Home>Genres>Classical>Who Is The First Important Classical Era Opera Composer


Classical
Who Is The First Important Classical Era Opera Composer
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the first influential opera composer of the Classical era. Learn about their contributions and impact on the development of classical opera.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Classical era, spanning from roughly 1750 to 1820, was a pivotal period in the history of opera. As the world entered a new era of artistic expression and cultural refinement, opera composers rose to prominence, creating enduring masterpieces that continue to captivate audiences to this day. In this article, we will delve into the lives and works of some of the most significant classical opera composers, exploring their musical contributions and understanding the impact they had on the genre.
Opera, a form of entertainment that combines music, singing, and drama, first surfaced during the late Renaissance period in Italy. However, it was during the Classical era that opera truly flourished, gaining recognition as a distinct and powerful art form. Composers of this era sought to create grand spectacles, fusing music and storytelling in extravagant productions that showcased the depth of human emotion.
During this transformative period in music history, three composers emerged as key figures in the world of opera: Christoph Willibald Gluck, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and Antonio Salieri. Each composer brought their unique style and contributions, forever shaping the course of opera.
In this article, we will explore the impact of these composers, shedding light on their innovative approaches and examining some of their most influential works. We will delve into Gluck’s revolutionary reforms to opera, Mozart’s unparalleled skill in writing for the voice, and Salieri’s pioneering contributions to the genre.
By understanding the lives and accomplishments of these composers, we gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and complexity of classical opera. Their work has left an indelible mark on the history of music, and their influence continues to inspire and captivate audiences around the world.
Join us as we embark on a journey through the Classical era, exploring the lives and legacies of the first important classical opera composers. Let us dive into the world of extraordinary melodies, captivating narratives, and timeless artistry that continues to captivate audiences centuries later.
The Birth of Opera in the Classical Era
The Classical era marked a significant turning point in the evolution of opera. Building upon the foundations laid during the Baroque period, opera in the Classical era underwent a transformation in style and approach. It was during this time that opera became more refined and focused on the expression of human emotion through music and drama.
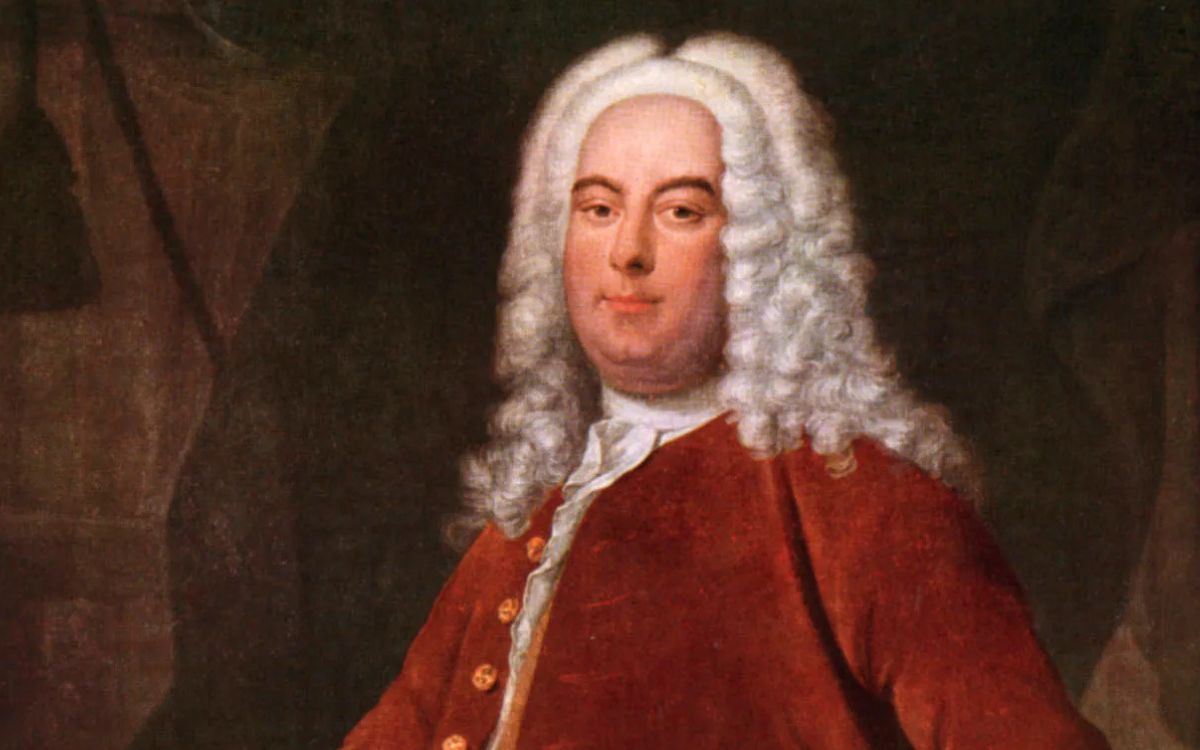
One of the key catalysts for this transformation was the composer Christoph Willibald Gluck. Gluck sought to reform opera, shifting the focus from the virtuosic displays of singers to the emotional impact of the story and the music itself. His approach, known as “reform opera,” aimed to create a more unified and naturalistic form of musical drama.
Gluck’s most famous work, “Orfeo ed Euridice,” exemplifies his reformist approach. The opera tells the tragic love story of Orpheus, a legendary musician who descends into the underworld to rescue his beloved Euridice. Through his innovative use of orchestration and expressive vocal writing, Gluck conveyed the deep emotions of the characters, immersing the audience in the story.
Another key development in the birth of opera in the Classical era was the rise of comic opera, also known as opera buffa. This lighter form of opera, often featuring humorous and relatable storylines, became incredibly popular during this time. Composers such as Mozart and Rossini embraced this genre, incorporating catchy melodies and comedic elements into their works.
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, a prodigious composer and child prodigy, made a lasting impact on opera during the Classical era. His operas, including “The Marriage of Figaro,” “Don Giovanni,” and “The Magic Flute,” are regarded as some of the greatest works in the opera repertoire. Mozart’s mastery of vocal writing and his ability to convey depth of emotion through music set a new standard for opera composers.
Antonio Salieri, though often overshadowed by Mozart, played a pivotal role in the development of opera during the Classical era. Salieri was a highly respected composer and conductor, and his contributions to the genre should not be underestimated. He was known for his skill in writing for the voice and his ability to create dramatic and emotional moments in his operas.
The birth of opera in the Classical era saw a shift towards a more emotionally driven and refined form of musical drama. Composers like Gluck, Mozart, and Salieri pushed the boundaries of what was possible in opera, revolutionizing the genre and leaving a lasting legacy that continues to inspire and captivate audiences to this day.
The Impact of Christoph Willibald Gluck
Christoph Willibald Gluck, a German composer of the Classical era, is renowned for his innovative approach to opera and his significant contributions to the genre. His reforms had a profound impact on the development of opera, reshaping it into a more emotionally charged and dramatically focused art form.
Gluck sought to break away from the extravagant and often excessive practices prevalent in opera during his time. He believed that the true purpose of opera was to convey the deepest emotions of the characters and engage the audience on a profound level. With this vision in mind, he introduced key reforms and principles that revolutionized the art of opera.
One of Gluck’s major accomplishments was his transformation of the role of the singer. In the Baroque era, opera singers were often revered for their technical virtuosity, with elaborate vocal displays overshadowing the dramatic aspects of the performances. Gluck sought to change this by placing the focus on the expression of emotion rather than vocal prowess. He aimed to create a more naturalistic style of singing that served the dramatic narrative of the opera.
To achieve this, Gluck made significant changes to the structure and content of his operas. He eliminated unnecessary and ornamental vocal embellishments, replacing them with expressive melodic lines that conveyed the emotions of the characters. This shift towards simplicity and directness allowed the audience to connect more deeply with the story and the music.
Gluck also introduced reforms in the realm of orchestration, recognizing the power of instrumental music in conveying emotions. He emphasized the role of the orchestra in supporting and enhancing the dramatic moments of the opera. Through strategic use of orchestral color and texture, Gluck was able to create powerful musical passages that intensified the emotional impact of his compositions.
One of Gluck’s most famous works, “Orfeo ed Euridice,” exemplifies his reformist ideals. In this opera, he simplified the vocal lines, eliminated excessive ornamentation, and focused on conveying the emotional journey of the characters. The result was a deeply moving and powerful opera that resonated with audiences in a profound way.
Gluck’s reforms were met with both praise and criticism during his time. However, his ideas laid the foundation for future generations of opera composers. His emphasis on the expression of emotion, the integration of music and drama, and the importance of simplicity and clarity in composition influenced composers such as Mozart, Beethoven, and Wagner.
The impact of Christoph Willibald Gluck on the world of opera cannot be overstated. His reforms paved the way for a new era of opera, inspiring generations of composers to explore the depths of human emotion through music and storytelling. Today, Gluck’s works continue to be performed and celebrated, a testament to his enduring legacy as a pioneer and visionary in the world of classical opera.
The Rise of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, one of the most renowned composers in history, played a significant role in the development of opera during the Classical era. Mozart’s exceptional talent and prolific output cemented his status as a musical genius, and his operatic works continue to captivate audiences with their beauty, complexity, and emotional depth.
From a young age, Mozart demonstrated extraordinary musical abilities. He began composing at the age of five and quickly gained recognition as a child prodigy. His command of melody, harmony, and structure was unmatched, and his compositions showcased a remarkable maturity beyond his years.
Mozart’s contributions to opera were multifaceted, spanning a wide range of styles and genres. His operas, such as “The Marriage of Figaro,” “Don Giovanni,” and “The Magic Flute,” are considered some of the greatest masterpieces in the opera repertoire.
One of Mozart’s key strengths as an opera composer was his ability to write for the voice. He had an innate understanding of the human voice and its capabilities, crafting vocal lines that were both challenging and expressive. His melodic flair, coupled with his understanding of character development, allowed him to create deeply nuanced and emotionally compelling music for his operatic characters.
In addition to his impeccable vocal writing, Mozart’s operas showcased his mastery of orchestration. His innovative use of the orchestra added depth and color to his compositions, heightening the emotional impact of the drama unfolding on stage. Mozart’s orchestral interludes, accompaniments, and instrumental solos served as a powerful means of storytelling, enriching the narrative and creating moments of profound beauty.
Mozart’s operas embodied the ideals of the Classical era, characterized by a balance between structure, emotion, and technical mastery. His ability to seamlessly blend elements of drama, comedy, and pathos within his compositions allowed him to create operas that were both musically engaging and intellectually stimulating.
Despite his immense talent, Mozart faced financial struggles and sometimes struggled to gain recognition for his groundbreaking work. However, his contributions to opera were not diminished by these challenges. His works continue to be revered for their exceptional craftsmanship and timeless appeal.
Mozart’s untimely death at the age of 35 cut short a career that showed immense promise and potential. Yet, the body of work he left behind transcends time and continues to inspire and move audiences around the world. Mozart’s operas represent the pinnacle of the Classical era and serve as a testament to his unparalleled genius as a composer.
The rise of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart marked a turning point in the history of opera. His innovation, technical skill, and unwavering commitment to musical excellence forever changed the landscape of opera. Mozart’s legacy as one of the greatest opera composers of all time is a testament to his enduring impact and his unparalleled ability to touch the hearts and souls of listeners.
The Pioneering Works of Antonio Salieri
While often overshadowed by his contemporaries, Antonio Salieri played a significant role in the development of opera during the Classical era. As a highly respected composer and conductor, Salieri made important contributions to the genre, leaving a lasting legacy that deserves recognition.
Born in Italy in 1750, Salieri achieved considerable success during his lifetime. He served as the court composer and conductor for the Habsburg monarchy in Vienna, where he composed numerous operas that garnered critical acclaim. Salieri’s compositions display a rich melodic language, skillful orchestration, and a deep understanding of dramatic storytelling.
One of Salieri’s pioneering works is his opera “Les Danaïdes” (The Danaids). Premiered in 1784, the opera tells the tragic story of the fifty daughters of King Danaus, who are forced to murder their husbands on their wedding night. Salieri’s intricate and emotionally charged music effectively conveys the turmoil and psychological conflicts faced by the characters, creating a captivating and dramatic experience for the audience.
Salieri was known for his skill in writing for the voice. He composed music that suited the individual vocal abilities of the performers, allowing the singers to shine on stage. His ability to capture the nuances of the human voice and infuse it with emotional depth contributed greatly to the success of his operatic works.
In addition to his role as a composer, Salieri was also a respected conductor. His understanding of orchestration and conducting techniques allowed him to bring out the best in his performers, resulting in dynamic and powerful performances of his operatic works.
Despite his accomplishments, Salieri’s reputation suffered in later years due to a longstanding rivalry with Mozart. The perception of Salieri as a jealous rival, fueled by popular depictions in literature and film, has overshadowed his true contributions to music history. However, it is important to acknowledge that Salieri was highly regarded in his time and was respected as a significant figure in the world of opera.
Salieri’s influence extended beyond his own compositions. As a teacher and mentor, he had a profound impact on a generation of composers, including Ludwig van Beethoven and Franz Schubert. His tutelage and guidance helped shape the musical landscape of the early 19th century, leaving an indelible mark on the development of opera and classical music as a whole.
While Salieri’s works may not be as well-known as those of Mozart or Gluck, his contributions to opera during the Classical era should not be underestimated. His pioneering efforts, expressive compositions, and commitment to vocal excellence set the stage for future generations of opera composers.
Antonio Salieri’s legacy lies in his ability to craft emotionally engaging and technically brilliant operas. His dedication to the art form, combined with his musical talent and influence as a teacher, make him a significant figure in the history of opera. It is time to recognize and appreciate Salieri for his pioneering works and his lasting impact on the world of classical music.
Conclusion
The Classical era witnessed a remarkable transformation in the world of opera, thanks to the contributions of pioneering composers such as Christoph Willibald Gluck, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and Antonio Salieri. These remarkable individuals revolutionized the genre with their innovative approaches, leaving a lasting impact on opera that continues to resonate with audiences today.
Christoph Willibald Gluck’s reforms paved the way for a more emotionally driven and dramatically focused form of opera. His emphasis on conveying the deepest human emotions through music and storytelling set a new standard for composers of the time. Gluck’s operas, such as “Orfeo ed Euridice,” showcased his ability to create powerful and emotionally immersive works that touched the hearts of audiences.
The rise of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart represented a pinnacle in the development of opera. Mozart’s unparalleled talent and mastery of vocal writing made him one of the greatest opera composers in history. His ability to create melodies that captured the essence of the characters, coupled with his skill in orchestration, set a new benchmark for composers to follow. Mozart’s operas continue to be celebrated for their complexity, beauty, and ability to evoke a myriad of emotions.
Antonio Salieri, often overshadowed by his contemporaries, made significant contributions to opera during the Classical era. His ability to write for the voice, coupled with his skill as a conductor, resulted in operas that were both technically impressive and emotionally compelling. Salieri’s influence as a mentor and teacher also played a crucial role in shaping the future of opera, with composers such as Beethoven and Schubert benefiting from his guidance.
Together, the works of Gluck, Mozart, and Salieri transformed opera from a mere spectacle of virtuosity to a powerful and meaningful art form. Their innovations in vocal writing, orchestration, and storytelling set the stage for future generations of composers to explore the boundaries of the genre.
As we reflect on the contributions of these remarkable composers, we gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and complexity of classical opera. Their works continue to be performed and cherished, captivating audiences with their expressive melodies, compelling narratives, and timeless artistry.
The legacy of Gluck, Mozart, and Salieri reminds us of the enduring power of music and its ability to connect with the deepest aspects of our humanity. Their pioneering efforts have left an indelible mark on the history of opera, ensuring that their contributions will be celebrated and cherished for generations to come.