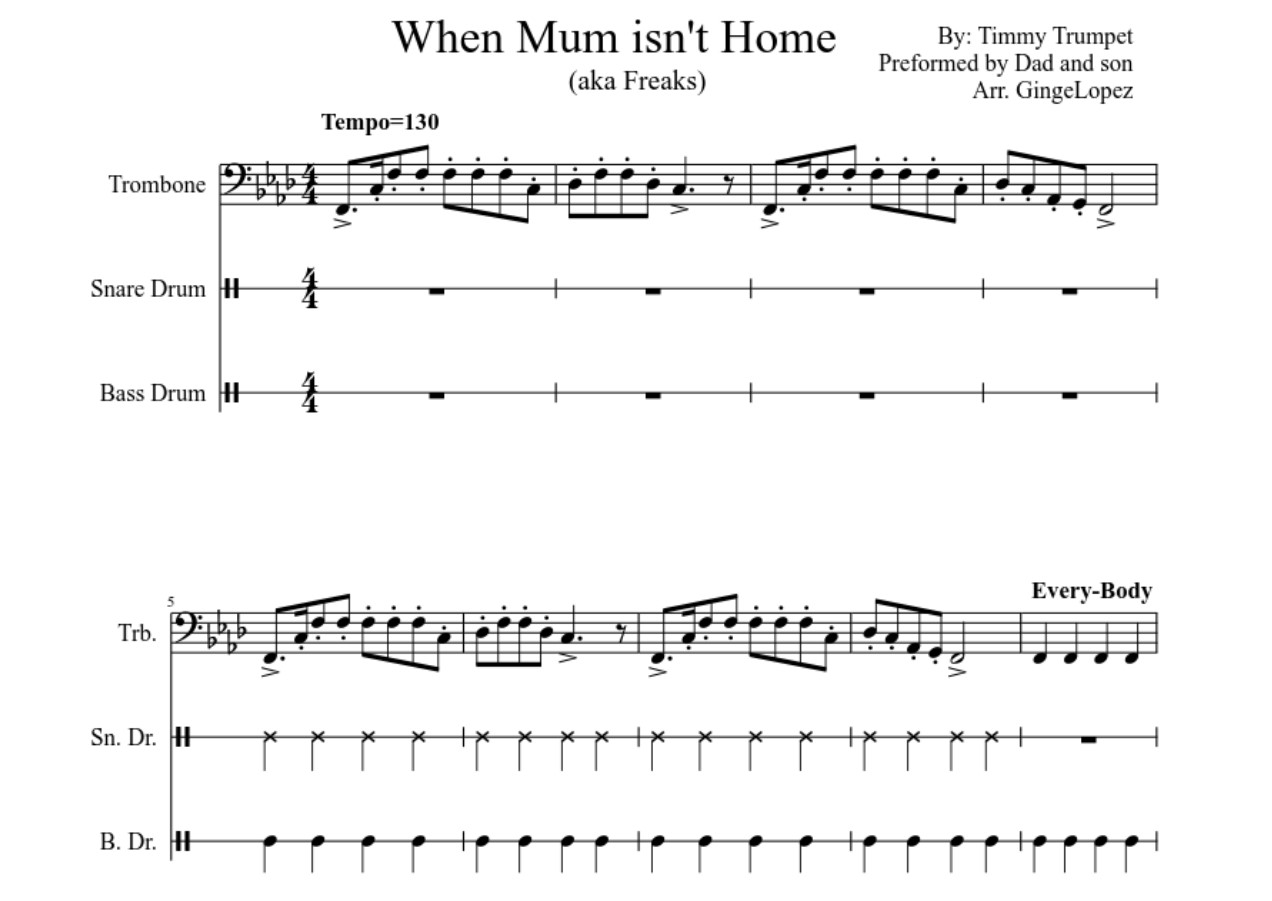
Home>Instruments>Bass>What Is A Bass Trombone
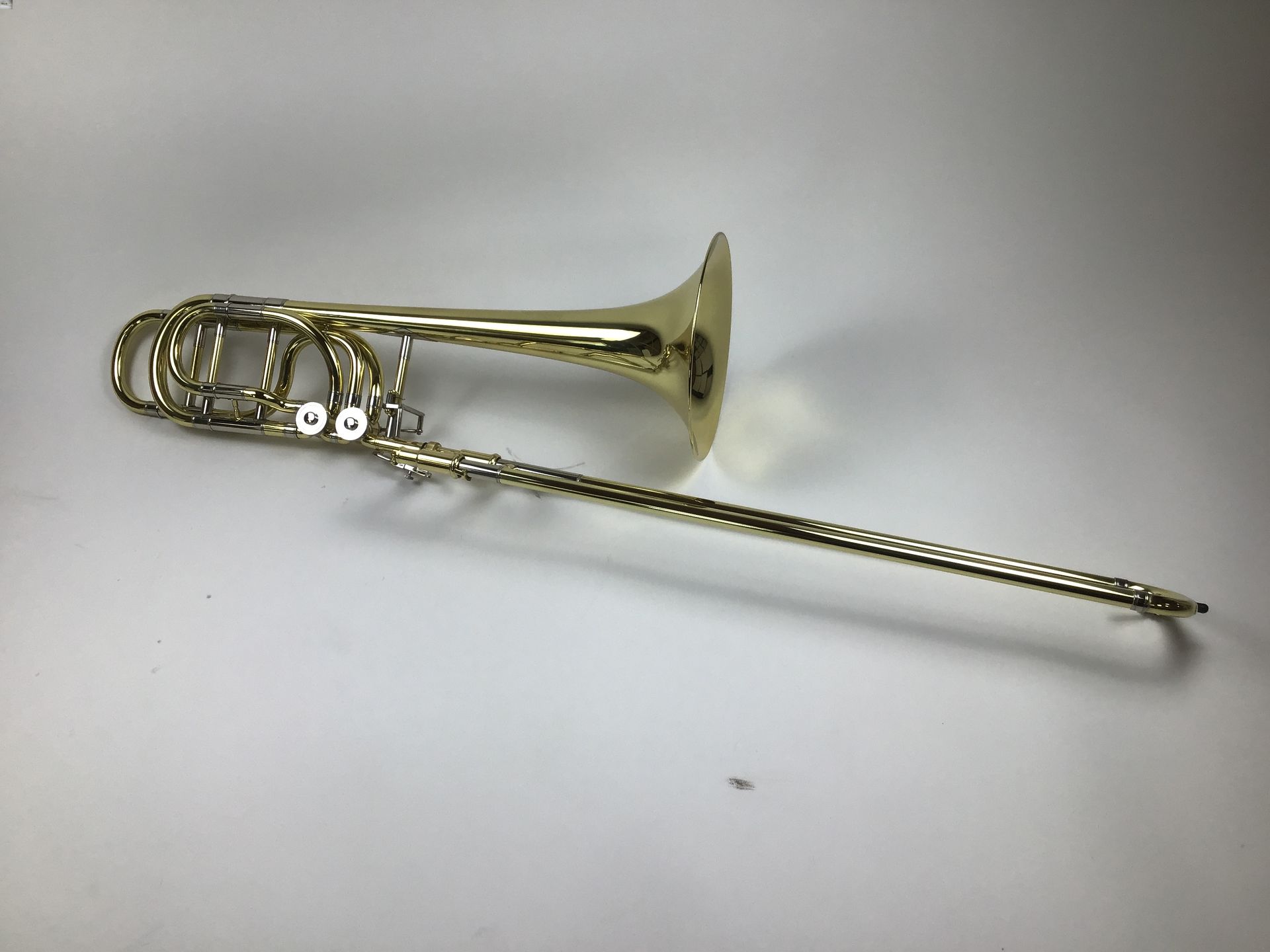


Bass
What Is A Bass Trombone
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the deep and powerful sound of the bass trombone. Learn about its unique features, range, and role in various music genres. Unleash the bass in your music with this versatile instrument.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The bass trombone is a captivating and versatile instrument that plays a crucial role in both classical and contemporary music genres. With its deep, rich, and resonant tones, the bass trombone adds a powerful foundation and unique color to any ensemble. Whether it’s in a symphony orchestra or a jazz big band, the bass trombone holds its own and demands attention.
Originating from the early 19th century, the bass trombone has developed and evolved over time into the instrument we know today. It is a larger and lower-pitched version of the tenor trombone, designed to produce lower frequencies and provide a solid bass support in various musical compositions.
The bass trombone possesses a distinct and unique sound. Its elongated tubing, wider bore, and larger bell contribute to its ability to produce lower, more resonant tones. These sonic characteristics make it the backbone of any ensemble’s low range, providing depth and richness to the overall sound.
Playing the bass trombone requires a high level of skill and technique. The player must have a strong embouchure and breath control to produce a consistent and resonant tone in the instrument’s lower range. Additionally, the bass trombonist must be proficient in slide technique, as the instrument does not have valves like a trumpet or a French horn.
The bass trombone is commonly used in a variety of musical settings. In symphony orchestras, it is often found in the brass section, providing a solid foundation and playing bass lines alongside the tuba and other low brass instruments. In jazz ensembles and big bands, the bass trombone takes on a more prominent role, often featured in solo passages and playing improvised solos.
Throughout the history of music, there have been many notable bass trombone players who have left a lasting impact. These virtuosos have showcased the instrument’s capabilities and pushed its boundaries in terms of technique and musical expression.
In this article, we will explore the origins and history of the bass trombone, delve into its anatomy and design, discuss playing techniques and sound production, highlight musical settings where the bass trombone shines, and pay tribute to some of the remarkable players who have made their mark on this instrument.
Origins and History of the Bass Trombone
The bass trombone has a fascinating history that dates back to the early 19th century when its predecessor, the tenor-bass trombone, started gaining popularity. This hybrid instrument featured a larger bore and bell, allowing it to produce lower pitches than the standard tenor trombone. As composers began to demand a deeper, more resonant sound in their compositions, the need for an instrument dedicated to the bass voice emerged.
It wasn’t until the mid-19th century that the bass trombone as we know it today began to take shape. Ludwig von Beethoven’s Symphony No. 9 was one of the first notable works to call for a dedicated bass trombone part. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that manufacturers and players started to adapt the instrument to meet the specific needs of bass trombonists.
The evolution of the bass trombone can be attributed to several key developments. First, the addition of a second valve, known as the dependent system, expanded the instrument’s range and improved intonation. This innovation allowed players to access lower notes and improve the overall accuracy in the low register. Later advancements, such as the addition of a second trigger and an independent valve system, further increased the bass trombone’s capabilities.
In addition to technical advancements, changes in musical styles and demands also influenced the development of the bass trombone. In the early 20th century, as jazz and swing music gained popularity, the bass trombone found its place in big bands and became an essential component of the rhythm section. Big band arrangements often featured the bass trombone playing vital bass lines and occasionally taking the spotlight with improvisational solos.
Today, the bass trombone is a standard member of the brass section in symphony orchestras and is seen in various musical genres, including classical, jazz, and even rock. Modern versions of the instrument feature advanced materials and construction techniques, resulting in improved playability and tonal characteristics.
Throughout its history, the bass trombone has played a crucial role in the evolution of music. It has inspired composers to explore new harmonies and textures, and its deep, resonant tones continue to captivate listeners and add depth to musical compositions.
Anatomy and Design of the Bass Trombone
The bass trombone is a brass instrument that shares many similarities with its tenor trombone counterpart but features specific design modifications to accommodate its lower pitch range. Understanding the anatomy of the bass trombone is essential for players and enthusiasts alike.
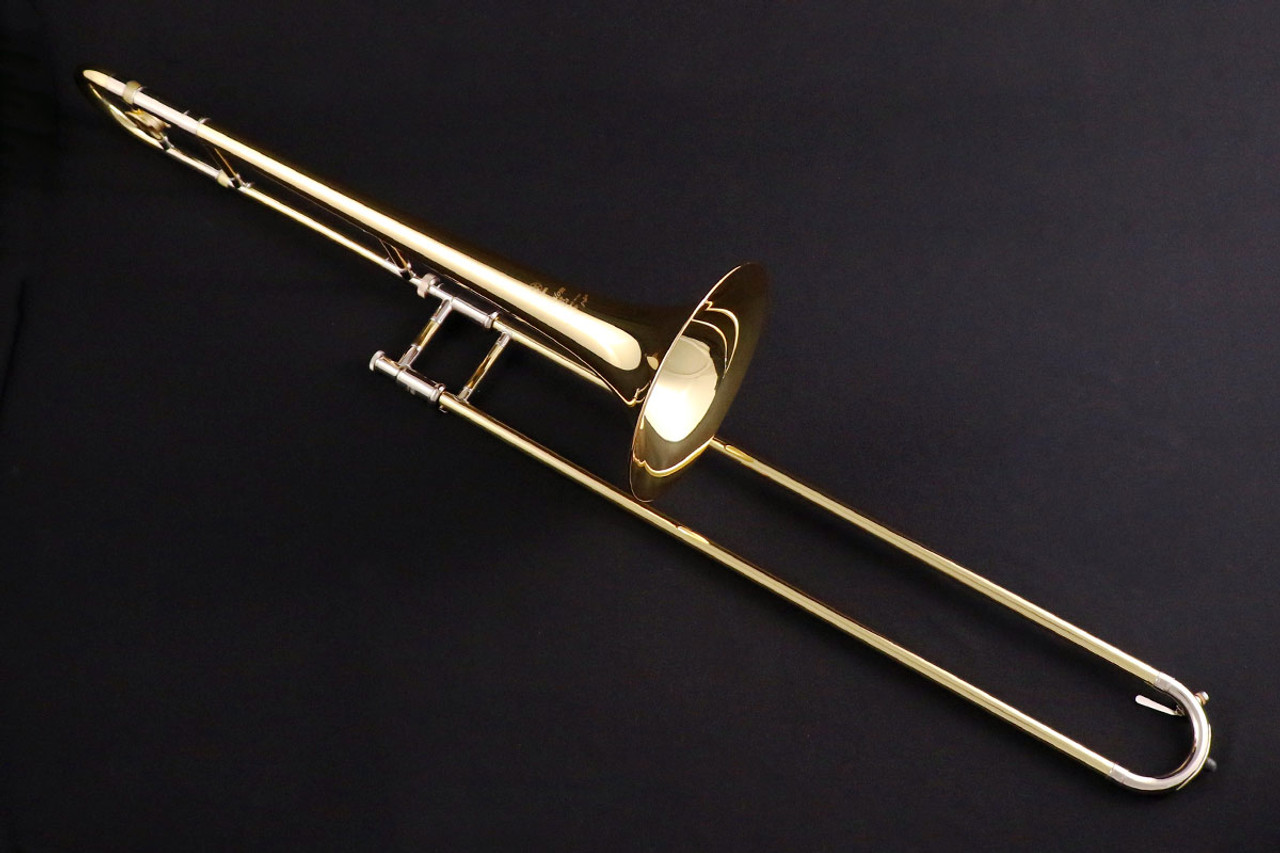
At first glance, the bass trombone appears larger and more imposing than the tenor trombone. It typically measures around 9.5 to 10.5 feet (2.9 to 3.2 meters) in length and features a wider bore and larger bell diameter. These design elements contribute to the instrument’s ability to produce deeper and more resonant sounds.
The main components of a bass trombone include the mouthpiece, leadpipe, slide, tuning slide, valves, and bell. The mouthpiece is an integral part of the instrument, as it allows the player to produce sound by buzzing their lips against the mouthpiece’s rim. Bass trombone mouthpieces are generally larger in diameter than those used for the tenor trombone, allowing for a more comfortable fit and better control in the lower register.
The leadpipe connects the mouthpiece to the slide and plays a crucial role in shaping the instrument’s overall tone and response. In bass trombones, the leadpipe is often larger and longer compared to tenor trombones, which helps to produce a rich and full sound.
One of the most distinct features of the bass trombone is its dual independent valve system. These valves, typically operated by the player’s thumb and trigger finger, are used to extend the instrument’s lower range. The addition of valves allows for more precise intonation and facilitates the production of low notes that would otherwise be challenging to play using only the slide.
The slide is another essential component of the bass trombone. It consists of a narrow outer slide tube and a wider inner slide tube that houses the trombone’s handslide. Sliding the inner and outer tubes in and out allows the player to adjust the pitch and produce different notes. A well-maintained slide, with smooth and precise movement, is crucial for accurate and effortless playing.
Finally, the bell of the bass trombone is larger and has a wider flare compared to the tenor trombone. The design of the bell contributes to the instrument’s characteristic low tones and provides a resonant projection of sound. The bass trombone’s bell is often detachable for ease of transport and storage.
In summary, the bass trombone’s distinct anatomy and design modifications, such as its larger size, wider bore, dual valve system, and larger bell, all contribute to its ability to produce deep, rich, and resonant sounds. These physical characteristics make the bass trombone an essential instrument in various musical settings, ensuring a strong presence in both the lower brass section of orchestras and the expressive solos of jazz ensembles.
Playing Techniques and Sound Production
Playing the bass trombone requires a combination of technical skill, musical understanding, and physical dexterity. Mastering the instrument involves understanding various playing techniques and sound production methods that allow the player to fully control and express the instrument’s unique tonal qualities.
One of the primary techniques used in playing the bass trombone is embouchure control. The embouchure refers to the formation of the lips, facial muscles, and oral cavity to produce a stable and resonant sound. Bass trombonists often develop a strong embouchure to support the lower register and produce clear and focused tones. Proper breath control is also crucial, as the player needs to supply a steady stream of air to support the tone and maintain control throughout long phrases.
An essential aspect of playing the bass trombone is slide technique. Unlike other brass instruments with valves, the bass trombone relies on a handslide to adjust the pitch. This requires precise coordination between the player’s hand movements and the air flow. The player must develop a keen sense of slide positions and intervals to accurately execute notes, glissandos, and legato passages. Regular slide maintenance, such as cleaning and lubrication, ensures smooth and effortless slide movement.
In addition to basic technique, bass trombonists also employ specific methods to produce various tonal qualities and effects. These include the use of vibrato, which adds warmth and expressiveness to the sound, and multiphonics, which involve playing multiple pitches simultaneously. Additionally, the player can utilize different articulation techniques, such as tonguing and slurring, to create distinct attacks and legato passages.
The sound production of the bass trombone is influenced not only by the player’s technique but also by instrument setup and mouthpiece choice. The bass trombone’s wider bore and larger bell allow for a deeper, darker, and more resonant sound compared to the tenor trombone. Players may experiment with different mouthpiece sizes and designs to find the optimal balance between playability and desired sound characteristics.
In ensemble settings, bass trombonists play various roles depending on the musical genre and composition. In orchestras, they often provide a solid foundation in the low brass section, playing bass lines and contributing to the harmonic richness of the ensemble. In jazz and big band contexts, the bass trombone can take on a more prominent role, featuring in improvised solos and playing intricate melodic lines.
Overall, playing the bass trombone requires a combination of technical mastery, musicality, and artistic expression. Through diligent practice and exploration of different playing techniques, bass trombonists can unlock the instrument’s full potential and contribute their distinct voice to the world of music.
Musical Settings for the Bass Trombone
The bass trombone is a versatile instrument that finds its place in various musical settings, showcasing its unique tonal qualities and adding depth and richness to the overall sound. From orchestras to jazz ensembles, the bass trombone plays an essential role in different genres and musical compositions.
In symphony orchestras, the bass trombone can be found in the brass section, alongside the tuba and other low brass instruments. It provides a solid foundation and plays bass lines, adding depth and weight to the ensemble’s sound. Composers often utilize the bass trombone to add power and richness to the lower register, enhancing the overall emotional impact of the music. From intense symphonies to delicate lyrical passages, the bass trombone seamlessly blends with the rest of the orchestra, creating a balanced and harmonious sound.
In jazz ensembles and big bands, the bass trombone takes on a more prominent and dynamic role. It often plays an essential part in the rhythm section, anchoring the harmonic structure of the music. In swing, bebop, and Latin jazz styles, the bass trombone provides a solid and driving foundation, creating a pulsating groove that propels the ensemble forward. Additionally, the bass trombone is frequently featured in improvisational solos, showcasing the player’s virtuosity and ability to navigate complex harmonic progressions.
Contemporary music genres, such as funk, fusion, and rock, also make use of the bass trombone’s unique sound. In these settings, the instrument adds a layer of richness and depth, complementing the electric guitars, keyboards, and drums. Bass trombone players in these genres often play melodic lines, doubling or harmonizing with other instruments. The instrument’s ability to blend well with different timbres and its versatility in creating both powerful and delicate tones make it a valuable addition to these modern musical landscapes.
Furthermore, the bass trombone is not limited to ensemble settings. It can also be featured as a solo instrument, showcased in solo performances, concertos, and recitals. These solo pieces highlight the instrument’s expressive capabilities and technical prowess, allowing the bass trombonist to shine and captivate the audience with virtuosic passages and melodic interpretations.
Regardless of the musical setting, the bass trombone brings a robust and commanding presence to the forefront. Its deep, resonant tones add a unique color to the overall sound, enhancing the musical experience for both performers and listeners alike.
Notable Bass Trombone Players
Throughout the history of music, many talented bass trombone players have made significant contributions to the instrument’s development and showcased its capabilities in various musical genres. These notable performers have left a lasting impact on the bass trombone repertoire and have become icons in the world of brass playing.
One prominent figure in the bass trombone world is George Roberts. Known for his incredible technique and mastery of the instrument, Roberts was a highly sought-after studio musician in Los Angeles during the mid-20th century. He played on countless recordings for popular artists and worked in the Hollywood film industry, adding his distinctive sound to the scores of well-known movies and television shows.
Another influential bass trombonist is Douglas Yeo. Yeo is renowned for his virtuosic playing and his work as a soloist, educator, and orchestral musician. He served as the bass trombonist of the Boston Symphony Orchestra for over 27 years, leaving a lasting legacy through his performances and contributions to the bass trombone literature. Yeo has also published educational materials and collaborated with instrument manufacturers to develop new equipment for the bass trombone.
Christian Jones is another notable bass trombonist who has made significant contributions to the instrument. Jones has held positions in renowned orchestras worldwide and has performed as a soloist with various ensembles. He is known for his expressive playing style and versatility in both classical and contemporary music genres. Jones also actively promotes the bass trombone through his teaching and masterclasses.
In the world of jazz, Dave Taylor stands out as a prominent bass trombonist. Taylor’s distinctive playing style and improvisational skills have made him a sought-after performer in the jazz and avant-garde music scenes. He has played with renowned jazz musicians and has recorded numerous albums as a leader, further expanding the possibilities of the bass trombone in jazz improvisation.
Other notable bass trombone players include Ray Premru, who contributed significantly to the classical chamber music repertoire for the instrument, and Brandt Attema, who has gained recognition as a soloist and chamber musician, pushing the boundaries of the bass trombone’s tonal capabilities.
These remarkable individuals are just a few examples of the many talented bass trombonists who have left their mark on the instrument and the music world. Their contributions have expanded the repertoire, elevated the instrument’s status, and inspired future generations of bass trombone players to explore new possibilities within their art.
Conclusion
The bass trombone is an extraordinary instrument that brings depth, richness, and power to the world of music. Its origins and evolution have shaped its unique design, allowing it to produce deep, resonant tones that add a solid foundation to musical compositions. Bass trombonists employ a combination of technical skill and musicality to master the instrument’s playing techniques and create expressive and captivating performances.
From symphony orchestras and jazz ensembles to contemporary music genres, the bass trombone finds its place in various musical settings, enhancing the overall sound and contributing to the artistic vision of composers and performers. Its versatility, ability to blend with different ensembles, and capacity for soloistic expression make it a valuable instrument in the world of brass playing.
Notable bass trombone players have left lasting impressions through their virtuosity, artistry, and contributions to the repertoire. Their performances and achievements have pushed the boundaries of the instrument, inspiring future generations of bass trombonists to explore new musical possibilities and possibilities.
Whether it’s the resonant melodies of a symphony, the driving bass lines of a jazz ensemble, or the dynamic solos in contemporary music, the bass trombone leaves a lasting impact on audiences with its commanding presence and unique tonal qualities.
In conclusion, the bass trombone continues to captivate listeners and musicians with its deep, rich sound. Its history, anatomy, and versatile playing techniques contribute to its importance in various musical genres. As the instrument evolves and more talented players emerge, the future of the bass trombone shines brightly, promising continued innovation, artistry, and the exploration of new musical horizons.