Home>Production & Technology>Treble>What Is Formed By Combining Treble Clef With Bass Clef

Treble
What Is Formed By Combining Treble Clef With Bass Clef
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the musical symbol formed by combining the treble clef with the bass clef. Explore the significance and meaning of this unique combination.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The treble clef and the bass clef are two fundamental musical symbols used to notate and represent different ranges of musical notes on sheet music. Individually, they serve distinct purposes in helping musicians read and interpret music. However, there are instances where these clefs are combined to create a unified representation of both high and low pitch notes. In this article, we will delve into the concept of combining the treble clef and bass clef, exploring its definition, application, and significance in music notation.
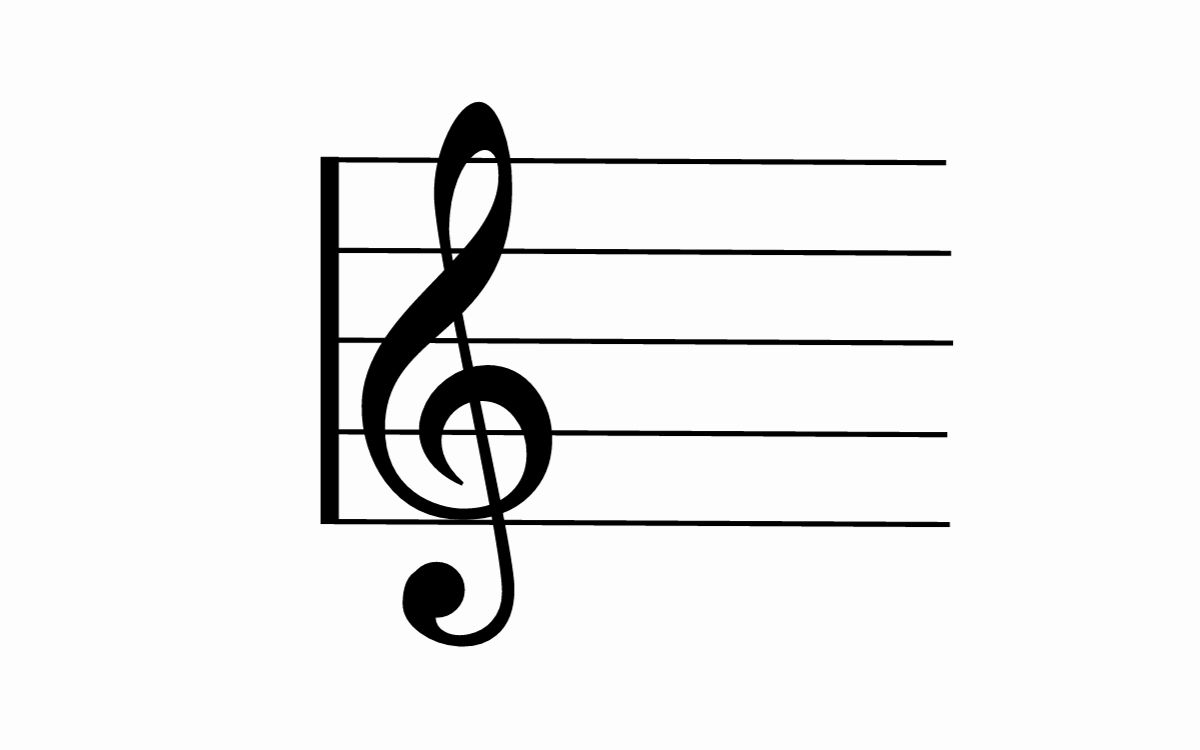
The treble clef, also known as the G clef, is a symbol representing the higher range of musical pitches. It is characterized by its intricate, curly shape and is placed on the second line of the staff. Musicians who play instruments such as the violin, flute, or trumpet read music notated in the treble clef. The notes represented by the treble clef typically lie in the higher frequencies and are associated with a brighter and more vibrant sound.
On the other hand, the bass clef, also known as the F clef, represents the lower range of musical pitches. It is distinguished by its unique, stylized design and is placed on the fourth line of the staff. Musicians who play instruments like the cello, bass guitar, or tuba read music notated in the bass clef. The notes represented by the bass clef tend to have lower frequencies and produce a rich, deep, and resonating sound.
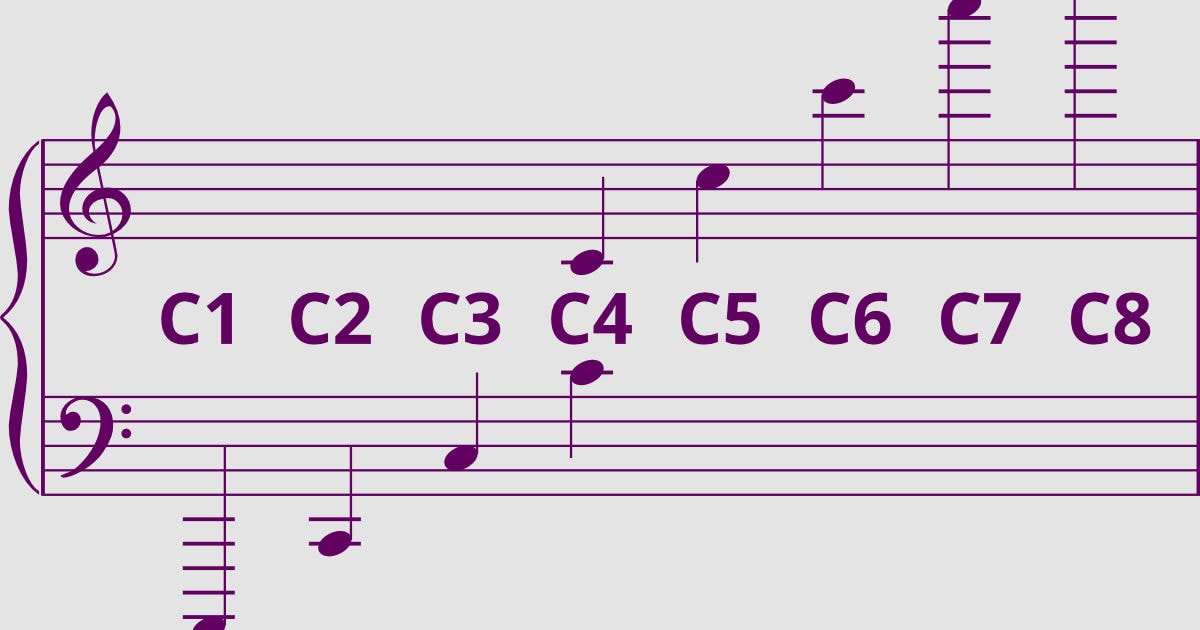
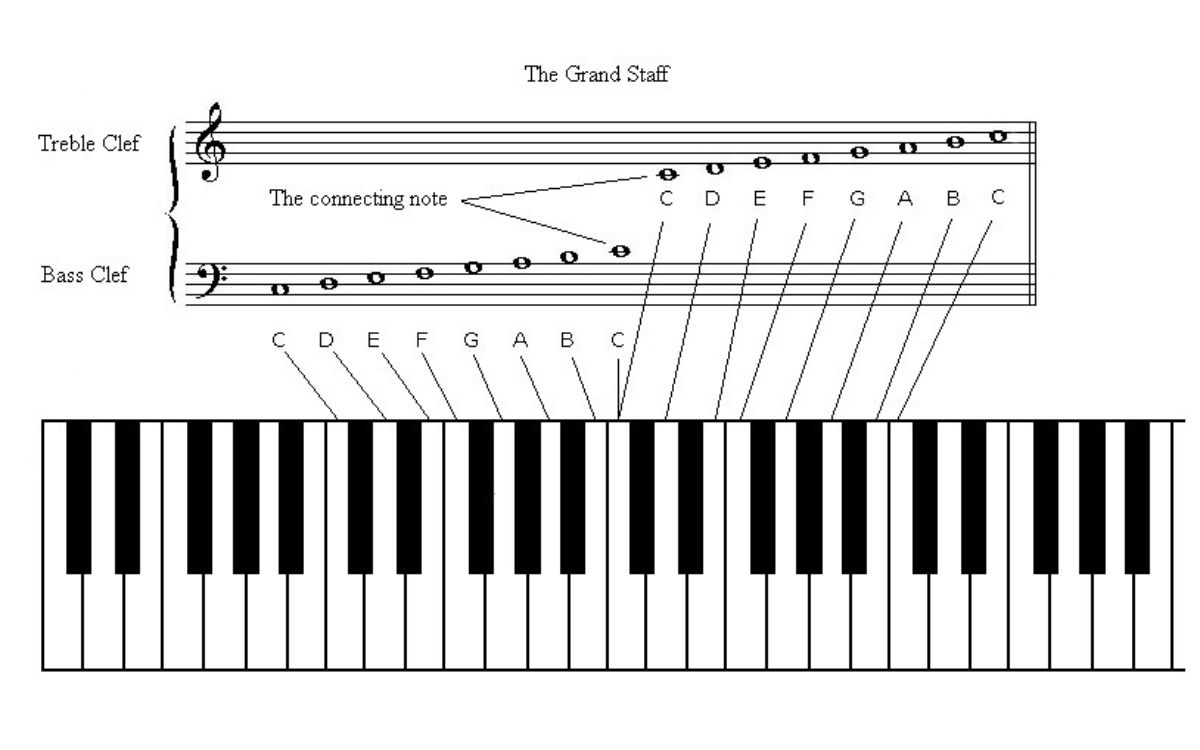
Combining the treble clef and the bass clef involves merging both symbols into a single clef known as the grand staff or the piano staff. The grand staff is a musical stave consisting of two sets of five lines and four spaces, with the treble clef appearing on the top and the bass clef appearing on the bottom. The grand staff is primarily used to notate music for instruments that cover a wide range of pitches, such as the piano.
The combination of the treble and bass clefs in the grand staff offers a comprehensive musical representation by covering a broader range of notes, from the lowest to the highest. This allows composers to notate complex musical compositions that include both high and low-pitched melodies, harmonies, and chords. It provides a unified system for musicians, enabling them to read and perform intricate music efficiently.
In addition to piano music, the grand staff is also commonly used in ensemble compositions, vocal music, and choral scores. By utilizing the combined clefs, composers can specify different vocal ranges or instrument parts within the same piece of music. This enhances communication between musicians and facilitates the accurate performance of the composition.
Overall, combining the treble clef and the bass clef into the grand staff is a significant development in music notation. It allows for the representation of a broader range of pitches and facilitates the accurate interpretation and performance of music. Whether you are a musician, music composer, or music enthusiast, understanding the concept of the combined clef is essential for appreciating and engaging with a wide variety of musical genres and compositions.
Definition of Treble Clef
The treble clef, also known as the G clef, is a musical symbol used to represent the higher range of musical notes on sheet music. This clef is easily recognizable by its curly shape and is placed on the second line of the staff.
The primary purpose of the treble clef is to indicate which notes should be played with a higher pitch. Musicians who play instruments such as the violin, flute, or trumpet rely on this clef to read and interpret music. The notes represented by the treble clef typically lie in the higher frequencies and are associated with a brighter and more vibrant sound.
The treble clef symbol itself resembles a stylized letter “G”, which is why it is often referred to as the G clef. The center curve of the symbol wraps around the second line of the staff, indicating that the note G is located on that line. All other notes on the staff can be deduced based on their position relative to the G. As such, the treble clef acts as a visual reference point for the pitch of the notes being played.
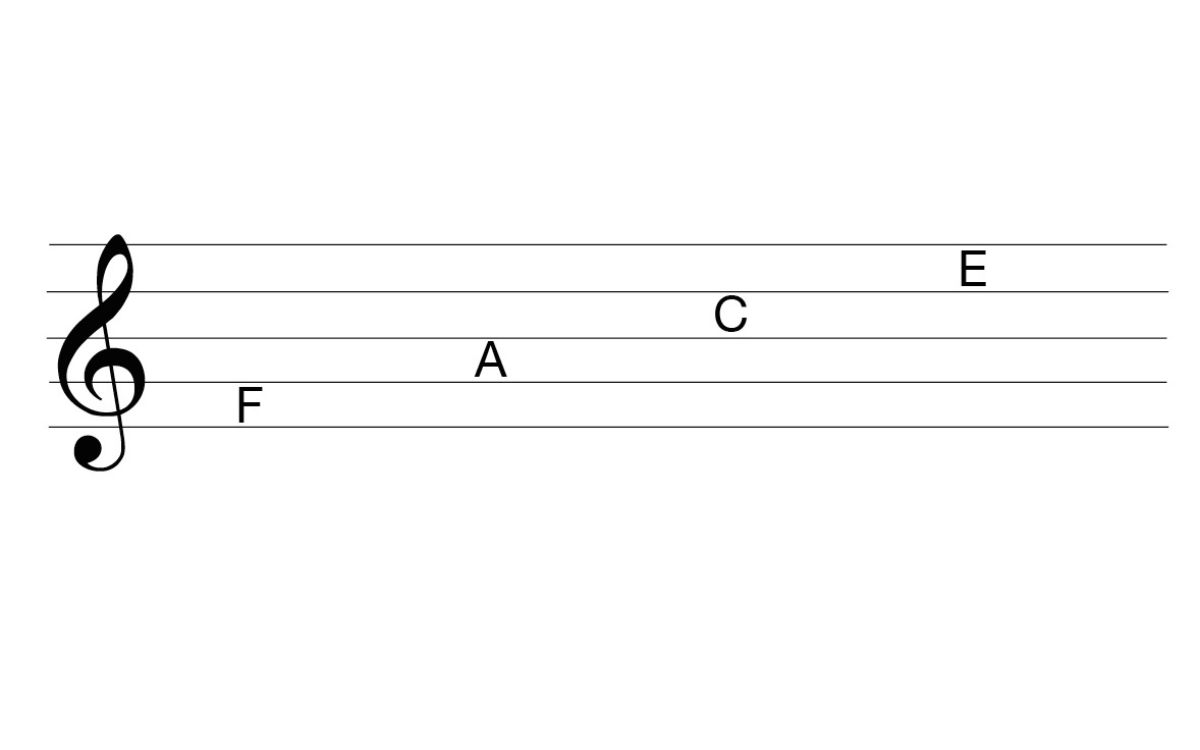
When reading music notated in the treble clef, each line and space represents a different note, and the position of the note on the staff determines its pitch. The lines of the treble clef, from bottom to top, represent the notes E, G, B, D, and F, while the spaces represent the notes F, A, C, and E. Additionally, there are also ledger lines above and below the staff to represent notes outside the standard range.
To help musicians orient themselves on the treble clef staff, certain mnemonic devices and phrases are commonly used. For instance, the phrase “Every Good Boy Deserves Fudge” is often taught to beginners to remember the notes of the lines, while “FACE” helps remember the notes within the spaces. These aids assist musicians in quickly identifying the notes and their corresponding pitches when reading music in the treble clef.
In summary, the treble clef is a musical symbol that signifies the higher range of musical notes. It is visually represented by a stylized “G” shape and is placed on the second line of the staff. Musicians who play instruments like the violin, flute, or trumpet rely on the treble clef to read and interpret music written for higher-pitched instruments, making it a fundamental element in the world of music notation.
Definition of Bass Clef
The bass clef, also known as the F clef, is a musical symbol used to represent the lower range of musical notes on sheet music. It is recognized by its distinct stylized design and is typically placed on the fourth line of the staff.
The primary purpose of the bass clef is to indicate which notes should be played with a lower pitch. Musicians who play instruments such as the cello, bass guitar, or tuba rely on this clef to read and interpret music. The notes represented by the bass clef tend to have lower frequencies and produce a rich, deep, and resonating sound.
The bass clef symbol resembles a stylized letter “F,” which is why it is often referred to as the F clef. The two dots of the symbol are placed on either side of the fourth line, and the line itself passes between the two dots. This line represents the note F, from which all other notes on the staff are determined based on their position relative to F.
When reading music notated in the bass clef, each line and space represents a different note, and the position of the note on the staff determines its pitch. The lines of the bass clef, from bottom to top, represent the notes G, B, D, F, and A, while the spaces represent the notes A, C, E, and G. As with the treble clef, there can also be additional ledger lines above and below the staff to represent notes outside the standard range.
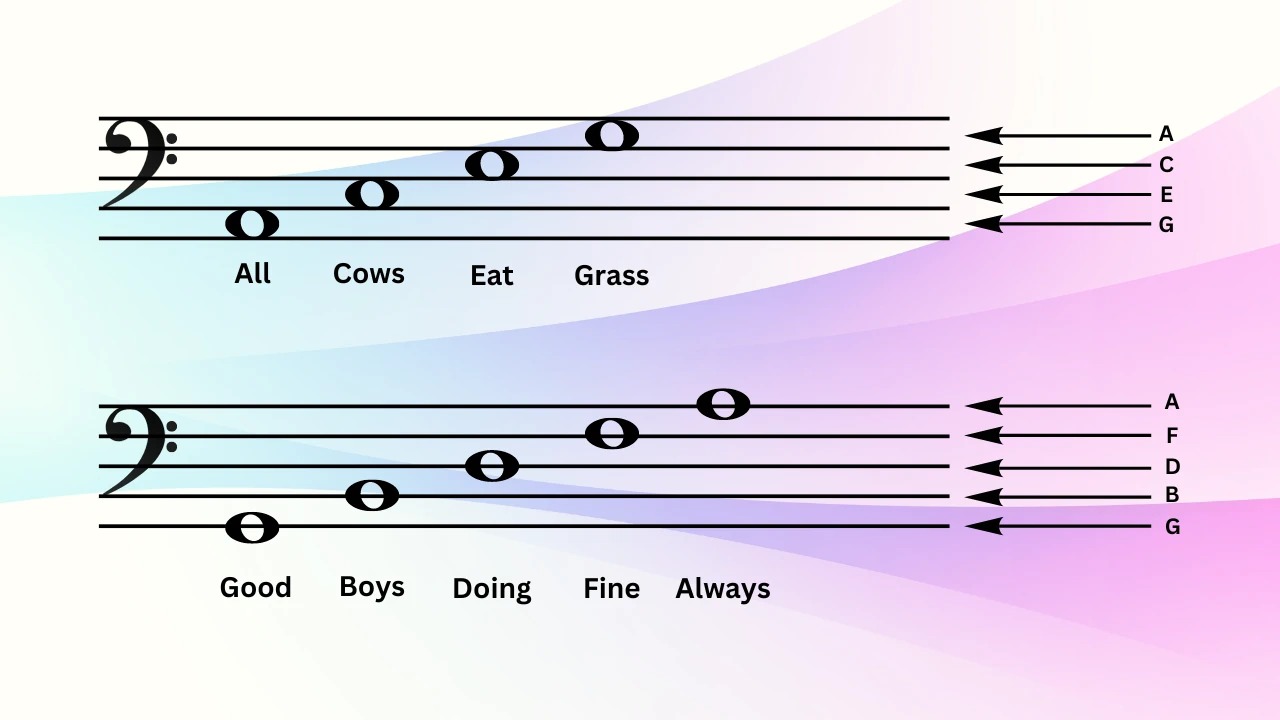
Similar to the treble clef, the bass clef also relies on mnemonic devices and phrases to help musicians quickly identify the notes and their corresponding pitches. Commonly used phrases include “Good Boys Do Fine Always” for the lines and “All Cows Eat Grass” for the spaces. These mnemonic aids assist musicians in efficiently reading music in the bass clef.
In summary, the bass clef is a musical symbol that signifies the lower range of musical notes. It is visually represented by a stylized “F” shape and is placed on the fourth line of the staff. Musicians who play instruments such as the cello, bass guitar, or tuba rely on the bass clef to read and interpret music written for lower-pitched instruments, making it an essential element in music notation.
Combining Treble Clef and Bass Clef
Combining the treble clef and the bass clef involves merging both symbols into a single clef known as the grand staff or the piano staff. The grand staff is a musical stave consisting of two sets of five lines and four spaces, with the treble clef appearing on the top and the bass clef appearing on the bottom.
The primary reason for combining the treble and bass clefs is to create a unified notation system that encompasses a wider range of musical pitches. By using the grand staff, composers and musicians can notate music that includes both high and low-pitched melodies, harmonies, and chords.
The treble clef, placed on the top of the grand staff, represents the higher range of notes. It is used to notate melodies played by instruments such as the violin, flute, or trumpet. The bass clef, positioned on the bottom of the grand staff, represents the lower range of notes and is used to notate melodies played by instruments like the cello, bass guitar, or tuba.
When combining the two clefs, the grand staff offers a comprehensive representation of the entire range of pitches. Musicians who read music written in the grand staff can easily identify and play both high and low-pitched notes within the same piece of music without the need for additional clef changes.
The grand staff is particularly prevalent in piano music notation. The treble clef represents the right hand’s melody and chords, which are typically played in the higher register of the piano. The bass clef represents the left hand’s accompaniment and basslines, which are played in the lower register of the piano. By utilizing the grand staff, pianists can easily read both hands’ parts simultaneously, enhancing the coordination and expressiveness of their performances.
In addition to piano music, the grand staff is also commonly used in ensemble compositions, vocal music, and choral scores. By utilizing the combined clefs, composers can specify different vocal ranges or instrument parts within the same piece of music. This facilitates communication between musicians and ensures accurate performance of the composition.
In summary, combining the treble clef and bass clef into the grand staff creates a unified musical notation system that covers a wider range of pitches. It allows composers to notate complex music that includes both high and low-pitched melodies, harmonies, and chords. Whether it is in piano music, ensemble compositions, or choral scores, the grand staff provides a versatile and comprehensive framework for musicians to read and perform music across various instruments and vocal ranges.
Application and Use of Combined Clef
The combined clef, represented by the grand staff or piano staff, finds its application in various musical contexts. It serves as a versatile notation system that allows for the representation of a broader range of pitches, facilitating accurate performance and interpretation. Here are some key applications and uses of the combined clef:
- Piano Music: One of the primary uses of the grand staff is in piano music notation. The treble clef represents the right hand’s melody and chords, typically played in the higher register of the piano, while the bass clef represents the left hand’s accompaniment and basslines, played in the lower register. The combination of the two clefs in the grand staff enables pianists to easily read and interpret both hands’ parts simultaneously, enhancing their playing technique and overall musical expression.
- Ensembles and Orchestras: The grand staff is frequently utilized in ensemble compositions, orchestral scores, and chamber music. It allows composers to notate music for multiple instruments that cover a wide range of pitches. By using the combined clef, different instrumental parts can be clearly represented in a single score, ensuring cohesive and synchronized performances among the ensemble members.
- Vocal Music and Choral Scores: The combined clef is commonly used in vocal music notation, particularly for choral arrangements. It allows composers to notate music for different vocal ranges within the same piece. The treble clef may be used to represent higher voices, such as sopranos or tenors, while the bass clef represents lower voices, such as altos or basses. This clear distinction in the grand staff ensures that each vocal part is accurately represented, facilitating effective vocal rehearsals and performances.
- Transcription and Arrangements: When transcribing or arranging music from one instrument to another, the combined clef provides a useful tool for musicians. For instance, if a piece of music was originally written for a solo violin, transcribing it for a solo cello would require utilizing the combined clef. This allows for accurate representation of the cello’s lower pitch range while maintaining the original melodic and harmonic structure of the composition.
- Music Education: The grand staff is an essential teaching tool in music education. It helps students understand the relationship between the treble and bass clefs and how they combine to form a comprehensive musical notation system. Learning to read music in the combined clef is necessary for aspiring pianists, composers, and musicians who aim to play instruments that utilize both high and low pitch ranges.
Overall, the application and use of the combined clef in various musical contexts allow for efficient and accurate representation of a wide range of pitches. Whether in piano music, ensemble performances, vocal music, or music education, the grand staff plays a crucial role in facilitating communication, enhancing musical expression, and ensuring seamless integration among different instrumental and vocal parts.
Conclusion
The combination of the treble clef and bass clef, represented by the grand staff or piano staff, offers a comprehensive musical notation system that encompasses a wider range of pitches. It serves as a vital tool in piano music notation, ensemble compositions, vocal music, and music education.
By combining the treble clef and bass clef, composers can notate complex music that includes both high and low-pitched melodies, harmonies, and chords. The grand staff provides a unified representation of these pitches, allowing musicians to accurately read and perform intricate compositions on instruments like the piano and within ensembles.
The combined clef is particularly essential in piano music, where the treble clef represents the right hand’s melody and chords, and the bass clef represents the left hand’s accompaniment and basslines. It enhances coordination and expressiveness, enabling pianists to confidently navigate and interpret both hands’ parts simultaneously.
Additionally, the grand staff finds widespread use in ensemble performances, orchestral scores, and vocal music. It allows composers to notate music for multiple instruments and vocal ranges within the same piece. This versatility promotes collaboration and synchronization, ensuring harmonious performances among musicians and vocalists.
Furthermore, the combined clef serves as an invaluable tool in music education. It aids in teaching aspiring musicians how to read and interpret music in both high and low pitch ranges. By understanding the relationship between the treble and bass clefs, students can develop a well-rounded musical proficiency and pursue their aspirations in various musical disciplines.
In conclusion, the combination of the treble clef and bass clef in the grand staff or piano staff is an essential element of music notation. It expands the range of pitches that can be represented and enables accurate performance and interpretation across a variety of musical contexts. Whether it be in piano music, ensembles, vocal compositions, or music education, the combined clef plays a vital role in enhancing communication, expression, and musical cohesion.