Home>Events & Info>Note>How To Read Music Note For Guitar


Note
How To Read Music Note For Guitar
Modified: February 13, 2024
Learn how to read music notes specifically for guitar. Master the art of deciphering musical notation and improve your guitar playing skills.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the wonderful world of reading music notes for guitar! Whether you are a beginner or an experienced guitarist looking to expand your musical horizons, learning how to read sheet music can greatly enhance your skills and open up a whole new world of playing opportunities.
Reading music may seem like a daunting task at first, but fear not! With a little guidance and practice, you can become proficient in deciphering musical notation and unlocking the secrets to playing any song you desire.
Why should you learn how to read music notes for guitar? Well, it offers numerous benefits that can greatly improve your overall musicianship. First and foremost, it allows you to accurately reproduce musical compositions as they were intended to be played. It gives you the ability to communicate and collaborate with other musicians, opening up opportunities for jamming and performing together. Additionally, reading music enhances your understanding of musical theory, enabling you to compose your own music and improvise with confidence.
One of the first steps to reading music notes for guitar is understanding the staff. The staff is a set of five horizontal lines and four spaces that musical notes are placed on. Each line and space represents a different pitch, creating a visual representation of the musical sound.
Once you grasp the concept of the staff, you will be introduced to two different clefs commonly used in guitar sheet music: the treble clef and the bass clef. These clefs indicate which range of notes the music is written for, allowing you to determine the appropriate finger positions and frets on the guitar.
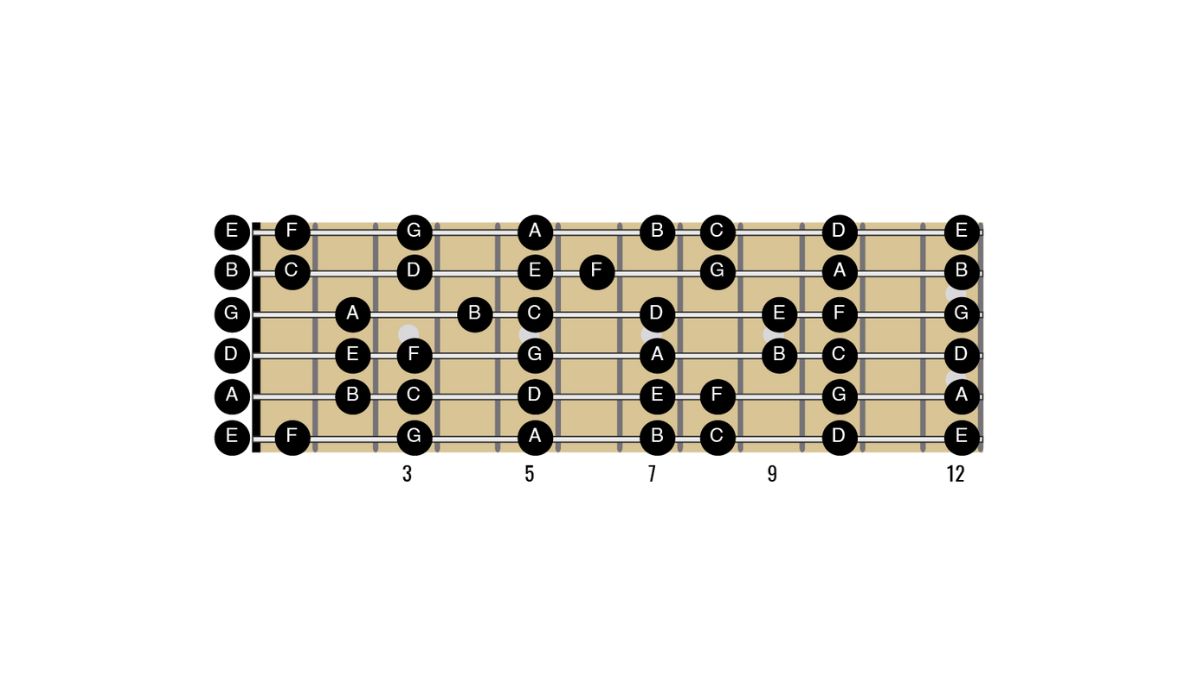
Reading notes on the guitar fretboard is another crucial skill to master. Each of the six strings on the guitar is designated with a specific letter name, and the notes on the fretboard are represented by dots placed on the corresponding string and fret. By knowing the names of the notes on the fretboard, you can easily identify and play any desired pitch on the guitar.
Guitar notation also includes symbols and markings that indicate the various techniques and expressions to be applied while playing. These can include bends, slides, hammer-ons, pull-offs, and many more. Familiarizing yourself with these notations will enable you to accurately reproduce the nuances and dynamics of a piece of music.
In addition to reading individual notes, it is essential to understand how to read rhythms and time signatures. This allows you to establish the correct timing and rhythmical patterns of a song, ensuring that you play it with the intended feel and groove.
Identifying guitar chords on sheet music is another valuable skill that will greatly enhance your playing. Chords are represented by a series of stacked notes, indicating which combinations of pitches should be played simultaneously. Being able to read chords from sheet music allows you to play complex chord progressions and strum patterns with ease.
Like any skill, learning to read music notes for guitar requires practice and patience. Dedicate regular time to study and review sheet music, gradually increasing the complexity of the pieces you tackle. Be sure to seek out various genres and styles to broaden your musical vocabulary.
So, are you ready to embark on this exciting musical journey? Grab your guitar, a sheet of music, and let’s dive into the world of reading music notes for guitar!
Understanding the Staff
The staff is a fundamental component of sheet music and serves as a visual representation of musical notes and pitches. It consists of five horizontal lines and four spaces, with each line and space representing a specific note on the musical scale.
When reading music notes for guitar, it’s essential to understand how the notes are positioned on the staff. The placement of a note on the staff indicates its pitch, which determines the sound it produces when played.
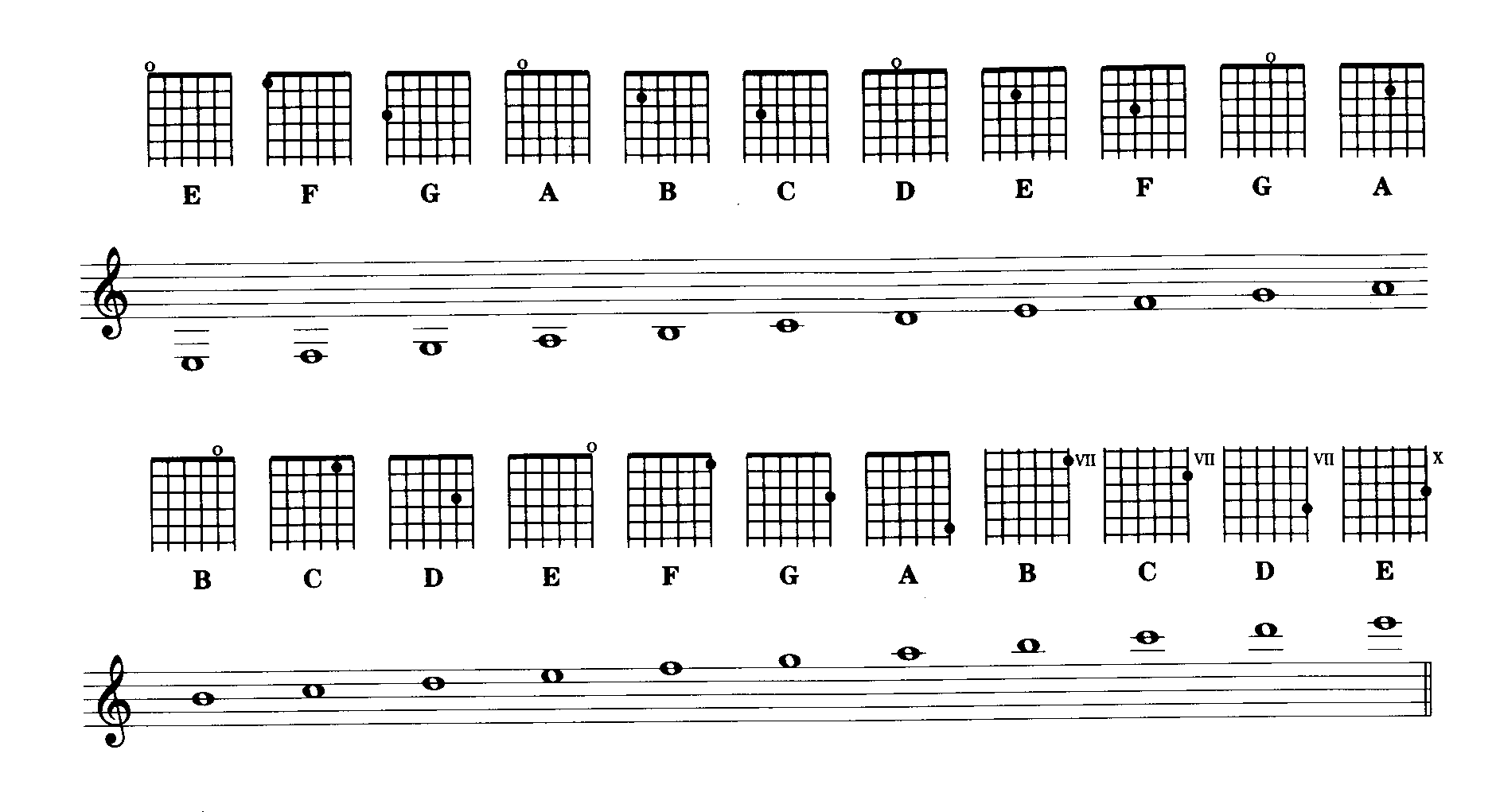
Let’s start by identifying the lines and spaces of the staff, as well as the corresponding notes. The lines, from bottom to top, are named E, G, B, D, and F. The spaces, from bottom to top, are named F, A, C, and E.
To help remember the names of the lines, a popular mnemonic device is commonly used: “Every Good Boy Does Fine.” Similarly, to remember the names of the spaces, the mnemonic “F-A-C-E” is often used.
It’s important to note that these note names are applicable when using the treble clef staff. The bass clef staff, on the other hand, utilizes different note names, which we will explore in a later section.
In addition to the lines and spaces, the staff also includes ledger lines. Ledger lines are small lines placed above or below the staff to represent notes that fall outside the range of the staff’s lines and spaces.
By understanding how notes are positioned on the staff, you can easily locate and identify specific pitches while reading sheet music for guitar. This knowledge is crucial for accurately reproducing melodies, chords, and various musical passages.
It’s important to mention that each line and space on the staff represents a specific pitch, not a specific fret on the guitar. The actual note to be played on the guitar will depend on the string and fret combination. However, the staff provides a visual reference for understanding the relative pitch of the notes in the music.
Take some time to familiarize yourself with the positioning of notes on the staff and practice identifying them. Start by locating and naming individual notes, then progress to identifying melodies and chords.
Understanding the staff is a crucial foundation for reading music notes for guitar. With practice and repetition, you will become more comfortable navigating the staff and interpreting the pitches represented by the notes, opening up a world of musical possibilities.
The Treble Clef
The treble clef is the most commonly used clef in guitar sheet music. It is also known as the G clef because of the way the symbol is shaped, with a spiral looping around the second line of the staff, indicating that this line represents the note G.
The treble clef is used to notate higher-pitched notes and is typically played on the higher strings of the guitar. When reading sheet music with the treble clef, you will primarily encounter melody lines, solos, and higher-pitched guitar parts.
Learning how to recognize and interpret the treble clef is essential for understanding the pitches and rhythms written on the guitar sheet music. By understanding the treble clef staff, you can determine which strings and frets to play on the guitar for the given notes.
Remembering the notes represented by the lines and spaces of the treble clef can be made simpler with the same mnemonic device used for the lines of the staff: “Every Good Boy Deserves Fudge.” This mnemonic represents the notes E, G, B, D, and F, which are represented by the lines of the treble clef staff, from bottom to top.
For the spaces of the treble clef staff, the notes are represented by the mnemonic “FACE,” just like in the general understanding of the staff. These spaces correspond to the notes F, A, C, and E, from bottom to top.
As a guitarist, understanding the treble clef and being able to identify the pitches represented by the notes on the staff will enable you to accurately play melodies and guitar solos written in sheet music. It also allows you to coordinate your left-hand finger positions and your right-hand picking or strumming techniques.
Practicing reading and playing music notes on the treble clef staff will gradually improve your ability to read sheet music fluently. Start with simple melodies and exercises, and gradually progress to more complex pieces. As you become more comfortable with the treble clef, you will find that reading music becomes more intuitive and natural.
Remember, mastering the treble clef is a skill that takes time and practice. But the ability to read and interpret this clef will greatly expand your musical repertoire and help you become a well-rounded guitarist.
The Bass Clef
In addition to the treble clef, another commonly used clef in guitar sheet music is the bass clef. Often referred to as the F clef, the bass clef indicates lower-pitched notes on the staff.
The bass clef is easily recognizable by its distinctive shape, resembling a stylized letter “F” with two dots flanking the fourth line of the staff. This line represents the note F, giving the clef its name.
When reading sheet music with the bass clef, you will typically encounter lower melody lines, basslines, and chord notations. This clef is commonly used for notating the lower-pitched strings of the guitar.
To help identify the pitches represented by the lines and spaces of the bass clef staff, a mnemonic device can be used. The lines on the bass clef staff, from bottom to top, can be remembered as “Good Boys Do Fine Always.” This mnemonic represents the notes G, B, D, F, and A.
Similarly, for the spaces of the bass clef staff, another mnemonic device can be employed. The spaces, from bottom to top, can be remembered using the phrase “All Cows Eat Grass,” representing the notes A, C, E, and G.
Understanding and interpreting the bass clef is crucial for playing lower-pitched melodies, basslines, and chords on the guitar. By recognizing the notes indicated on the staff, you can determine the appropriate finger positions and frets to play on the lower strings of the guitar.
Practicing reading and playing music notes on the bass clef staff will enhance your ability to read sheet music accurately and play musical passages intended for the lower range of the guitar. Start with simple exercises and progress to more complex pieces as your skill and familiarity with the bass clef improve.
Mastering the bass clef, along with the treble clef, will greatly expand your proficiency as a guitarist and allow you to tackle a broader range of music. By being able to read and interpret both clefs, you will have the flexibility to play melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions with ease, enabling you to become a versatile and well-rounded musician.
Remember, like any new skill, becoming proficient in reading the bass clef takes time and practice. However, with perseverance and dedication, you will develop the ability to read and play sheet music written in the bass clef, furthering your musical journey on the guitar.
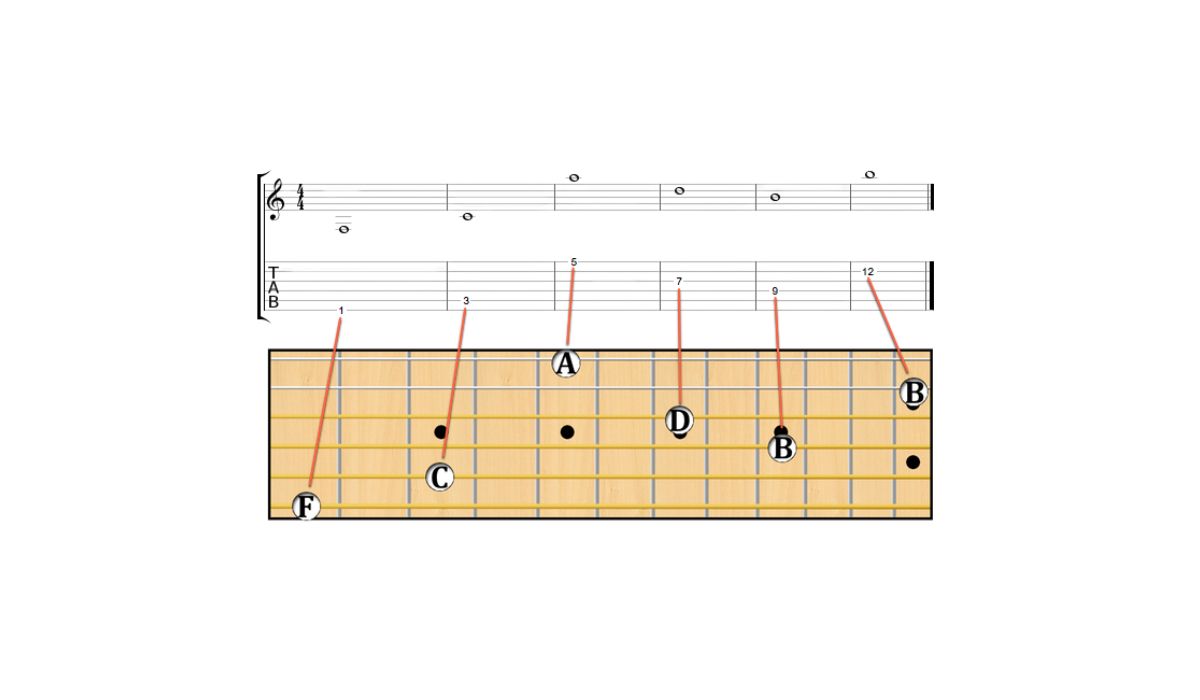
Reading Notes on the Guitar Fretboard
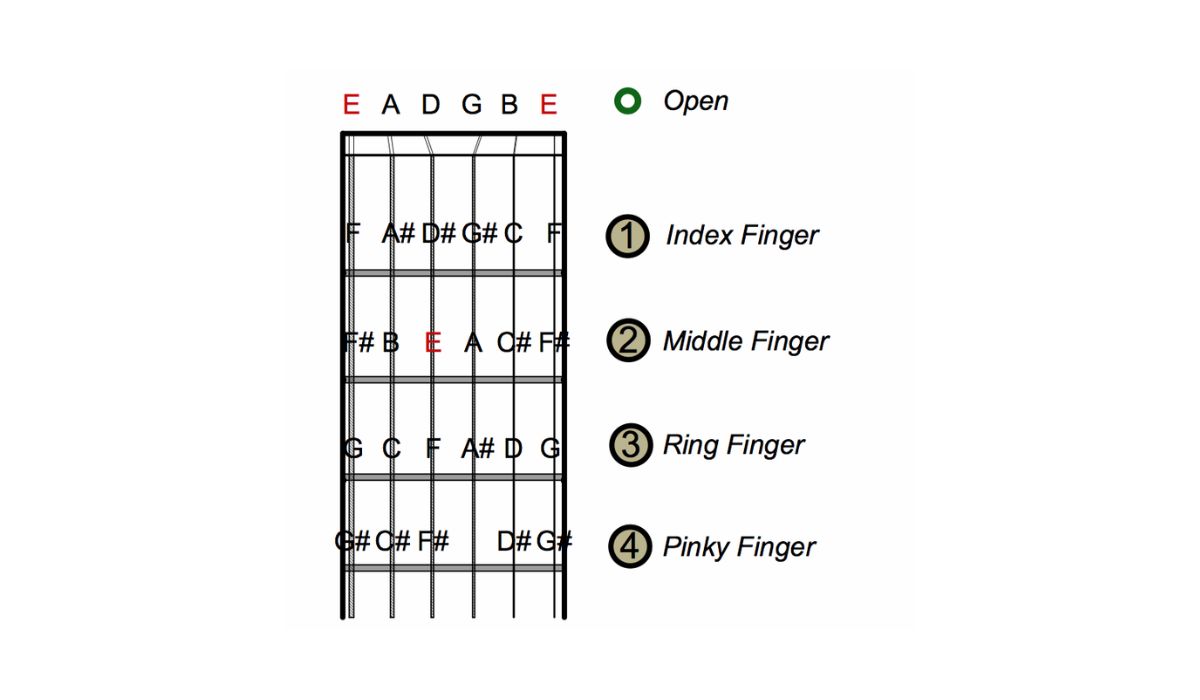
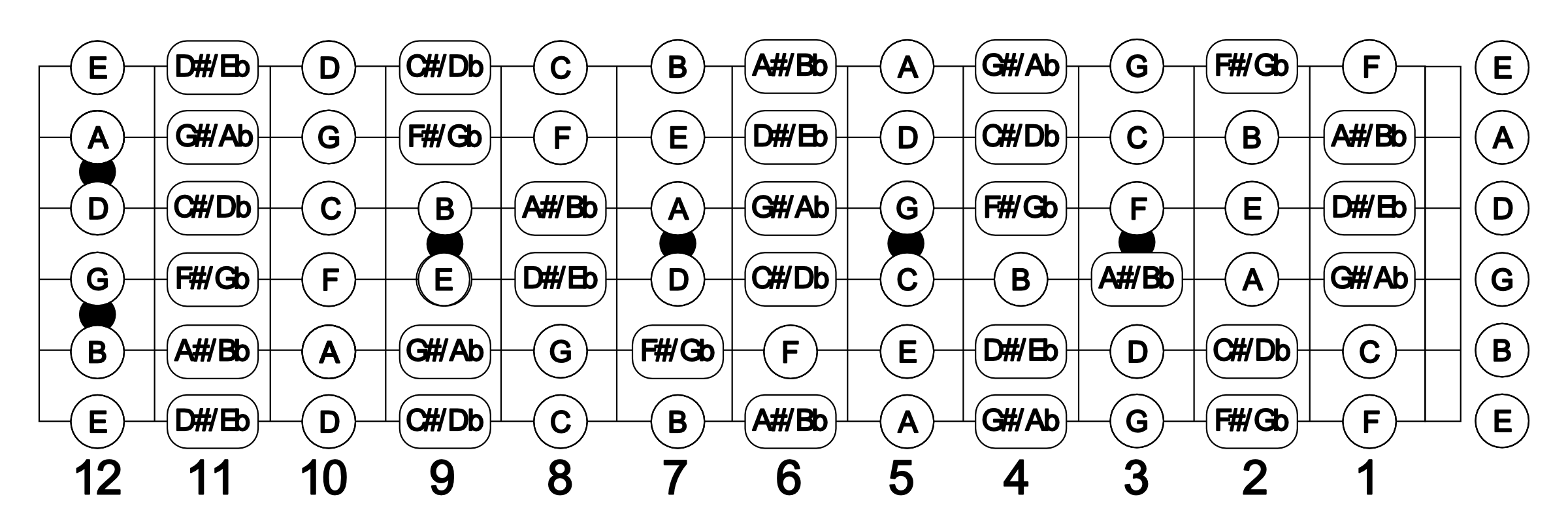
When it comes to reading music notes for guitar, understanding how to locate and play the notes on the guitar fretboard is essential. Each string on the guitar is associated with a specific letter name, and notes on the guitar fretboard are represented by dots placed on the corresponding string and fret.
Learning the names of the notes on the guitar fretboard is crucial for reading sheet music accurately and efficiently. Starting from the thinnest string (high E string) to the thickest string (low E string), the standard tuning of the guitar is E, B, G, D, A, E. Each fret on each string corresponds to a different note.
For example, when you press down the third fret on the low E string (thickest string), you are playing the note G. Similarly, pressing down the fifth fret on the same string would produce the note A. These relationships between frets and notes apply to each string on the guitar.
Familiarizing yourself with the names of the notes on the guitar fretboard allows you to quickly identify the pitches indicated on the sheet music and apply them to the corresponding frets on the guitar. This skill enables you to play melodies, chords, and other musical passages accurately.
As you progress in your guitar playing journey, reading notes on the guitar fretboard will become second nature. You will be able to identify the notes on the sheet music and play them directly on the guitar without hesitation. This fluency in reading notes on the guitar fretboard enhances your ability to learn and perform music from various genres and styles.
One helpful exercise to improve your note-reading skills on the guitar is to practice playing scales and exercises using sheet music. This allows you to reinforce the connection between the notes on the sheet music and their corresponding positions on the guitar fretboard.
Additionally, there are online resources and apps available that offer interactive fretboard exercises and drills to help you memorize the notes on the guitar. These tools provide a visual interface that allows you to practice identifying notes on the guitar fretboard and develop muscle memory.
Remember, reading notes on the guitar fretboard is a skill that requires practice and repetition. Take the time to study and familiarize yourself with the notes on each string, starting from the open strings and gradually working your way up the fretboard. With consistent practice, you will become more proficient in reading music notes for guitar and open up new possibilities for your playing.
Recognizing Common Guitar Notation
When learning to read music notes for guitar, it’s important to become familiar with the common notation symbols and markings specific to the guitar. These symbols provide valuable information about how to play the music accurately and expressively.
One of the most commonly used symbols in guitar notation is the note head. The shape of the note head indicates the duration of the note. A solid note head represents a quarter note, while a note head with a stem can indicate different note durations, such as eighth notes, sixteenth notes, and so on.
Another essential symbol in guitar notation is the rhythmic notation, which includes rests. Rests indicate moments of silence in the music, allowing for pauses between notes or beats. Rests are represented by various symbols, such as a filled-in rectangle for a whole rest or a smaller vertical line for a quarter rest.
In addition to note heads and rests, guitar notation includes various markings and symbols that represent specific techniques and expressions. For example, a downward arrow indicates a downward pick stroke, while an upward arrow represents an upward pick stroke. Hammer-ons and pull-offs are denoted by curved lines connecting two notes. Additionally, symbols such as bends, slides, vibrato, and palm muting are used to indicate specific playing techniques.
Chord notation is another essential aspect of guitar notation. Chords are represented by a series of stacked notes, indicating which combinations of pitches should be played simultaneously. Each note in the chord is usually indicated by a note head, and the fret number is shown on the corresponding string.
It’s important to mention that guitar notation also incorporates tablature, often referred to as tabs. Tabs provide a visual representation of the guitar fretboard, with numbers indicating which frets and strings to play. Tabs are commonly used in combination with standard notation to provide precise finger positioning on the guitar.
Alongside the symbols and notation specific to the guitar, you will also encounter standard notation symbols used in general music notation. These symbols include key signatures, time signatures, dynamics (such as pianissimo or forte), and other expressive markings that contribute to the interpretation of the music.
To become proficient in recognizing guitar notation, it’s important to practice reading sheet music that incorporates these symbols and markings. Start with simple exercises and gradually progress to more complex pieces. As you encounter different symbols and notations, refer to a guitar notation guide or music theory resources to understand their meanings.
By becoming comfortable with recognizing common guitar notation, you will gain the knowledge and skills needed to accurately and expressively bring music to life on the guitar. Practice regularly, pay attention to details, and embrace the beauty of reading and interpreting the intricacies of guitar notation.
Reading Rhythms and Time Signatures
Reading rhythms and understanding time signatures is vital for accurately interpreting and playing music notes for guitar. Rhythm refers to the duration and pattern of notes, and time signatures provide a framework for organizing these rhythms within a piece of music.
A time signature consists of two numbers stacked vertically at the beginning of a staff. The top number indicates the number of beats or counts per measure, while the bottom number represents the note value that receives one beat. For example, in a 4/4 time signature, there are four beats per measure, and a quarter note receives one beat. This is the most common time signature in music.
Other common time signatures include 3/4, which indicates three beats per measure with a quarter note receiving one beat, and 6/8, which signifies six beats per measure with an eighth note receiving one beat. More complex time signatures, such as 5/4 or 7/8, are also used to create unique rhythmic patterns and meters.
When reading rhythms, it’s important to understand note values and their corresponding durations. The most basic note value is the whole note, which receives four beats in a 4/4 time signature. A half note receives two beats, a quarter note receives one beat, an eighth note receives half a beat, and so on.
To further complicate the rhythm, rests also have corresponding durations. A whole rest occupies a full measure of silence, a half rest takes up two beats, a quarter rest represents one beat, and an eighth rest denotes half a beat.
Learning to read rhythms involves understanding how these different note and rest values fit into the given time signature. By counting the beats and subdividing them, you can accurately interpret the rhythm and play it with the intended timing.
Notating rhythm in guitar sheet music may also include additional symbols and markings to indicate specific rhythmic patterns, such as syncopation, dotted notes, ties, and accents. These markings provide guidance on how to rhythmically interpret the music and add depth to the performance.
Practicing reading rhythms and time signatures can be done by using rehearsal exercises and playing along with a metronome. Start with simple exercises, focusing on counting and playing the rhythms accurately, and gradually progress to more complex pieces as your rhythmic reading skills improve.
Remember, the ability to read and interpret rhythms and time signatures is an essential skill for any guitarist. It allows you to play music with the correct rhythm, groove, and timing, enabling you to effectively communicate and connect with other musicians. Dedicate time to regularly practice reading rhythms to enhance your overall musicianship and become a more well-rounded guitarist.
Identifying Guitar Chords on Sheet Music
Being able to identify guitar chords on sheet music is a valuable skill that allows you to play complex chord progressions and strum patterns accurately. Chords are represented by a series of stacked notes on the staff, indicating which combinations of pitches should be played simultaneously.
Guitar chords are typically notated using chord symbols or chord diagrams. Chord symbols consist of a letter or letters representing the root note of the chord, followed by additional symbols or numbers that indicate the chord quality and any necessary modifications.
For example, a basic major chord, such as C major, is represented by the letter “C”. A minor chord, such as A minor, is indicated by the letter “A” followed by a lowercase “m”. Other symbols, such as “+” for a major chord with an added note, or “dim” for a diminished chord, may also be used to denote specific chord qualities.
Chord diagrams provide a visual representation of the guitar fretboard along with dots or numbers indicating which strings and frets to press down to form the chord. These diagrams are especially helpful for beginners or those who prefer a visual reference for finger placement. They allow you to see the exact finger positioning required for a particular chord shape.
When reading sheet music that includes guitar chords, it’s important to pay attention to the context and timing of the chords within the musical arrangement. Chord changes may be indicated by vertical lines, chord symbols written above the staff, or simply by the timing of the lyrics or melody.
To identify and play guitar chords accurately from sheet music, start by familiarizing yourself with basic chord shapes and their corresponding chord symbols. Learn the root notes, finger positions, and variations of common chords such as major, minor, and seventh chords.
Having a solid foundation in chord theory and chord shapes will greatly enhance your ability to identify and play chords from sheet music. With practice, you’ll become more proficient in recognizing chord symbols and diagrams, allowing you to quickly execute chord changes and play along with confidence.
It’s worth noting that in addition to chord symbols and diagrams, guitar sheet music may also include chord notation within the staff. This form of notation indicates the individual notes of the chord and their respective rhythms, allowing for more nuanced interpretations of chord voicings and inversions.
To improve your chord-reading skills, practice playing chord progressions from various genres and styles. Start with simple progressions and gradually progress to more complex arrangements. This will develop your ability to read and transition between chords fluidly, expanding your repertoire and enabling you to play a wider range of songs.
Developing the skill to identify guitar chords on sheet music opens up a world of musical possibilities. It empowers you to accurately reproduce songs and perform them with the intended harmony and structure. Dedicate time to practice and study chord notation, and soon you’ll be able to effortlessly navigate and interpret guitar chords on sheet music.
Tips for Practicing Reading Music Notes for Guitar
Reading music notes for guitar is a skill that requires practice, patience, and dedication. The more you practice, the more comfortable and proficient you will become. Here are some tips to help you enhance your reading skills:
- Start with simple exercises: Begin by practicing simple exercises that focus on individual notes, such as playing melodies or scales. This will help you become familiar with the positions of the notes on the staff and on the guitar fretboard.
- Gradually increase difficulty: As you gain confidence, gradually work your way up to more complex pieces of music. Start incorporating chords, different rhythms, and challenging passages to expand your reading abilities.
- Practice sight-reading: Sight-reading is the ability to read and play music on the spot without prior preparation. Set aside dedicated time to practice sight-reading exercises and pieces. This will improve your ability to quickly process and play unfamiliar music.
- Use a metronome: By practicing with a metronome, you can develop a strong sense of timing and improve your rhythmic accuracy. Start at a slower tempo, allowing yourself to read and play the notes accurately, and gradually increase the speed as you become more comfortable.
- Study music theory: Understanding music theory will greatly assist you in reading music notes for guitar. Learn about key signatures, scales, intervals, and common chord progressions. This knowledge will give you a deeper understanding of the musical patterns you encounter in sheet music.
- Practice with different genres: Explore sheet music from various styles and genres of music. This will expose you to different musical patterns, rhythms, and chord progressions, helping you become a versatile and well-rounded guitarist.
- Use visualization techniques: Practice visualizing the notes on the staff and relating them to the guitar fretboard. Mentally go through the motions of playing the notes on the correct strings and frets. This visualization exercise strengthens the connection between the staff notation and the physical act of playing.
- Work with a teacher or mentor: Consider taking lessons from a guitar teacher who specializes in reading music. A knowledgeable instructor can provide guidance, feedback, and personalized exercises to help you improve your reading skills more effectively.
- Record yourself: Record your practice sessions and listen back to them. This will help identify areas where you may need improvement and allow you to track your progress over time.
- Be consistent: Regular practice is key to developing your reading skills. Aim for consistent, focused practice sessions rather than sporadic, lengthy ones. Even dedicating 15-30 minutes each day can lead to significant progress over time.
Remember, learning to read music notes for guitar is a journey that requires perseverance and commitment. Celebrate your successes along the way, and stay motivated by setting achievable goals. With practice and determination, you will become a skilled music reader, allowing you to explore and appreciate a vast repertoire of music on the guitar.
Conclusion
Congratulations on embarking on the exciting journey of reading music notes for guitar! This valuable skill will unlock endless possibilities for your playing and musical growth. Remember, learning to read sheet music takes time, patience, and consistent practice.
Throughout this article, we have explored the fundamentals of reading music notes for guitar, including understanding the staff, identifying the treble clef and bass clef, reading notes on the guitar fretboard, recognizing common guitar notation, and accurately interpreting rhythms and time signatures. We’ve also provided tips for practicing and improving your reading skills.
As you delve further into reading music, you’ll start to notice improvements in your playing, musical understanding, and ability to communicate and collaborate with other musicians. Reading music opens up a world of opportunities, allowing you to explore various genres, play complex melodies, and express yourself more fully through the guitar.
Remember to practice regularly, start with simple exercises, and gradually increase the difficulty. Develop your sight-reading skills, utilize tools such as metronomes, and study music theory to deepen your understanding of notation and chord progressions.
Don’t be discouraged by challenges along the way. Learning to read music notes for guitar is a process that requires dedication and perseverance. Embrace the journey and celebrate your progress, no matter how small it may seem.
Finally, keep in mind that reading music notes for guitar is just one aspect of your musical journey. Continue to explore other areas of guitar playing, such as improvisation, songwriting, and performance, as these skills will complement and enhance your ability to read music.
So pick up your guitar, grab some sheet music, and immerse yourself in the world of reading music notes. Enjoy the process of discovery, and let your newfound reading skills take your guitar playing to new heights. Happy practicing!