Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>What Is An Escape Tone In Music Theory

Music Theory
What Is An Escape Tone In Music Theory
Published: January 31, 2024
Discover the concept of escape tone in music theory and its significance. Gain a deeper understanding of music theory and its application in creating captivating melodies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of music theory! For those who have a passion for music and a desire to delve deeper into its intricacies, understanding the various concepts and techniques is key. One such concept is the escape tone, which adds a unique flavor to musical compositions. In this article, we will explore what an escape tone is, its function and purpose, examples of its use in music, and its relationship to other musical concepts.
The study of music theory is not only limited to composers and performers but is also valuable for music enthusiasts who want to deepen their understanding and appreciation of the art form. By gaining knowledge of fundamental concepts like the escape tone, we can develop a greater appreciation for the genius and creativity behind musical compositions.
Before we dive into the world of escape tones, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of music theory. Music theory encompasses the rules and principles that govern the structure, composition, and performance of music. It provides us with a framework through which we can analyze and interpret the elements of music, such as melody, harmony, rhythm, and form.
Now, let’s embark on this journey and explore the intriguing concept of escape tones in music theory.
Definition of an Escape Tone
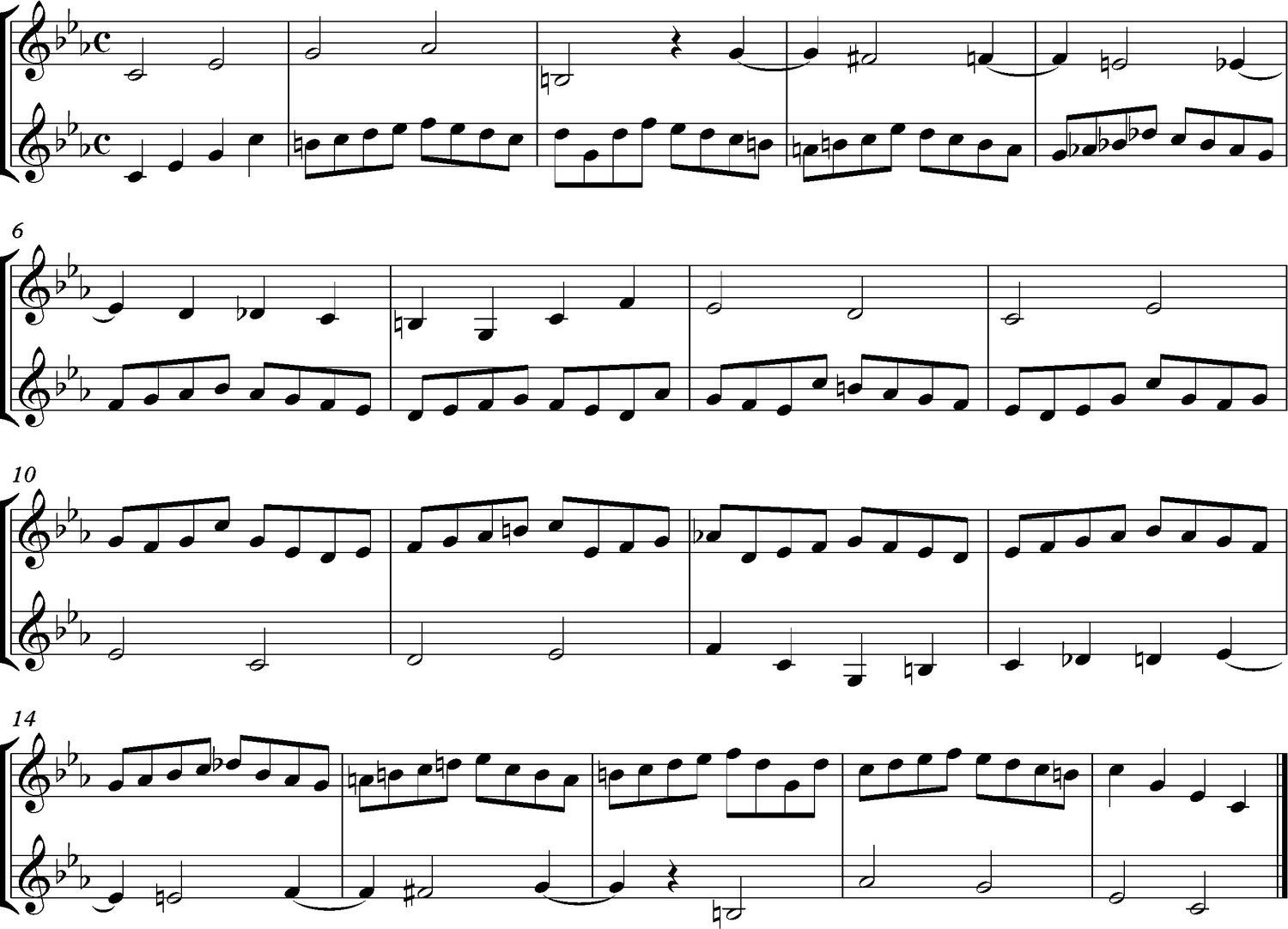
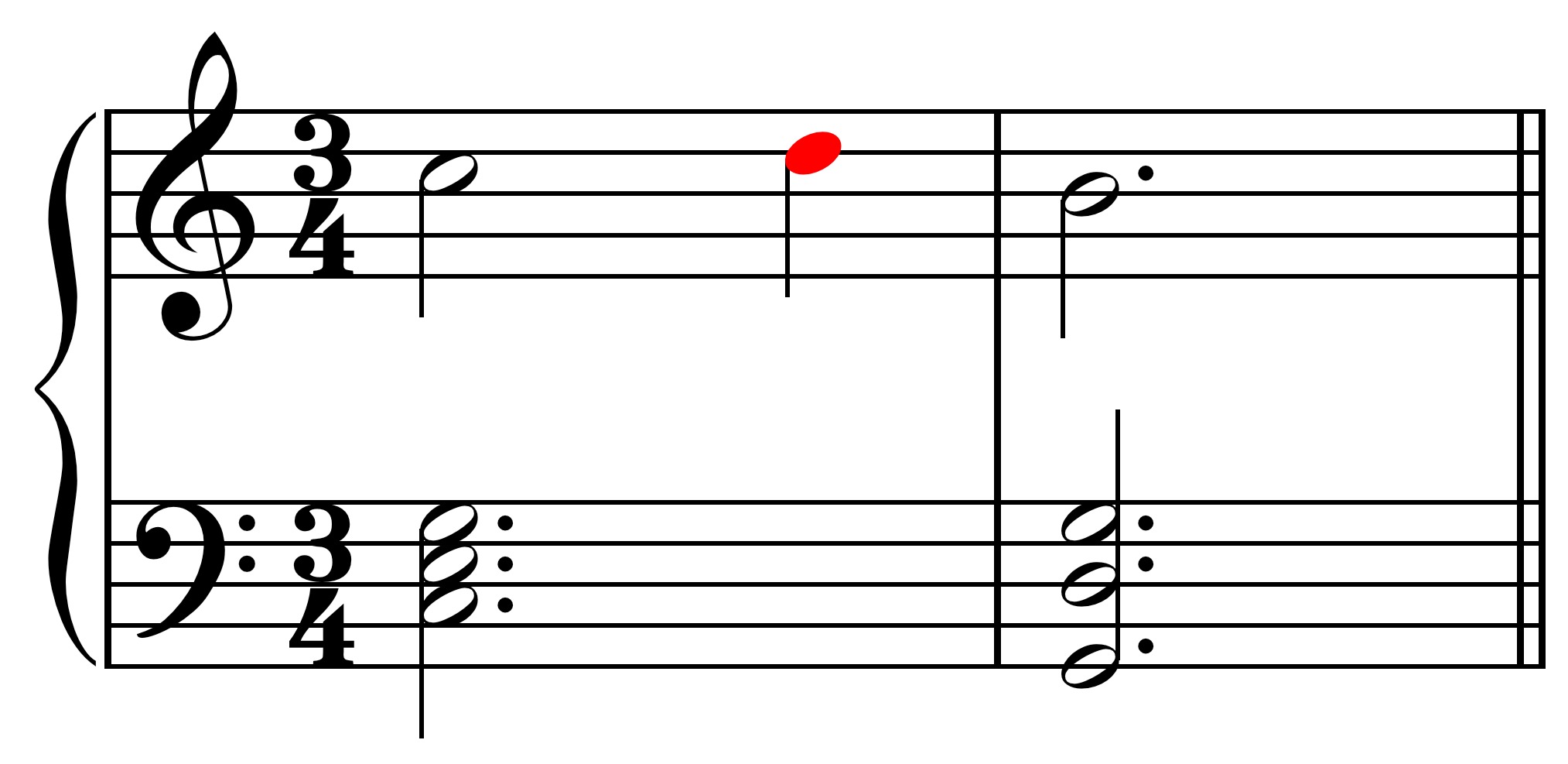
An escape tone, also known as an appoggiatura, is a type of non-chord tone in music theory. It is a melodic note that is approached by a consonant or chord tone and resolved by a dissonant or non-chord tone. The escape tone creates tension in the music and provides a sense of resolution when it is resolved.
Escape tones are typically played on weak beats, emphasizing their fleeting and transitional nature. They add a touch of unexpectedness and surprise to a melody, captivating the listener’s ear. The term “escape” comes from the notion that the escape tone “escapes” from its consonant or chord tone and resolves to a nearby dissonant note.
The interval between the escape tone and the resolving note is often a step or a small leap. The escape tone is typically accented and held slightly longer than surrounding notes to create emphasis.
In notation, an escape tone is represented as a small note (usually in the form of an eighth note) with a slur connecting it to the resolving note. The slur indicates that the escape tone is approached from above or below and should be played smoothly and connected to the next note.
It’s important to note that the escape tone is different from neighboring tones like the passing tone or the neighboring tone. While these neighboring tones connect to the surrounding chord tones, the escape tone moves away from the chord tone, creating a sense of tension and release.
Escape tones can be found in various styles and genres of music, from classical compositions to modern pop songs. They are a valuable tool in the composer’s arsenal for creating emotive and expressive melodies.
Function and Purpose of an Escape Tone
The function of an escape tone in music is to create tension and provide a momentary departure from the expected, adding interest and emotion to a composition. By introducing a brief dissonance before resolving it, escape tones add a sense of anticipation and release, enhancing the overall musical experience.
One of the primary purposes of an escape tone is to create an emotional impact on the listener. The momentary dissonance captures attention and evokes a range of feelings, whether it’s a sense of longing, surprise, or poignancy. The resolution provides a satisfying resolution to the tension, leaving the listener with a sense of resolution and closure.
Escape tones also serve a melodic function. They can embellish a melody, adding intricacy and ornamentation. By introducing unexpected notes, escape tones lend a touch of unpredictability to a composition, preventing it from becoming monotonous or predictable.
Additionally, escape tones contribute to the overall harmonic texture of a piece. When used in conjunction with chord progressions, they highlight the tensions and resolutions within the harmony, creating a dynamic interplay between consonance and dissonance.
Furthermore, escape tones can be used to guide the listener’s attention and emphasize certain notes or phrases. By accentuating the escape tone, composers can draw attention to a particular melodic line or highlight a climactic moment in the music.
Overall, the function and purpose of an escape tone are to add depth, emotion, and interest to a composition. They are vital tools for composers to manipulate tension and release, evoke emotional responses, and create memorable melodies.
Examples of Escape Tones in Music
The use of escape tones can be found in a wide range of musical genres and styles. Let’s explore some notable examples of escape tones in different compositions:
-
Johann Sebastian Bach – “Prelude in C Major” (Well-Tempered Clavier)
In Bach’s famous prelude, we can find the use of escape tones to add expressive color to the melodic lines. As the music unfolds, we encounter moments where a consonant note is approached by a dissonant tone, creating tension and resolving to a satisfying harmonization. This interplay of consonance and dissonance adds depth and richness to the composition.
-
Frederic Chopin – Nocturne in E-Flat Major, Op. 9, No. 2
Chopin’s Nocturne in E-Flat Major showcases the use of escape tones in a romantic context. The delicate melody is adorned with tasteful embellishments, including escape tones, which enhance the expressiveness of the piece. These embellishments create a sense of longing and add a touch of melancholy to the nocturne.
-
The Beatles – “She’s Leaving Home”
Even in contemporary popular music, escape tones can be found. The Beatles’ song “She’s Leaving Home” features an example of an escape tone in the opening vocal melody. As the phrase “She…” is sung, the note “F#” acts as the escape tone, creating a momentary tension that is resolved by the following note, “B”. This use of an escape tone adds emotional depth and captures the listener’s attention from the very beginning of the song.
-
John Williams – “Hedwig’s Theme” (Harry Potter Film Series)
In a more contemporary context, escape tones can even be found in film scores. John Williams’s iconic “Hedwig’s Theme” from the Harry Potter film series utilizes escape tones in the memorable melody. As the melody ascends and descends, escape tones are strategically placed to add a sense of wonder and magic to the composition.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and expressive potential of escape tones in different musical genres. Whether in classical compositions, popular songs, or film scores, escape tones provide a powerful tool for composers to evoke emotions, create tension, and captivate audiences.
Relationship to Other Musical Concepts
The concept of escape tones in music theory is closely related to various other musical concepts, including chord progressions, dissonance and consonance, and melodic ornamentation.
Regarding chord progressions, escape tones often occur within the context of specific harmonic frameworks. They add color and tension to chord progressions by introducing fleeting moments of dissonance before resolving to consonant tones. Understanding the relationship between escape tones and chord progressions allows composers to create harmonic motion that engages the listener’s ear and creates a sense of forward momentum.
Escape tones also play a significant role in the interplay between dissonance and consonance. As non-chord tones, they introduce controlled dissonance into a musical phrase, providing a contrast to the prevailing consonant tones. The resolution of the escape tone to a consonant note brings a sense of resolution and stability, creating a satisfying musical experience for the listener.
In addition, escape tones can be seen as a form of melodic ornamentation. Ornamentation involves embellishing a melody with additional notes or variations. Escape tones serve as one of the many tools composers and performers use to add variety and interest to a melody. By introducing unexpected notes, escape tones add nuance and expressiveness to the overall melodic line.
Moreover, escape tones share common ground with other non-chord tones, such as passing tones, neighboring tones, and suspensions. These non-chord tones all contribute to the complex palette of dissonance and consonance within a musical piece, creating tension and release that shape the overall emotional landscape of the composition.
Understanding the relationship between escape tones and these other musical concepts allows composers to harness their expressive power effectively. By skillfully incorporating escape tones into chord progressions and melodic phrases, composers can create dynamic and engaging musical compositions that captivate and move the listener.
Conclusion
Exploring the concept of escape tones in music theory reveals the fascinating ways in which composers utilize tension and release to create emotional impact and captivate listeners. Escape tones add depth, interest, and emotion to musical compositions by introducing moments of dissonance that resolve to consonant tones.
From the classical works of Bach and Chopin to contemporary pop songs and film scores, escape tones have found their place in various genres, showcasing their versatility and expressive potential. They serve multiple purposes, including generating emotional impact, embellishing melodies, and highlighting harmonic tensions and resolutions.
Understanding the relationship between escape tones and other musical concepts, such as chord progressions, dissonance and consonance, and melodic ornamentation, allows composers to harness their power effectively. By skillfully incorporating escape tones, composers can create dynamic and engaging musical compositions that not only captivate but also evoke a range of emotions.
As you continue your journey in music theory, the concept of escape tones will undoubtedly serve as a valuable tool for analysis, composition, and appreciation. By recognizing and appreciating the power of escape tones, you will navigate the rich and intricate world of music with a deeper understanding and a heightened sense of appreciation.
So, let the enchanting allure of escape tones accompany you as you delve deeper into the boundless realm of music theory, and let it inspire you on your musical journey.