Home>Instruments>Bass>What Is Bass In Music


Bass
What Is Bass In Music
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn the fundamentals of bass in music and discover how it adds depth and rhythm to your favorite songs. Explore the importance and techniques of playing the bass.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the world of music, the bass plays a crucial role, providing the foundation and adding depth to various musical compositions. Defined as the lowest part of the musical range, the bass creates a solid and rhythmic backbone that supports other instruments and vocals. Whether it’s the thumping bassline in a catchy pop song or the driving bass groove in a funk track, the importance of bass cannot be overstated.
Understanding the fundamentals of bass in music is essential for aspiring musicians, producers, and even casual music lovers. In this article, we will explore the definition, role, and significance of bass in music, as well as delve into the different types of bass instruments, famous bass players, and techniques for playing bass.
So, whether you’ve always been fascinated by the low-end frequencies or you’re just starting to explore the world of bass, join us on this journey as we dive deep into the world of bass in music.
Definition of Bass
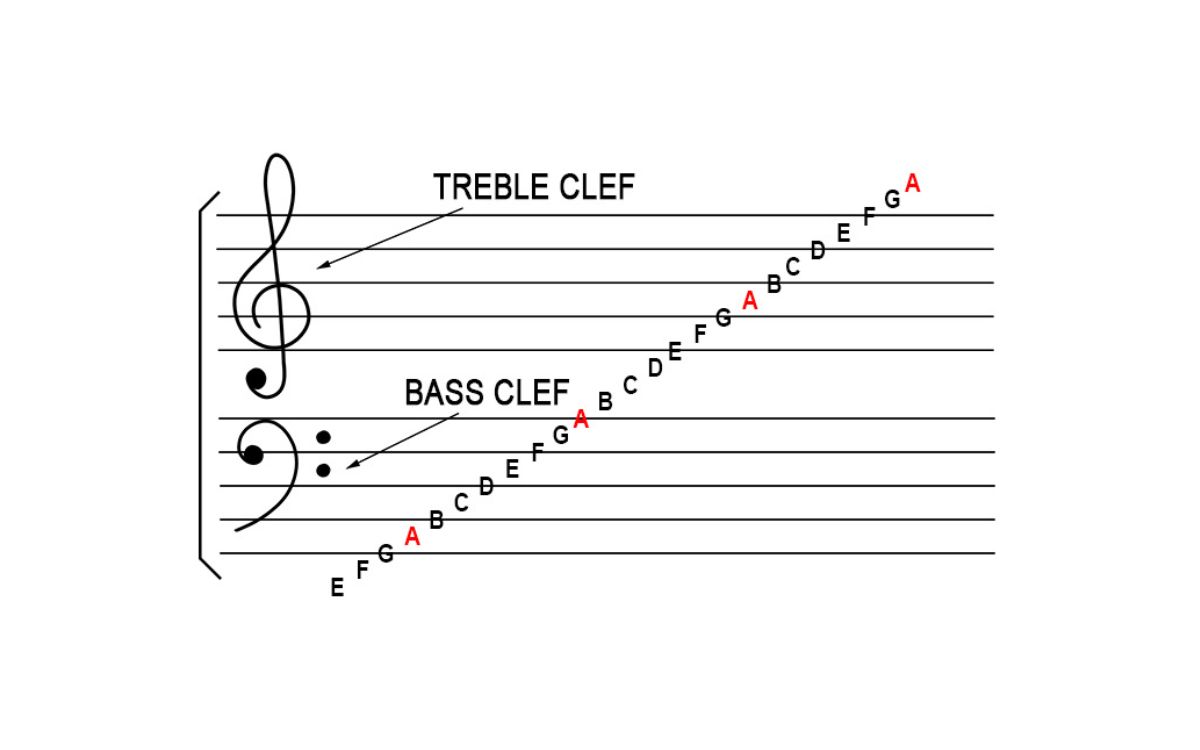
The term “bass” refers to the lowest range of musical sound frequencies. It is both a musical note and a category of instruments that produce low-pitched sounds. In musical notation, bass is indicated with a lowercase letter “b” or by the symbol “_”.
When we talk about bass in the context of music, we’re not only referring to a specific instrument but also to a range of frequencies. Bass instruments are designed to produce low-pitched sounds, typically in the range of 60 to 250 Hz, which is lower than the frequencies produced by most other instruments. The bass note provides a solid foundation for the melody and harmonies in a musical composition.
It’s important to note that bass is not limited to one specific instrument. It can be played on various instruments, such as the bass guitar, double bass, electric bass, tuba, or synthesizers programmed with bass sounds. Each instrument produces bass sounds with its unique tonal characteristics, but they all serve the same purpose of providing a low-end foundation in music.
The bass note is an essential component of the harmonic structure of a piece of music. It helps to create a sense of stability, grounding the composition and providing a sense of rhythmic pulse. The bassline, or the sequence of notes played by the bass instrument, often interacts with the drums and other instruments to establish the groove and drive the rhythm forward.
In summary, bass in music refers to the lowest range of musical frequencies and encompasses both a specific note and a category of instruments. It provides the foundation and rhythmic backbone in various musical compositions, playing a crucial role in creating a sense of stability and driving the overall sound.
Role of Bass in Music
The role of bass in music goes beyond simply playing low notes. It serves as the glue that holds everything together, providing structure, depth, and a sense of rhythm to a composition. Here are some key roles that the bass fulfills in music:
- Fundamental Foundation: The bass creates the foundation for the composition, acting as the anchor for other instruments to build upon. It establishes the tonal center, root notes, and harmonies, giving the music a solid and stable base.
- Rhythmic Drive: The bass, along with the drums, is responsible for driving the rhythm and groove of a song. It sets the pace, providing a pulsating feel that makes people want to tap their feet or dance. The rhythmic patterns played by the bass help to establish the overall feel and energy of the music.
- Enhancement of Melodies and Harmonies: The bass adds depth and richness to melodies and harmonies. By playing complementary notes to the chords and melodies, it fills out the sound spectrum, creating a fuller and more balanced musical composition.
- Transitions and Dynamics: The bass is crucial in smoothly transitioning between different sections of a song, such as verses and choruses. It adds dynamics and helps to create tension and release by playing different rhythms, fills, and variations.
- Emotional Impact: The lower frequencies produced by the bass can evoke strong emotional responses in listeners. Whether it’s a melancholic bassline or a funky groove, the bass has the power to shape the mood and atmosphere of a musical piece, enhancing its emotional impact.
Overall, the role of bass in music is to anchor the composition, drive the rhythm, enhance melodies and harmonies, create smooth transitions, and contribute to the emotional impact of the music. It is a vital element that brings depth, structure, and cohesion to any musical piece.
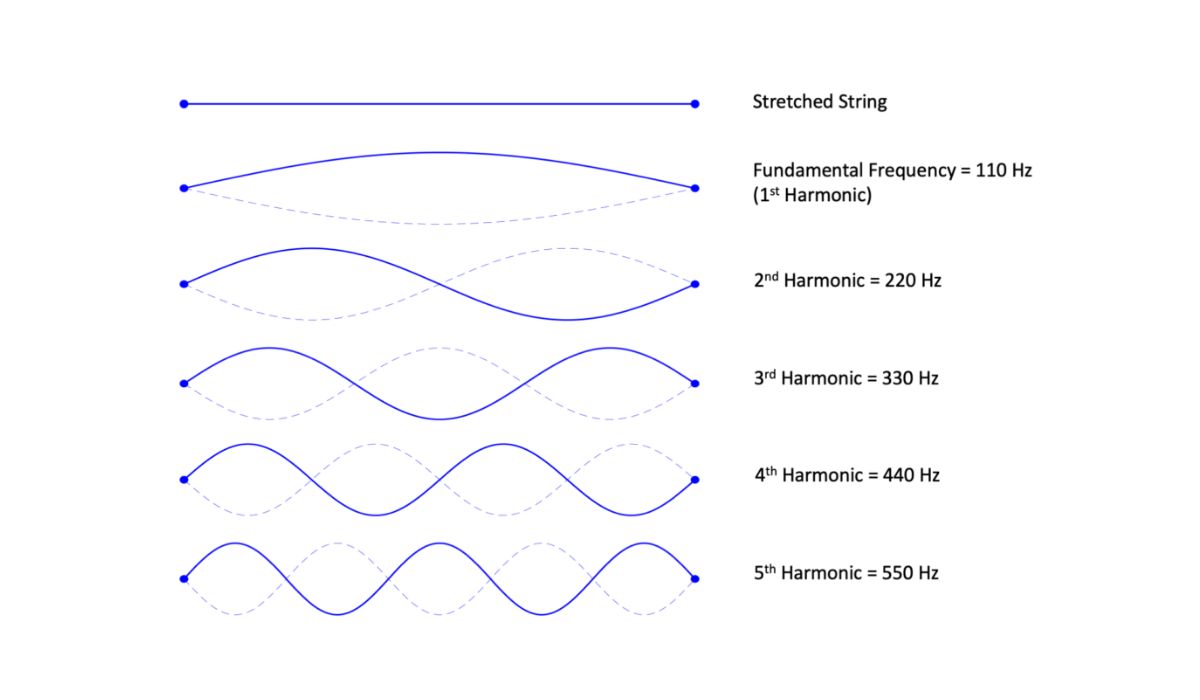
Frequency Range of Bass
The bass range encompasses the lower end of the audio frequency spectrum. It is characterized by deep, resonant tones that add richness and fullness to music. The frequency range of bass typically extends from around 60 Hz to 250 Hz, although this can vary depending on the specific instrument or sound source.
At the lower end of the frequency spectrum, around 60 to 80 Hz, you’ll find the sub-bass range. These frequencies are felt more than they are heard, producing a rumbling sensation that can be felt in the chest or floor. Sub-bass tones are commonly used in genres such as electronic music, hip-hop, and dubstep to create a powerful and immersive listening experience.
As the frequency range moves higher, from 80 to 120 Hz, we enter the bass region. This is where the foundational notes of many basslines sit, providing a solid and driving rhythm. The bass frequencies in this range add warmth and depth to a musical composition, anchoring the overall sound and giving it a sense of fullness.
Moving up further, from 120 to 250 Hz, we reach the lower midrange frequencies. This is the range where the bass notes start to blend with the lower harmonics of other instruments, such as guitars and keyboards. Within this range, the bass provides clarity and definition to the overall mix, ensuring that the low-end frequencies are well-balanced and properly articulated.
It’s worth noting that the frequency range of bass can vary depending on the instrument being used. For example, the double bass, often used in classical and jazz music, has a slightly wider frequency range that can extend below 60 Hz. On the other hand, the electric bass guitar is typically tuned to cover the standard bass range of 60 to 250 Hz.
Understanding the frequency range of bass is essential for musicians, producers, and sound engineers. It allows them to sculpt the mix, ensuring that the bass frequencies are well-balanced and complement the other elements of the composition. By harnessing the power of the bass frequencies, musicians can create music that is not only heard but also deeply felt.
Types of Bass Instruments
There are several types of instruments that are commonly used to produce bass sounds in music. Each instrument has its unique characteristics, tonal qualities, and playing techniques. Here are some of the most popular types of bass instruments:
- Bass Guitar: The bass guitar is one of the most widely recognized and commonly used bass instruments. It typically has four strings, although there are five and six-string variants as well. The bass guitar is played by plucking or strumming the strings, and it is known for its deep, resonant tones that provide the foundation for many musical genres.
- Double Bass: Also known as the upright bass or contrabass, the double bass is a large, bowed or plucked string instrument. It is commonly used in classical, jazz, and orchestral music. The double bass produces rich and deep tones, providing a solid low-end foundation for ensembles and adding a touch of elegance to the music.
- Electric Bass: The electric bass is similar in appearance and playing technique to the bass guitar. However, it uses electronic pickups and amplification to produce a louder and more versatile sound. The electric bass is commonly used in rock, funk, and pop music, providing a punchy and powerful low-end presence.
- Tuba: The tuba is a brass instrument with a deep, mellow sound. It is often used in marching bands, brass ensembles, and classical music. The tuba produces rich, resonant bass tones that add depth and gravitas to the music.
- Synthesizer Bass: With advancements in technology, synthesizers have become increasingly popular for creating bass sounds. Synthesizer bass tones can replicate the sounds of traditional bass instruments or create unique, otherworldly bass textures. Synthesizers provide a wide range of sonic possibilities and are commonly used in electronic and experimental genres.
While these are some of the main types of bass instruments, there are other variations and hybrids that exist, such as the electric upright bass, bass synthesizers, and fretless bass guitars. Each instrument brings its own distinctive character and tonal qualities to the music, allowing musicians to express their creativity and shape the overall sound of a composition.
Whether it’s the thumping bassline of a catchy pop song or the melodic grooves of a jazz bass solo, the different types of bass instruments play a vital role in enhancing the sonic landscape and adding depth and richness to music.
Importance of Bass in Music
The bass serves a fundamental role in music, playing a crucial role in shaping the overall sound and feel of a composition. Here are some reasons why bass is important in music:
- Foundation and Rhythm: The bass provides the foundation for a musical piece, acting as the anchor that holds everything together. It establishes the tonal center and provides the rhythmic pulse that drives the composition forward. Without the bass, music can feel empty and lacking in solidity.
- Enhances Harmonies and Melodies: The low frequencies produced by the bass complement the higher-pitched instruments and vocals, adding depth and richness to the overall sound. It fills out the harmonic and melodic structures, giving them a sense of completeness and complexity.
- Musical Texture and Depth: The bass adds texture and depth to the music, creating a sense of space and dimension. It provides a solid and grounding element that gives the listener something to latch onto, making the composition feel more immersive and captivating.
- Impact and Emotion: The bass has the power to evoke strong emotional responses in listeners. The low frequencies can create a sense of tension, anticipation, or even evoke a deep emotional connection. A well-crafted bassline can greatly enhance the emotional impact of a musical piece.
- Defines Genre and Style: The bass is instrumental in defining the genre and style of music. Different genres have distinct approaches to bass, whether it’s the walking basslines of jazz, the driving bass grooves of funk, or the booming sub-bass of electronic music. Bass plays a pivotal role in shaping the musical identity and setting the mood.
- Collaboration and Communication: The bass interacts closely with the drums and other rhythm instruments, forming the backbone of the rhythm section. This collaboration and communication between the instruments create a tight and cohesive sound, allowing the band or ensemble to groove and play off each other.
Overall, the importance of bass in music cannot be overstated. It provides the foundation, rhythm, and depth that propel a composition forward. The bass enhances harmonies and melodies, adds texture and emotion, defines genre and style, and facilitates collaboration among musicians. When all these elements are brought together, the result is a rich and captivating musical experience.
Techniques for Playing Bass
Playing the bass requires a unique set of techniques that are specific to the instrument. These techniques allow the bass player to create a solid and rhythmic foundation while adding depth and complexity to the music. Here are some common techniques used in playing bass:
- Fingerstyle: Fingerstyle is a popular technique where the bass player uses their fingers to pluck the strings. This technique allows for greater control and precision, enabling the player to create a wide range of tones and dynamics. The fingers can be used individually or in combination to create complex bass lines and patterns.
- Slap and Pop: Slap and pop is a percussive technique commonly used in funk, slap bass, and certain rock genres. It involves using the thumb to slap the strings against the fretboard, producing a sharp and percussive sound. The other fingers then “pop” the strings, creating a distinctive, funky sound. This technique adds rhythmic flair and groove to the bassline.
- Palm-Muting: Palm-muting is a technique where the player rests their palm near the bridge of the bass, dampening the strings slightly. This produces a muted and percussive sound, similar to the sound of a muted electric guitar. Palm-muting is commonly used in rock and heavy metal genres to create a tight and punchy bass sound.
- Slides and Hammer-ons: Slides and hammer-ons are techniques used to smoothly transition between notes. Slides involve sliding the finger along the string to change pitch, while hammer-ons involve using the fretting hand to produce a note without plucking the string. These techniques can add fluidity and expressiveness to the bassline.
- Double Stops and Harmonics: Double stops refer to playing two notes simultaneously on adjacent strings, creating a chord-like effect. Harmonics, on the other hand, involve lightly touching the string at specific fret locations to produce chiming, bell-like tones. Double stops and harmonics add texture and interest to the bassline, allowing for more intricate and complex musical passages.
- Walking Basslines: Walking basslines are commonly used in jazz and blues music. This technique involves playing a steady stream of quarter notes, moving from one chord root to another. Walking basslines provide a melodic and rhythmic foundation, supporting the other instruments and adding harmonic complexity.
These are just a few of the many techniques employed by bass players. Each technique adds a distinct flavor and character to the bassline, allowing the musician to express their creativity and musicality. Mastering these techniques takes practice and experimentation, but they are essential in developing a versatile and dynamic style of playing.
Famous Bass Players
Throughout the history of music, there have been many influential and talented bass players who have made a significant impact. Their innovative playing styles, technical prowess, and musical contributions have shaped the way the bass is perceived and played. Here are some famous bass players who have left an indelible mark on the world of music:
- Paul McCartney: Paul McCartney, of The Beatles fame, is renowned for his melodic and inventive bass lines. Songs like “Something,” “Come Together,” and “Hey Jude” showcase his versatility and musicality, solidifying his status as one of the most influential bass players of all time.
- Jaco Pastorius: Jaco Pastorius revolutionized the role of the bass guitar in jazz and fusion music. His virtuosic playing, unique chordal and fretless techniques, and melodic solos have inspired countless bass players. Albums like “Jaco Pastorius” and “Word of Mouth” are testaments to his groundbreaking style.
- Geddy Lee: Geddy Lee, the bassist and vocalist of Rush, is known for his intricate bass playing and soaring vocal range. His distinctive tone and complex bass lines can be heard in songs like “Tom Sawyer,” “YYZ,” and “Limelight,” cementing his status as a progressive rock icon.
- James Jamerson: James Jamerson, a session bassist for Motown Records, is often regarded as one of the greatest bass players in history. His melodic and fluid bass lines on songs like “My Girl” by The Temptations and “What’s Going On” by Marvin Gaye have become enduring classics of the Motown sound.
- John Entwistle: John Entwistle, the bassist of The Who, was known for his powerful and aggressive playing style. His energetic bass lines in songs like “My Generation” and “Baba O’Riley” contributed to The Who’s distinctive sound and established him as a legend in rock bass playing.
- Victor Wooten: Victor Wooten is famous for his virtuosic and innovative approach to playing bass. His exceptional technical abilities, unique slap and tap techniques, and ability to blend various musical genres can be heard in his solo work and collaborations with artists such as Bela Fleck and the Flecktones.
These are just a few examples of the many talented and influential bass players who have left a lasting impact on the world of music. Each of them has pushed the boundaries of what the bass can do, inspiring future generations of bass players to explore new possibilities and continue to push the instrument forward.
Conclusion
The bass is an essential and foundational component of music, providing rhythm, depth, and harmony to compositions across diverse genres. By defining the low end of the frequency spectrum, the bass creates a solid and rhythmic foundation that supports other instruments and drives the overall sound of a musical piece.
Whether it’s the melodic and inventive basslines of Paul McCartney, the groundbreaking fretless playing of Jaco Pastorius, or the powerful bass solos of John Entwistle, the world of bass is filled with legendary players who have redefined what is possible on the instrument.
Understanding the importance of bass in music allows us to appreciate the complex interplay of different instruments and how they contribute to the overall sonic landscape. From providing the groove and rhythm to enhancing melodies and harmonies, the bass plays a vital role in shaping the emotional impact and identity of a composition.
Learning the techniques of playing bass, such as fingerstyle, slap and pop, and palm-muting, opens up a world of possibilities for musicians to create their unique sound. The mastery of these techniques allows bass players to add depth, complexity, and expression to their playing, contributing to the overall musical experience.
So, next time you listen to your favorite song, take a moment to appreciate the bassline and its role in the music. From the heart-thumping bass drops in electronic music to the melodic grooves in jazz and the driving basslines in rock, the bass adds a richness and dimension that is truly transformative.
In conclusion, the bass is not just an instrument or a range of frequencies. It is the backbone of music, the heartbeat that keeps the rhythm alive, and the sonic anchor that holds everything together. The world of music would be incomplete without the power, presence, and artistry of the bass.