Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>How Can I Learn Music Theory


Music Theory
How Can I Learn Music Theory
Published: February 1, 2024
Looking to learn music theory? Discover effective methods and resources to enhance your understanding and proficiency in music theory.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Music theory forms the foundation of every musical composition. It is the study of how music is structured, including the principles of harmony, melody, rhythm, and form. Understanding music theory can greatly enhance your musical abilities, whether you’re a musician, composer, or music enthusiast.
Learning music theory allows you to unlock the intricacies of music and provides you with a deeper appreciation for the art form. It helps you recognize patterns, explore different musical styles, and communicate effectively with other musicians. Whether you’re interested in classical, jazz, rock, or any other genre, a solid understanding of music theory will undoubtedly enrich your musical journey.
Many aspiring musicians may feel intimidated by the prospect of diving into music theory, thinking it is too complex or academic. However, with the right approach and a bit of dedication, anyone can grasp the fundamentals of music theory and apply them to their musical endeavors.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of learning music theory, step by step. We will cover essential concepts, from understanding basic notations to analyzing chord progressions and exploring melody and harmony. We will also discuss how to apply music theory to songwriting and provide tips for practicing and mastering your knowledge.
So, if you’ve ever wondered how you can learn music theory, fear not! By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid foundation to embark on your musical journey and unravel the mysteries of music theory.
Importance of Music Theory
Music theory plays a vital role in the world of music. It serves as a framework that musicians use to create, interpret, and understand music. Here are some reasons why learning music theory is important:
- Enhanced Musical Skills: Understanding music theory allows you to have a deeper understanding of the music you create or perform. It helps you recognize patterns, analyze chord progressions, and make informed musical decisions. With a strong foundation in music theory, you can improvise, harmonize, and compose music more effectively.
- Effective Communication: Music theory provides a common language for musicians. It enables you to communicate musical ideas, collaborate with other musicians, and perform in a cohesive manner. Whether you’re playing in a band, orchestra, or any other ensemble, a shared understanding of music theory ensures smoother rehearsals and performances.
- Musical Appreciation: Understanding music theory allows you to appreciate music on a deeper level. It enables you to recognize the compositional techniques employed by different composers and genres. By analyzing the harmonic progressions, melodic structures, and rhythmic patterns, you can develop a greater appreciation for the artistry and complexity of the music you listen to.
- Creative Expression: Music theory provides you with the tools and vocabulary to express your musical ideas. It allows you to experiment with different chord progressions, scales, and modes. By understanding the principles of music theory, you can break free from common patterns and create unique and innovative compositions.
- Versatility: Whether you’re interested in playing classical, jazz, pop, or any other genre, a solid foundation in music theory is essential. Music theory principles are universal and can be applied to any style of music. It opens doors to different musical genres and allows you to adapt and explore new musical territories.
Overall, learning music theory not only improves your technical skills but also deepens your connection to music. It expands your musical horizons, enhances your creative abilities, and empowers you to express yourself musically with confidence.
Getting Started with Music Theory
Embarking on your journey to learn music theory may seem overwhelming at first, but with the right approach, it can be an exciting and rewarding experience. Here are some steps to help you get started:
- Set Clear Goals: Before diving into music theory, it’s important to clarify your goals and what you hope to achieve. Do you want to become proficient in reading sheet music? Do you want to improve your songwriting skills? Setting clear goals will guide your learning process and help you stay focused.
- Start with the Basics: Begin by familiarizing yourself with the fundamentals of music theory. Learn to read sheet music, understand the musical staff, and grasp the concept of rhythm and time signatures. Online tutorials, books, and video lessons can be valuable resources for learning these basics.
- Learn Musical Notations: Music theory relies heavily on notations to represent musical ideas. Familiarize yourself with essential symbols such as clefs, notes, rests, and dynamics. Practice reading and interpreting sheet music, as it will strengthen your ability to understand and analyze different musical pieces.
- Study Scales and Chords: Scales and chords are building blocks of music. Study major and minor scales, as well as different types of chords – triads, seventh chords, and extended chords. Understand their construction and learn to play them on your instrument. This knowledge will form the basis for harmony and melody in your musical journey.
- Analyze Songs: Take the time to analyze your favorite songs. Start with simple tunes and identify the chord progressions and melodies. Pay attention to how they fit together and create musical tension and resolution. Analyzing songs will develop your ear for music and deepen your understanding of music theory in practice.
- Experiment and Apply: Once you have a solid grasp of the basics, don’t be afraid to experiment and apply what you’ve learned. Try composing your own melodies, harmonize existing tunes, or create chord progressions. The more you actively engage with music theory, the better you’ll understand its concepts and their practical application.
- Seek Guidance: Consider taking music theory lessons or finding a mentor who can provide guidance and answer your questions. They can help clarify difficult concepts, provide feedback on your progress, and offer valuable insights and practical tips.
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, learning music theory requires consistent practice. Set aside dedicated time each day or week to review concepts, practice reading and playing music, and explore new exercises. Regular practice will reinforce your understanding and help you progress faster.
Remember, learning music theory is a gradual process. Start with the basics, be patient with yourself, and enjoy the journey. As you continue to expand your knowledge, you’ll find that the world of music theory opens up endless possibilities for your musical growth and creativity.
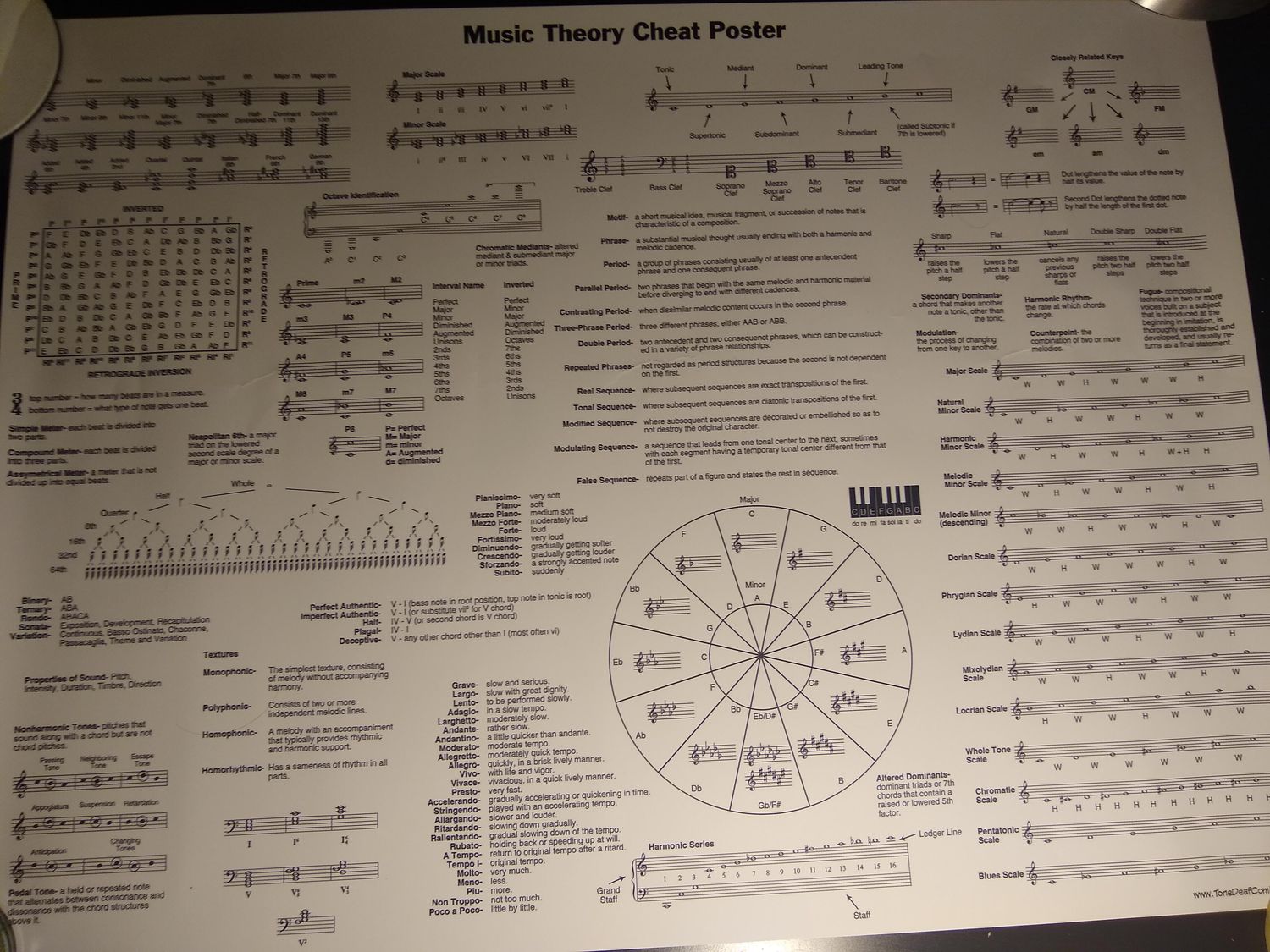
Understanding Basic Notations
When learning music theory, it is essential to familiarize yourself with basic notations. These symbols and markings convey important musical information and enable musicians to read and interpret sheet music accurately. Here are some key notations to understand:
- Musical Staff: The musical staff consists of five horizontal lines and four spaces. Notes and other symbols are placed on or between these lines and spaces to represent different pitches.
- Clef: Clefs indicate the range of notes and instruments used in a piece of music. The most common clefs are the treble clef (also known as the G clef) and the bass clef (also known as the F clef).
- Notes: Notes represent different pitches in music. The pitch of a note is determined by its position on the musical staff. The most common types of notes are whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, eighth notes, and sixteenth notes.
- Rests: Rests represent periods of silence in music. They indicate when to briefly pause and not play any notes. Rests come in various durations, similar to notes.
- Time Signature: The time signature indicates the meter and rhythm of a piece of music. It consists of two numbers stacked vertically. The top number represents the number of beats in each measure, while the bottom number denotes the value of each beat.
- Key Signature: The key signature is a set of sharps or flats placed at the beginning of each staff line. It indicates which notes are altered throughout the piece. The key signature determines the tonality of the music.
- Dynamics: Dynamics indicate the volume or intensity of a musical passage. Common dynamic markings include pianissimo (very soft), piano (soft), mezzo piano (moderately soft), mezzo forte (moderately loud), forte (loud), and fortissimo (very loud).
- Articulation: Articulation marks denote how a note should be played or sung. They include symbols such as staccato (short and detached), legato (smooth and connected), accent (emphasized attack), and many more.
Understanding these basic notations is crucial for reading and interpreting sheet music accurately. Practice recognizing and identifying these symbols as you encounter them in musical scores. As you become more proficient, you will be able to read and perform music with greater fluency and precision.
Additionally, there are many online resources, books, and tutorials available to help you further explore and understand basic notations in music theory. The more you familiarize yourself with these symbols, the more confident you will become in your ability to interpret and communicate musical ideas through sheet music.
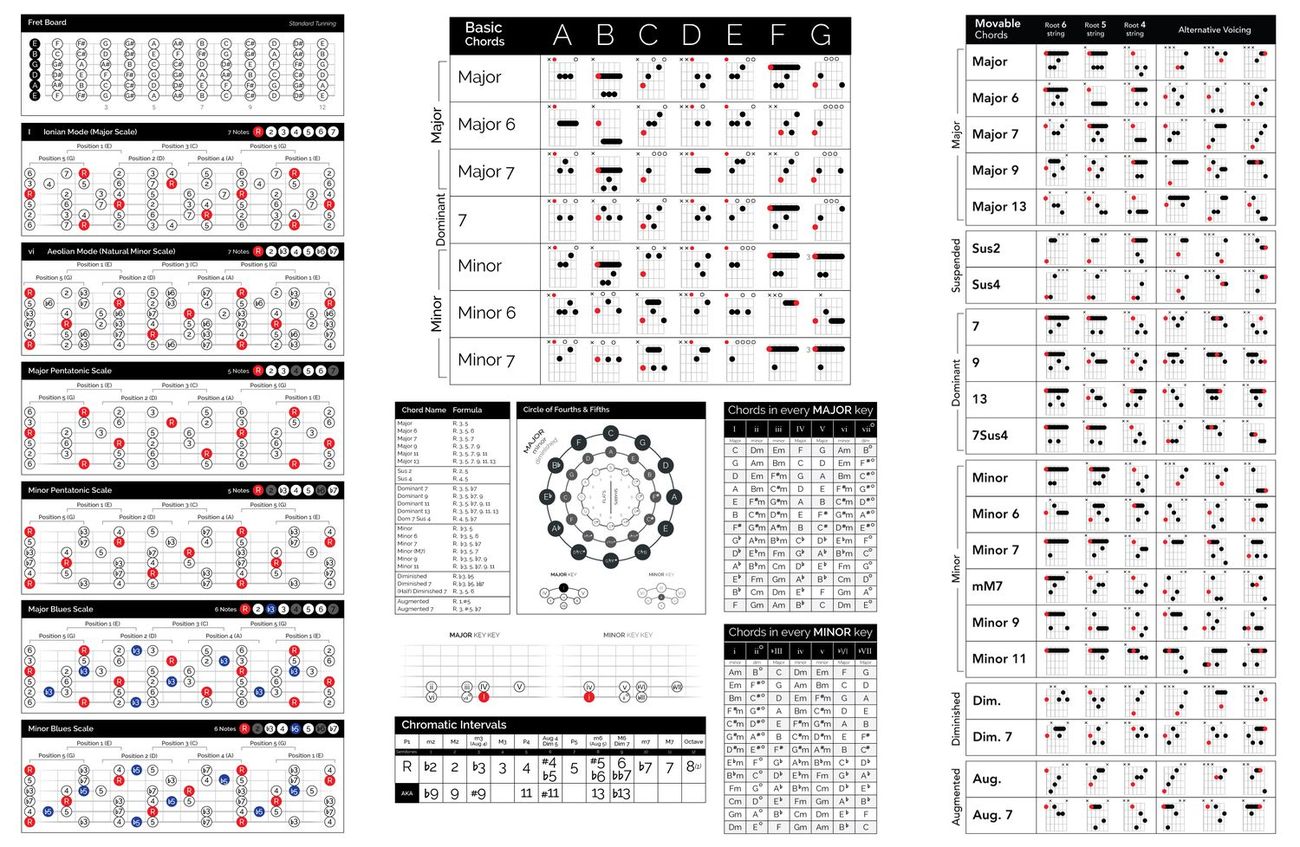
Learning Scales and Chords
Scales and chords are fundamental building blocks of music. They give structure and harmony to melodies, providing a foundation for creating and understanding music. Here are some key concepts to grasp when learning scales and chords:
- Scales: A scale is a sequence of notes arranged in ascending or descending order. It defines the pitch relationships within a specific key or tonality. Major and minor scales are the most common types in Western music. They consist of seven different notes, each representing a specific degree of the scale.
- Major Scale: The major scale is a foundational scale in music theory. It follows a specific pattern of whole steps (W) and half steps (H) between notes. The formula for a major scale is W-W-H-W-W-W-H. Understanding the major scale’s structure and the relationship between its notes is essential for building chords, melodies, and harmonies.
- Minor Scale: The minor scale has a different sound and emotional quality than the major scale. It also follows a specific pattern of whole steps and half steps. The formula for a natural minor scale is W-H-W-W-H-W-W.
- Chords: A chord is a combination of three or more notes played simultaneously. It provides harmony and richness to music. Chords are built upon scales, using specific formulas and intervals. The most basic chord is the triad, consisting of a root note, a third (either major or minor), and a fifth. There are also extended chords, like seventh chords, which add additional notes.
- Chord Progressions: Chord progressions are sequences of chords played in a particular order. They form the backbone of many songs, as they create tension and release. Understanding common chord progressions and their relationships within a key is essential for both composition and improvisation.
- Intervals: Intervals define the distance between two notes. They are an essential concept when building chords and scales. Intervals can be classified as major, minor, perfect, augmented, or diminished, depending on the distance between the notes.
- Harmonic Function: Each chord within a key has a specific function and role. The three primary functions are tonic (resting or stable), dominant (leading to a resolution), and subdominant (providing tension towards the dominant). Understanding these functions helps in creating chord progressions that create a sense of musical movement and resolution.
Learning scales and chords takes practice and repetition. Start with the major and minor scales and practice playing them on your instrument or singing them. As you become more comfortable, explore different chord types and progressions. Analyze songs to identify the scales and chords used, and try incorporating them into your own compositions or improvisations.
There are various resources available, such as scale charts, chord diagrams, and online lessons, to aid your learning. Remember to practice regularly and experiment with different combinations of scales and chords to expand your musical vocabulary. By mastering scales and chords, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the harmonic language of music and enhance your ability to create and express yourself musically.
Analyzing Chord Progressions
Chord progressions are at the heart of musical composition. They provide the harmonic framework for a piece of music, creating a sense of tension, release, and musical direction. Analyzing chord progressions involves understanding the relationship between chords, their function within a key, and the overall emotional impact they convey. Here are some essential steps to analyze chord progressions:
- Identify the Chords: Begin by identifying the chords in the progression. Write them down and determine their root notes and quality (major, minor, or other chord types). This step helps you visualize and audibly understand the progression.
- Determine the Key: Once you’ve identified the chords, determine the key of the progression. The key is usually indicated by the first and last chord or the tonal center of the song. Understanding the key provides context for analyzing the chords and their relationships.
- Analyze the Chord Functions: Each chord within a progression has a specific function. The three primary functions are tonic, dominant, and subdominant. The tonic chord provides a sense of stability, the dominant chord creates tension leading to resolution, and the subdominant chord adds tension towards the dominant. Analyzing the functions of the chords helps you understand the overall structure and emotional flow of the progression.
- Look for Common Progressions: Many chord progressions are commonly used in various musical genres. These include the I-IV-V progression (common in blues and rock), the ii-V-I progression (common in jazz), and the vi-IV-I-V progression (common in pop). Understanding these common progressions and spotting them in songs can provide insight into the song’s genre and harmonic language.
- Observe Chord Modulations or Borrowed Chords: Some chord progressions may include modulations or borrowed chords. Modulations involve changing the key temporarily, while borrowed chords come from a parallel key. Identifying these instances adds complexity and interest to the progression.
- Analyze Melodic Support: Pay attention to how the melody interacts with the chord progression. Identify the notes in the melody that align with the chord tones and those that create tension or dissonance. The combination of the melody and the chords working together creates a harmonious musical experience.
- Consider Emotional Impact: Each chord within a progression contributes to the overall emotional impact of the music. Major chords often evoke a bright and uplifting feeling, while minor chords convey a sense of sadness or tension. Analyze how the progression’s chords work together to create a specific emotional atmosphere.
Analyzing chord progressions requires attentive listening and practice. Study and analyze different songs across various genres to develop a deeper understanding of how chord progressions are utilized. Use your findings as inspiration for your own compositions or improvisations.
There are also resources available, such as music theory books, online tutorials, and chord progression libraries, to aid in your analysis. The more you practice analyzing chord progressions, the better you’ll become at recognizing patterns, understanding musical relationships, and crafting your own compelling harmonic sequences.
Exploring Melody and Harmony
Melody and harmony are two interconnected elements of music that work together to create depth, emotion, and musical texture. Understanding and exploring both melody and harmony can greatly enhance your musical compositions and performances. Here’s a closer look at each of them:
- Melody: The melody is the main theme or musical line that stands out, establishing the memorable and recognizable part of a song. It is the series of notes played or sung sequentially and carries the essence of a musical piece. Melodies can be simple or complex, and they often follow the rhythm and phrasing of the song. Experiment with different note choices, rhythm patterns, and contour to create captivating melodies that leave a lasting impact.
- Harmony: Harmony refers to the simultaneous sounding of multiple notes or chords that support the melody. It adds depth, color, and richness to the music. Harmony is created by combining different pitches, often played or sung by accompanying instruments or voices. Understanding chord progressions, chord voicings, and chord inversions is crucial for building harmonies that complement and enhance the melody.
- Interplay Between Melody and Harmony: The interplay between melody and harmony is what gives a piece of music its unique character. The melody often defines the tonal center and guides the direction of the song, while harmony provides support and adds emotional depth. Experiment with different chord progressions that harmonically interact with the melody, creating tension, release, and unique tonal qualities.
- Counterpoint: Counterpoint is the art of combining melodies that are distinct and independent yet harmonically connected. It involves creating multiple melodic lines that work together harmoniously. Studying counterpoint helps you understand the relationship between different melodic voices and how they interact to create intricate musical compositions.
- Texture: Texture in music refers to the overall sound and combination of different melodic and harmonic elements. It can be thin or thick, sparse or dense, monophonic (single melody line) or polyphonic (multiple independent melodic lines). Experiment with different textures to create varied and engaging musical experiences.
- Emotion and Expression: Both melody and harmony play a significant role in evoking emotion and expressing musical ideas. They can convey a wide range of moods, from joy and excitement to sadness and introspection. Experiment with different melodies and harmonies to find the right combination that expresses the emotions you want to convey in your music.
There are numerous resources available that delve further into melody and harmony, including music theory books, composition tutorials, and studying the works of composers from different musical eras and genres. Analyzing and transcribing melodies and harmonies from your favorite songs can also provide valuable insights.
By exploring and understanding the interplay between melody and harmony, you can create well-crafted, expressive, and captivating music that resonates with your listeners.
Applying Music Theory to Songwriting
Music theory serves as a powerful tool for songwriters, providing a framework to structure and enhance their musical compositions. By applying music theory principles to songwriting, you can create melodies, harmonies, and arrangements that are cohesive, engaging, and emotionally resonant. Here are some ways you can use music theory in your songwriting process:
- Building Chord Progressions: Understanding chord progressions allows you to create a strong foundation for your songs. Experiment with different chord progressions, using your knowledge of scales, modes, and harmony. Consider the emotional impact each chord progression conveys and how it supports the lyrics and melody of your song.
- Creating Melodies: Utilize your understanding of scales, intervals, and melodic contour to craft memorable and expressive melodies. Experiment with different rhythms, phrasing, and note choices to bring your lyrics to life and capture your desired emotional tone.
- Adding Harmonic Variations: By applying music theory concepts, you can add harmonic variations to your songs to create interest and tension. This could include using borrowed chords, modulation, or chromaticism to add depth and surprise to your harmonic progressions.
- Structuring Your Song: Use music theory principles to guide the overall structure of your song. Understand the typical song forms such as verse-chorus, AABA, or ABAB, and apply them to create a cohesive and well-organized composition. Consider the pacing, dynamics, and transitions between different sections to create an engaging musical journey for your listeners.
- Lyric-Melody Match: Align your lyrics and melodies to create a strong connection between the words and the music. Consider the syllabic rhythm and natural cadence of the lyrics, and ensure that the melody emphasizes the important words or phrases. Pay attention to how the melody and lyrics interact, conveying the intended mood and message of the song.
- Experimenting with Song Structures and Genres: Use your knowledge of music theory to experiment with different song structures and genres. Break free from traditional patterns and explore unconventional chord progressions or rhythmic patterns to add a unique flavor to your compositions. Understanding music theory also allows you to blend different genres and styles, creating a signature sound that is distinctively yours.
- Utilizing Instrumentation and Arrangement: Music theory can guide your decisions in terms of instrumentation and arrangement. Consider the role of each instrument, their harmonic and melodic contributions, and how they interact with one another. Experiment with different textures, dynamics, and arrangement techniques to create a well-balanced and captivating sonic experience.
Remember, while understanding music theory is valuable, it’s important to let your creativity and intuition guide your songwriting process. Music theory is a tool to assist and enhance your musical expression. As you apply music theory principles to your songwriting, you’ll develop a stronger sense of musicality, deepen your understanding of the craft, and create songs that resonate with your audience.
Practicing and Mastering Music Theory
Mastering music theory requires consistent practice, dedication, and a systematic approach. Here are some tips to help you effectively practice and develop your understanding of music theory:
- Review and Reinforce: Regularly review the fundamental concepts of music theory to reinforce your knowledge. This includes understanding scales, chords, intervals, and key signatures. Set aside dedicated time each week to revisit and practice these foundational elements.
- Ear Training: Developing your ear is crucial for applying music theory in a practical sense. Practice ear training exercises, such as identifying intervals, chord progressions, and melodies by ear. This will improve your ability to recognize and reproduce musical elements accurately.
- Apply Theory to Real Songs: Take the concepts you learn in music theory and apply them to real songs. Analyze and transcribe music that resonates with you, focusing on understanding the chords, melody, and overall structure. This hands-on approach will deepen your understanding and make theory more tangible.
- Compose and Arrange: Practice composition and arrangement exercises to apply music theory in a creative way. Experiment with writing melodies, harmonizing chords, and arranging instrumental parts. This will strengthen your understanding of how theory shapes musical compositions.
- Play and Practice with Others: Collaborate with fellow musicians to practice music theory in a group setting. Jamming or playing alongside others will help you apply theory practically, improve your instrumental skills, and develop a sense of musical interaction and communication.
- Use Technology and Resources: Take advantage of technology and resources available to aid in your music theory practice. Online platforms, mobile apps, and software provide interactive lessons, exercises, and tools for studying music theory. Utilize these resources to reinforce your learning and progress at your own pace.
- Seek Guidance: Consider taking music theory lessons from a qualified instructor or seeking guidance from experienced musicians. They can provide valuable insights, answer specific questions, and offer personalized feedback to help you overcome challenges and deepen your understanding of music theory concepts.
- Be Patient and Consistent: Remember that mastering music theory takes time and consistent effort. Be patient with yourself and embrace the incremental progress. Set realistic goals, practice regularly, and celebrate each milestone along the way.
By incorporating these practices into your routine, you will develop a strong foundation in music theory and enhance your ability to apply it in a meaningful way. As you practice and master music theory, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of music and find new avenues for creative expression.
Conclusion
Music theory is a powerful tool that opens the door to a deeper understanding and appreciation of music. Whether you’re a musician, composer, or music enthusiast, learning music theory is a valuable investment in your musical journey. By understanding the principles of harmony, melody, rhythm, and form, you can unlock the secrets of music and enhance your ability to create, perform, and appreciate music.
In this article, we explored the importance of music theory and how it enhances your musical skills and communication with other musicians. We discussed the steps to get started with music theory, including understanding basic notations, learning scales and chords, analyzing chord progressions, and exploring melody and harmony. We also explored how to apply music theory to songwriting and provided tips for practicing and mastering music theory.
By utilizing music theory, you can build strong chord progressions, create impactful melodies, and structure your songs in a way that engages the listener. Music theory offers a framework for creativity and empowers you to express yourself musically with confidence and intention.
Remember, mastering music theory is a gradual process that requires consistent practice, patience, and a willingness to explore. Embrace the learning journey and approach music theory with curiosity and creativity. As you deepen your understanding and application of music theory, you’ll find yourself becoming a more versatile and expressive musician.
So, whether you’re a beginner just starting to explore music theory or an experienced musician looking to expand your musical horizons, take the time to delve into the fascinating world of music theory. The knowledge you gain will enrich your musical experience and open up new possibilities for artistic expression.