Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>Music Theory What Is Sequence

Music Theory
Music Theory What Is Sequence
Published: January 29, 2024
Learn the basics of music theory and understand what is sequence. Explore the patterns and repetitions in musical compositions with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Music theory is a fascinating field that provides a framework for understanding the structure, composition, and performance of music. One concept that holds significant importance in music theory is the idea of a sequence. Sequences play a crucial role in the development and progression of musical compositions, adding depth, complexity, and a sense of cohesion to the music.
At its core, a sequence in music refers to a recurring melodic or harmonic pattern that is repeated and transposed. It is like a musical phrase that is echoed and moved to different pitches or keys. The use of sequences can be found in a wide range of musical genres and styles, from classical to jazz, from pop to rock. Whether you are a musician, composer, or just an avid listener, understanding the concept of sequences can help you appreciate and analyze music more deeply.
In this article, we will explore the definition of sequences in music theory, discuss their characteristics, delve into their types and patterns, and examine their significance in different musical styles. Whether you are a seasoned musician or a beginner, this article will shed light on the intriguing world of musical sequences and their role in creating captivating compositions.
Definition of Sequence in Music Theory
In music theory, a sequence refers to a specific melodic or harmonic pattern that is repeated and transposed at different pitches or keys. It is a crucial concept that adds structure, unity, and development to musical compositions. The idea of a sequence can be traced back to the Baroque era, where composers like Johann Sebastian Bach used them extensively in their works.
A sequence typically consists of a short melodic or harmonic phrase that is repeated in succession, either ascending or descending, with each repetition transposed to a higher or lower pitch. This repetition and transposition create a sense of continuity and progression, allowing the music to move forward and evolve. Think of it as a musical echo that gradually moves up or down a musical scale.
Sequences can occur in both melodic and harmonic contexts. In melodic sequences, a specific melodic pattern is repeated and transposed, while in harmonic sequences, a harmonic progression or chord sequence is repeated and transposed. Both types of sequences contribute to the overall structure and form of a musical piece.
Sequences can be found in various musical elements, including melodies, basslines, chord progressions, and even rhythmic patterns. They can be short and simple, consisting of just a few notes, or long and complex, spanning several measures or even entire sections of a composition.
It is important to note that not every repetition of a musical phrase qualifies as a sequence. A sequence involves a deliberate and systematic repetition of a specific pattern with transposition. It is this repetition and transposition that distinguish a sequence from a simple repetition or variation of a musical motif.
Next, we will explore the characteristics of sequences in music theory, which will help us further understand this important concept and its role in creating engaging and dynamic musical compositions.
Characteristics of Sequences
Sequences in music possess several distinct characteristics that contribute to their impact and significance within a musical composition. These characteristics help shape the structure, development, and overall musical experience.
One of the primary characteristics of sequences is their repetition. A sequence involves the repeated presentation of a melodic or harmonic pattern, creating a sense of familiarity and establishing a musical motif. This repetition allows the listener to identify and recognize the sequence as it unfolds throughout the composition.
Another characteristic of sequences is transposition. As the sequence is repeated, it is transposed to different pitches or keys. This transposition adds variety and interest to the music, preventing it from becoming monotonous or predictable. The movement of the sequence to different pitches or keys also contributes to the sense of progression and development within the composition.
Sequences often exhibit a specific intervallic pattern. This means that the melodic or harmonic intervals between the notes in the sequence follow a particular pattern, such as ascending by steps or descending by thirds. The intervallic pattern provides a cohesive structure to the sequence, highlighting its distinctive musical identity.
Another important characteristic of sequences is their rhythmic aspect. The rhythmic pattern of the sequence can vary, ranging from simple and steady to more intricate and syncopated. The rhythm of the sequence adds a rhythmic drive and energy to the music, enhancing its overall impact and creating a sense of movement and momentum.
Sequences can also exhibit variations and alterations within their repetitions. These variations can involve changing the rhythm, adding embellishments, altering the intervals, or modifying the overall contour of the sequence. These variations contribute to the creativity and artistic expression of the composer, allowing them to shape and evolve the sequence within the composition.
Overall, sequences in music possess a set of characteristics that make them distinctive and compelling. Their repetition, transposition, intervallic patterns, rhythmic qualities, and potential for variations all contribute to their importance in creating engaging and memorable musical compositions.
Types of Sequences
Sequences in music theory come in various forms and styles, each with its unique characteristics and qualities. Let’s explore some of the common types of sequences:
- Exact or Repetitive Sequence: This type of sequence involves the exact repetition of a melodic or harmonic pattern at different pitches or keys. It creates a sense of consistency and reinforces the musical motif throughout the composition.
- Sequential Repetition: In this type of sequence, the melodic or harmonic pattern is repeated but with slight variations or alterations in contour, rhythm, or intervallic structure. It adds a subtle twist to the sequence, offering a sense of progression and development.
- Real Sequence: A real sequence involves the complete transposition of a melodic or harmonic pattern to a different pitch or key, maintaining the same intervallic structure. It creates a strong sense of repetition and transposition, contributing to the structural coherence of the composition.
- Tonal Sequence: Tonal sequences are characterized by the transposition of a melodic or harmonic pattern within the same tonal key. They maintain the harmonic relationships and tonal center, creating a sense of tonal stability and coherence throughout the sequence.
- Chromatic Sequence: Chromatic sequences involve the transposition of a melodic or harmonic pattern by half steps or chromatic intervals. They often create tension and dissonance, adding a dramatic or intense quality to the music.
- Descending or Ascending Sequence: Descending sequences involve the repetition of a melodic or harmonic pattern descending in pitch, while ascending sequences involve the repetition in an ascending direction. These types of sequences create a sense of rising or falling motion, adding a dynamic and expressive element to the music.
These are just a few examples of the types of sequences commonly found in music. Composers often utilize combinations of different sequence types, or even create unique variations, to achieve specific musical effects and evoke emotions. By understanding these various types of sequences, music enthusiasts can appreciate the complexity and creativity involved in their composition.
Sequential Patterns
Sequential patterns are a fundamental aspect of music composition that utilize sequences to create engaging and memorable musical phrases. These patterns involve the repetition and variation of melodic or harmonic motifs to add structure and cohesion to a composition.
One common type of sequential pattern is the sequential progression, where a melodic or harmonic motif is repeated and transposed at regular intervals. This creates a sense of forward motion and development within the music. The repetition and transposition of the motif can occur in a variety of ways, such as ascending, descending, or alternating directions.
Sequential patterns can also incorporate rhythmic variations, where the melodic or harmonic motif is repeated with different rhythmic figures or patterns. This adds a dynamic and rhythmic interest to the sequence, making it more engaging and captivating for the listener.
In addition to the repetition and transposition of motifs, sequential patterns can also include variations in contour, intervallic structure, and ornamentation. These variations help to keep the sequential pattern fresh and interesting, preventing it from becoming monotonous or predictable.
Sequential patterns can be found in various musical elements, such as melodies, basslines, chord progressions, and even rhythmic patterns. They are used in a wide range of musical genres and styles, from classical to jazz, from pop to rock.
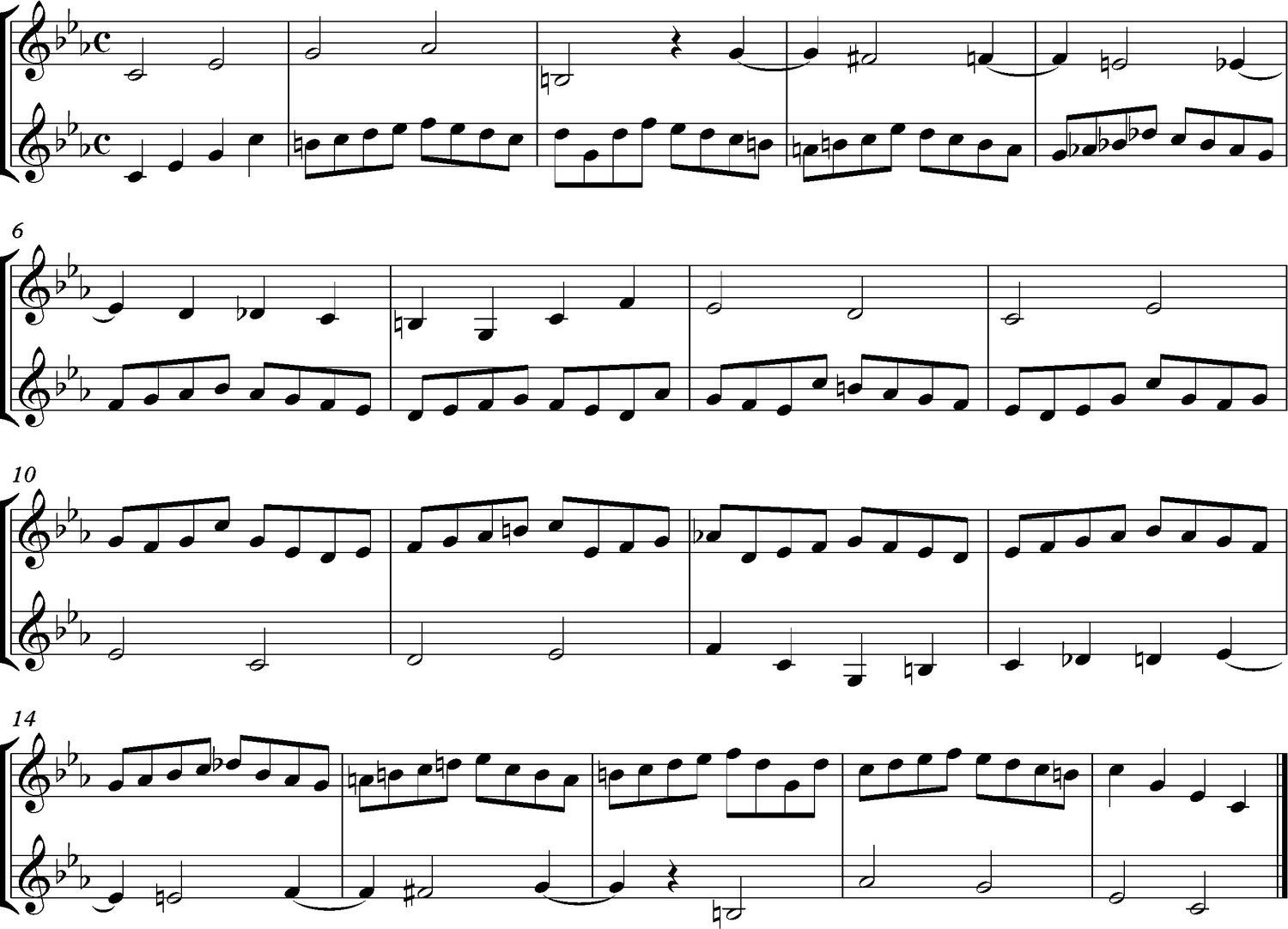
An example of a well-known sequential pattern can be found in Johann Sebastian Bach’s “Brandenburg Concerto No. 3” where a simple melodic motif is repeated and transposed multiple times throughout the composition, creating a sense of unity and development.
Overall, sequential patterns provide a powerful tool for composers to structure their musical compositions and create a sense of continuity and progression. By utilizing repetition, transposition, and variation, sequential patterns enhance the overall musical experience and captivate the listener’s attention.
Next, we will explore how sequences are utilized in different musical styles, showcasing their versatility and adaptability in creating unique and distinctive compositions.
Sequences in Different Musical Styles
Sequences play a significant role in shaping the sound and style of different musical genres and styles. From classical to jazz, from pop to rock, sequences can be found in various forms, showcasing their versatility and adaptability across different musical contexts.
In classical music, sequences are prevalent, particularly in Baroque and Classical-era compositions. The works of composers such as Johann Sebastian Bach, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and Ludwig van Beethoven feature intricate and elaborate sequences that serve as a foundation for their musical structures. These sequences contribute to the elegance, complexity, and emotional depth of classical compositions.
In jazz, sequences are utilized in improvisation and chord progressions. Jazz musicians often use melodic sequences as a foundation for their solos, exploring different variations and transpositions to create intricate and harmonically-rich improvisations. Additionally, the use of harmonic sequences in jazz standards and arrangements adds a sophisticated and dynamic element to the music.
In pop music, sequences are prevalent in the form of catchy hooks and melodic phrases. Pop songs often incorporate repetitive melodic patterns that are easily recognizable and memorable, creating an instant connection with the listeners. These sequences contribute to the infectious and commercial appeal of pop music.
In rock music, sequences are used to create powerful riffs and guitar solos. The repetitive and transposed patterns in rock songs add a sense of energy and drive, allowing for memorable musical moments. Rock bands like Led Zeppelin, Deep Purple, and AC/DC are known for their skillful use of sequences to create iconic and impactful rock anthems.
Additionally, sequences can be found in various ethnic and indigenous musical styles across the world. From the intricate patterns in Indian classical music to the rhythmic repetition in African drumming, sequences are utilized to create unique and culturally rich musical expressions.
Sequences are not limited to these specific genres and styles but are rather a universal tool in music composition. They can be found in varying degrees of complexity and prominence, depending on the artistic intention and musical aesthetics of the composer.
Understanding the role of sequences in different musical styles allows us to appreciate the diversity and richness of music across various cultures and genres. It showcases the universality of sequences as a musical element and their ability to create captivating compositions in a wide range of musical expressions.
In the next section, we will explore the notation and analysis of sequences, providing insights into how composers and analysts approach the study and interpretation of these musical elements.
Notation and Analysis of Sequences
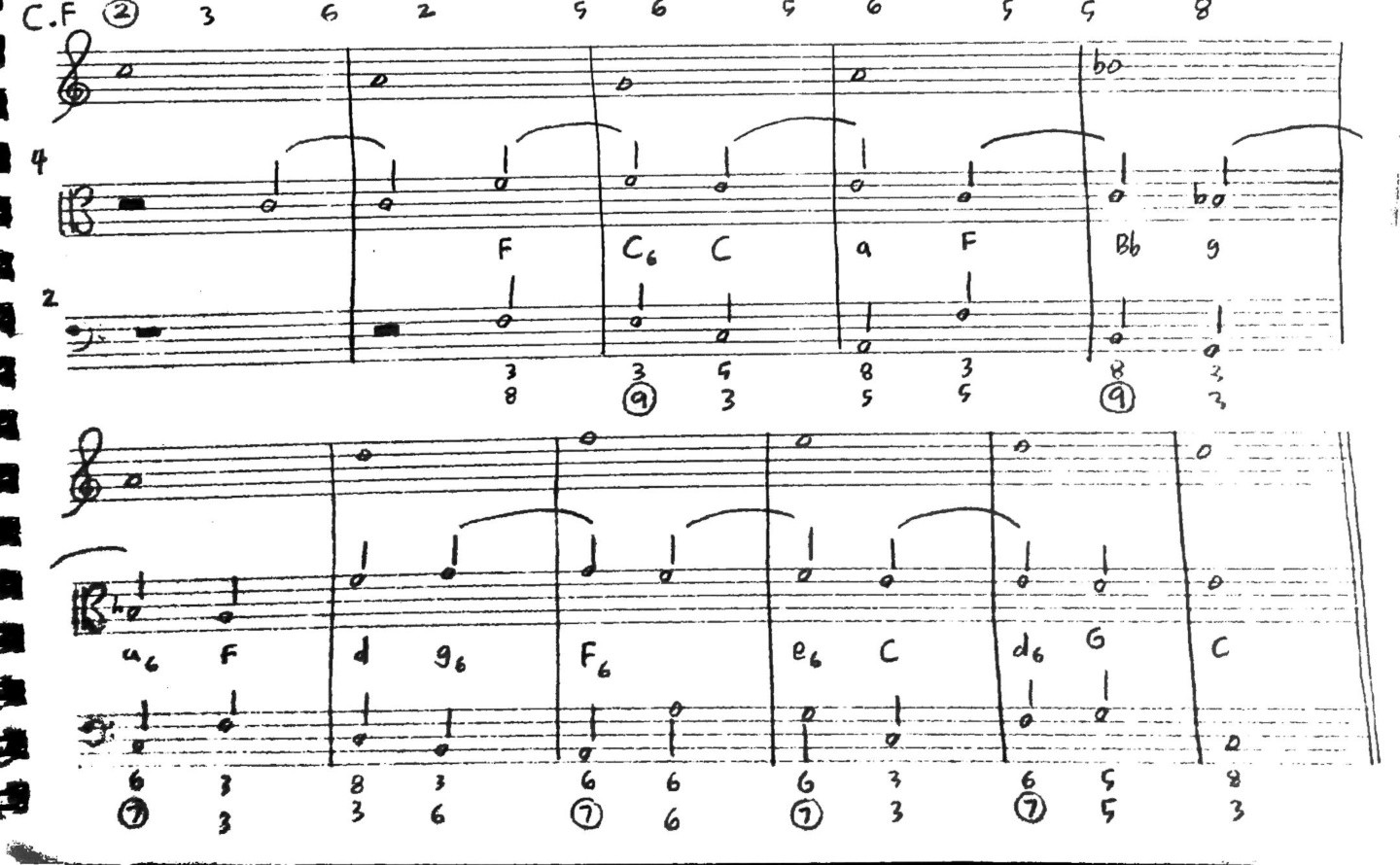
In music notation, sequences are typically represented by repeating the melodic or harmonic pattern and indicating the transpositions. This is often done through the use of bracketed lines or a sequence symbol, followed by the specific instructions for the transpositions.
For example, a melodic sequence can be indicated by placing a bracket over the repeated phrase with an arrow above or below, indicating the direction of the transposition. Harmonic sequences are commonly notated using Roman numerals or chord symbols to indicate the transposed chords or harmonic progression.
When analyzing sequences, music theorists and analysts focus on identifying the pattern, determining the intervallic relationship between the repetitions, and examining the overall structure and function within the composition. This analysis helps in understanding the composer’s use of sequences and how they contribute to the musical narrative and emotional impact.
Analysts may classify sequences based on their type, such as exact or repetitive sequences, sequential progressions, or tonal sequences. They also examine the intervallic relationships within the sequence, looking for patterns and variations that contribute to the overall musical effect.
Furthermore, the harmonic implications of the sequence are analyzed to understand how it contributes to the harmonic progression of the composition. This involves studying the chord progressions and identifying any tonal or modulatory aspects that arise from the sequence.
Notation and analysis of sequences provide valuable insights into the structure and composition of a musical piece. It allows musicians, composers, and scholars to better understand the creative choices made by the composer, as well as the impact of sequences on the overall musical experience.
By examining notation and analyzing sequences, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate craftsmanship that goes into the creation of music and gain further insights into the elements that make a composition engaging and compelling.
Next, we will explore the importance of sequences in music composition, highlighting their role in creating coherent and captivating musical works.
Importance of Sequences in Music Composition
Sequences play a crucial role in music composition, contributing to the overall structure, coherence, and emotional impact of a musical work. Composers utilize sequences to create engaging and memorable compositions in various ways:
Structural Coherence: Sequences provide a sense of unity and structure within a composition. By repeating and transposing melodic or harmonic patterns, sequences establish musical motifs that are recognized and developed throughout the piece. These motifs connect different sections of the composition, creating a cohesive musical narrative.
Development and Progression: Sequences help to propel the musical development of a composition. As the sequence is repeated and transposed, it creates a sense of forward motion and evolution. This gradual transformation of the musical material adds tension, excitement, and a sense of musical growth, keeping the listener engaged and captivated.
Emotional Impact: Sequences can evoke specific emotions and moods within a musical piece. The repetition and transposition of a melodic or harmonic pattern can create a sense of familiarity, comfort, or anticipation. Alternatively, variations within the sequence can introduce tension, surprise, or excitement. Composers carefully choose and manipulate sequences to elicit specific emotional responses from the listener.
Unity and Contrast: Sequences can contribute to both unity and contrast within a composition. When a sequence is used consistently throughout a piece, it creates a sense of unity, providing a recurring theme or motif that ties the composition together. On the other hand, variations or alterations within the sequence can introduce contrast, adding depth and variety to the music.
Artistic Expression and Creativity: Sequences offer composers a creative and expressive tool to shape their musical ideas. Composers can experiment with different patterns, transpositions, rhythms, and variations within a sequence to develop their unique musical style and voice. Sequences provide a framework for composers to explore and innovate, fostering their artistic creativity.
In summary, sequences are of utmost importance in music composition. They establish structural coherence, drive musical development, evoke emotions, provide unity and contrast, and serve as a canvas for artistic expression. Whether in classical, jazz, pop, or rock genres, sequences shape the very fabric of a musical composition, leaving a lasting impression on the listener.
Finally, let’s conclude our exploration of sequences in music theory.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sequences are a fundamental concept in music theory that enhances the structure, cohesion, and emotional impact of musical compositions. They involve the repetition and transposition of melodic or harmonic patterns, creating familiarity, progression, and development within the music.
Sequences exhibit distinct characteristics such as repetition, transposition, intervallic patterns, and rhythmic variations. They can be found in various musical elements and are utilized in different genres and styles, including classical, jazz, pop, and rock.
Notation and analysis of sequences allow for a deeper understanding of their patterns, intervallic relationships, and harmonic implications, revealing the intricacies of a composition. Sequences provide structural coherence, contribute to the development and progression of a composition, evoke specific emotions, and offer opportunities for artistic expression and creativity.
By recognizing the importance of sequences in music composition, musicians, composers, and enthusiasts gain a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship and artistic choices made by composers. Whether it’s creating catchy pop hooks, intricate jazz improvisations, or powerful rock riffs, sequences serve as a vehicle for musical expression and captivate the listener.
Understanding and harnessing the power of sequences can elevate the quality of musical compositions and enhance the listening experience. So, next time you listen to a piece of music, pay attention to the sequences at play and discover how they contribute to the magic of the composition.
Sequences are not just theoretical concepts; they are the building blocks of musical expression, weaving a captivating tapestry of melodies, harmonies, and emotions. Embrace the beauty and intricacy of sequences in music, and embark on a fascinating journey through the rich world of musical theory and composition.