Home>Events & Info>Note>What Music Note Is Treble Clef 6 Line


Note
What Music Note Is Treble Clef 6 Line
Modified: January 22, 2024
Find out what music note is associated with the treble clef on the 6-line staff. Learn about the significance of this note in music theory and composition.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of music notation! If you’ve ever wondered what those squiggly lines and symbols on a sheet of music mean, then you’re in the right place. In this article, we’ll be exploring the treble clef and specifically focusing on the 6 line staff that is associated with it.
Music notation is the universal language that allows musicians to communicate their musical ideas, and the treble clef is one of the most widely used symbols in this system. The treble clef, also known as the G clef, is used to represent higher-pitched notes and is typically played by instruments such as the piano, violin, flute, and trumpet.
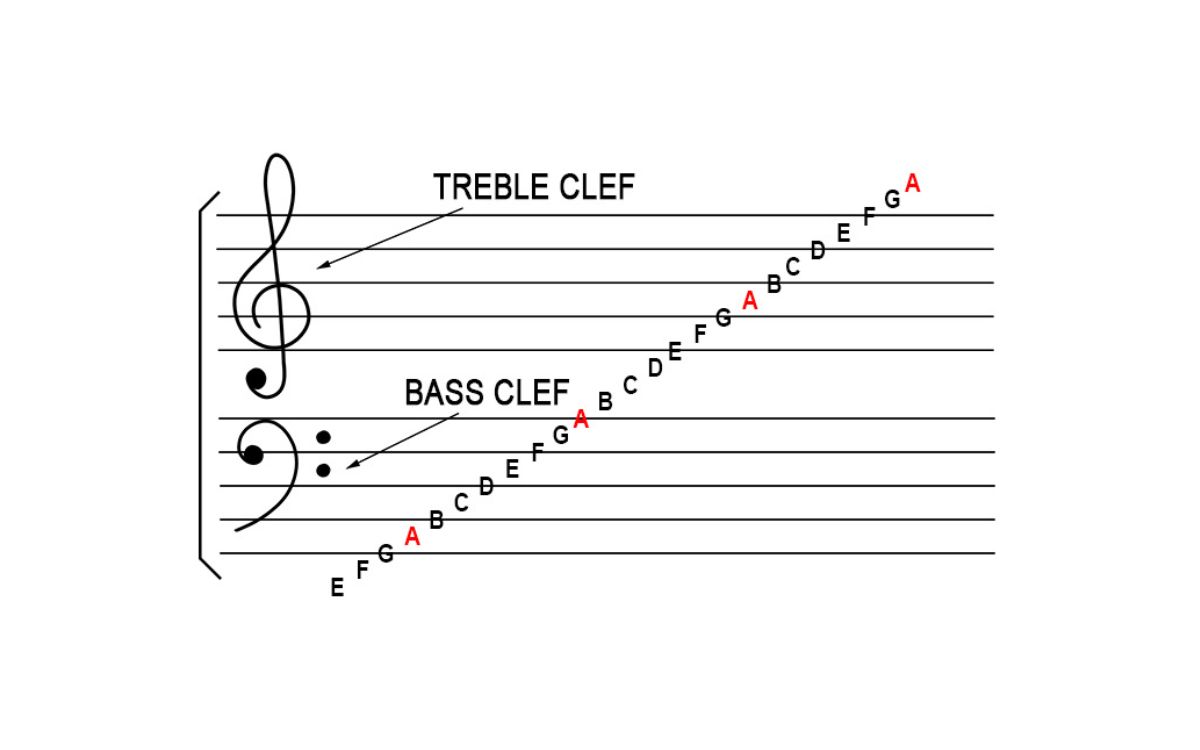
The treble clef consists of a stylized letter “G” that wraps around the second line of the staff, also known as the G line. This positioning determines the pitch range assigned to the notes on the staff. The spaces and lines on the staff represent specific notes, and by understanding the relationship between them, musicians can read and play music with precision.
One particular variation of the treble clef is the 6 line staff. While the standard treble clef utilizes 5 lines and 4 spaces, the 6 line staff expands the range of notes that can be represented. This allows for an even greater level of musical expression and complexity. In the next sections, we will delve deeper into the structure of the 6 line staff and explore how to identify specific notes on it.
So, whether you’re a musician looking to expand your knowledge of music notation or simply have a curious mind, continue reading to unravel the secrets of the treble clef 6 line staff and discover the magic behind the notes.
Understanding the Treble Clef
Before we dive into the intricacies of the 6 line staff, let’s first gain a solid understanding of the treble clef itself. The treble clef is a symbol used in music notation to indicate the pitch range of higher-register notes. It is typically placed on the second line of the staff, also known as the G line.
The treble clef is characterized by its distinctive shape, resembling an ornate letter “G” with a swirling tail. This design dates back to the Middle Ages when it was developed as a way to notate the higher voices in choral music. Over time, it became the standard symbol for instruments that primarily play in the higher registers.
By positioning the treble clef on the G line, it assigns that line as the pitch-G. The notes that fall above this line are progressively higher in pitch, while the notes that fall below are lower. The lines and spaces above and below the G line represent specific notes, enabling musicians to read and interpret melodies accurately.
The treble clef is commonly encountered in piano music, where it represents the right hand’s part. It is also used in solo vocal music, string instruments like the violin, and woodwind instruments like the flute. The treble clef serves as a valuable tool for musicians, allowing them to navigate the higher pitches of their instruments with precision and clarity.
Understanding the treble clef is fundamental to reading and interpreting sheet music, as it provides a visual roadmap to musical notation. By familiarizing yourself with the shape and positioning of the treble clef, you will be well-equipped to tackle the complexities of the 6 line staff, which expands the pitch range even further.
Now that we have a firm grasp on the treble clef, let’s explore the unique characteristics of the 6 line staff and how it impacts the notation of musical notes.
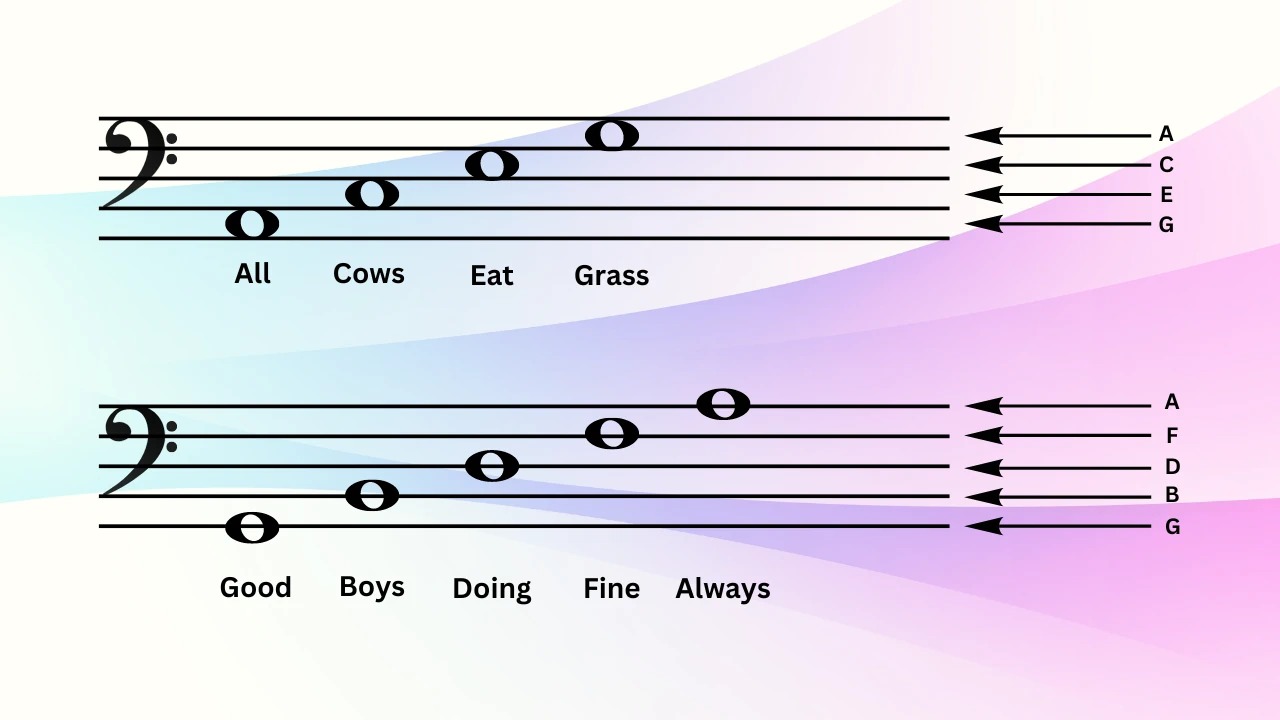
The 6 Line Staff
In traditional music notation, the staff consists of five lines and four spaces, allowing for the representation of a wide range of musical notes. However, there are occasions when the standard five-line staff is not enough to capture the full complexity of a musical composition. This is where the 6 line staff comes into play.
The 6 line staff is an extended version of the traditional staff that adds an extra line above and below the five lines. This additional line provides space for notes that fall outside the pitch range of the standard staff. By expanding the staff to six lines, composers and arrangers can notate music that requires a broader range of pitches.
The 6 line staff can be particularly useful in compositions for instruments with an extended range, such as the piccolo, soprano saxophone, or high soprano voice. It allows for more precise notation of complex melodies and facilitates the reading and interpretation of high-register passages.
When reading music on a 6 line staff, it is important to note that the extra lines above and below the standard staff follow the same naming convention. The topmost line is considered the highest pitch, while the bottommost line represents the lowest pitch. This expansion provides a seamless continuation of the naming scheme used in the five-line staff, making it easier to navigate the additional pitches.
While the 6 line staff may not be as commonly encountered as the standard staff, it is an essential tool in the notation of music that requires a wider pitch range. By utilizing the versatility of the extended staff, composers and musicians can confidently express their musical ideas without being limited by the constraints of the standard notation system.
Now that we understand the purpose and structure of the 6 line staff, let’s explore how we can identify specific music notes on this extended staff and bring our compositions to life.
Identifying the Music Note on the 6 Line Treble Clef
Now that we have acquainted ourselves with the concept of the 6 line staff, let’s explore how we can identify specific music notes on this extended treble clef. At first glance, the additional lines may seem overwhelming, but with a little practice, reading notes on the 6 line treble clef becomes second nature.
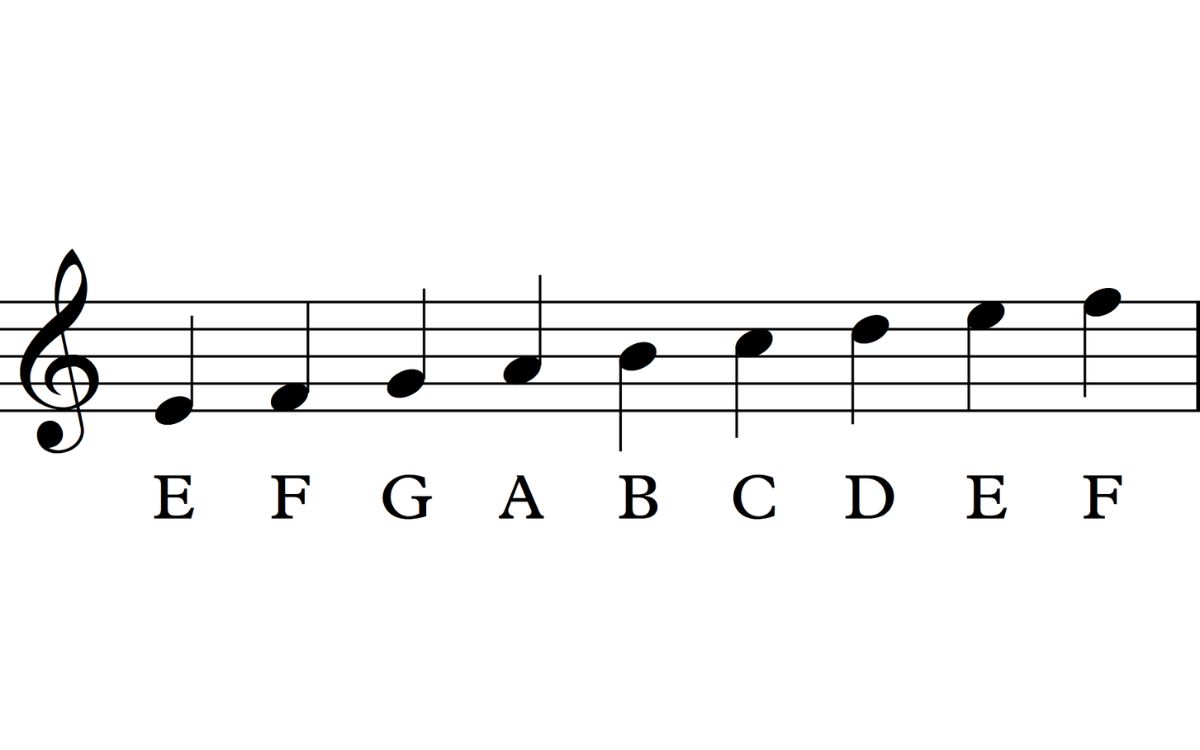
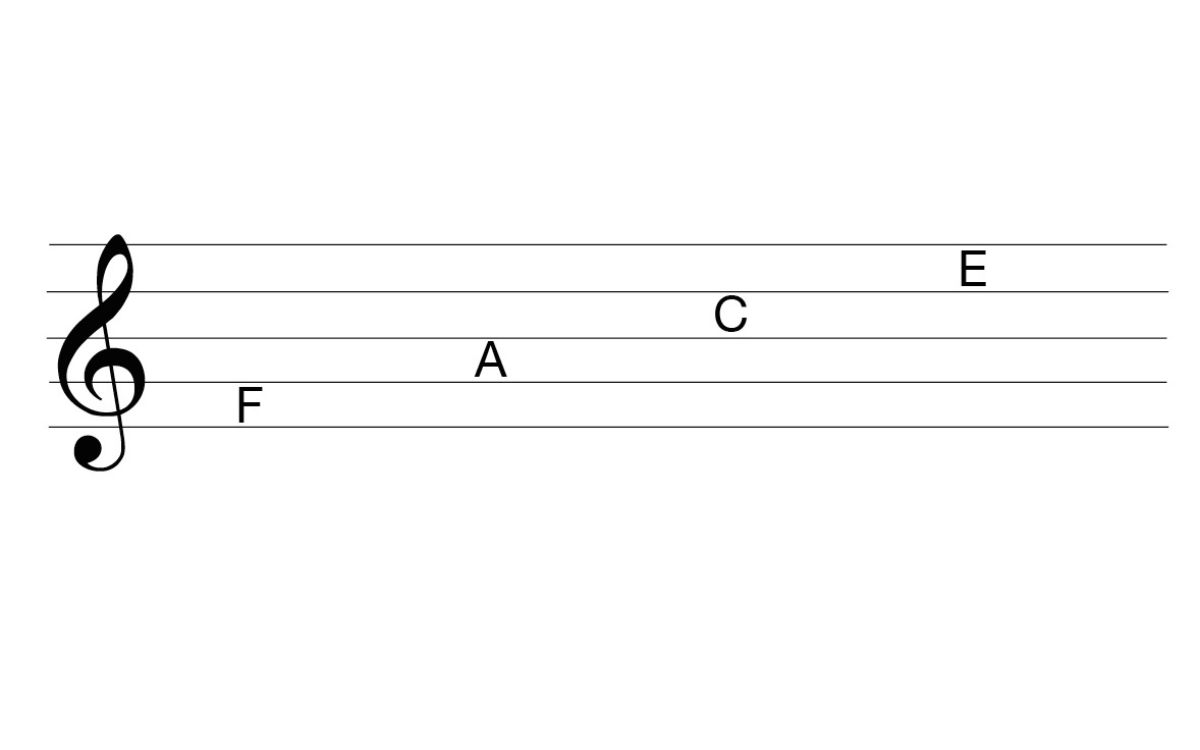
Just like on the standard 5 line treble clef, notes on the 6 line staff are represented by their position on the lines and spaces. Each line and space corresponds to a specific pitch, allowing musicians to accurately interpret the intended melody. However, with the addition of the extra line above and below, the notation covers a wider range of pitches.
To identify a music note on the 6 line treble clef, we start by locating the position of the note on the staff. The lines and spaces are named using letters from the musical alphabet: E, G, B, D, and F for the lines, and F, A, C, and E for the spaces. The line designated as G always represents the G note, while the subsequent lines and spaces follow the alphabetical sequence.
When a note falls on one of the additional lines, we continue the alphabetical sequence accordingly. For example, if a note is on the first additional line below the staff, it is an F, as it is one step below the lowest line in the standard treble clef. Likewise, if a note is on the first additional line above the staff, it is an A, as it follows the alphabetical progression from G.
As you become more familiar with the 6 line treble clef, reading notes on this extended staff becomes more intuitive. The abundance of lines and spaces provides a greater range for pitch representation, giving musicians the freedom to explore the higher and lower registers of their instruments.
Ultimately, reading music notes on the 6 line treble clef is a skill that develops with practice. By regularly exposing yourself to sheet music that utilizes this extended staff, you will enhance your ability to identify and play notes accurately, expanding your musical repertoire and artistic expression.
As you dive into the world of music notation, embrace the challenges presented by the 6 line treble clef, and let it be a catalyst for your growth as a musician.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the treble clef 6 line staff adds a new dimension to music notation, allowing for the representation of a wider range of pitches. By expanding the standard five-line staff with an additional line above and below, composers and musicians can more accurately notate melodies that require a broader pitch range.
Understanding the treble clef and its positioning on the staff is crucial for reading and interpreting sheet music. The treble clef serves as a visual guide, indicating the pitch range of higher-register notes. With this knowledge in hand, musicians can navigate the complexities of the 6 line staff and confidently play the desired musical notes.
While the 6 line staff may not be encountered as frequently as the standard staff, its usage is invaluable in compositions that demand a wider range of pitches. Instruments with extended ranges, such as the piccolo or soprano saxophone, benefit from the additional lines, enabling more precise notation of intricate melodies.
Identifying music notes on the 6 line treble clef requires a familiarity with the letter-based naming system used for lines and spaces. As musicians practice reading and playing music on this extended staff, they become more adept at recognizing and executing the intended musical notes, expanding their artistic capabilities.
So, whether you’re a composer looking to notate intricate melodies or a musician seeking to explore new musical territories, the 6 line treble clef offers a platform for expanded expression and creative possibilities.
As you continue your musical journey, embrace the challenges posed by the 6 line staff. With practice and dedication, you will master the art of reading and playing music on this extended treble clef, opening the door to new heights of musical elegance and artistic expression.