Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>Voice Lead Music Theory How To

Music Theory
Voice Lead Music Theory How To
Published: January 29, 2024
Learn music theory easily with Voice Lead Music Theory How To. Improve your understanding of music principles and enhance your musical abilities with our comprehensive guides and tutorials.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of voice leading in music theory. If you’ve ever wondered how different musical notes interact with one another to create harmonies and melodies, then you’re in the right place. Voice leading is a fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in the structure and beauty of music.
In essence, voice leading is the art of smoothly transitioning from one musical note to another within a composition. It involves the movement of individual voices, whether they be in a choir, a band, or a piece of music with multiple instruments.
Proper voice leading allows for a seamless and coherent progression of chords and melodies, creating a sense of unity and connectedness throughout a piece of music. It is the glue that holds together the various elements of a composition, ensuring that the harmonic and melodic components flow effortlessly.
By understanding and applying the principles of voice leading, composers and musicians can create captivating harmonic progressions, expressive melodies, and emotionally resonant musical arrangements. It is a skill that can elevate the overall musical experience, making it more engaging and captivating for both the listeners and the performers.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the basic principles of voice leading, common techniques used in voice leading, its application in chord progressions and melodies, and tips and tricks for effective voice leading. Whether you are a student studying music theory, a composer looking to enhance your compositions, or simply a music lover interested in gaining a deeper understanding of how music works, this article will provide you with valuable insights.
So, let’s dive in and unravel the wonderful world of voice leading in music theory!
What is Voice Leading?
In music theory, voice leading refers to the movement of individual melodic lines or voices within a composition. It determines how the musical intervals between different notes progress smoothly and seamlessly, ensuring a harmonically coherent and aesthetically pleasing result.
Each voice in a piece of music, whether it be a vocalist or an instrument, has its own unique melodic line. Voice leading governs how these individual lines interact with each other, creating a sense of unity and connection.
At its core, voice leading focuses on two main elements: melodic motion and harmonic progression. Melodic motion involves the movement of each voice to create a cohesive and expressive melody. Harmonic progression, on the other hand, deals with the movement of chords and the relationship between them.
Effective voice leading ensures that melodic lines move smoothly, avoiding large jumps or awkward intervals that may sound dissonant or create a sense of disconnection. By guiding each voice through logical and musically pleasing paths, voice leading creates a sense of flow and continuity within a composition.
When thinking about voice leading, it’s important to consider the principles of consonance and dissonance. Consonant intervals, such as octaves, fifths, and thirds, generally sound pleasing to the ear and create a sense of stability. Dissonant intervals, such as seconds or tritones, create tension and often require resolution to a more consonant interval.
By utilizing consonant intervals and resolving dissonances appropriately, voice leading can shape the emotional and expressive qualities of a piece of music. It allows composers and musicians to craft intricate melodies, rich harmonies, and evocative chord progressions that resonate with the listener.
The Importance of Voice Leading in Music Theory
Voice leading plays a pivotal role in music theory as it ensures the coherence and integrity of a composition. Here are a few reasons why voice leading is important:
1. Enhances Musical Flow: Voice leading ensures a smooth and flowing progression of chords and melodies. It allows each voice to transition from one note to the next in a logical and musically pleasing manner, creating a sense of continuity and coherence. This flow keeps the listener engaged and captivated throughout the musical journey.
2. Creates Harmonic Unity: Through proper voice leading, the different voices in a composition work together harmonically. It ensures that the notes within each voice complement one another, resulting in a harmonically unified sound. By carefully selecting and arranging the voices, composers can create rich and complex harmonies that evoke specific emotions and moods.
3. Establishes Melodic Interest: Voice leading helps to craft captivating melodies. By guiding each voice through well-chosen melodic paths, composers can create melodies that are memorable, expressive, and emotionally engaging. Voice leading allows for melodic lines to weave together gracefully, creating interesting musical lines that capture the listener’s attention.
4. Enhances Expressiveness and Emotion: The movement and interaction between voices in voice leading can convey a wide range of emotions and moods. By carefully choosing the harmonic progression and melodic movement, composers can evoke feelings of joy, melancholy, tension, resolution, and much more. Voice leading adds depth and emotional impact to the music, making it more relatable and resonant with the listener.
5. Facilitates Effective Communication: In vocal ensembles or instrumental arrangements, proper voice leading allows each voice to be heard clearly and distinctly. By avoiding clashing intervals and giving each voice its own space, voice leading ensures that the intended musical message is conveyed effectively to the listener. This is crucial for conveying the intended emotions and musical ideas.
Overall, voice leading is an essential aspect of music theory that brings together the various elements of a composition into a cohesive and compelling whole. By mastering the principles of voice leading, musicians and composers can create impactful and captivating musical experiences that resonate with both performers and listeners alike.
Basic Principles of Voice Leading
When it comes to voice leading, there are several fundamental principles that guide the movement and interaction of voices within a composition. Understanding and applying these principles can greatly enhance the coherence and expressiveness of your music. Here are the basic principles of voice leading:
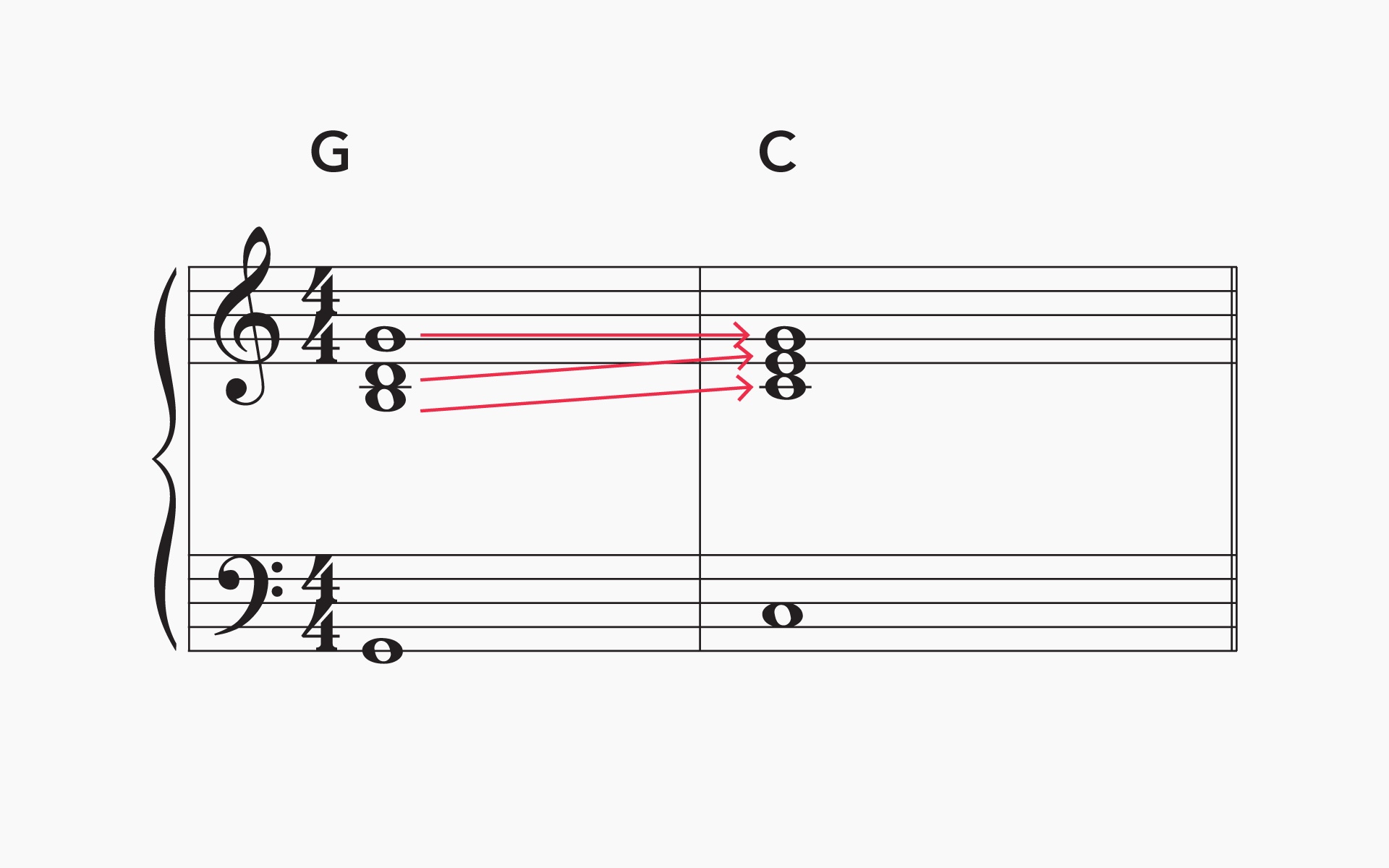
- Smooth Voice Leading: Smooth voice leading involves avoiding large and awkward leaps between notes. Instead, strive for stepwise or small interval movements when transitioning from one note to another. This creates a seamless and flowing melodic line that is pleasing to the ear.
- Avoiding Parallel Fifths and Octaves: It is important to avoid parallel fifths and octaves, as they can create a sense of harmonic instability and diminish the individuality of each voice. Parallel fifths occur when two voices move in perfect fifths in the same direction. Similarly, parallel octaves occur when two voices move in perfect octaves in the same direction. By avoiding these parallel movements, you maintain independence and clarity among the voices.
- Contrary and Oblique Motion: Contrary motion refers to two voices moving in opposite directions. This creates a harmonic richness and can establish a sense of tension and release. Oblique motion, on the other hand, occurs when one voice remains stationary while the other voice moves. These types of movements add interest and variety to the melodic lines.
- Voice Crossing: Voice crossing happens when one voice moves to a pitch that is higher or lower than another concurrent voice. While voice crossing can be used for expressive purposes, it should be used sparingly to maintain clarity and prevent melodic confusion.
- Proper Resolution of Dissonances: Dissonances, such as suspensions or passing tones, add tension to the music and require resolution to consonant intervals. The proper resolution of dissonances contributes to the overall harmonic progression and creates a sense of resolution and release.
- Spatial Balance: In ensemble settings, achieving a balanced sound among the voices is essential. Provide each voice with its own space within the frequency spectrum, ensuring that no one voice overpowers the others. This enhances the clarity and intelligibility of the individual melodic lines.
By following these basic principles of voice leading, you can create harmonically rich melodies, expressive harmonies, and a balanced interaction between voices. These principles serve as a foundation for more advanced voice leading techniques and allow for creative interpretation and experimentation within the rules of musical cohesion.
Common Voice Leading Techniques
Voice leading encompasses a wide array of techniques that composers and musicians employ to create smooth and expressive musical lines. These techniques enhance the overall harmonic and melodic progression of a composition. Here are some common voice leading techniques:
- Chord Inversions: Using different chord inversions can create interesting and unique voice leading. By rearranging the order of the notes within a chord, you can create smooth voice leading by minimizing the distance between consecutive chords.
- Voice Doubling: Voice doubling involves having multiple voices play or sing the same note within a chord. Doubling the root or the fifth of a chord is common and can contribute to a stronger and more balanced harmonic sound.
- Voice Leading in Four-Part Chorale: Four-part chorale voice leading refers to the arrangement of voices in a choir or a vocal ensemble. It typically involves a bass voice, tenor voice, alto voice, and soprano voice. Each voice has its own melodic line, and the voices move in parallel or independent motion while following the principles of proper voice leading.
- Voice Crossing: Voice crossing occurs when one voice moves to a pitch that is higher or lower than another voice. This technique can add tension and interest to the music but should be used judiciously to maintain clarity and avoid confusion.
- Leading Tones and Tendency Tones: Leading tones are notes that strongly resolve to the tonic or the root of a chord. They create a sense of tension and resolution, adding emotional depth to the music. Tendency tones, such as the seventh scale degree in a dominant seventh chord, also create a desire for resolution to a consonant interval.
- Voice Exchanges: Voice exchanges occur when two voices switch notes with each other. This technique can create interesting and unexpected harmonic shifts, adding variety and musical intrigue to the composition.
- Hidden Parallels: Hidden parallels refer to parallel fifths or octaves that are implied by the melodic movement, rather than by direct movement between voices. While hidden parallels are generally avoided in traditional voice leading, they can be used selectively to achieve specific harmonic effects.
These techniques are just a few examples of the many possibilities within voice leading. Composers and musicians continually explore and experiment with these techniques, pushing the boundaries of harmonic and melodic possibilities while maintaining a sense of musical cohesion. By incorporating these techniques into your compositions or arrangements, you can create rich and engaging musical lines that captivate the listener.
Voice Leading in Chord Progressions
Voice leading plays a crucial role in shaping chord progressions, creating harmonically compelling and musically satisfying sequences of chords. By implementing proper voice leading techniques, composers can ensure smooth transitions between chords and maintain a coherent harmonic progression. Here are some key considerations for voice leading in chord progressions:
1. Selecting Voicing: When voicing chords, it’s important to distribute the notes among the voices in a way that allows for smooth voice leading. This involves avoiding large leaps between notes and ensuring that each voice moves in a logical and musical manner.
2. Common Tones: Incorporating common tones between chords is an effective way to create smooth voice leading. Common tones are notes that remain the same between consecutive chords, which helps to connect them harmonically and maintain a sense of continuity.
3. Voice Leading in Root Movement: Paying attention to the movement of the root note between chords can greatly influence the overall voice leading in a chord progression. For example, using a descending bass line can create a sense of stability and resolution, while an ascending bass line can generate tension and anticipation.
4. Doubling Strategy: When doubling notes within chords, consider the impact on voice leading. Doubling the root or the fifth of a chord can help maintain a strong and stable foundation. However, avoid doubling notes that may create awkward voice leading or clash with other voices.
5. Seventh Chord Resolutions: Seventh chords, such as dominant seventh or diminished seventh chords, often have specific tendencies for resolution. Proper voice leading involves resolving the dissonant intervals present in these chords in a way that leads to a more consonant and stable sound.
6. Chromatic Voice Leading: Introducing chromatic voice leading can add color and tension to a chord progression. Using chromatic passing tones or chromatic substitutions can create unexpected and interesting harmonic relationships, adding depth and complexity to the music.
7. Voice Crossing: While voice crossing between consecutive chords can create unique and expressive moments, it should be used judiciously to maintain clarity and prevent melodic confusion. Voice crossing can be particularly effective in creating emotional impact or highlighting certain melodic lines.
By considering these aspects of voice leading, composers can craft chord progressions that are harmonically rich, expressive, and compelling. Attention to detail in how the voices move and interact within the chords enhances the overall musical experience and evokes a range of emotions and responses from the listener.
Voice Leading in Melodies
Voice leading is not limited to chord progressions; it also plays a significant role in shaping melodies. The movement of individual voices within a melody can greatly impact the overall expressiveness and musicality of a composition. Here are some important considerations for voice leading in melodies:
1. Smooth Melodic Motion: Just as in chord progressions, smooth voice leading is crucial in melodies. Aim for stepwise or small interval movements between notes to create a seamless and flowing melodic line. Avoid large leaps that may disrupt the overall melodic coherence.
2. Sensible Contour: The contour of a melody refers to the overall shape and direction of the melodic line. It’s important to consider the contour in voice leading to ensure a compelling and emotionally engaging melody. Consider the rise and fall of the melody and the overall shape it creates.
3. Use of Passing Tones and Appogiaturas: Passing tones and appoggiaturas are melodic embellishments that create tension and resolution in a melody. Incorporating these dissonant tones in a way that resolves to a consonant pitch enhances the expressive quality of the melody.
4. Balance and Range: Voice leading in melodies should ensure a proper balance and distribution of pitches. Avoid having one voice dominate the melody while neglecting the others. Also, consider the range of the melody to ensure that it falls within a comfortable and musically appropriate register for the instrument or voice.
5. Cadences and Phrase Endings: Voice leading also plays a role in the resolution of phrases and the ending of musical ideas. Consider incorporating proper cadences and melodic resolution points to provide satisfying musical closure. This can be achieved through the movement of the final note or the use of appropriate melodic intervals.
6. Use of Melodic Sequences: Melodic sequences involve repeating a series of musical intervals or patterns at different pitch levels. When incorporating sequences in a melody, pay attention to the voice leading to ensure smooth transitions and maintain the melodic integrity.
7. Unique Intervallic Relationships: Experiment with unique intervallic relationships to create distinctive melodic lines. Using unexpected intervals can add variety and interest to the melody. However, be mindful of the overall melodic coherence and ensure that the intervals fit harmonically within the context of the composition.
By implementing these voice leading techniques in melodies, composers can create captivating and emotive musical lines. Carefully guiding the movement and interaction of voices within the melody enhances the expressiveness and impact of the composition, making it more memorable and engaging for both performers and listeners.
Voice Leading in Harmonic Analysis
Voice leading is an essential tool in the process of harmonic analysis, allowing us to understand the relationships between chords and how they interact within a musical composition. By examining the movement of individual voices, we can gain insights into the harmonic structure and the underlying progressions. Here’s how voice leading contributes to harmonic analysis:
Identifying the Chord Quality: Voice leading provides clues about the quality of chords and their function within a progression. The combination of intervals present in the voices can help determine whether a chord is major, minor, dominant, diminished, or augmented. By analyzing the intervals and melodic movements, we can decipher the harmonic content of a piece.
Recognizing Harmonic Function: Voice leading aids in identifying the functional relationships between chords in a progression. It reveals the tendency tones, the resolution patterns, and the overall harmonic movement. This understanding is crucial in categorizing chords into their respective functions, such as tonic, dominant, or subdominant, and comprehending the larger harmonic framework.
Following Voice Leading Patterns: By observing voice leading patterns, we can uncover common sequences or progressions that occur in a piece. Certain progressions, such as the ii-V-I or the circle of fifths, have distinct voice leading patterns that create a sense of musical cohesion and progression. Recognizing these patterns deepens our understanding of the harmonic language used in the composition.
Uncovering Modulations: Voice leading helps in detecting modulations, or key changes, within a piece. By examining the movement of individual voices, we can identify when chords shift to a different key or tonal center. This shift is often accompanied by specific voice leading patterns as the music transitions to the new harmonic context.
Revealing Inner Voices and Counterpoint: Voice leading analysis allows us to focus on the individual lines or inner voices within a composition. Examining the movement and interaction of these voices provides insights into the contrapuntal aspect of the music. We can discern contrapuntal techniques, such as imitation, canon, or counterpoint, and how they contribute to the overall harmonic complexity.
Examining Tensions and Dissonances: Voice leading analysis helps us understand the use of tensions and dissonances within a composition. Tensions and dissonant intervals add color and create harmonic tension that seeks resolution. By examining their voice leading and resolution patterns, we can appreciate the emotional impact and resolution of these musical elements.
Through voice leading analysis, we gain a deeper understanding of the harmonic structure, functional relationships, and melodic interactions within a composition. It allows us to appreciate the nuances of the music and the intentional choices made by the composer in constructing harmonically rich and expressive pieces.
Tips and Tricks for Effective Voice Leading
Mastering effective voice leading techniques requires practice and a keen ear for musical cohesion. Here are some tips and tricks to help you improve your voice leading skills:
- Study Classical Music: Classical compositions from various periods are great resources for learning voice leading techniques. Analyzing the works of renowned composers such as Bach, Mozart, and Beethoven can provide valuable insights into effective voice leading practices.
- Experiment with Harmonic Progressions: Try out different chord progressions and observe how the voice leading changes. Experimenting with different combinations of chords and analyzing how they sound when transitioning from one to another will deepen your understanding of how voice leading influences the overall harmony.
- Use the Circle of Fifths: The circle of fifths is a powerful tool for understanding key relationships and chord progressions. It can guide you in creating smooth voice leading when modulating between keys or transitioning between related chords.
- Pay Attention to Voice Ranges: When arranging voices or writing counterpoint, be mindful of the ranges of the instruments or voices involved. Avoid extreme leaps that compromise the melodic flow and consider the practicality of the range for performers or ensembles.
- Listen Carefully: Develop your listening skills to discern the individual voices within a composition. Focus on understanding how each voice interacts melodically and harmonically with the others. This will sharpen your ability to recognize effective voice leading and help you apply it in your own compositions.
- Practice Voice Leading Exercises: Work on specific voice leading exercises to strengthen your skills. These exercises may involve writing melodies using certain intervallic patterns or arranging chords in different voicings to create smooth transitions.
- Consider Melodic Contour: Think about the contour and shape of each individual voice when crafting melodies or harmonies. Aim for a coherent melodic arc, avoiding excessive repetition or stagnant movement.
- Embrace Dissonance and Tension: Properly utilizing dissonance and tension can enhance the emotional impact of your music. Experiment with suspensions, passing tones, and other dissonant intervals, ensuring they resolve harmonically for a satisfying resolution.
- Record and Analyze: Record your compositions or arrangements and listen back critically. Analyze the voice leading choices you made and identify areas for improvement. Actively seeking feedback from others, such as instructors or fellow musicians, can also provide valuable insights.
- Continuously Learn and Explore: Voice leading is a lifelong journey of discovery and refinement. Continually study and explore different musical genres, time periods, and composers to expand your knowledge and understanding of voice leading techniques.
By incorporating these tips and tricks into your practice routine and compositional process, you can develop effective voice leading skills. Remember to trust your ears, be attentive to harmony and melody, and strive for coherence and musicality in your compositions. With time and dedication, you will enhance your ability to create harmonically rich and expressive music through thoughtful and skilled voice leading.
Conclusion
Voice leading is a fundamental aspect of music theory, encompassing the art of smooth melodic and harmonic transitions within a composition. By mastering the principles and techniques of voice leading, composers and musicians can create harmonically rich and emotionally evocative music.
In this comprehensive guide, we explored the various aspects of voice leading, including its definition, importance, and application in chord progressions, melodies, and harmonic analysis. We discussed the relevance of smooth voice leading, avoiding parallel fifths and octaves, and utilizing contrary and oblique motion. We also examined the significance of voice leading in chord progressions, melodies, and harmonic analysis.
Throughout the guide, we provided tips and tricks to help you develop effective voice leading skills. Studying classical music, experimenting with harmonic progressions, and paying attention to voice ranges are just a few examples of the strategies you can employ to improve your voice leading abilities.
Remember that voice leading is a skill that requires practice, attentive listening, and a deep understanding of musical relationships. As you continue to refine your voice leading techniques, you will gain the ability to craft harmonically coherent and expressive compositions that resonate with audiences.
So, whether you are a student of music theory, a composer, or an aspiring musician, embrace the art of voice leading and harness its power to create music that captivates and moves listeners. With dedication and the knowledge shared in this guide, you are well on your way to mastering the intricate world of voice leading in music theory.











