Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>What Is Sus Chord In Music Theory


Music Theory
What Is Sus Chord In Music Theory
Published: January 31, 2024
Learn about the sus chord in music theory and its role in creating tension and resolution. Explore the fundamentals of music theory and enhance your musical understanding.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of music theory, where notes, chords, and harmonies come together to create beautiful melodies. One concept that often sparks curiosity and intrigue is the “sus chord.” In this article, we will explore the definition, structure, types, and practical application of sus chords in music.
Music theory is the backbone of understanding how music works, and it provides a framework for musicians to express their creativity. Whether you’re a songwriter, composer, or simply someone who enjoys listening to music, learning about sus chords can add depth and richness to your musical journey.
Sus, short for “suspended,” refers to a specific alteration of a chord that replaces the third with either the second or the fourth degree of the scale. This substitution creates a distinct and unique sound that adds tension and intrigue to a musical composition.
Throughout this article, we will delve into the intricacies of sus chords, examining their structure, variations, and usage. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to incorporate sus chords into your musical repertoire.
Definition of Sus Chord
A sus chord, short for “suspended chord,” is a type of chord alteration that replaces the third degree of a major or minor triad with either the second or the fourth degree of the scale. The resulting chord creates a unique and distinctive sound that adds tension and interest to a musical composition.
The term “suspended” refers to the fact that the third of the chord is temporarily “suspended” or put on hold, allowing the second or fourth degree to take its place. This alteration creates a sense of anticipation, as it suggests a resolution back to the original major or minor triad.
The main distinction between sus chords and major/minor chords lies in the quality of the third. In a major or minor chord, the third is considered the defining characteristic that determines the chord’s tonality. In a sus chord, however, the third is replaced, leading to a suspended sound that is neither fully major nor minor.
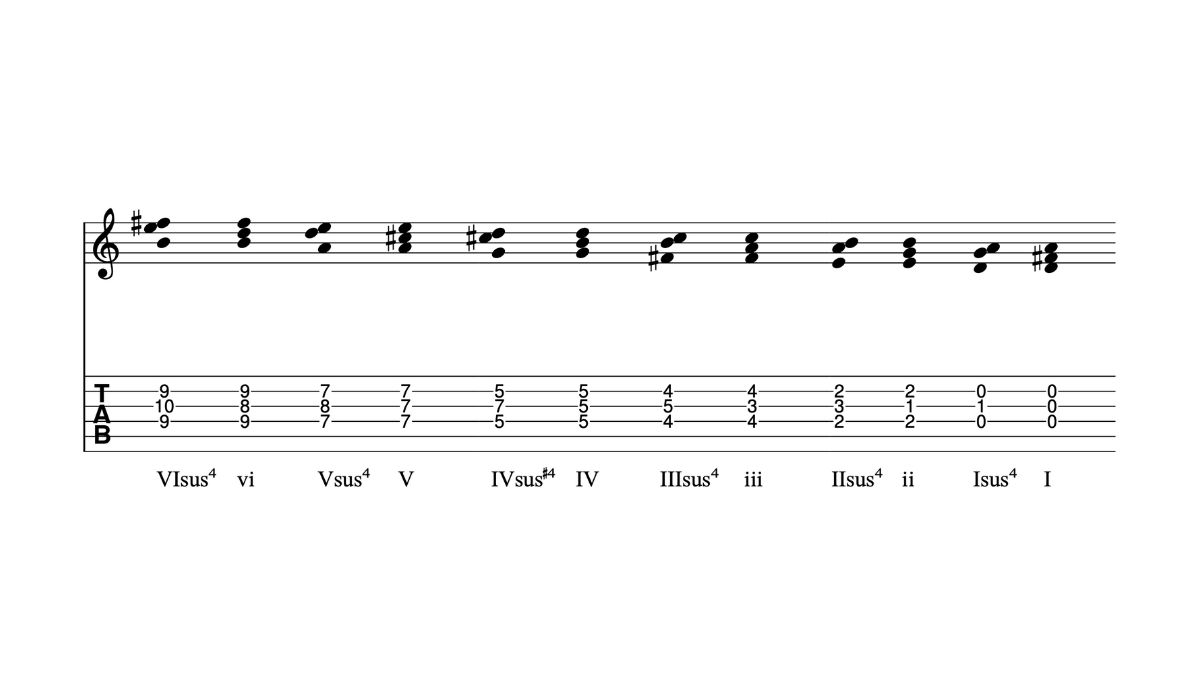
There are two main types of sus chords: sus2 and sus4. A sus2 chord replaces the third with the second degree of the scale, while a sus4 chord replaces the third with the fourth degree. Both types of sus chords have their own unique characteristics and offer different tonal possibilities.
It’s important to note that a sus chord should not be confused with a power chord. While they may sound similar, power chords are actually just two-note chords consisting of the root and the fifth, with no third. Sus chords, on the other hand, contain either the second or fourth degree in place of the third, creating a more complex and nuanced sound.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what a sus chord is, let’s explore its structure and how it differs from traditional major and minor chords.
Structure of a Sus Chord
The structure of a sus chord differs from that of a traditional major or minor chord due to the substitution of the third degree with either the second or the fourth degree. Let’s take a closer look at the components that make up a sus chord.
A sus chord consists of three notes: the root, the sus note (either the second or the fourth), and the fifth. The root note determines the fundamental pitch of the chord, while the sus note defines the unique sound of the sus chord. The fifth provides stability and support to the chord.
To illustrate the structure of a sus chord, let’s consider a C major triad and its sus2 and sus4 alterations:
– C Major Chord: C (root), E (third), G (fifth)
– C sus2 Chord: C (root), D (sus2), G (fifth)
– C sus4 Chord: C (root), F (sus4), G (fifth)
In the C sus2 chord, the third note (E) of the C major chord is replaced by the second note (D) of the C major scale. This substitution creates a sus2 sound, characterized by its gentle and dreamy quality.
On the other hand, in the C sus4 chord, the third note (E) of the C major chord is replaced by the fourth note (F) of the C major scale. This alteration creates a sus4 sound, which is known for its tension and a desire for resolution.
It’s worth noting that the sus note in a sus chord often creates dissonance, as it clashes with the other notes in the chord. This dissonance is what gives a sus chord its unique character and allows for interesting harmonic possibilities.
Now that we understand the structure of a sus chord, let’s explore the different types of sus chords and their specific characteristics.
Types of Sus Chords
There are two main types of sus chords: sus2 and sus4. Each type has its own distinct characteristics and can be used to create a variety of musical moods. Let’s explore these types in more detail:
1. Sus2 Chord: In a sus2 chord, the third degree of a major or minor triad is replaced with the second degree of the scale. For example, in a C sus2 chord, the notes would be C (root), D (sus2), and G (fifth). The sus2 chord has a dreamy and ethereal quality, providing a sense of openness and gentle tension. It is often used to create a peaceful and introspective atmosphere in music.
2. Sus4 Chord: In a sus4 chord, the third degree of a major or minor triad is replaced with the fourth degree of the scale. For example, in a C sus4 chord, the notes would be C (root), F (sus4), and G (fifth). The sus4 chord introduces a strong sense of tension and anticipation, as the fourth degree wants to resolve back to the third. It is frequently used to create a sense of energy or to add a touch of edginess to a musical composition.
In addition to the basic sus2 and sus4 chords, there are also extended and altered sus chords that incorporate additional notes. These variations can further enhance the tonal possibilities and complexity of sus chords.
Now that we have explored the different types of sus chords, let’s dive into how they can be effectively used in music compositions and arrangements.
How to Use Sus Chords in Music
Sus chords offer a unique and versatile tool for musicians and composers to add texture and interest to their musical compositions. Here are some effective ways to incorporate sus chords in your music:
1. Add Tension and Release: One of the primary functions of sus chords is to create tension and a desire for resolution. Use sus chords to introduce tension in a section of your music and then resolve it by transitioning to a major or minor chord. This technique can create a dynamic and emotional impact on the listener.
2. Create Musical Suspense: Sus chords can be used to create a sense of suspense or anticipation in your music. By using a sus chord before resolving to a major or minor chord, you can build anticipation and engage the listener’s attention.
3. Emphasize Melodic Movement: Incorporating sus chords can help highlight the melodic movement of a song. By using sus chords on certain notes of a melody, you can add richness and depth to the overall musical expression.
4. Enhance Harmonic Progressions: Sus chords can be used to enhance and embellish traditional harmonic progressions. Experiment with substituting major or minor chords in your progressions with sus chords to add a fresh and unique touch to your music.
5. Create Contrast and Variation: Introducing sus chords can add variety and contrast to your music. By alternating between major or minor chords and sus chords, you can create interesting musical textures and prevent your composition from becoming predictable.
Remember that the use of sus chords ultimately depends on your musical preferences and the emotional impact you want to convey. Don’t be afraid to experiment and trust your ears to guide you in incorporating sus chords effectively in your music.
Now that we have explored how to use sus chords in music, let’s examine some common progressions that involve sus chords to further expand our musical toolbox.
Common Progressions Involving Sus Chords
Sus chords can be used in a wide variety of progressions, adding depth and character to your musical compositions. Here are some common progressions where sus chords are often employed:
1. I – IV – V Progression with Sus4: In a major key, replacing the IV (fourth) chord with a sus4 chord can add a touch of tension and interest. For example, in the key of C major, the progression C – F – G becomes C – F sus4 – G. This alteration gives the progression a unique flavor and can create a sense of resolution when the sus4 resolves to the major IV chord.
2. Sus2 to Major Chord Progression: Transitioning from a sus2 chord to a major chord can create a subtle yet impactful change in your music. For instance, going from C sus2 to C major can evoke a feeling of resolution and release. This progression can be used to add emotion and depth to a section of your music.
3. Modal Interchange Progression: Modal interchange refers to borrowing chords from parallel scales. By incorporating sus chords from parallel modes, you can create unique and evocative progressions. For example, using a sus2 chord from the Dorian mode in a major key progression can introduce an intriguing tonal color.
4. Extended Chord Progressions: Sus chords can also be used in extended chord progressions, such as using a sus4 chord as a passing chord between two major or minor chords. This can create a smooth and seamless harmonic flow in your music.
5. Embellishing Turnarounds: When adding embellishments to turnarounds or chord sequences at the end of a musical phrase, sus chords can provide a unique twist. Experiment with replacing traditional chords with sus chords to create an interesting and unexpected resolution.
Remember, these are just a few examples of how sus chords can be integrated into common progressions. Feel free to explore and experiment with different combinations and variations to find the ones that resonate with your musical style and expression.
It’s worth mentioning that while sus chords can add flavor and interest to a composition, it’s essential to use them judiciously and in the context of the overall musical composition. Overusing or misplacing sus chords can result in a disjointed or dissonant sound. Trust your ears and intuition to find the right moments to incorporate sus chords effectively.
Now that you have a solid understanding of sus chords, their structure, and their usage, you can confidently incorporate these unique and captivating chords into your musical creations.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have now embarked on a journey into the captivating world of sus chords in music theory. By understanding the definition, structure, types, and practical application of sus chords, you have gained a valuable tool to enhance your musical compositions.
Sus chords offer a unique and versatile way to add tension, release, suspense, and variation to your music. They can be used to create emotional depth, highlight melodic movement, and enhance harmonic progression. Whether you’re a songwriter, composer, or simply an admirer of music, incorporating sus chords into your musical repertoire can open up a world of creative possibilities.
Remember to use sus chords judiciously, allowing them to serve as moments of tension and resolution within your compositions. By blending sus chords with traditional major and minor chords, you can create dynamic and captivating musical arrangements.
As you continue on your musical journey, feel free to experiment with the different types of sus chords, explore their usage in various progressions, and trust your instincts to create unique and compelling compositions.
Music theory is a vast and ever-evolving discipline, and sus chords are just one of the many exciting concepts within it. Keep exploring, learning, and discovering new things about music theory, as it will undoubtedly enrich your understanding and appreciation of the art form.
So go ahead, pick up your instrument, sit at the piano, or fire up your digital audio workstation, and let the captivating sounds of sus chords inspire your musical creations. Happy composing!