Home>Events & Info>Ballet>Why Is Ballet Art?


Ballet
Why Is Ballet Art?
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the beauty and artistry of ballet as we delve into the reasons why this classical dance form continues to captivate audiences worldwide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Background
- Techniques and Movements in Ballet
- Importance of Ballet as an Art Form
- Expression and Emotion in Ballet
- Ballet as a Reflection of Society and Culture
- Ballet as a Visual Spectacle
- The Role of Music in Ballet
- Ballet’s Influence on Other Art Forms
- Ballet as a Means of Storytelling
- The Creative Process in Ballet Productions
- Challenges and Criticisms in Ballet as an Art Form
- Conclusion
Introduction
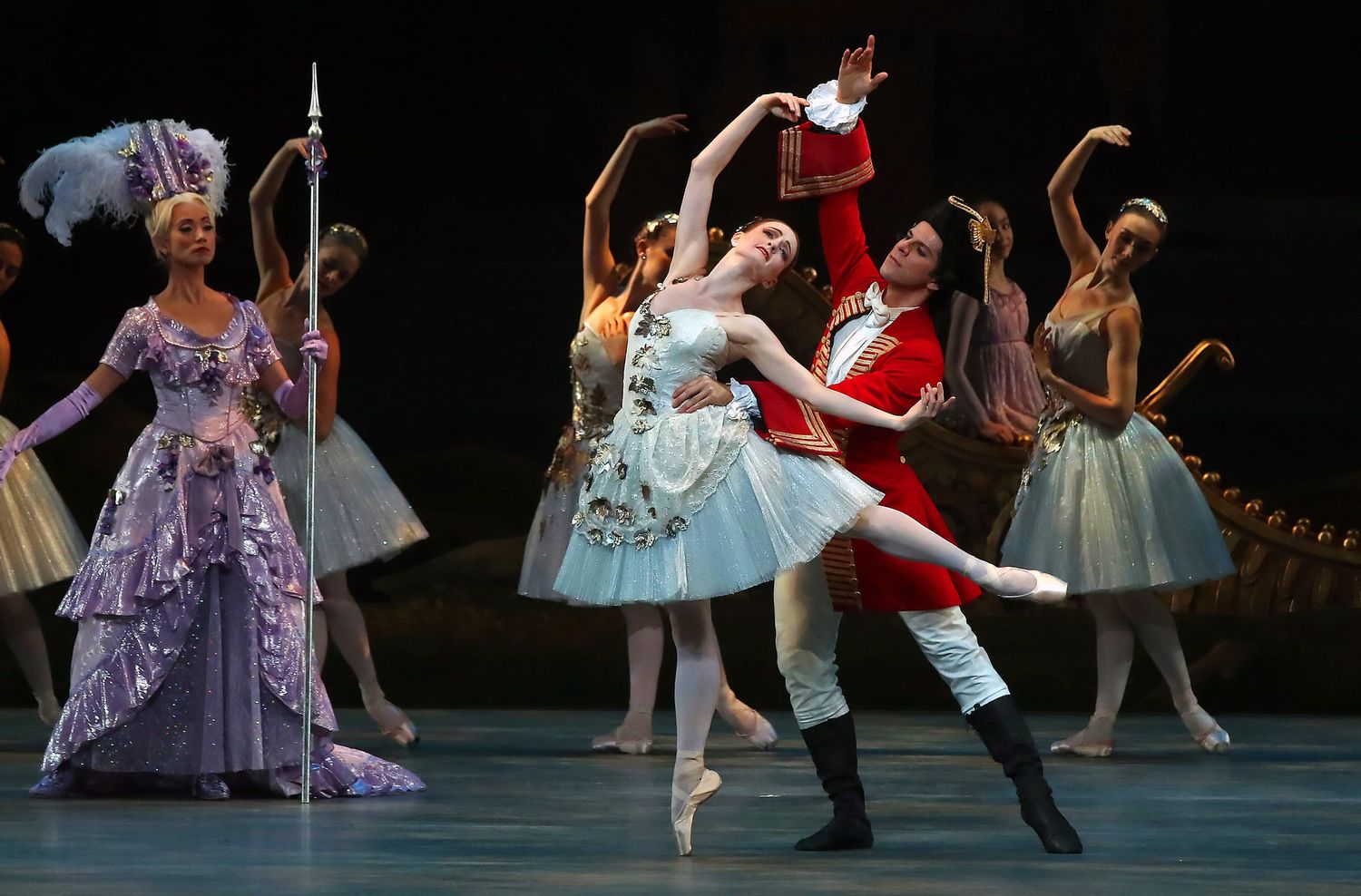
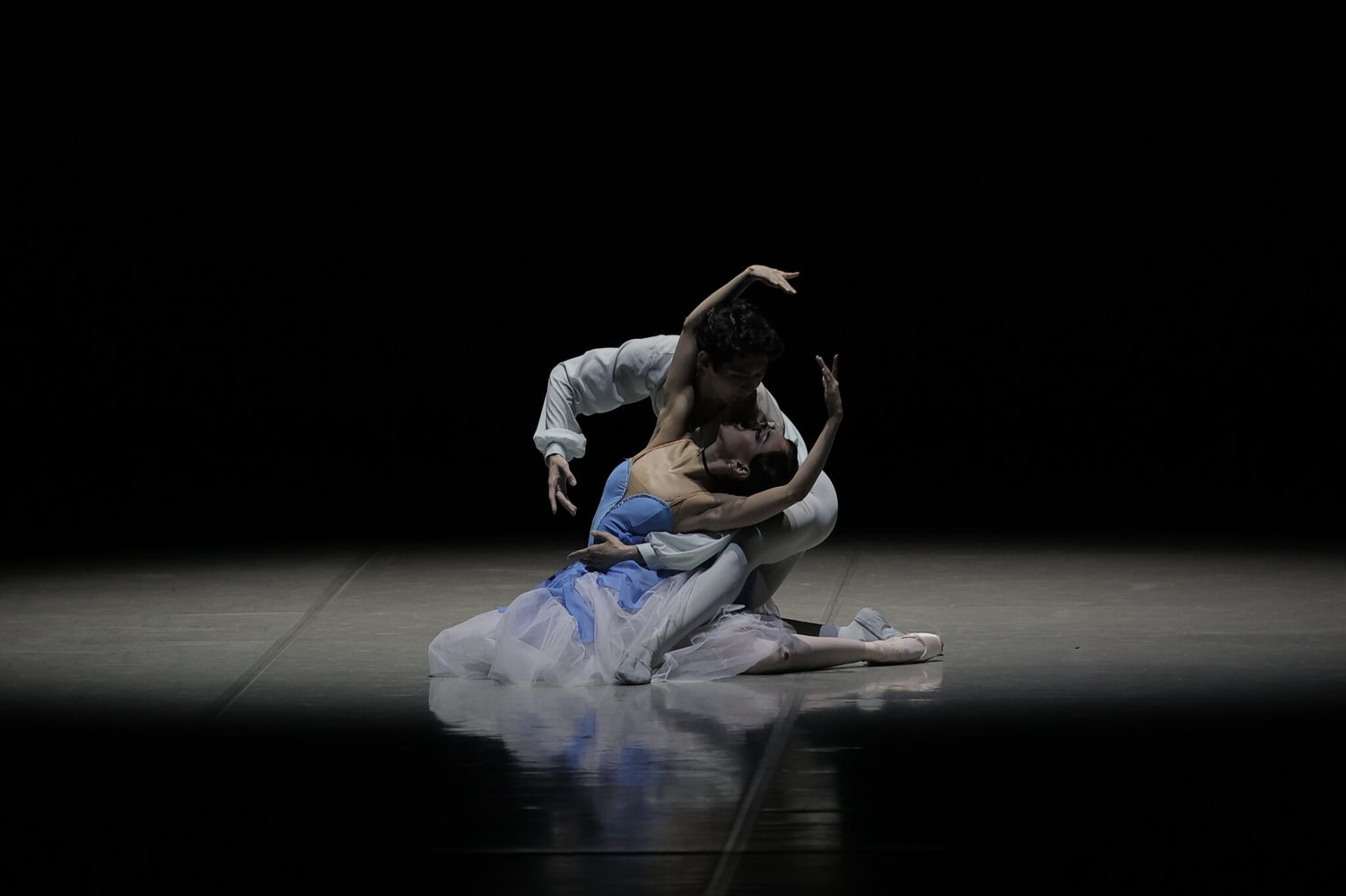
Ballet, a captivating and beautiful art form, has been enchanting audiences for centuries. With its graceful movements, intricate techniques, and expressive storytelling, ballet is more than just a dance—it is a powerful form of artistic expression. Whether it’s the ethereal beauty of a swan in “Swan Lake” or the passionate love story of Romeo and Juliet, ballet has the unique ability to transport us to another world and evoke a wide range of emotions.
Rooted in rich history and steeped in tradition, ballet originated in the courts of Renaissance Italy and France before spreading throughout Europe. Over the years, ballet has evolved and transformed, incorporating different techniques and styles while maintaining its core principles and artistic integrity.
In this article, we will explore the art of ballet, discussing its historical background, the intricacies of its techniques and movements, and its importance as a form of artistic expression. We will delve into how ballet reflects society and culture, the role of music in enhancing the performance, and its influence on other art forms. Additionally, we will shed light on the creative process behind ballet productions and address the challenges and criticisms faced by this art form.
Join us on this journey as we unravel the world of ballet, diving deep into its artistic significance and uncovering the magic that lies within its performances.
Historical Background
Ballet has a long and storied history that dates back to the Italian Renaissance of the 15th century. It was during this time that noble courts in Italy began hosting elaborate spectacles and festivities, featuring dance as a prominent form of entertainment. These early Renaissance dances laid the foundation for what would eventually become ballet.
However, it wasn’t until the reign of King Louis XIV of France in the 17th century that ballet truly flourished as an art form. King Louis XIV, himself a passionate dancer, played a pivotal role in the development and codification of ballet technique. He established the first professional ballet company, known as the Académie Royale de Danse, and laid the groundwork for the five basic positions of ballet that are still taught and practiced today.
Throughout the centuries, ballet continued to evolve and expand, with new techniques and styles emerging. In the 19th century, classical ballet reached its golden age with influential choreographers such as Marius Petipa and composers like Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky creating iconic ballets such as “Swan Lake,” “The Nutcracker,” and “Sleeping Beauty.” These ballets, with their intricate choreography and captivating storytelling, became timeless classics that are still performed and cherished today.
In the 20th century, ballet experienced a period of innovation and experimentation. Choreographers like George Balanchine challenged traditional ballet conventions, breaking away from narrative-driven ballets and focusing more on pure movement and form. This new approach, known as neoclassical ballet, brought a fresh perspective to the art form and paved the way for modern ballet.
Today, ballet continues to evolve and push boundaries, with contemporary choreographers merging classical techniques with new styles and influences. The art form has become more inclusive and diverse, embracing dancers from various backgrounds and celebrating individual expression.
Understanding the historical background of ballet is crucial in appreciating its evolution and the impact it has had on the world of dance and art as a whole. By tracing its roots and examining its progression, we gain a deeper appreciation for the artistry and dedication that goes into every ballet performance.
Techniques and Movements in Ballet
Ballet is renowned for its precise and technical movements that require years of training and dedication. At its core, ballet focuses on the alignment of the body, control, and balance, as well as the seamless execution of intricate steps. Let’s explore some of the key techniques and movements that define ballet.
Turnout: One of the defining features of ballet is the “turnout” technique, in which the legs are rotated outward from the hip joints. This creates a visually striking appearance and allows for greater range of movement and flexibility.
Pointe work: Pointe work is a technique in which female dancers dance on the tips of their toes, supported by specially designed pointe shoes. This requires immense strength in the feet and ankles, as well as precise balance and control.
Plié: The plié is a fundamental movement in ballet, in which the dancer bends and straightens their knees. It serves as a warm-up exercise and is also used to transition between steps and movements. There are two types of plié: demi-plié, where the dancer’s heels remain on the floor, and grand plié, in which the heels are lifted off the ground.
Arabesque: The arabesque is a graceful pose in which the dancer extends one leg behind them while balancing on the other leg. This position showcases the dancer’s flexibility, strength, and control.
Jeté: Jeté, meaning “to throw,” is a dynamic and powerful movement in which the dancer jumps from one leg, extending the other leg outwards in the air. It is often performed in a series, giving the illusion of gliding through the air.
Pirouette: Pirouette, derived from the French word for “spin,” is a spinning movement typically executed on one leg. The dancer turns their body while keeping the supporting leg in position, creating a graceful and spinning effect.
These are just a few examples of the many techniques and movements that form the foundation of ballet. Each movement requires precision, strength, and a deep understanding of body alignment and control. Ballet dancers spend years honing their technique, striving for perfection in every step they take on stage.
It is through the mastery of these techniques and movements that ballet dancers can convey emotion, tell stories, and captivate audiences with their artistry. The combination of the technical elements of ballet and the expression of the dancers creates a truly mesmerizing and awe-inspiring experience.
Importance of Ballet as an Art Form
Ballet holds a significant place in the world of performing arts and has a profound impact on both individuals and society as a whole. Let’s delve into the importance of ballet as an art form and the value it brings to our lives.
Personal Development: Ballet demands dedication, discipline, and perseverance. Through rigorous training, dancers develop physical strength, flexibility, and endurance. They also cultivate mental focus, determination, and a strong work ethic. These qualities extend beyond the stage and have a positive influence on dancers’ personal and professional lives, fostering self-confidence and resilience.
Emotional Expression: Ballet offers a unique platform for emotional expression. Dancers convey a wide range of emotions, from joy and love to sorrow and despair, through their movements and facial expressions. This ability to communicate without words allows audiences to connect with and experience the art form on a deeply emotional level.
Cultural Preservation: Ballet, with its rich history and traditions, serves as a custodian of cultural heritage. It preserves and celebrates the artistic legacy of past generations, ensuring that their contributions to the art form are not forgotten. From classical ballets to regional variations, ballet captures the essence of diverse cultures and keeps them alive for future generations to appreciate.
Physical Well-being: Ballet is a physically demanding art form that contributes to overall health and well-being. Regular ballet training improves posture, coordination, and alignment. It enhances strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness. Engaging in ballet also promotes a sense of body awareness and mindfulness, allowing individuals to connect with their physical selves in a profound way.
Artistic Collaboration: Ballet is a collaborative art form that brings together dancers, choreographers, musicians, costume designers, and set designers, among others. This collaborative process fosters creative exchange and teamwork. Each artist contributes their unique skills and expertise, resulting in a harmonious and visually stunning production.
Education and Appreciation: Ballet exposes audiences of all ages to the arts and serves as a gateway to other art forms. It cultivates an appreciation for music, costume design, and storytelling. Ballet performances often inspire curiosity and encourage individuals to explore other aspects of the arts, broadening their cultural horizons.
Social Commentary: Ballet has the power to reflect societal issues and challenges. Choreographers often use ballet as a platform for social commentary, addressing topics such as inequality, oppression, and human emotions. These performances provide a thought-provoking experience and encourage dialogue and reflection on important societal themes.
The importance of ballet as an art form extends far beyond the stage. It impacts the lives of individuals, contributes to cultural preservation, and fosters creativity and collaboration. Through its universal language of movement, ballet has the ability to touch our souls, ignite our imaginations, and connect us to our shared humanity.
Expression and Emotion in Ballet
Ballet is a powerful art form that allows dancers to convey a wide range of emotions and tell poignant stories through their movements. From grace and elegance to passion and despair, ballet provides a platform for deep emotional expression. Let’s explore how expression and emotion are integral to the beauty and impact of ballet.
Physical Expression: One of the distinctive aspects of ballet is its ability to communicate emotions through physical movements. Dancers use their bodies, including their arms, legs, and torso, to express joy, sorrow, love, anger, and all the nuances of human emotion. Every step, every gesture, and every lift communicates a story or a feeling, reaching beyond words.
Facial Expression: While ballet is primarily a movement-based art form, facial expressions also play a crucial role in conveying emotions. Dancers use their facial expressions to bring life and depth to their characters. They convey happiness, sadness, determination, or vulnerability through subtle changes in their facial expressions, allowing the audience to connect with the emotional journey of the performance.
Music as an Emotional Catalyst: Ballet is intrinsically tied to music, with choreography responding to the rhythm, melody, and mood of the music. The music serves as an emotional catalyst, amplifying the feelings and intentions of the dancers. As the dancers move in sync with the music, the emotional impact is heightened, creating an immersive experience for both dancers and audience members.
Storytelling through Movement: Ballet often tells stories, whether through classic narrative ballets like “Giselle” or contemporary pieces that explore abstract concepts. The choreography and movements are carefully crafted to reflect the narrative, enhancing the emotional depth of the story being portrayed. Dancers use their bodies to communicate the narrative arc, capturing the essence of characters and their emotional journey.
Physicality and Vulnerability: The physical demands of ballet require dancers to push their bodies to the limits, infusing their movements with passion and intensity. This physicality, combined with vulnerability and emotional openness, allows dancers to connect with audiences on a profound level. It is this unique combination of strength and vulnerability that makes ballet performances so captivating and emotionally resonant.
The transformative power of expression and emotion in ballet allows audiences to experience a range of feelings and connect with the performers on a deep emotional level. Whether it is the ethereal delicacy of a pas de deux or the raw intensity of a solo, ballet has the ability to evoke strong emotions, leaving a lasting impact on all who witness its beauty.
Ballet as a Reflection of Society and Culture
Ballet, as an art form, has the unique ability to reflect the values, beliefs, and social dynamics of the society and culture in which it thrives. Throughout its history, ballet has evolved and adapted to mirror the ever-changing world around it. Let’s explore how ballet serves as a reflection of society and culture.
Historical Context: Ballet has been deeply intertwined with historical events and cultural movements. For instance, during the Romantic era in the 19th century, ballet experienced a surge in popularity and showcased themes of fantasy, passion, and individualism. This mirrored the broader cultural fascination with romanticism and emphasized the emotions and individual experiences. Similarly, in the 1960s and 1970s, neoclassical ballet explored abstract concepts, reflecting the experimental and avant-garde spirit of the time.
Gender Roles: Ballet has often been shaped by societal expectations and gender roles. Traditionally, male dancers portrayed powerful and heroic characters, while female dancers embodied grace and vulnerability. However, contemporary ballet has evolved to challenge these gender stereotypes. Choreographers now explore non-traditional casting, allowing both male and female dancers to portray a wider range of characters and emotions.
Cultural Diversity: As ballet continues to evolve, it has become more inclusive and representative of different cultures and backgrounds. Ballet companies around the world now showcase diverse casts, recognizing the importance of cultural representation on stage. Choreographers incorporate cultural elements, such as music, costumes, and movements, to celebrate and honor the richness of various cultural heritages.
Social Issues: Ballet has the power to address and shed light on social issues and challenges. Choreographers have created works that explore subjects such as discrimination, environmental issues, mental health, and political unrest. Through their artistry, ballet dancers can raise awareness and provoke dialogue on important societal topics, fostering empathy and understanding among audiences.
Artistic Freedom: Ballet also reflects the artistic freedoms and limitations within a particular society or culture. It can be influenced by political ideologies, censorship, or societal expectations. Ballet companies may produce works that align with the prevailing cultural norms while also pushing boundaries and challenging conventions, testing the limits of artistic expression.
By examining the themes, stories, and styles present in ballet, we gain a deeper understanding of the societal and cultural context in which it exists. Ballet serves as both a mirror that reflects our world and a window that allows us to glimpse alternative perspectives. It continues to evolve and adapt to the ever-changing cultural landscape, reflecting the concerns, aspirations, and values of societies past and present.
Ballet as a Visual Spectacle
Ballet is not only a captivating art form in terms of expression and storytelling; it is also a visual spectacle that mesmerizes audiences with its elegance, grace, and sheer beauty. From dazzling costumes to stunning set designs, ballet engages the senses and immerses viewers in a world of aesthetic wonder. Let’s explore how ballet captivates as a visual spectacle.
Costumes: Ballet costumes are meticulously designed to enhance the movements and evoke the characters and themes of the performance. They are crafted with attention to detail, using luxurious fabrics, intricate embellishments, and vibrant colors. From tutus and tiaras in classical ballet to contemporary and avant-garde designs, the costumes contribute to the overall visual impact, adding an element of fantasy and grandeur on stage.
Set Designs: The sets in ballet productions create a magical and immersive environment. From ornate ballrooms to enchanted forests, the sets transport the audience to different worlds and enhance the storytelling. Elaborate backdrops, props, and stage effects, such as lighting and projections, further amplify the visual experience, creating a multi-dimensional and visually captivating performance.
Stagecraft: The art of stagecraft in ballet plays a crucial role in creating a visually stunning spectacle. Stage directors and choreographers carefully consider the spatial elements, including formations, groupings, and entrances/exits, to showcase the dancers’ movements and compositions effectively. The precise coordination of dancers on stage, their formations, and the synchronized execution of complex movements all contribute to the visual appeal of ballet performances.
Lighting: Lighting design is instrumental in creating ambiance and enhancing the mood of ballet performances. The interplay of light and shadow highlights the dancers’ movements and adds depth and dimension to the stage. From soft warm hues to dramatic spotlights, the strategic use of lighting evokes emotions and guides the audience’s attention, creating a visually dynamic experience.
Athleticism and Elegance: The combination of athleticism and elegance displayed by ballet dancers is itself a visual spectacle. The dancers’ fluid movements, impeccable technique, and aerial leaps seem to defy gravity. The strength, control, and grace with which they perform leave audiences in awe, mesmerized by the sheer physicality and artistry on display.
Artistic Expression: Ballet’s visual spectacle lies not only in the external aesthetics, but also in the dancers’ ability to embody emotion and tell stories through their movements. Their expressive faces, artful gestures, and evocative body language communicate complex emotions and narratives, captivating audiences on a deeper level.
Ballet is a synthesis of visual and performing arts, blending aesthetics with athleticism to create a truly captivating experience. Its stunning costumes, set designs, lighting, and the sheer beauty of the dancers’ movements make ballet a visual feast for the eyes. Whether experiencing the classic elegance of a traditional ballet or the innovative and contemporary aesthetics of modern dance, the visual spectacle of ballet is undeniably enchanting.
The Role of Music in Ballet
Music is an integral part of ballet, serving as the driving force and emotional foundation of the performance. The harmonious and symbiotic relationship between music and dance is what brings ballet to life and creates a truly immersive experience for the audience. Let’s explore the significant role that music plays in the world of ballet.
Enhancing the Narrative: Music in ballet is carefully selected to complement and elevate the storytelling. It sets the tone, establishes the mood, and enhances the emotional depth of the performance. Whether it’s the soaring melodies of Tchaikovsky’s “Swan Lake” or the energetic rhythms of Stravinsky’s “The Rite of Spring,” the music serves as a guide, guiding the dancers and immersing the audience in the narrative.
Rhythm and Timing: Ballet dancers rely on the music’s rhythm to guide their movements and maintain synchronization with fellow dancers. The music’s tempo, beat, and phrasing provide the structure and timing for choreography, ensuring the fluidity and precision of each step. The tight interplay between music and dance creates a visually harmonious and aesthetically pleasing performance.
Expressing Emotion: Music has the power to evoke and intensify emotions, and in ballet, it works in tandem with the dancers’ movements to convey complex feelings. The melodies, harmonies, and dynamics of the music amplify the emotional impact of the performance, allowing the audience to connect with the story and characters on a deeper level. From the haunting melodies of tragic ballets to the jubilant and celebratory tunes of joyful pieces, the music in ballet elicits a wide range of emotions.
Collaborative Process: The collaboration between composers, choreographers, and dancers is essential in producing a ballet. Composers create original scores or select existing music that resonates with the choreographer’s vision. Choreographers, in turn, interpret the music and create movements that both respond to and enhance its musicality. The mutual influence between music and dance in the creative process results in a harmonious fusion of the two art forms.
Dynamic Interplay: The relationship between music and dance in ballet is incredibly dynamic, with moments of synchronization, contrast, and counterpoint. Dancers interpret the music through their movements, emphasizing the rhythmic patterns or enhancing the melodic phrases. Conversely, the music responds to the dancers’ energy and motions, amplifying their expressions and adding depth to the overall performance. This interplay creates a synergistic connection between the auditory and visual components of ballet.
The role of music in ballet cannot be overstated. It is the driving force that fuels the dancers’ movements, shapes the narrative, and evokes emotion. The harmonious marriage between music and dance elevates the artistic impact of ballet, transporting audiences into a world of beauty and passion. By immersing ourselves in the enchanting combination of music and movement, we experience the magic and power of this art form.
Ballet’s Influence on Other Art Forms
Ballet, with its grace, beauty, and expressive storytelling, has exerted a profound influence on various art forms throughout history. Its impact can be seen in areas such as visual arts, literature, film, and fashion. Let’s explore how ballet has influenced and inspired other creative disciplines.
Visual Arts: Ballet’s stunning aesthetic and artistry have captivated artists through the ages. Painters, sculptors, and photographers have drawn inspiration from the elegance and poise of ballet dancers, capturing their graceful movements and using them as subjects in their creations. Artists like Edgar Degas, who famously depicted ballet dancers in their rehearsal and performance settings, demonstrated the enduring influence of ballet on visual arts.
Literature: Ballet has served as a source of inspiration for numerous literary works. Writers have drawn upon ballet’s rich narratives and characters, weaving them into novels, poems, and plays. Alexander Pushkin’s “Eugene Onegin,” inspired by the ballet of the same name, and Hans Christian Andersen’s “The Red Shoes” are just a few examples of how ballet has influenced the literary world and enriched storytelling.
Film: Ballet’s combination of expressive movements, storytelling, and visual spectacle has found its way onto the big screen. Filmmakers have incorporated ballet sequences into movies, showcasing the art form’s beauty and drama. From classic films such as “The Red Shoes” and “Black Swan” to animated features like “Fantasia,” ballet’s influence on film is evident, highlighting its ability to transcend the confines of the stage and reach a broader audience.
Fashion: The ethereal grace and elegance of ballet have left an indelible mark on the world of fashion. Ballet-inspired ensembles, from delicate tutus and flowing dresses to ballet flats and wraparound ribbons, have become fashion staples. Designers often incorporate ballet’s soft color palettes, lightweight fabrics, and romantic silhouettes into their collections, paying homage to the art form’s aesthetic allure.
Music and Composition: Ballet’s marriage of movement and music has also influenced composers and musicians. Composers like Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky and Igor Stravinsky, who created iconic scores for ballets such as “Swan Lake” and “The Rite of Spring,” have left an enduring legacy in the world of classical music. The rhythmic patterns, melodies, and emotive qualities of ballet music have inspired composers across genres, shaping their compositions and adding a touch of balletic elegance to their works.
Choreography and Dance Forms: Ballet has also influenced other dance forms, leading to the development of new styles and techniques. Contemporary dance, for example, draws upon ballet’s principles while incorporating a more diverse range of movement vocabulary and storytelling approaches. Ballet’s influence even extends to popular dance genres, with elements of ballet technique incorporated into everything from ballroom dancing to hip-hop and modern dance.
The influence of ballet on other art forms is a testament to its enduring appeal and artistic significance. From visual arts to literature, film, fashion, music, and dance itself, ballet serves as a source of inspiration, fueling creativity and innovation in countless creative endeavors. It is a testament to the power of this captivating art form to transcend its own boundaries and inspire the artistic expression and imagination of others.
Ballet as a Means of Storytelling
Ballet is a unique art form that combines music, movement, and visual elements to tell compelling stories without the use of words. Through the elegant and expressive movements of dancers, ballet has the remarkable ability to convey narratives, emotions, and complex characters. Let’s explore how ballet serves as a captivating means of storytelling.
Movement and Expression: In ballet, every movement is purposeful and deliberate, providing a visual language that communicates the essence of a story. Dancers use their bodies to express emotions, depict characters, and convey the dynamics between individuals. With their gestures, facial expressions, and the positions of their arms and legs, dancers bring the narrative to life, capturing the audience’s attention and imagination.
Choreography: The choreography in ballet plays a crucial role in storytelling. Choreographers craft sequences of movements that reveal the relationships and interactions between characters, create dramatic tension, and depict key plot points. The choreographer’s artistic choices, such as the use of formations, groupings, and partnering, guide the narrative flow and enhance the emotional impact of the story.
Character Development: Ballet enables the development of multifaceted characters through movement alone. Whether it’s a tragic heroine, a mischievous sprite, or a powerful antagonist, dancers embody these roles, allowing the audience to witness their transformation and growth. Through their movements and expressions, dancers breathe life into the characters, enabling the viewers to connect with their journey and motivations.
Symbolism and Metaphor: Ballet often employs symbolism and metaphor to convey deeper meanings and emotions. Through the use of specific movements, gestures, or inanimate objects, abstract concepts can be represented visually. For example, a sweeping gesture may signify freedom, while a carefully crafted pas de deux can illustrate love and unity. These symbolic elements enrich the narrative, engaging the audience’s imagination and interpretation.
Musical Collaboration: The collaboration between music and ballet further enhances the storytelling. Composers create scores that match the mood, pace, and underlying emotions of the narrative. The music mirrors the dancers’ movements, intensifying their emotional expression and enriching the audience’s experience. The seamless integration of music and movement in ballet allows for a more nuanced and immersive storytelling experience.
Cultural and Historical Context: Ballet often draws inspiration from cultural and historical contexts, making it a means of preserving and conveying these narratives. From classical ballets based on folk tales and myths to contemporary works that address current societal issues, ballet reflects the cultural and historical fabric of its time. It allows audiences to connect with stories from different eras and gain insights into different cultures and perspectives.
Through its movement, choreography, symbolic elements, and collaboration with music, ballet transcends language barriers to tell stories that resonate with viewers. It evokes emotions, captures the essence of characters, and transports audiences to different worlds. Ballet’s unique ability to convey narratives through the power of dance and visual storytelling is a testament to its timeless and enduring appeal as an art form.
The Creative Process in Ballet Productions
The creation of a ballet production is a complex and collaborative endeavor that involves a multitude of artists, from choreographers and composers to designers and dancers. The creative process is a delicate and intricate journey that brings together diverse artistic talents and visions. Let’s explore the key elements of the creative process in ballet productions.
Conceptualization: The creative process begins with the conceptualization of the ballet. Choreographers often draw inspiration from various sources, such as literature, history, or personal experiences. They develop a vision for the narrative, characters, and overall theme of the production. Collaborating closely with composers and designers, they lay the foundation for bringing the ballet to life.
Composition and Musical Score: Composers collaborate with choreographers to create the musical score for the ballet. The music is composed to suit the narrative, characters, and emotions of the production. Composers and choreographers work together to ensure that the music aligns with the choreographic vision, guiding the dancers and enhancing the overall storytelling.
Choreography: The choreographer takes the lead in creating the movements and sequences that shape the ballet. They collaborate closely with the dancers, exploring various techniques, steps, and formations to bring their artistic vision to life. The choreographer’s creative process involves experimentation, refining movements, and finding the most effective ways to convey the narrative and emotions through dance.
Costume and Set Design: Costume and set designers play a crucial role in the creative process, translating the choreographer’s vision into tangible visual elements. They collaborate closely with the choreographer and often draw inspiration from the era, theme, or cultural context of the ballet. Through their designs, they enhance the aesthetics, atmosphere, and character portrayal, complementing the movements and narrative with their artistic choices.
Rehearsals: Rehearsals are a fundamental part of the creative process in ballet productions. Dancers work closely with the choreographer, refining their movements, perfecting their technique, and embodying the characters. Rehearsals involve countless hours of practice, trial and error, and collaboration between the dancers and the choreographer to achieve a cohesive and polished performance.
Technical Elements: The creative process also encompasses technical elements such as lighting, stage effects, and sound design. Lighting designers collaborate with the choreographer to create atmosphere, highlight focal points, and enhance the mood of the performance. Stage effects and sound design further amplify the visual and auditory elements, contributing to the overall artistic impact of the ballet.
Collaboration and Iteration: Throughout the creative process, collaboration is key. Choreographers, composers, designers, and dancers work together, providing feedback, exchanging ideas, and refining their respective contributions. This iterative process allows for experimentation, growth, and the creation of a cohesive artistic vision that reflects the collective talents and skills of the creative team.
The creative process in ballet productions is a journey of exploration, collaboration, and refinement. It involves weaving together various artistic elements to create a cohesive and captivating performance. Through the combined efforts and artistic vision of choreographers, composers, designers, and dancers, ballet productions come to life, enchanting audiences with their beauty, storytelling, and artistry.
Challenges and Criticisms in Ballet as an Art Form
Ballet, like any art form, is not without its challenges and criticisms. Despite its enduring popularity and cultural significance, ballet faces various obstacles and scrutiny that shape its evolution and perception. Let’s explore some of the challenges and criticisms faced by ballet as an art form.
Rigorous Training and Physical Demands: One of the biggest challenges in ballet is the rigorous training required. Dancers undergo years of intense practice, discipline, and physical conditioning to master the techniques and movements. The demands can put a strain on the body, leading to injuries and physical limitations. Additionally, the pressure to achieve technical perfection can create high levels of stress and competition within the ballet community.
Limited Diversity and Representation: Ballet has historically struggled with inclusivity and diversity. The lack of representation from different ethnicities and body types has been a subject of criticism. Efforts are being made to rectify this by fostering diversity in casting, choreography, and programming. Increasingly, ballet companies are working towards ensuring that ballet is accessible and representative of people from all backgrounds.
Gender Stereotypes: Ballet has long perpetuated traditional gender roles, with men performing more powerful and acrobatic movements, and women being expected to embody grace and ethereal beauty. These gender norms can limit artistic expression and restrict opportunities for both male and female dancers to explore a wider range of characters and movement styles. Modern ballet is challenging these gender stereotypes, with choreographers and dancers pushing boundaries and reshaping traditional gender roles within the art form.
Elitism and Accessibility: Ballet has often been associated with a perception of elitism due to its historical connection to aristocratic circles. The high cost of training, tickets, and the perceived exclusivity of ballet can create barriers to accessibility. Efforts are being made to make ballet more inclusive and accessible to broader audiences through initiatives such as community outreach programs, affordable ticket options, and educational opportunities.
Innovation versus Tradition: Ballet, as a traditional art form, faces a delicate balance between preserving its historical legacy and pushing boundaries to stay relevant. There can be criticism around the balance between maintaining classical repertoire and embracing new choreographic approaches or contemporary themes. Ballet companies and choreographers continuously navigate the tension between tradition and innovation in their pursuit of artistic growth and audience engagement.
Body Image and Pressures: Ballet’s emphasis on aesthetics and physique can contribute to body image issues and intense scrutiny for dancers. The pressure to maintain a certain body type and appearance, combined with the competitive nature of the art form, can have an impact on dancers’ mental and physical well-being. Efforts are being made to promote a more holistic and inclusive approach to body diversity and wellness within the ballet community.
It is important to acknowledge these challenges and criticisms to foster continued growth and improvement within the ballet community. By addressing issues of representation, accessibility, gender norms, and well-being, ballet can evolve into a more inclusive and progressive art form that resonates with diverse audiences and empowers its dancers.
Conclusion
Ballet is an extraordinary art form that seamlessly combines athleticism, grace, and storytelling to create a deeply captivating and emotive experience. From its historical roots to the present day, ballet has evolved and adapted, reflecting the societal and cultural landscapes in which it exists. It has influenced other art forms, inspired generations of artists, and created a lasting impact on the world of performing arts.
Through its precise techniques and expressive movements, ballet serves as a means of artistic expression, allowing dancers to convey a wide range of emotions and tell powerful stories. With each leap, turn, and arabesque, ballet dancers captivate audiences, taking them on an enchanting journey filled with passion, joy, and heartache.
Ballet serves as a reflection of society and culture, mirroring historical events, challenging gender norms, and addressing important social issues. It celebrates diversity and invites individuals from all backgrounds to appreciate its beauty and artistry. Ballet’s ability to communicate without words transcends language barriers, making it a universal language that touches the hearts of people around the world.
While ballet has faced challenges and criticisms, there is an ongoing commitment within the ballet community to address these concerns and foster inclusivity, accessibility, and artistic innovation. Efforts are being made to redefine traditional gender roles, promote body diversity, and ensure that ballet is accessible to all, regardless of social or economic background.
In its collaborative and iterative creative process, ballet involves the choreographers, composers, designers, and dancers who bring visions to life on stage. The seamless integration of music, movement, and visual elements creates a visual spectacle that transports audiences to enchanting worlds of imagination.
As we appreciate the artistry and dedication that goes into ballet, we must also recognize the immense influence it has had on other art forms. Ballet has inspired painters, writers, musicians, filmmakers, and fashion designers, leaving an indelible mark on the broader cultural landscape.
In conclusion, ballet is a testament to the power of human expression, combining technique, emotion, and visual splendor to create a profound and timeless art form. It is an ongoing journey of creativity, innovation, and self-discovery, pushing boundaries and captivating audiences worldwide. Through its continued evolution and commitment to accessibility and inclusivity, ballet will undoubtedly continue to inspire, delight, and touch the hearts and souls of generations to come.