Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>How To Harmonize Melodies Music Theory


Music Theory
How To Harmonize Melodies Music Theory
Published: January 29, 2024
Learn how to harmonize melodies with music theory. Explore essential concepts and techniques to create rich and cohesive musical arrangements. Enhance your understanding of music theory with practical examples and exercises.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Music theory is a fascinating discipline that allows us to understand the inner workings of music and how different elements come together to create harmonious compositions. One crucial aspect of music theory is melody harmonization, which is the process of adding chords to a melody to enhance its musicality and create a fuller sound.
Harmonizing melodies is an essential skill for musicians and composers, as it provides a foundation for creating rich and vibrant musical arrangements. Whether you are a songwriter looking to create more captivating tunes or a music student diving into the world of music theory, understanding how to harmonize melodies is key.
In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of melody harmonization, step-by-step techniques for harmonizing melodies, common chord progressions, voice leading techniques, and valuable tips for effective melody harmonization.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to enhance melodies with harmonies, allowing you to elevate your musical compositions to new heights.
Understanding Melodies
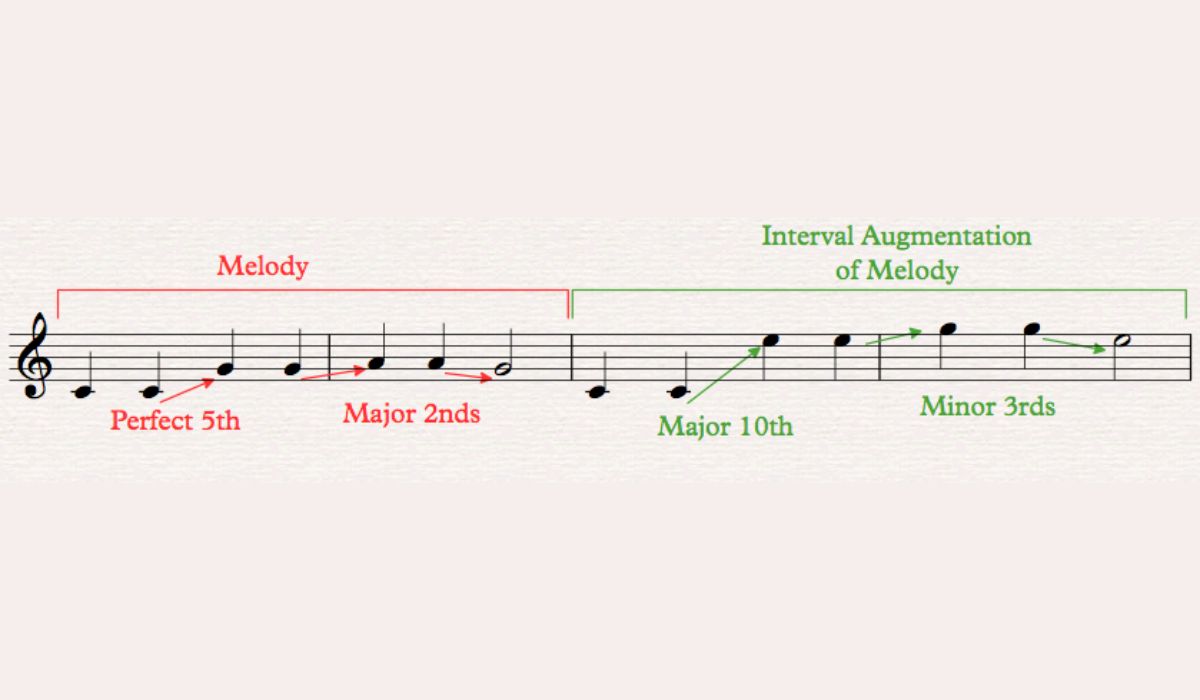
Before we dive into the art of harmonizing melodies, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of what exactly a melody is. A melody is a sequence of musical notes played in a specific rhythm that creates a memorable and identifiable musical line. It is the main theme or tune in a piece of music.
A melody is often distinguished by its rhythmic and melodic patterns, pitch variations, and contour. It carries the emotional and expressive aspects of a composition, and harmonizing it adds depth and complexity to the overall musical experience.
When it comes to harmonizing melodies, it’s crucial to analyze the melody itself. Pay attention to the key signature, as it will determine the available chords for harmonization. Consider the scale degrees of the melody notes and identify any patterns or recurring intervals.
Additionally, understanding the structural elements of a melody is essential. An understanding of phrases, motifs, cadences, and overall tonal progression will help you make informed decisions when harmonizing the melody.
It’s worth noting that not all melodies are created equal. Some melodies may have a more straightforward structure, allowing for straightforward harmonization, while others may have complex rhythms and pitch variations, demanding a more nuanced approach to harmonization.
By studying and analyzing melodies, you gain insights into their unique characteristics and can utilize that knowledge to craft harmonies that complement and enhance the original melodic line.
Basics of Harmony
Harmony is the simultaneous sounding of two or more different musical notes, played together to create a pleasing and coherent sound. In the context of melody harmonization, harmony refers to the chords that are added to a melody to create a harmonic framework.
When harmonizing a melody, it’s essential to understand the basic principles of harmony. One fundamental concept is the notion of major and minor keys. The key of a piece determines the set of notes and chords that can be used harmonically. Major keys tend to produce a bright and uplifting sound, while minor keys evoke a more melancholic and introspective mood.
Chords serve as the building blocks of harmony. They are created by stacking specific pitches together in predetermined intervals. The most commonly used chords for harmonization include triads, which are three-note chords built on the first, third, and fifth scale degrees of a key.
For example, in the key of C major, the C major triad consists of the notes C, E, and G. Similarly, in the key of A minor, the A minor triad is made up of the notes A, C, and E.
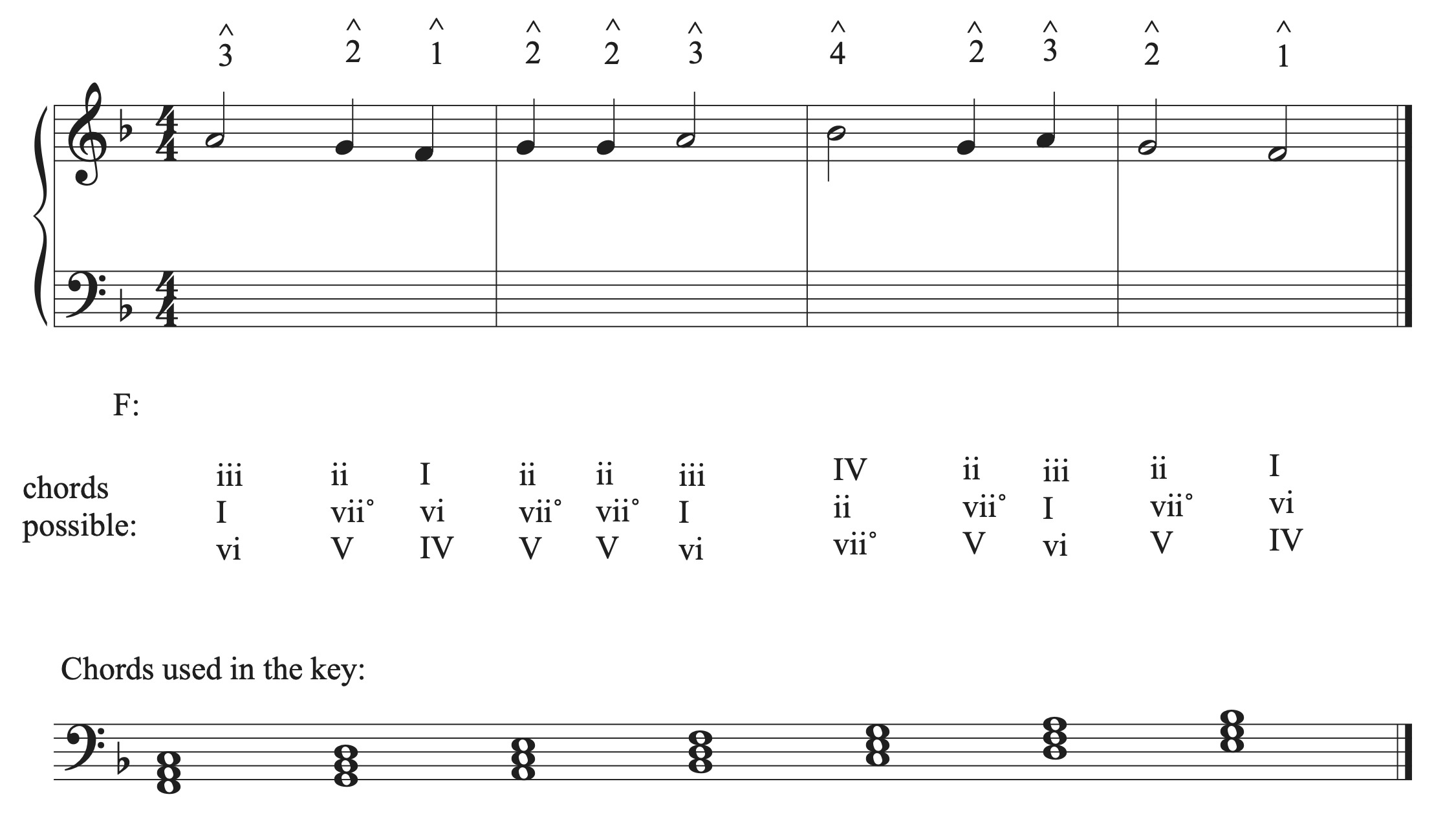
Understanding the harmony of a melody involves identifying the underlying chord progression that best supports the melody. This can be done by analyzing the relationships between the melody notes and the corresponding chords.
Harmony can also be expressed through various chord inversions and extensions, which add different tonal colors and create unique harmonic textures. Inversions occur when the notes of a chord are played in an order other than the root position, while extensions involve adding extra notes beyond the basic triad.
By grasping the basic concepts of harmony and how chords are constructed and used, you lay the foundation for harmonizing melodies in a thoughtful and musically appealing way. It’s important to remember that while there are established guidelines in harmony, there is also room for creative exploration, allowing you to add your own unique touch to the harmonization process.
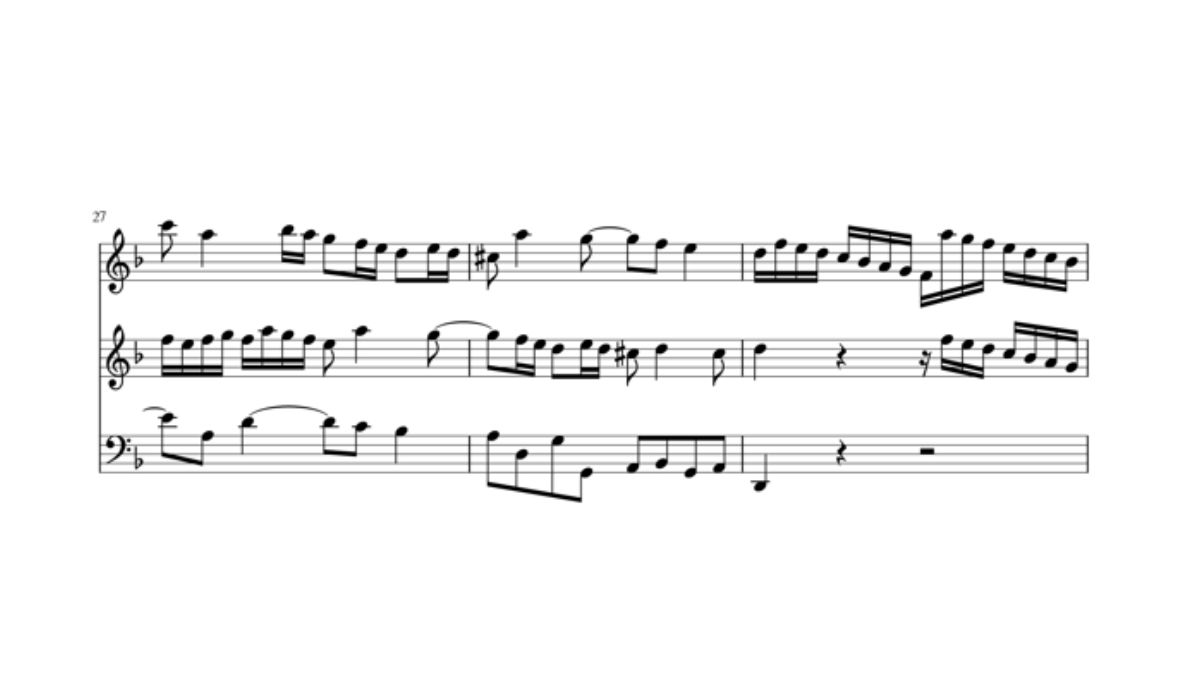
Harmonizing Melodies Step by Step
Harmonizing melodies is a systematic process that involves carefully selecting chords that complement the melody and create a harmonious sound. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you harmonize melodies effectively:
- Analyze the melody: Start by thoroughly analyzing the melody in terms of rhythm, pitch, and structure. Identify the key signature and scale degrees of the melody notes.
- Determine the chord tones: Look for the chord tones within the melody. These are the notes that represent the harmonies. Chord tones usually fall on the first, third, and fifth scale degrees of the key.
- Choose appropriate chord progressions: Based on the key and the chord tones present in the melody, select chord progressions that harmonically support the melody. Popular progressions include the I-IV-V progression, the ii-V-I progression, and the I-vi-IV-V progression.
- Add chords to the melody: Assign the chosen chords to the melodic notes. Experiment with different inversions and voicings to create interesting harmonic textures.
- Consider the rhythmic placement: Pay attention to the rhythmic placement of the chords. Ensure that the chords align with the melodic rhythm, creating a seamless integration of melody and harmony.
- Listen for consonance and dissonance: Balance consonant and dissonant sounds within the harmonization. Consonant chords provide stability and resolution, while dissonant chords add tension and intrigue.
- Apply voice leading techniques: Smoothly transition between chords by utilizing voice leading techniques. This involves moving individual voices (notes) in the chord as little as possible to create a smooth melodic flow.
- Refine and revise: Take the time to listen and evaluate the harmonization. Make any necessary adjustments to improve the overall balance and musicality of the composition.
Remember that harmonization is both a technical and creative process. It requires a solid understanding of music theory principles, but also allows room for personal expression and experimentation. With practice and an attentive ear, you can develop the skill to harmonize melodies in a way that elevates the emotional impact and musical depth of your compositions.
Chord Progressions for Melody Harmonization
Choosing the right chord progressions is crucial when harmonizing melodies. The chord progression sets the tonal framework for the melody and determines the mood and overall musical direction. Here are some common chord progressions that can be used for melody harmonization:
- I-IV-V Progression: The I-IV-V progression is one of the most widely used chord progressions in music. In a major key, the I chord is the tonic chord, the IV chord is the subdominant chord, and the V chord is the dominant chord. This progression provides a strong sense of resolution and stability. For example, in the key of C major, the I-IV-V progression would consist of the chords C, F, and G.
- ii-V-I Progression: The ii-V-I progression is commonly used in jazz and popular music. It adds a sense of tension and release to the harmonization. In this progression, the ii chord functions as the subdominant, the V chord as the dominant, and the I chord as the tonic. For example, in the key of C major, the ii-V-I progression would include the chords Dm, G, and C.
- I-vi-IV-V Progression: This progression is frequently used in pop and rock music. It offers a catchy and memorable harmonic structure. In major keys, the I chord is the tonic, the vi chord is the relative minor, the IV chord is the subdominant, and the V chord is the dominant. For instance, in the key of C major, the I-vi-IV-V progression would consist of the chords C, Am, F, and G.
- Descending Bassline Progression: This progression creates a melodic and harmonic contour by using a descending bassline. The bassline moves downward while the chords change accordingly. This technique adds movement and interest to the harmony. An example of a descending bassline progression is C, Bm, Am, G.
- Suspension Progression: Suspension occurs when a note from a previous chord is sustained or carried over to the next chord, creating a dissonant sound that eventually resolves. This technique adds tension and plays with the listener’s expectations. An example of a suspension progression is C, Csus4, C.
These are just a few examples of chord progressions that can be used for melody harmonization. Remember to experiment with different progressions and explore how they interact with the melody to create the desired musical effect. Trust your ears and intuition to find the chord progressions that best enhance and complement your melodies.
Voice Leading Techniques
Voice leading techniques play a significant role in creating smooth and cohesive melodic lines within harmonized melodies. Voice leading involves the movement of individual voices (notes) in the chords to create a seamless flow from one chord to another. Here are some essential voice leading techniques to consider when harmonizing melodies:
- Common Tone: Maintain a common tone between consecutive chords whenever possible. This means keeping at least one note the same as you transition from one chord to the next. This technique helps establish a sense of continuity and smoothness.
- Stepwise Motion: Prefer stepwise melodic motion when transitioning between chord tones. Moving the voices in small intervals of a whole or half step creates a more natural and fluid melodic line. Avoid large melodic leaps, unless intentionally desired for a specific musical effect.
- Voice Leading By Thirds: When possible, move one voice up or down a third (counting inclusively) in relation to the adjacent voice. This technique creates pleasing harmonic intervals and adds interest to the melodic movement.
- Contrary Motion: Use contrary motion, where one voice moves up while the other moves down. This technique creates a sense of counterpoint and adds depth to the harmony. Contrary motion is particularly effective during chord changes or moments of tension and resolution.
- Chromatic Voice Leading: Consider incorporating chromatic movement in the voices to add color and tension. Chromatic voice leading involves using notes outside the key signature to create unique and captivating harmonic progressions. However, use this technique sparingly to avoid overwhelming the listener.
By implementing these voice leading techniques, you can create harmonized melodies that flow seamlessly and sound musically appealing. While it’s important to keep these principles in mind, trust your musical intuition and listen attentively to ensure that the melody and harmonies work together to create a cohesive and pleasing musical composition.
Tips for Effective Melody Harmonization
Harmonizing melodies is both an art and a skill. It requires careful consideration and attention to detail to create a harmonious and cohesive musical composition. Here are some tips to help you harmonize melodies effectively:
- Start with simplicity: Begin by harmonizing melodies with simple chord progressions. This allows you to focus on the relationship between the melody and the chords without overwhelming the composition.
- Consider the melody’s emotional intent: Pay attention to the emotional character and intent of the melody. Choose chords that support and enhance the intended mood, whether it be joyful, somber, or introspective.
- Experiment with different textures: Try different chord inversions, voicings, and extensions to create unique harmonic textures. Don’t be afraid to break away from traditional harmonization techniques and explore new sonic possibilities.
- Use chord embellishments sparingly: While embellishing chords can add interest and color to the harmonization, be cautious not to overdo it. Use embellishments sparingly and purposefully, ensuring they enhance the melody rather than distract from it.
- Balance consonance and dissonance: Strike a balance between consonant and dissonant chord progressions. Consonant chords provide stability and resolution, while occasional dissonance adds tension and creates musical interest.
- Listen for the overall blend: Pay attention to the overall blend between the melody and harmonies. Ensure that the melody remains prominent while the added chords enhance and support it, rather than overpowering it.
- Take advantage of dynamics: Utilize dynamics to highlight and emphasize certain moments within the harmonization. This can help add depth and emotion to the musical composition.
- Consider the context: Keep in mind the intended context of the composition. Consider the genre, instrumentation, and overall arrangement. Adapt your harmonization choices to fit within the broader musical framework.
- Trust your musical intuition: Ultimately, trust your instincts and musical intuition. Experiment, listen critically, and make adjustments as needed to create the harmonization that resonates with you and effectively conveys the desired musical message.
Remember that harmony should enhance and support the melody, bringing out its full potential. With practice, careful consideration, and a willingness to explore creative possibilities, you can develop the skills necessary to harmonize melodies effectively and create captivating musical compositions.
Conclusion
Harmonizing melodies is an essential skill in music theory that allows us to add depth, complexity, and emotional richness to our compositions. By understanding melodies, the basics of harmony, and employing various voice leading techniques, we can create harmonies that enhance the overall musical experience.
Throughout this article, we explored the step-by-step process of harmonizing melodies, from analyzing the melody and selecting appropriate chord progressions to applying voice leading techniques. We also discussed the importance of choosing the right chord progressions and provided tips for effective melody harmonization.
Remember, harmony is both a technical and creative endeavor. While it’s important to understand the theoretical concepts, don’t be afraid to trust your musical intuition and explore new ideas. By experimenting with different chord progressions, voicings, and textures, you can create harmonies that are unique and captivating.
Always keep in mind the emotional intent of the melody and strive to create a harmonization that supports and enhances its intended mood. Balance consonance and dissonance, listen for the overall blend, and utilize dynamics to add depth and emphasis where needed.
With practice and an attentive ear, you will develop a deeper understanding of melody harmonization and be able to create harmonically rich and engaging compositions. So, dive into the world of harmonizing melodies, embrace your creativity, and let the magic of harmony bring your musical compositions to life.