Home>Events & Info>Music History>Why Was Giacomo Puccini Important To Music History
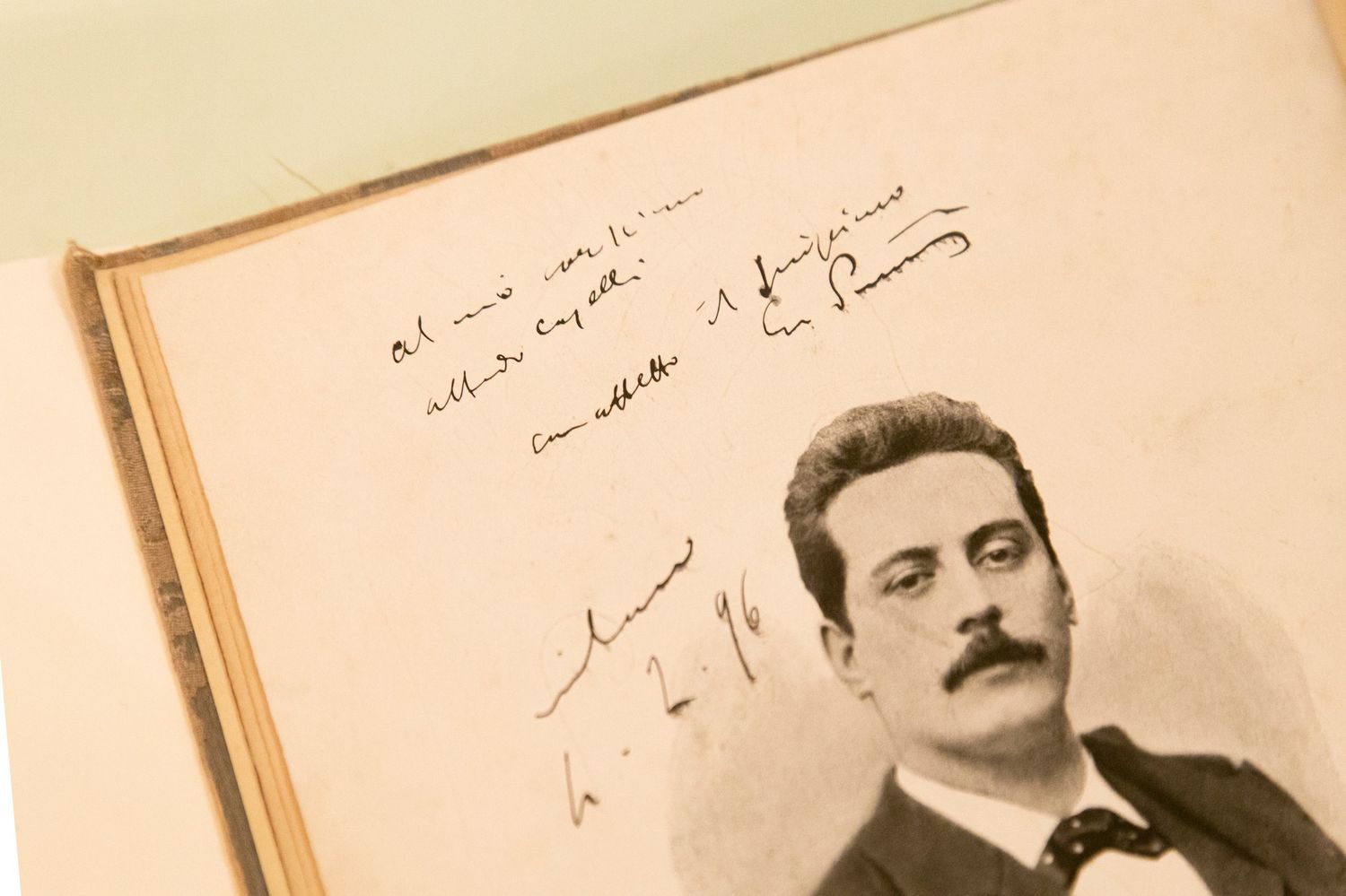
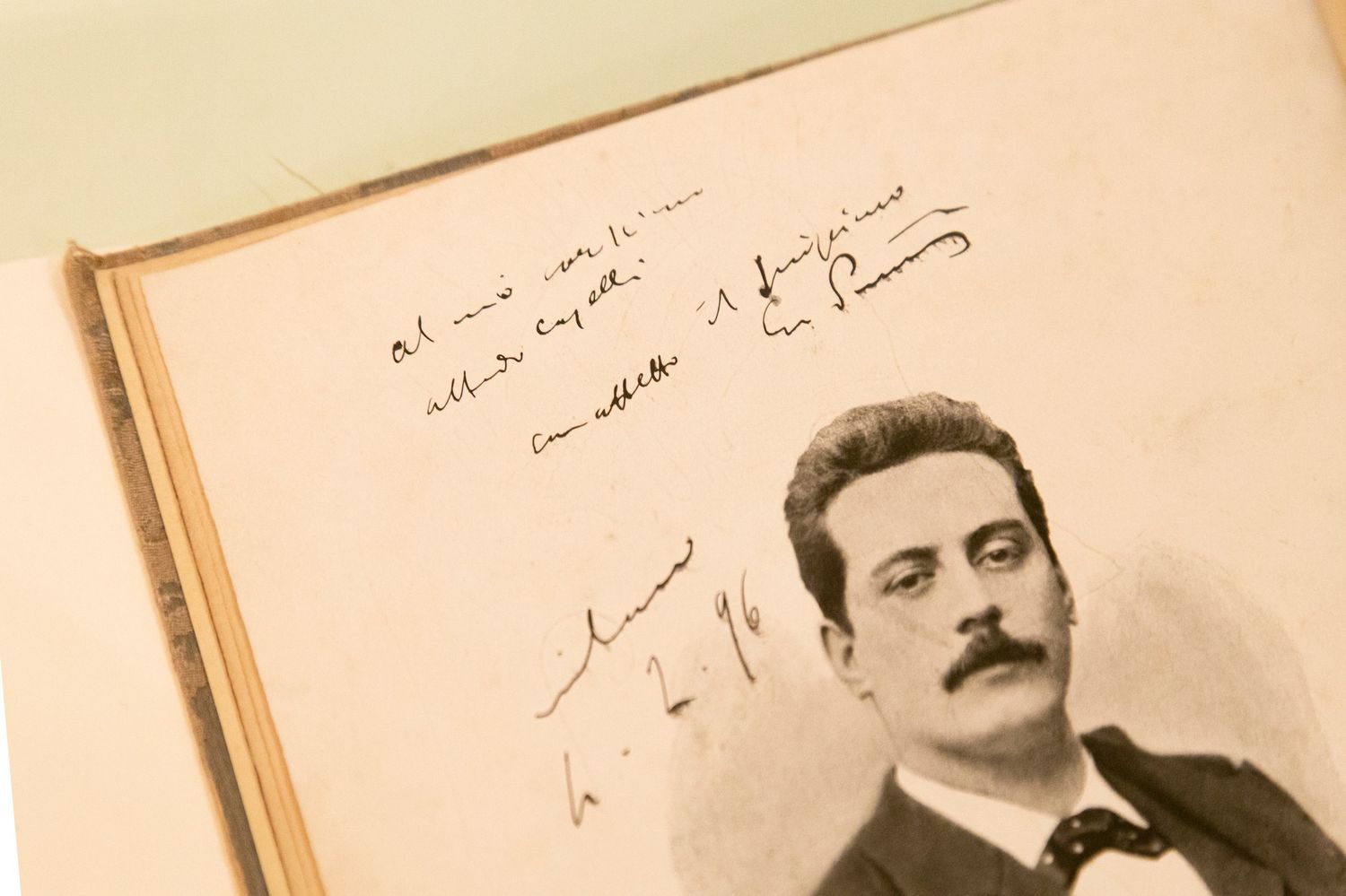
Music History
Why Was Giacomo Puccini Important To Music History
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the profound impact of Giacomo Puccini, renowned composer and his significant contributions to the rich tapestry of music history.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Giacomo Puccini, born on December 22, 1858, in Lucca, Italy, is considered one of the most influential composers in the history of music. His operatic works have endured the test of time and continue to captivate audiences around the world. Puccini’s ability to blend emotional depth with memorable melodies and intricate harmonies has cemented his place in the pantheon of musical geniuses.
Puccini’s impact on music history cannot be overstated. He expanded upon the traditions of Italian opera, infusing it with realism, intensity, and profound characterization. His works, such as “Tosca,” “La Bohème,” and “Madama Butterfly,” are celebrated for their ability to evoke a range of emotions, from heart-wrenching tragedy to soaring romanticism.
In this article, we will delve into the life, accomplishments, and musical genius of Giacomo Puccini. We will explore his early life and education, his breakthrough piece “Manon Lescaut,” his collaboration with librettists, his unique musical style, his relationship with Richard Wagner, and his lasting legacy in the world of classical music.
Join us on a journey through Puccini’s life and works, as we uncover the profound impact that this visionary composer has had on the rich tapestry of music history.
Early Life and Education
Giacomo Puccini was born into a family with a long-standing musical tradition in the town of Lucca, Italy. His father, Michele Puccini, was a composer and organist, and his ancestors had been musicians for several generations. Growing up in this musical environment, it was no surprise that Puccini showed an early aptitude for music.
At the age of five, Puccini started learning to play the piano from his uncle, Fortunato Magi, who was a skilled musician. Puccini quickly displayed prodigious talent, and by the age of nine, he was already composing his own music. Recognizing his immense potential, his family sent him to study composition at the Conservatorio di Musica in Milan.
Under the guidance of his teachers, Amilcare Ponchielli and Antonio Bazzini, Puccini honed his skills as a composer and pianist. He immersed himself in the rich musical culture of Milan, attending performances at La Scala and becoming familiar with the works of Verdi, Wagner, and other prominent composers of the time.
Puccini’s education was not without its challenges. Financial difficulties forced him to take on various odd jobs, including playing the organ and providing music lessons, to support himself during his studies. However, these hardships only fueled his determination to succeed.
During his time at the Conservatorio, Puccini composed several orchestral and choral works, showcasing his emerging talent and ability to craft compelling musical narratives. His early compositions highlight a growing confidence in his unique musical voice and foreshadow the masterpieces he would create later in his career.
After completing his studies at the Conservatorio, Puccini faced another setback when his first opera, “Le Villi,” was initially rejected. However, with the support of influential friends and mentors, Puccini persevered, and his opera eventually premiered to critical acclaim.
The early life and education of Giacomo Puccini served as the foundation for his remarkable musical career. His formative years in Lucca and Milan shaped his artistic sensibilities and provided the necessary tools for him to become one of the greatest opera composers in history.
Breakthrough with “Manon Lescaut”
“Manon Lescaut” marks a significant turning point in Giacomo Puccini’s career. Premiering in 1893, this opera not only showcased Puccini’s compositional brilliance but also established him as a prominent figure in the world of opera.
Based on the novel by Abbé Prévost, “Manon Lescaut” tells the tragic love story of the young and beautiful Manon and her lover, Des Grieux. Through Puccini’s masterful music and emotive storytelling, the opera captures the audience’s hearts, evoking a range of emotions from love and passion to despair and betrayal.
The success of “Manon Lescaut” lies in Puccini’s ability to infuse the characters with depth and complexity. His music elegantly reflects their inner turmoil and desires, creating a powerful connection between the audience and the characters. This ability to portray human emotions with such vividness and authenticity would become a hallmark of Puccini’s work.
The opera’s premiere in Turin was a resounding success, catapulting Puccini into the spotlight. Critics praised the young composer’s talent and the beauty of the music, recognizing his unique ability to craft melodies that resonated deeply with audiences. “Manon Lescaut” established Puccini as a true master of opera and set the stage for his subsequent triumphs.
One of the standout features of “Manon Lescaut” is Puccini’s innovative use of orchestration. He skillfully blends the voices and instruments, creating a rich and vibrant sound palette that enhances the dramatic tension of the opera. From the sweeping melodies of the romantic duets to the tumultuous crescendos of the climactic moments, Puccini’s orchestration adds a layer of depth and intensity to the story.
Furthermore, “Manon Lescaut” further solidifies Puccini’s reputation for creating compelling female characters. Manon, with her complex desires and inner conflicts, emerges as a fully realized and relatable protagonist. Puccini’s ability to capture the essence of female characters would continue to be a defining aspect of his later works.
The success of “Manon Lescaut” propelled Puccini to new heights of artistic achievement and firmly established his position as one of the preeminent opera composers of his time. This breakthrough opera not only showcased Puccini’s immense talent but also laid the foundation for the extraordinary works that he would go on to create in the years to come.
Opera Masterpieces: Tosca and La Bohème
Giacomo Puccini’s career reached new heights with the creation of his two iconic opera masterpieces, “Tosca” and “La Bohème.” These works not only solidified Puccini’s status as a leading composer of his time but also continue to be beloved and frequently performed today.
“Tosca,” first premiered in 1900, is a thrilling tale of love, jealousy, and political intrigue set in Rome during the Napoleonic era. Puccini’s music intensifies the dramatic tension of the story, capturing the emotional depth of the characters and the high stakes of their actions. From the passionate arias of Tosca to the menacing melodies of the villainous Scarpia, Puccini weaves a musical tapestry that immerses the audience in the world of the opera. The opera’s climactic moments, including Tosca’s iconic aria “Vissi d’arte,” continue to captivate audiences with their power and poignancy.
“La Bohème,” premiered in 1896, depicts the lives of a group of struggling artists in bohemian Paris. With its beautiful melodies, vibrant orchestration, and poignant storytelling, the opera captures the joys, sorrows, and romantic aspirations of its characters. Puccini’s gift for creating emotionally resonant music is particularly evident in the famous arias “Che gelida manina” and “Mi chiamano Mimì.” “La Bohème” is a testament to Puccini’s ability to create vivid and relatable characters and to craft music that embodies the spirit of the story.
Both “Tosca” and “La Bohème” showcase Puccini’s incredible talent for combining powerful storytelling with memorable melodies and evocative harmonies. His music effortlessly expresses the range of human emotions, from passionate love to heartbreaking tragedy, drawing listeners into the world of the opera and leaving a lasting impact.
Furthermore, Puccini’s operas reflected the changing musical landscape of the time. He embraced the verismo style, which emphasized realistic and gritty portrayal of everyday life. By infusing his works with this authenticity and emotional depth, Puccini revolutionized the opera genre and became its leading figure during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
“Tosca” and “La Bohème” not only catapulted Puccini to the pinnacle of operatic success but also continue to be widely performed and celebrated today. Their timeless themes, exquisite music, and compelling characters ensure their enduring popularity and secure Puccini’s place as one of the greatest opera composers in history.
Collaboration with Librettists
One of the key factors behind the success of Giacomo Puccini’s opera masterpieces was his collaboration with talented librettists. Puccini understood the importance of working closely with skilled writers to craft compelling narratives that paired seamlessly with his music. He sought out librettists who could bring his musical ideas to life and create characters with depth and complexity.
One of Puccini’s most notable collaborations was with Luigi Illica and Giuseppe Giacosa. Together, they worked on several of Puccini’s operas, including “Manon Lescaut,” “La Bohème,” “Tosca,” and “Madama Butterfly.” Illica and Giacosa were adept at creating poetic and evocative texts that perfectly complemented Puccini’s musical language. Their expertise in storytelling and their ability to capture the essence of the characters elevated Puccini’s operas to new artistic heights.
Puccini’s collaboration with librettist Luigi Illica gave birth to some of his most beloved works. Illica’s careful attention to detail and his ability to create vivid and emotionally resonant dialogue greatly contributed to the success of operas like “La Bohème” and “Tosca.” Together, Puccini and Illica crafted stories that delved into the depths of human emotions, exploring themes of love, jealousy, sacrifice, and redemption.
Another significant partnership was formed between Puccini and librettist Giuseppe Giacosa. Their collaboration resulted in the timeless masterpiece “Madama Butterfly,” among others. Giacosa’s delicate treatment of the libretto, combined with Puccini’s poignant melodies, vividly portrayed the tragic tale of love and cultural clash in a complex and deeply moving way.
Puccini’s collaboration with librettists was characterized by a strong sense of mutual respect and a shared vision for creative storytelling. He valued the input and expertise of his librettist partners, allowing them to shape the narratives and contribute their own artistic insights. The synergy between composer and librettist was instrumental in creating works that continue to resonate with audiences to this day.
It is worth noting that Puccini’s collaborations were not limited to Illica and Giacosa. He also worked with other skilled writers, such as Adami and Forzano, on operas like “Turandot” and “Gianni Schicchi.” Each partnership brought a unique perspective and artistic sensibility to Puccini’s music, resulting in a diverse and rich body of work.
The collaboration between Giacomo Puccini and his talented librettists helped shape the narrative brilliance and emotional depth of his operas. Through their combined talents, they created timeless stories that transcend language and cultural barriers, leaving a lasting impact on the world of opera.
Puccini’s Unique Musical Style
Giacomo Puccini’s contributions to music history extend beyond his captivating storytelling and collaboration with librettists. His distinct musical style, marked by lush harmonies, memorable melodies, and innovative use of orchestration, sets him apart as a true master of the craft.
Puccini possessed a remarkable ability to create music that resonated deeply with listeners, evoking a wide range of emotions. His melodies have a singularity and immediacy that make them instantly recognizable and emotionally compelling. From the soaring arias to the tender love duets, Puccini’s music captures the essence of the human experience.
One of Puccini’s stylistic trademarks is his skillful use of leitmotifs, or recurring musical themes associated with specific characters, ideas, or emotions. These motifs serve as musical anchors throughout his operas, underscoring dramatic moments and adding depth to the storytelling. The use of leitmotifs allows Puccini to seamlessly weave together the various elements of the narrative, creating a cohesive and immersive experience for the audience.
Another hallmark of Puccini’s musical language is his vibrant and rich orchestration. He employed a diverse range of instrumental colors, utilizing the full potential of the orchestra to enhance the emotional impact of his works. From delicate solos to dramatic crescendos, Puccini imbued his compositions with a dynamic and evocative sound palette.
Puccini’s unique musical style also emerged in his harmonies. He skillfully blended traditional tonal structures with chromaticism, creating tension and color in his compositions. These harmonic complexities lend a sense of emotional depth and complexity to his music, adding layers of meaning to the narrative he unfolds.
Furthermore, Puccini embraced the verismo style, which sought to portray realistic and gritty aspects of everyday life. This translated into his music, where he emphasized the raw and passionate emotions of his characters. Puccini’s ability to capture the essence of human emotions with authenticity and intensity is a testament to his unique musical voice.
Despite his innovative approach, Puccini remained firmly rooted in the Italian operatic tradition. His works echo the influence of composers like Verdi, while also expanding upon their foundations, pushing the boundaries of what opera could accomplish as an art form.
Puccini’s unique musical style and his ability to fuse powerful melodies, rich harmonies, innovative orchestration, and authentic storytelling have made his music timeless and beloved by audiences around the world. His compositions continue to captivate listeners, evoking profound emotions and leaving an indelible mark on the history of music.
Relationship with Richard Wagner
The relationship between Giacomo Puccini and Richard Wagner, two towering figures in the world of opera, was both complex and influential. While Puccini was greatly influenced by Wagner’s innovative musical approach, he also carved out his own distinct artistic path.
Puccini’s admiration for Wagner’s work can be seen in his incorporation of certain Wagnerian elements into his operas. He was particularly drawn to Wagner’s use of leitmotifs and his ability to weave together music and drama seamlessly. Puccini recognized the power of these techniques in enhancing the emotional impact of the storytelling and sought to incorporate them into his own compositions.
However, Puccini did not simply imitate Wagner. He adapted Wagnerian techniques to his own unique musical language and Italian opera tradition. While he adopted the use of leitmotifs, Puccini utilized them in a more subtle and restrained manner compared to Wagner’s grandiose approach. He focused on creating memorable melodic motifs that enhanced the characters and their emotions without overpowering the narrative.
Puccini’s relationship with Wagner extended beyond musical influences. In 1884, Puccini traveled to Bayreuth, the home of the Wagner festival, to attend a performance of Wagner’s “Parsifal.” The experience left a lasting impression on him, solidifying his admiration for Wagner’s artistry and his belief in the transformative power of opera.
Despite his admiration for Wagner, Puccini maintained a sense of independence as a composer. He did not fully align himself with the Wagnerian ideal of “Gesamtkunstwerk” or the concept of opera as a total work of art that integrates various artistic forms. Instead, Puccini focused on creating emotionally compelling stories through his music, while giving due importance to the libretto and the stage production.
Puccini’s compositions diverged from Wagner’s in terms of subject matter and style. While Wagner explored mythological and historical themes in his grand operatic epics, Puccini focused on realistic portrayals of everyday life and the human condition. His operas resonated with audiences through their relatability and emotional depth, often featuring characters from different social backgrounds and exploring universal themes like love, passion, and sacrifice.
Despite their differences, Wagner’s influence on Puccini cannot be denied. Puccini’s engagement with Wagner’s techniques and ideas added a new layer of depth and complexity to his own compositions. His unique blend of Italian operatic traditions and Wagnerian techniques became a hallmark of his musical style.
Giacomo Puccini’s relationship with Richard Wagner was one of admiration and artistic inspiration. Puccini’s exploration of Wagner’s techniques, combined with his own individuality as a composer, resulted in a musical legacy that continues to enchant and captivate audiences to this day.
Last Works and Legacy
In the final years of his life, Giacomo Puccini created some of his most celebrated and enduring works. Despite battling illness, he continued to innovate and push the boundaries of opera, leaving an indelible mark on the musical world.
One of Puccini’s last major compositions was “Turandot,” an epic tale set in ancient China. Collaborating with librettists Giuseppe Adami and Renato Simoni, Puccini weaved together a story of love, power, and sacrifice. “Turandot” stands out for its grandeur, larger-than-life characters, and powerful choruses. The opera is best known for the famous aria “Nessun Dorma,” which has become synonymous with Puccini’s name and has been performed by countless artists across the world.
Puccini’s final opera was “Gianni Schicchi,” a one-act comedic masterpiece. This lighthearted and witty work showcases Puccini’s versatility as a composer, demonstrating his ability to seamlessly transition from intense drama to comedic storytelling. “Gianni Schicchi” is filled with memorable melodies and showcases Puccini’s skill for creating vibrant and memorable characters.
Puccini’s untimely death in 1924, before completing his opera “Turandot,” left the ending unfinished. His colleague, Franco Alfano, was tasked with completing the work based on Puccini’s sketches and indications. “Turandot” premiered posthumously in 1926 and became a part of Puccini’s legacy, showcasing his ability to captivate audiences with his unbridled imagination and innovative approach to opera.
Giacomo Puccini’s legacy extends far beyond his own lifetime. His works continue to be regularly performed and cherished by audiences worldwide. The emotional depth, memorable melodies, and relatable characters in operas like “La Bohème,” “Tosca,” and “Madama Butterfly” have ensured their enduring popularity.
Furthermore, Puccini’s influence can be seen in the works of subsequent composers. His innovative use of leitmotifs, rich orchestrations, and emotionally charged storytelling helped pave the way for the development of modern opera. Composers such as Samuel Barber, Leonard Bernstein, and Benjamin Britten have acknowledged Puccini’s impact on their own works.
Additionally, Puccini’s ability to blend traditional Italian operatic conventions with new ideas reflected the changing cultural landscape of his time. His operas captured the spirit of the fin de siècle, embracing both the grandeur of the past and the emerging modern sentiment.
The mark Puccini left on the world of opera is immeasurable. His ability to create music that resonates deeply with audiences, combined with his masterful storytelling and command of the stage, solidified his status as one of the greatest opera composers in history. His works continue to inspire and move audiences, ensuring that his legacy remains vivid and cherished in the tapestry of music history.
Conclusion
Giacomo Puccini’s contributions to music history are nothing short of extraordinary. His ability to blend powerful storytelling, memorable melodies, and innovative techniques has made him one of the most influential composers in the world of opera.
From his early breakthroughs with operas like “Manon Lescaut” to his enduring masterpieces like “Tosca” and “La Bohème,” Puccini’s works continue to captivate audiences with their emotional depth and timeless appeal. His collaboration with talented librettists like Luigi Illica and Giuseppe Giacosa elevated his operas to new artistic heights, while his distinct musical style blended rich harmonies, evocative orchestration, and authentic characterizations.
Puccini’s relationship with Richard Wagner, though complex, left a significant impact on his artistic development. While he drew inspiration from Wagner’s techniques, Puccini forged his own path, incorporating Wagnerian elements into his signature style and creating operas that were undeniably his own.
In his last works, Puccini displayed his unwavering commitment to innovation, crafting “Turandot” and “Gianni Schicchi” with his characteristic brilliance and imagination. Despite his untimely death, his legacy continued to flourish, with his works remaining popular and his influence felt by generations of composers to come.
Giacomo Puccini’s impact on music history cannot be overstated. His ability to translate complex human emotions into music, his dedication to storytelling, and his unwavering pursuit of artistic excellence have solidified his place among the legendary composers of all time.
As his operas continue to be performed on stages across the globe, Puccini’s legacy lives on, inspiring and captivating audiences with their beauty, passion, and profound emotional resonance. His genius as a composer, his ability to transport listeners to worlds of love, tragedy, and human connection, ensures that his name will forever be synonymous with the power and enchantment of opera.











