Folk
What Is Folk Dance?
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the vibrant world of folk dance and explore its rich cultural traditions. Learn about the history, costumes, and various styles of this captivating art form.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Folk Dance
- Origin and History of Folk Dance
- Characteristics of Folk Dance
- Cultural Significance of Folk Dance
- Different Types of Folk Dance
- Traditional Costumes and Music in Folk Dance
- Popular Folk Dances Around the World
- Regional Variations in Folk Dance
- Preservation and Evolution of Folk Dance
- Conclusion
Introduction
Folk dance is a vibrant and colorful form of cultural expression that has been passed down through generations. It serves as a window into the rich heritage and traditions of different communities around the world. Whether it’s a lively jig from Ireland, a graceful waltz from Vienna, or a rhythmic tribal dance from Africa, folk dancing is deeply rooted in the history, customs, and values of a particular region or group.
At its core, folk dance is a communal activity, bringing people together to celebrate, share stories, and express emotions. It embodies the unique identity of a community and reflects the cultural diversity of a region. Through intricate choreography, lively music, and traditional costumes, folk dance creates a vibrant tapestry of movement and symbolism.
Unlike its formal counterpart, classical dance, which often follows a strict set of rules and techniques, folk dance is characterized by its spontaneity and improvisation. It is danced by ordinary people, not necessarily trained professionals, and is often performed at social gatherings, festivals, and special occasions. This accessibility and inclusiveness are what make folk dance so captivating and relatable.
Throughout history, folk dance has evolved and adapted to changing times, yet it has managed to retain its essence and cultural significance. It serves not only as a form of entertainment but also as a medium for preserving traditions, conveying messages, and fostering a sense of community. In today’s globalized world, where cultures are becoming increasingly interconnected, folk dance acts as a reminder of our roots and a way to honor our ancestors.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of folk dance, its origins, characteristics, and regional variations. We will delve into the cultural significance of folk dance and its role in preserving and promoting cultural heritage. Join us on this journey as we discover the beauty and diversity of folk dance from around the world.
Definition of Folk Dance
Folk dance can be defined as a traditional form of dance that originates from a specific region or community and is passed down through generations. It is an integral part of a culture’s customs, rituals, and celebrations, reflecting the history, beliefs, and values of the people who perform it.
Unlike other forms of dance, folk dance is not choreographed by a single choreographer, but rather evolves organically within a community over time. It is a collective creation, shaped by the experiences and influences of generations. This makes folk dance a living art form, constantly evolving and adapting while maintaining its traditional elements.
One of the defining characteristics of folk dance is its connection to a particular place or group. It is deeply rooted in the cultural identity of a community, serving as a means of expression and communication. Through intricate footwork, gestures, and formations, folk dance tells stories, conveys emotions, and preserves the cultural heritage of a people.
Folk dance is often accompanied by traditional music and instruments that enhance the rhythm and ambiance of the performance. The dance movements are usually simple and accessible, allowing for active participation from the community members. This inclusivity creates a sense of unity, fostering social cohesion and reinforcing cultural bonds.
Furthermore, folk dance is not limited to a specific age group or skill level. It can be enjoyed and performed by people of all ages, from young children to the elderly. It serves as a means of intergenerational communication, allowing knowledge and traditions to be passed down from one generation to another.
Overall, folk dance is a dynamic and diverse art form that celebrates the cultural diversity of the world. It is a testament to the creativity, resilience, and collective spirit of a community. Whether it is a joyful celebration dance, a solemn ritual dance, or a narrative storytelling dance, folk dance showcases the unique traditions and customs of a particular region, leaving a lasting impression on both performers and spectators alike.
Origin and History of Folk Dance
The origins of folk dance can be traced back to ancient times when communities celebrated various aspects of life through movement and music. Since communication was not as advanced as it is today, dance became a way to express emotions, tell stories, and pass down cultural traditions.
Folk dances have diverse origins, with each region having its unique styles and influences. Some folk dances can be traced back thousands of years, while others have been created more recently. The development of folk dance was influenced by factors such as geography, climate, religious beliefs, social customs, and historical events.
The history of folk dance is intertwined with the migration of populations, cultural exchanges, and the blending of different traditions. As people moved and settled in new areas, they brought their dance forms with them, leading to a mixing of styles and the birth of new dances. For example, the influence of African, European, and Indigenous traditions can be seen in various folk dances in the Americas.
In many cultures, folk dance was also performed as a part of religious or spiritual rituals. These dances were believed to invoke divine blessings, ward off evil spirits, or bring abundance to the community. Over time, these religious elements may have diminished, but the symbolism and spiritual significance attached to certain movements and gestures continue to be preserved in folk dances today.
During times of political upheaval or colonization, folk dance played a crucial role in preserving cultural identity and resisting assimilation. It became a powerful form of cultural expression and a way to assert national pride. Additionally, folk dance provided a sense of unity and solidarity among members of a community, fostering a shared identity and reinforcing social bonds.
In the modern era, folk dance has evolved in response to changing times and influences from other dance forms. It has incorporated elements from ballet, modern dance, and even street dance, resulting in a fusion of traditional and contemporary styles. This evolution has helped keep folk dance relevant and appealing to younger generations, ensuring its continued existence and vitality.
Today, folk dance remains an integral part of cultural celebrations, festivals, and social gatherings around the world. It serves as a way to honor and preserve cultural heritage, connect with ancestral traditions, and celebrate the diversity of human expression. Whether performed in traditional costumes, with live music, or in more contemporary settings, folk dance continues to captivate and inspire people of all ages and backgrounds.
Characteristics of Folk Dance
Folk dance is characterized by various distinct features that set it apart from other forms of dance. These characteristics not only define the aesthetics of the dance but also reflect the cultural values and traditions of the community from which it originates.
- Community-oriented: Folk dance is a communal activity that brings people together. It is often performed in groups, allowing for social interaction and a sense of belonging. The dance movements are designed to foster unity, cooperation, and connection among the participants.
- Simple and accessible: Unlike more complex dance forms, folk dance movements are usually simple and easy to learn. This accessibility allows people of all ages and skill levels to participate and enjoy the dance. Folk dance is inclusive, bringing together individuals with varied levels of experience to create a shared experience.
- Tradition-based: Folk dance is deeply rooted in tradition and cultural heritage. The dance forms have been passed down through generations, often preserving elements of historical significance. These traditions are maintained and respected, ensuring the continuity and authenticity of the dance.
- Storytelling and expression: Folk dance is a form of storytelling, conveying narratives, myths, and historical events through movement. It allows for the expression of emotions, such as joy, sorrow, love, and celebration. The dancers use their bodies and facial expressions to communicate and evoke feelings in the audience.
- Symbolism and meaning: Folk dance is rich in symbolism, with specific movements and gestures representing cultural, religious, or spiritual beliefs. These symbolic elements often have deep meanings associated with the history, myths, and values of the community. They contribute to the overall narrative and cultural significance of the dance.
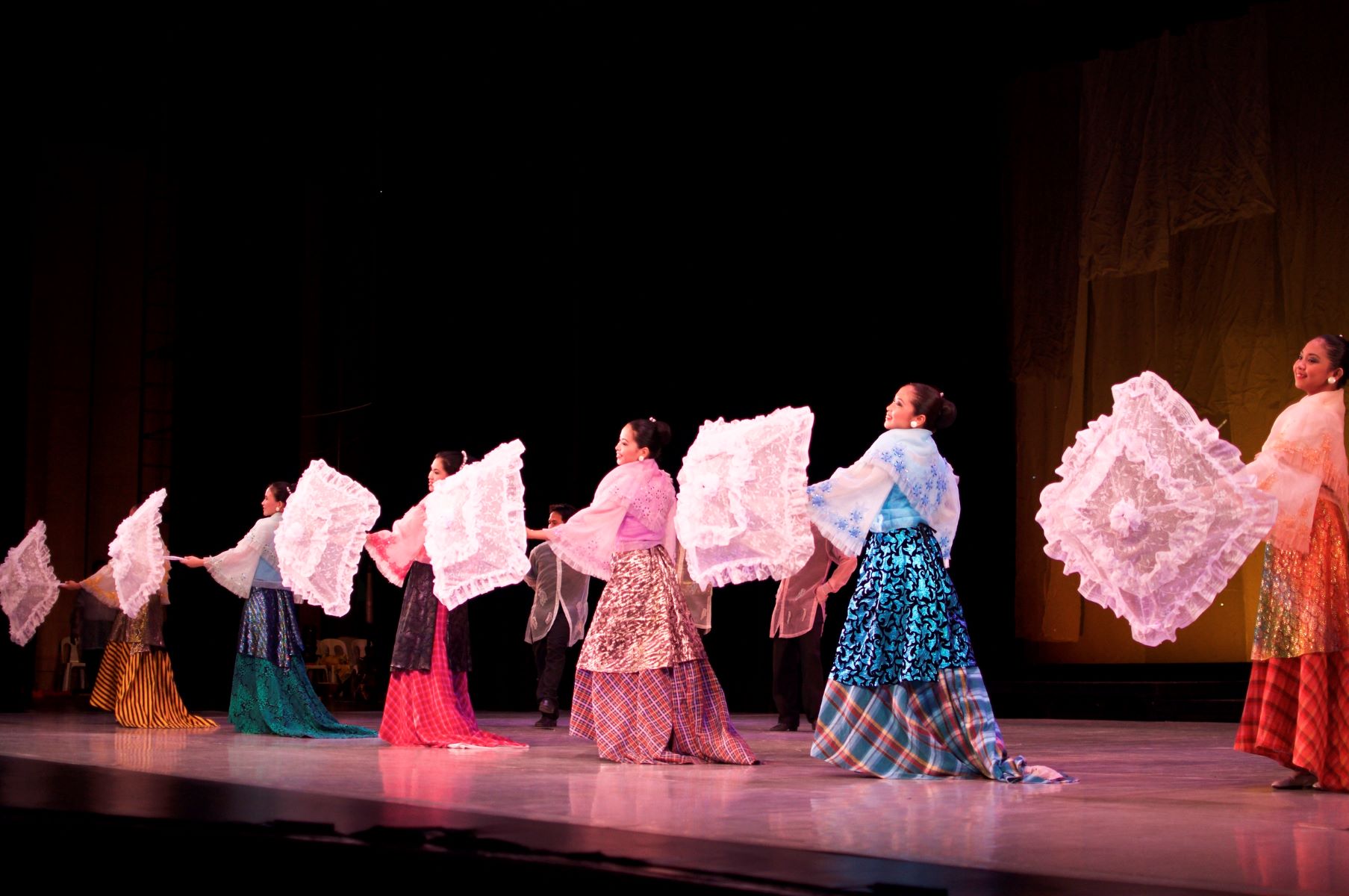
- Costumes and props: Traditional costumes and props are integral to folk dance, adding visual appeal and further enhancing the cultural context of the performance. The costumes often reflect the region’s heritage, using vibrant colors, intricate patterns, and traditional textiles. Props such as ribbons, tambourines, or handkerchiefs may also be used to accentuate the movements and rhythms of the dance.
- Rhythm and music: Folk dance is closely associated with traditional music and rhythms. The choreography is intricately woven into the music, and the dancers synchronize their movements with the beats and melodies. The music creates an immersive experience, setting the pace and energy of the dance.
These characteristics make folk dance a captivating and culturally significant art form. It serves as a means of cultural preservation, community bonding, and artistic expression. Through its simplicity, inclusivity, and rich symbolism, folk dance continues to thrive and evolve, captivating audiences around the world and keeping the traditions of diverse cultures alive.
Cultural Significance of Folk Dance
Folk dance holds immense cultural significance as it serves as a powerful medium for expressing and preserving the traditions, values, and identities of a community or region. It acts as a reflection of the cultural heritage, history, and social fabric of a particular group of people, and plays a vital role in fostering a sense of belonging and pride.
One of the key aspects of folk dance is its ability to bring people together and create a sense of unity. It serves as a communal activity, allowing individuals to form connections, strengthen social bonds, and promote a sense of belonging within their cultural group. Folk dance often becomes an integral part of community celebrations, festivals, and rituals, providing a platform for collective joy and shared experiences.
Through the dynamic movements, gestures, and music, folk dance becomes a means of storytelling and cultural expression. It can convey historical events, mythological tales, and daily life experiences of the people. By performing folk dances, communities not only entertain but also educate and pass down their history, traditions, and values to future generations.
Folk dance also serves as a medium for cultural exchange and understanding. When different communities come together, whether through festivals or cultural events, folk dance becomes a way to showcase and appreciate the diversity of cultures. It allows individuals to learn about other traditions, foster respect, and create a sense of global connectedness.
Furthermore, folk dance plays a crucial role in the preservation and promotion of cultural heritage. It provides a platform for the transmission of intangible cultural practices, such as dance movements, musical styles, and traditional costumes. By practicing and performing folk dances, communities ensure the continuity of their cultural identity and safeguard their heritage from being lost or forgotten.
In addition, folk dance can become a significant economic asset for a community. It can attract tourists, promote cultural tourism, and contribute to the local economy. Many countries actively promote and support folk dance as a way to revitalize and sustain cultural tourism, bringing economic benefits while also preserving cultural traditions.
Beyond its cultural significance within a community, folk dance also has the power to inspire and captivate audiences around the world. It transcends language barriers and touches the hearts of people from different backgrounds. Folk dance performances and festivals serve as platforms for cultural diplomacy and intercultural understanding, fostering dialogue and appreciation among diverse communities.
Overall, the cultural significance of folk dance cannot be overstated. It is a treasure trove of rich traditions, stories, and values that continues to thrive and evolve. Through its celebration of diversity, promotion of social cohesion, and preservation of cultural heritage, folk dance plays a vital role in connecting people, fostering cultural pride, and enriching the world with its vibrant expressions.
Different Types of Folk Dance
Folk dance encompasses a wide array of dance forms, each uniquely tied to the culture, history, and traditions of a specific region or community. From lively and energetic dances to slow and graceful movements, folk dances showcase the diversity of human expression. Let’s explore some of the different types of folk dance found around the world:
- Line Dances: Line dances are characterized by dancers standing in a line or several lines, performing synchronized movements in unison. These dances often involve simple steps and repetitive patterns, making them accessible and enjoyable for large groups. Examples include traditional square dances in the United States and Maypole dances in Northern Europe.
- Circle Dances: Circle dances are performed with dancers forming a circle, holding hands or linking arms. The movements in these dances are often fluid and circular, representing unity and continuity. Circle dances can be found in various cultures, such as the Hora in Eastern Europe and the Sufi Whirling dance in the Middle East.
- Couple Dances: Couple dances involve a pair of dancers, often a man and a woman, performing coordinated movements together. These dances emphasize the connection and partnership between the couple. Examples include the Viennese Waltz from Austria and the Tango from Argentina.
- Group Dances: Group dances involve a larger number of dancers, typically divided into smaller groups or formations. These dances can be intricate and dynamic, requiring precise coordination and timing. Flamenco in Spain and Bhangra in Punjab, India, are examples of group dances.
- Cultural and Ethnic Dances: Many folk dances are specific to particular cultures or ethnic groups, showcasing their unique traditions and customs. For instance, the Irish Stepdance, known for its quick footwork and lively rhythms, is strongly associated with Irish culture. Similarly, the Maori Haka of New Zealand is a powerful ancestral dance performed by the indigenous Maori people.
- Ritual and Ceremonial Dances: Ritual and ceremonial dances hold deep spiritual and cultural significance. These dances are performed as part of religious or social ceremonies, marking important events or paying homage to deities. The Native American Powwow dances and the Garba dance during Navratri in India are examples of ritual dances.
It’s important to note that these categories are not rigid, and there can be overlaps and variations within each type. Additionally, different regions within the same country may have their own distinct folk dances, showcasing the diverse cultural tapestry within a nation.
Each type of folk dance has its own set of movements, music, and costumes that reflect the unique cultural context in which it originates. Whether performed at weddings, festivals, or other social gatherings, folk dances offer a glimpse into the history, traditions, and values of a community, captivating audiences with their beauty, rhythm, and cultural significance.
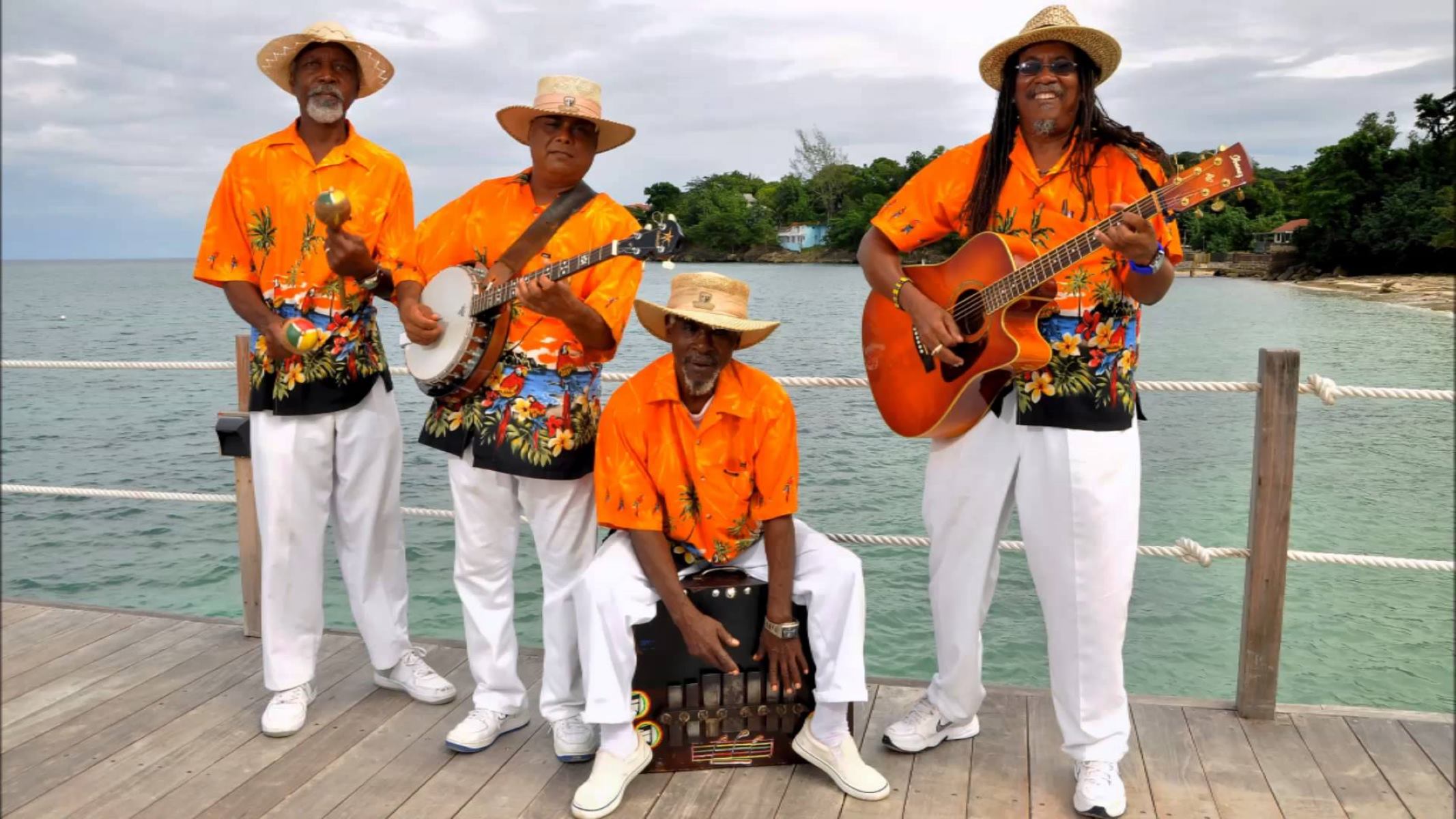
Traditional Costumes and Music in Folk Dance
Traditional costumes and music play a vital role in enhancing the cultural richness and visual appeal of folk dance performances. They not only reflect the historical heritage and traditions of a particular region but also contribute to the overall storytelling and ambiance of the dance. Let’s explore the significance of traditional costumes and music in folk dance:
Traditional Costumes: Folk dance costumes are often intricate, vibrant, and unique to each culture or region. These costumes serve several purposes:
- Symbolism: Traditional costumes in folk dance often carry symbolic meanings. Colors, patterns, and accessories can represent specific aspects of the culture or rituals associated with the dance. For example, the flowing skirts and colorful shawls of Flamenco dancers in Spain evoke the passion and flamboyance of the dance form.
- Identity and Tradition: Traditional costumes help preserve cultural identity and distinguish one folk dance from another. They reflect the historical clothing styles and craftsmanship of a particular period and region. Costumes may include specific garments, such as embroidered blouses, headgear, or jewelry, that are unique to that dance form.
- Aesthetics: The visual appeal of traditional costumes adds to the overall spectacle of the dance performance. The vibrant colors, intricate designs, and fluid movements of the dancers create a visual feast that captivates and engages the audience.
- Unity and Group Identity: In group or ensemble dances, matching or coordinated costumes create a sense of unity and coherence. The dancers become a visual representation of their community or region, projecting a shared cultural identity.
Traditional Music: Music is an essential component of folk dance, influencing the rhythm, tempo, and emotions expressed through movements. The traditional music accompanying folk dances brings authenticity and cultural context to the performances:
- Regional Styles and Instruments: Traditional folk music is often deeply rooted in the historical and geographical context of a region. Different genres of folk music may utilize distinct instruments and melodic patterns. For instance, the lively fiddles and accordions in Irish folk music complement the energetic movements of Irish step dancing.
- Rhythmic Structure: The rhythmic structure of the music dictates the choreography and timing of dance movements. Dancers synchronize their steps and gestures with the beats and melodies of the music, creating a harmonious connection between movement and sound.
- Emotional Expression: Folk music conveys the cultural emotions and sentiments associated with a dance form. Joy, celebration, melancholy, or solemnity are expressed through the melodies and lyrics, guiding the dancers in portraying the intended emotional nuances of the dance.
- Preservation of Oral Traditions: In many cultures, folk music has been passed down through generations as an oral tradition. It acts as a vessel for storytelling, historical narratives, and transmitting cultural knowledge from one generation to another.
Traditional costumes and music in folk dance contribute to the overall authenticity, beauty, and cultural significance of the performances. Together, they create a multisensory experience, connecting the dancers and the audience to the heritage, values, and traditions of a specific community. They play an integral role in preserving and promoting cultural identity, storytelling, and artistic expression through the vibrant art form of folk dance.
Popular Folk Dances Around the World
Folk dances are deeply embedded in the cultural fabric of communities all over the world, showcasing the diversity, beauty, and vitality of different cultures. Here are some examples of popular folk dances from various regions:
- Hula (Hawaii): Hula is a traditional Hawaiian dance form characterized by graceful movements and storytelling through hand gestures and hip swaying. It is accompanied by chants or songs and often performed in colorful grass skirts and floral leis.
- Samba (Brazil): Samba is a vibrant and energetic dance style associated with the annual Carnival celebrations in Brazil. It features fast footwork, hip movements, and colorful costumes. Samba embodies the festive spirit and cultural heritage of Brazil.
- Flamenco (Spain): Flamenco is a passionate and expressive dance form originating from the Andalusian region of Spain. It combines percussive footwork, intricate hand movements, and intense facial expressions. Dancers wear traditional flamenco dresses and use castanets for rhythmic accompaniment.
- Bhangra (Punjab, India): Bhangra is a lively and energetic folk dance form originating from the state of Punjab in India. It is characterized by lively music, high-energy movements, and traditional Punjabi attire such as bright-colored turbans, long shirts, and flowing skirts.
- Irish Step Dance (Ireland): This popular Irish dance style is characterized by lightning-fast footwork and an upright body posture. Dancers perform intricate rhythmic patterns while wearing traditional costumes, including curly wigs for female dancers and kilts for male dancers.
- Kathak (India): Kathak is a classical dance form originating in North India but with folk influences. It is known for its intricate footwork, spins, and storytelling through expressive hand gestures. Dancers wear ornate costumes adorned with bells that add a rhythmic element to the performance.
- Cossack Dance (Russia/Ukraine): Cossack dance is an energetic and acrobatic dance style associated with the Cossack people of Russia and Ukraine. It features high jumps, kicks, and intricate footwork. Dancers wear traditional Cossack clothing, including wide-brimmed hats and embroidered tunics.
- Karagöz (Turkey): Karagöz is a traditional shadow puppetry art form from Turkey that combines storytelling, music, and dance. Performers manipulate intricately designed puppets behind a lighted screen while accompanied by traditional Turkish music.
- Maori Haka (New Zealand): The Maori Haka is a powerful ancestral dance performed by the indigenous Maori people of New Zealand. It involves vigorous movements, war cries, and facial expressions to convey strength, unity, and cultural identity.
These folk dances represent just a small glimpse of the rich tapestry of traditional dance forms found worldwide. They showcase the unique heritage, cultural expressions, and craftsmanship of different regions, captivating audiences with their vibrant movements, rhythmic beats, and stunning costumes. Folk dances bridge the gap between the past and the present, preserving cultural heritage while continuing to evolve as living art forms.
Regional Variations in Folk Dance
Folk dance is a diverse and dynamic form of cultural expression, with distinct regional variations that highlight the unique traditions, history, and cultural identities of specific areas. Here, we’ll explore some of the regional variations in folk dance from around the world:
- Ballet Folklorico (Mexico): Ballet Folklorico is a vibrant folk dance style that originated in Mexico. It celebrates the diverse cultural traditions and regional variations within the country. Each region in Mexico has its own unique folk dances, costumes, and music, influenced by indigenous, Spanish, and African cultures.
- Ahlan Wa Sahlan (Middle East): Ahlan Wa Sahlan is a popular folk dance in the Middle East, which varies in style and name across the region. In Egypt, it is known as the “Raqs Sharqi,” featuring lyrical movements and expressive gestures. In Lebanon, it is the “Dabke,” a line dance accompanied by lively music and performed at celebrations and weddings.
- Scottish Highland Dancing (Scotland): Scottish Highland Dancing showcases the unique traditional dances of Scotland. These dances, performed in Scottish kilts and tartans, reflect the rich Scottish heritage and history. Each dance has distinct steps, including the Highland Fling and the Sword Dance.
- Kathakali (India): Kathakali is a highly stylized classical folk dance form from the southern Indian state of Kerala. It is characterized by elaborate makeup, colorful costumes, and facial expressions that convey dramatic stories from Hindu epics. The movements and gestures in Kathakali are precise and symbolic.
- Hakka Dance (China): Hakka Dance is a form of Chinese folk dance originating from the Hakka-speaking regions of China, particularly in Guangdong and Fujian provinces. It is known for its graceful hand movements, precise footwork, and colorful costumes. Hakka dances reflect the rich cultural heritage of the Hakka people.
- Gumboot Dance (South Africa): The Gumboot Dance is a unique form of folk dance that originated in the mining communities of South Africa. It involves performers using their boots, or gumboots, to create rhythmic sounds and movements. The dance was developed as a means of communication and expression during a time of oppression.
- Square Dance (United States): Square dance is a folk dance form that originated in the United States and features different regional variations across the country. Styles such as Appalachian Square Dance and Western Square Dance reflect the diverse cultural influences from various regions and communities.
- Tabla Dance (Mexico): Tabla Dance is a traditional Mexican folk dance performed with a wooden board, called a tabla. This style is unique to the Veracruz region and is often accompanied by live music, such as marimba or guitar. The dance blends indigenous, African, and Spanish influences.
These examples illustrate the incredible diversity and regional variations in folk dance. Each dance form embodies the vibrant cultural traditions, histories, and customs of the communities that practice them. Through their distinct movements, music, costumes, and symbolic gestures, regional folk dances celebrate the cultural richness and individuality of specific regions, serving as a testament to the importance of local identity and heritage.
Preservation and Evolution of Folk Dance
Folk dance, as an integral part of cultural heritage, has undergone a remarkable journey of preservation and evolution throughout history. The conservation of folk dance traditions and their adaptation to changing times have been vital in ensuring their continued existence and relevance in contemporary society.
Preservation: Preserving folk dance involves efforts to safeguard its authenticity, cultural significance, and traditional elements. Various methods have been employed to ensure the continuity of folk dance traditions:
- Oral and Intergenerational Transmission: While some folk dances have been documented in written form, many are still primarily passed down orally from one generation to the next. This oral transmission involves experienced practitioners teaching the dance to younger members of the community, ensuring that the intricacies and subtleties of the dance style are preserved.
- Community Involvement and Cultural Institutions: Communities play a central role in preserving folk dances. Cultural organizations, folk dance troupes, and institutions dedicated to cultural heritage work actively to revive, teach, and perform traditional dances. These initiatives create platforms for the transmission, education, and presentation of folk dances to wider audiences.
- Archiving and Documentation: The documentation of folk dances through audio recordings, videos, photographs, and written records ensures that knowledge about the dances is preserved for future generations. Archives and cultural institutes collect and preserve these materials, serving as valuable resources for research and educational purposes.
- Revival and Cultural Revitalization: In instances where certain folk dances have faded or been lost, efforts have been made to revive and reintroduce them. This involves researching historical references, collaborating with elders and community members, and reconstructing the dance based on available information. Revival efforts breathe new life into forgotten dances, reclaiming their cultural importance.
Evolution: While preservation is crucial, the evolution of folk dance is equally important for its continued relevance and sustainability. Folk dance has demonstrated its ability to adapt to changing times and embrace new influences while retaining its essential character:
- Contemporary Interpretations: Folk dance has evolved to incorporate contemporary elements, drawing influence from other dance forms and cultural trends. Choreographers and dancers create innovative fusions of traditional and modern styles, infusing folk dances with fresh energy and relevance.
- Cross-Cultural Exchange: In a globalized world, folk dances have become bridges for cultural exchange. As people travel, migrate, and share their traditions, folk dances gain exposure to new ideas and influences from diverse cultures. This interaction enriches the folk dance repertoire and leads to unique cross-cultural collaborations.
- Artistic Interpretation: Folk dances provide a foundation for artistic interpretation, allowing for individual creativity and expression while still honoring the core elements of the dance. Dancers and choreographers add their personal touch, pushing boundaries while maintaining respect for the traditional roots of the dance.
- Inclusion and Adaptation: Folk dance has evolved to become more inclusive, embracing diverse participants regardless of age, gender, or cultural background. Adaptations of traditional dances now cater to a wider range of abilities and preferences, ensuring that the art form remains accessible and relevant to all.
Through preservation efforts and evolutionary adaptations, folk dance continues to thrive as a living art form. It bridges the past and the present, preserving cultural heritage while embracing the spirit of innovation. The interplay between preservation and evolution ensures the longevity and vibrancy of folk dances, allowing them to capture the imagination and captivate audiences for generations to come.
Conclusion
Folk dance is a captivating and dynamic form of cultural expression that showcases the rich heritage, traditions, and diversity of communities around the world. Its distinct characteristics, regional variations, and cultural significance make it a vital part of our global cultural tapestry.
Through intricate movements, vibrant costumes, and rhythmic music, folk dance tells stories, conveys emotions, and preserves cultural identities. It brings people together, fostering community bonds and creating a sense of belonging. Folk dance is not just a form of entertainment; it is a means of communication, a preservation of history, and a celebration of cultural heritage.
The preservation and evolution of folk dance play crucial roles in ensuring its continued existence and relevance. Efforts to pass down traditional dances, archive and document their practices, and revive forgotten forms are essential for maintaining cultural heritage. At the same time, the evolution and adaptation of folk dance allow it to engage with contemporary influences, appeal to new generations, and facilitate cross-cultural exchange.
As we explore the world of folk dance, we witness the beauty of different regional styles, from the lively samba in Brazil to the graceful Kathakali in India. We experience the symbolic gestures, intricate footwork, and colorful costumes that capture the essence of each culture. And, most importantly, we recognize the power of folk dance in promoting cultural understanding, fostering unity, and celebrating our shared humanity.
As we look to the future, it is crucial that we continue to appreciate, support, and participate in folk dance. By doing so, we can uphold the cultural traditions of various communities, provide platforms for artists and performers, and cultivate a global society that values cultural diversity and heritage.
So, let us embrace the joy and richness of folk dance. Let us celebrate the stories, the rhythms, and the heritage embedded in each movement. Folk dance allows us to connect with our roots, appreciate our collective history, and honor the beauty of cultural expressions from around the world.