shedding light on the captivating blend of technical prowess and artistic finesse that defines this remarkable profession.
Education and Training
Becoming a proficient sound engineer requires a blend of formal education, hands-on training, and a deep passion for audio technology. While there is no singular path to entering this field, acquiring a solid educational foundation is crucial for mastering the technical and creative aspects of sound engineering.
Many aspiring sound engineers pursue a degree in audio engineering, sound production, or a related field from accredited institutions or specialized audio engineering schools. These programs provide a comprehensive understanding of sound theory, acoustics, signal processing, and the operation of industry-standard audio equipment. Additionally, coursework often covers topics such as digital audio workstations (DAWs), mixing and mastering techniques, live sound reinforcement, and studio recording practices.
Hands-on training is equally vital in honing the practical skills essential for success in this field. Many educational programs incorporate internships, practicums, or cooperative work experiences, allowing students to gain real-world exposure to professional audio environments. This immersive learning experience provides invaluable insights into studio operations, live event production, and the intricacies of audio equipment maintenance and troubleshooting.
In addition to formal education, staying abreast of the latest advancements in audio technology is paramount for sound engineers. Continuous learning through workshops, seminars, and industry certifications ensures that professionals remain at the forefront of emerging audio trends and innovations. This ongoing commitment to skill development empowers sound engineers to adapt to evolving industry standards and harness cutting-edge tools and techniques in their craft.
Furthermore, cultivating a deep understanding of musical theory and composition can greatly enrich a sound engineer's capabilities. Familiarity with various musical genres, instrumentation, and performance styles enables sound engineers to communicate effectively with musicians and producers, facilitating seamless collaboration and elevating the overall quality of audio productions.
Ultimately, the journey to becoming a proficient sound engineer is a dynamic blend of formal education, practical training, and a perpetual thirst for knowledge. By embracing a multidisciplinary approach to learning and skill development, aspiring sound engineers can embark on a fulfilling and impactful career in the realm of audio engineering and production.
Job Responsibilities
As the architects of sound, sound engineers shoulder a diverse array of responsibilities that are integral to the creation, refinement, and delivery of high-quality audio content. Their role extends across various domains, including music production, live event engineering, broadcast media, and post-production facilities. Here's a comprehensive look at the multifaceted job responsibilities of sound engineers:
-
Recording and Mixing: Sound engineers are entrusted with the crucial task of capturing and refining audio recordings in studio environments. They meticulously set up microphones, calibrate recording equipment, and oversee the recording process to ensure optimal sound quality. Additionally, they employ their expertise in mixing and mastering to balance audio levels, apply effects, and enhance the sonic characteristics of recorded tracks.
-
Live Sound Reinforcement: In the realm of live events, sound engineers play a pivotal role in orchestrating the audio experience for audiences. From concerts and theatrical performances to corporate events and conferences, they are responsible for setting up sound systems, managing audio levels during performances, and ensuring seamless sound distribution across venues of varying sizes.
-
Equipment Operation and Maintenance: Sound engineers are adept at operating a wide range of audio equipment, including mixing consoles, amplifiers, signal processors, and recording devices. They are also tasked with maintaining and troubleshooting this equipment to uphold optimal performance and minimize technical disruptions during recording sessions or live events.
-
Collaboration with Artists and Producers: Sound engineers work closely with musicians, producers, and other audio professionals to actualize the sonic vision of a project. They provide technical guidance, offer creative input, and facilitate a cohesive working environment to bring forth the best possible audio outcomes.
-
Sound Design and Foley Artistry: In the realm of post-production and sound design for film, television, and gaming, sound engineers are instrumental in creating immersive auditory experiences. They craft sound effects, design ambient audio landscapes, and synchronize audio elements with visual content to evoke emotional responses and enhance storytelling.
-
Quality Control and Technical Compliance: Sound engineers meticulously review audio content to ensure adherence to technical specifications, industry standards, and client requirements. They conduct thorough quality assessments, address any audio imperfections, and optimize audio files for distribution across various platforms.
-
Adaptation to Diverse Environments: Whether in a bustling recording studio, a dynamic concert venue, or a fast-paced film set, sound engineers adeptly navigate diverse work environments. They remain adaptable, resourceful, and composed under pressure, ensuring that audio productions maintain their integrity and excellence across varied settings.
In essence, the job responsibilities of sound engineers encompass a rich tapestry of technical proficiency, artistic finesse, and collaborative prowess. Their contributions resonate throughout the realms of music, entertainment, and media, shaping the way we experience and appreciate the power of sound.
Work Environment
The work environment of a sound engineer is a dynamic and multifaceted landscape that spans a diverse array of settings, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities for audio professionals. Whether in the controlled confines of a recording studio, the electrifying ambiance of a live concert venue, or the fast-paced realm of post-production facilities, sound engineers navigate a rich tapestry of work environments that demand adaptability, technical acumen, and a keen artistic sensibility.
In the realm of recording studios, sound engineers find themselves immersed in an environment meticulously designed to capture and refine audio recordings with precision and finesse. These studios are equipped with state-of-the-art recording equipment, acoustically treated spaces, and an array of instruments, offering a sanctuary for musicians and audio professionals to collaborate and create. The controlled acoustic environment of a studio allows sound engineers to exercise their technical expertise in capturing pristine audio, manipulating sonic textures, and sculpting the sonic identity of a recording.
Live event environments present a stark contrast, pulsating with energy and adrenaline as sound engineers orchestrate the audio experience for audiences. From concert halls and outdoor amphitheaters to intimate club venues, sound engineers navigate the logistical complexities of setting up sound systems, managing audio levels during performances, and ensuring seamless sound distribution across diverse spaces. The live environment demands quick thinking, adaptability, and a keen understanding of audio dynamics to deliver an immersive sonic experience that resonates with audiences.
In the realm of post-production facilities for film, television, and gaming, sound engineers immerse themselves in a world of creative audio manipulation and storytelling. These environments are characterized by cutting-edge audio software, Foley studios, and sound design suites, where sound engineers craft immersive auditory experiences that complement visual narratives. The post-production realm demands meticulous attention to detail, creative ingenuity, and a deep understanding of audiovisual synchronization to bring forth captivating soundscapes that elevate storytelling.
Amidst these varied work environments, sound engineers embody versatility, technical prowess, and a profound appreciation for the artistry of sound. Their ability to seamlessly transition between recording studios, live event venues, and post-production facilities underscores their indispensable role in shaping the sonic fabric of our auditory experiences.
In essence, the work environment of a sound engineer is a captivating amalgamation of technical precision, artistic expression, and adaptability, offering a rich tapestry of experiences that define the essence of this remarkable profession.
Challenges and Rewards
The realm of sound engineering presents a compelling dichotomy of challenges and rewards, shaping a career path that is as demanding as it is gratifying. Let's delve into the intricacies of these contrasting facets that define the professional journey of sound engineers.
Challenges
-
Technical Complexity: Sound engineering entails navigating a labyrinth of technical intricacies, from mastering complex audio equipment to troubleshooting intricate signal processing systems. The constant evolution of audio technology demands a perpetual commitment to staying abreast of emerging tools and techniques, presenting a formidable yet invigorating challenge for sound engineers.
-
Pressure and Precision: Whether in a live concert setting or a high-stakes recording session, sound engineers operate under immense pressure to deliver flawless audio experiences. The need for precision in capturing, mixing, and mastering audio amidst demanding timelines and exacting standards requires unwavering focus and composure.
-
Artistic Interpretation: Balancing technical proficiency with artistic sensibility poses a unique challenge for sound engineers. They must harness their technical expertise to realize the creative vision of musicians and producers, harmonizing sonic elements to evoke emotion and resonance.
Rewards
-
Sonic Artistry: The ability to sculpt and refine audio, shaping it into a captivating auditory tapestry, is a deeply rewarding aspect of sound engineering. The transformative power of sound allows engineers to imbue life and emotion into every composition, creating immersive sonic experiences that resonate with audiences.
-
Collaborative Fulfillment: Collaborating with diverse artists, producers, and creative professionals fosters a sense of shared accomplishment. The synergy of collective creativity and technical prowess culminates in the realization of sonic visions, forging enduring connections and a profound sense of fulfillment.
-
Impactful Artistic Contribution: Sound engineers play a pivotal role in bringing music and audio content to life, leaving an indelible mark on the artistic landscape. Their contributions extend beyond technical proficiency, influencing the way audiences perceive and connect with sound, thereby enriching the cultural tapestry of society.
In essence, the challenges and rewards inherent in sound engineering converge to form a career path that demands unwavering dedication, technical finesse, and a profound appreciation for the transformative power of sound. It is a profession that continually inspires and challenges, offering a deeply fulfilling journey for those who embark on the captivating odyssey of shaping the world of audio.
Skills and Qualities
Becoming a proficient sound engineer necessitates a diverse skill set and a unique blend of personal qualities that transcend the realms of technical expertise and artistic finesse. Here are the essential skills and qualities that define a successful sound engineer:
Technical Proficiency:
Sound engineers must exhibit a deep understanding of audio equipment, signal processing, and digital audio workstations (DAWs). Proficiency in operating mixing consoles, microphones, amplifiers, and recording devices is paramount. Additionally, a comprehensive grasp of acoustics, sound theory, and audio signal flow is essential for optimizing sound quality in diverse environments.
Critical Listening:
A discerning ear for sound nuances and the ability to critically evaluate audio quality are indispensable traits for sound engineers. They must adeptly identify imperfections, balance audio levels, and refine sonic textures to achieve optimal clarity and emotional impact in audio productions.
Problem-Solving Aptitude:
The dynamic nature of sound engineering demands quick thinking and adept problem-solving skills. Sound engineers must troubleshoot technical issues, adapt to unforeseen challenges, and devise innovative solutions to ensure seamless audio production and delivery.
Collaboration and Communication:
Effective collaboration with musicians, producers, and fellow audio professionals hinges on strong communication skills and a collaborative mindset. Sound engineers must articulate technical concepts, offer creative input, and foster a harmonious working environment to realize the sonic vision of a project.
Adaptability and Resilience:
Navigating diverse work environments, from recording studios to live event venues, requires adaptability, resilience, and a composed demeanor under pressure. Sound engineers adeptly pivot between varied settings, demonstrating resourcefulness and composure in delivering exceptional audio experiences.
Creativity and Artistic Sensibility:
Beyond technical prowess, sound engineers must possess a keen artistic sensibility and a flair for creative expression. The ability to infuse emotion and narrative depth into audio compositions, coupled with a passion for sonic artistry, distinguishes exceptional sound engineers.
Attention to Detail:
Meticulous attention to detail is a hallmark of sound engineering excellence. From meticulous microphone placement to precise audio editing, sound engineers meticulously refine every sonic element, ensuring a polished and cohesive auditory experience.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
The ever-evolving landscape of audio technology necessitates a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation. Sound engineers must stay abreast of emerging tools, techniques, and industry trends, embracing a lifelong journey of skill development and innovation.
In essence, the skills and qualities that define a successful sound engineer encompass a rich tapestry of technical acumen, artistic finesse, and interpersonal adeptness. It is the seamless integration of these attributes that empowers sound engineers to shape the sonic landscape, leaving an indelible mark on the world of audio production and appreciation.
Career Opportunities
The realm of sound engineering offers a myriad of diverse and rewarding career opportunities that cater to a broad spectrum of audio production and technology. Sound engineers possess a versatile skill set that transcends traditional boundaries, positioning them for impactful roles across various industries. Here are some compelling career paths and opportunities available to sound engineers:
-
Studio Recording Engineer: Studio recording engineers play a pivotal role in capturing and refining audio recordings in controlled studio environments. They collaborate with musicians, producers, and artists to achieve the desired sonic vision, employing their technical expertise to ensure optimal sound quality and artistic expression.
-
Live Sound Engineer: Live sound engineers orchestrate the audio experience for audiences in diverse settings, including concerts, theatrical performances, corporate events, and festivals. They are adept at setting up sound systems, managing audio levels, and delivering immersive sonic experiences in dynamic live environments.
-
Broadcast and Media Production: Sound engineers find compelling opportunities in broadcast media, working in radio stations, television networks, and online streaming platforms. They contribute to the creation of captivating audio content for news, entertainment, sports, and advertising, shaping the auditory landscape of diverse media platforms.
-
Post-Production and Sound Design: The realm of post-production offers exciting prospects for sound engineers to delve into sound design, Foley artistry, and audio post-production for film, television, and gaming. They craft immersive auditory experiences, synchronize audio with visual content, and contribute to the storytelling process through captivating soundscapes.
-
Acoustic Consultant: Sound engineers with a deep understanding of acoustics and sound theory can pursue careers as acoustic consultants. They offer expertise in architectural acoustics, noise control, and audio system design, contributing to the creation of acoustically optimized spaces for various applications, including concert halls, theaters, and commercial venues.
-
Audio Software Development and Technology: Sound engineers with a passion for innovation and technology can explore careers in audio software development, digital signal processing, and hardware design. They contribute to the creation of cutting-edge audio tools, plugins, and digital audio workstations, driving advancements in the field of audio technology.
-
Educator and Trainer: Experienced sound engineers often transition into roles as educators and trainers, sharing their wealth of knowledge and practical insights with aspiring audio professionals. They contribute to the development of future talent in audio engineering schools, workshops, and industry training programs.
-
Freelance and Entrepreneurship: Many sound engineers embark on entrepreneurial ventures, offering freelance services in audio production, mixing and mastering, live event engineering, and sound system consultation. They establish their own studios, production companies, or consulting firms, leveraging their expertise to cater to a diverse clientele.
The diverse career opportunities available to sound engineers underscore the expansive reach and impact of this profession. Whether shaping the sonic landscape in recording studios, live events, broadcast media, or technological innovation, sound engineers play an indispensable role in defining the auditory experiences that enrich our lives. This breadth of opportunities reflects the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of sound engineering, offering a wealth of pathways for professionals to channel their passion for audio into impactful and fulfilling careers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the realm of sound engineering stands as a captivating intersection of technical prowess, artistic finesse, and collaborative ingenuity. It is a profession that transcends the boundaries of traditional careers, offering a dynamic and multifaceted journey for those passionate about the transformative power of sound. From the controlled confines of recording studios to the electrifying ambiance of live event venues, sound engineers navigate a rich tapestry of work environments, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities for creative expression.
The journey to becoming a proficient sound engineer is marked by a blend of formal education, hands-on training, and a perpetual commitment to continuous learning. Aspiring sound engineers embark on a multidisciplinary odyssey, honing their technical expertise, critical listening skills, and problem-solving aptitude to navigate the labyrinth of audio technology with precision and finesse. Moreover, the seamless integration of personal qualities such as adaptability, resilience, and a keen artistic sensibility empowers sound engineers to shape the sonic landscape, leaving an indelible mark on the world of audio production and appreciation.
The challenges and rewards inherent in sound engineering converge to form a career path that demands unwavering dedication, technical finesse, and a profound appreciation for the transformative power of sound. It is a profession that continually inspires and challenges, offering a deeply fulfilling journey for those who embark on the captivating odyssey of shaping the world of audio.
Furthermore, the diverse career opportunities available to sound engineers underscore the expansive reach and impact of this profession. Whether shaping the sonic landscape in recording studios, live events, broadcast media, or technological innovation, sound engineers play an indispensable role in defining the auditory experiences that enrich our lives. This breadth of opportunities reflects the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of sound engineering, offering a wealth of pathways for professionals to channel their passion for audio into impactful and fulfilling careers.
In essence, being a sound engineer is not merely a profession; it is a calling that beckons individuals to immerse themselves in the artistry of sound, to harness the power of audio technology, and to leave an indelible mark on the auditory landscape. It is a journey that resonates with creativity, technical mastery, and collaborative synergy, shaping the way we experience and appreciate the profound impact of sound in our lives.