Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>What Are The Chords For A Phrygian + Basic Music Theory

Music Theory
What Are The Chords For A Phrygian + Basic Music Theory
Published: January 31, 2024
Learn the chords for a Phrygian scale and gain a solid understanding of basic music theory with our comprehensive guide. Enhance your musical knowledge with the fundamentals of Music Theory.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of music theory! If you’ve ever found yourself grooving to the unique sounds of the Phrygian mode and wondered how those captivating chords are constructed, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of chord construction and explore the intricacies of the Phrygian mode.
Music theory is the backbone of every musical composition. It provides us with a deeper understanding of how melodies, harmonies, and chords work together to create beautiful and expressive music. By comprehending the theory behind different musical modes, such as the Phrygian mode, we can unlock endless creative possibilities and expand our musical horizons.
The Phrygian mode is one of the seven diatonic modes derived from the major scale. It has a distinct exotic or mysterious sound that is widely used in various genres such as flamenco, metal, and jazz fusion. Understanding how to construct chords in the Phrygian mode is crucial for musicians and composers looking to infuse their compositions with its characteristic tonality.
In this article, we will guide you through the basics of chord construction and explain how common chord progressions can be applied within the Phrygian mode. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of the chords used in the Phrygian mode and be able to create your own captivating musical compositions.
So, let’s dive into the exciting world of music theory and uncover the secrets behind the chords of the Phrygian mode!
Understanding Phrygian Mode
The Phrygian mode is a musical mode that is derived from the major scale. It has a distinct tonality that gives it a unique and exotic sound. It is often associated with Spanish flamenco music and is also commonly used in heavy metal and jazz fusion genres.
To understand the Phrygian mode, it is important to have a basic understanding of the major scale. The major scale is a diatonic scale consisting of seven notes, which are usually labeled with the letters A to G. Each note of the major scale corresponds to a degree or step of the scale.
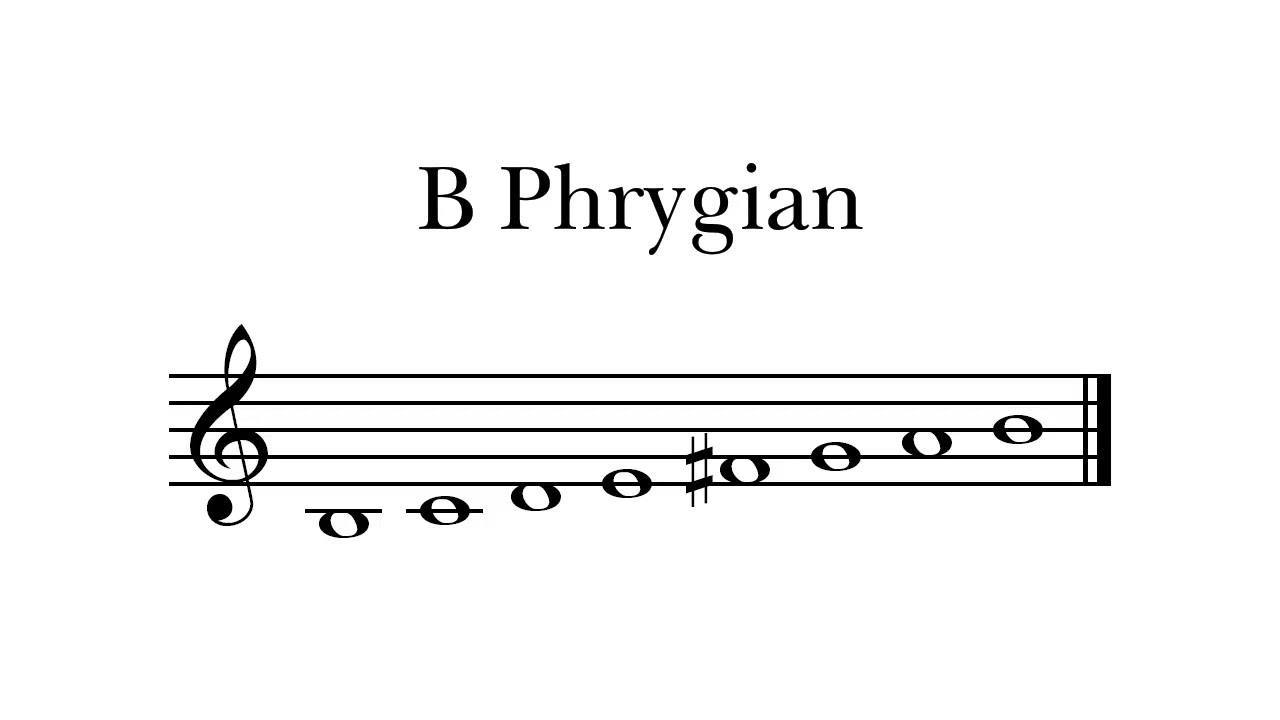
The Phrygian mode is formed by starting on the third degree of the major scale and playing all the notes from that point until the next octave. For example, if we take the C major scale (C-D-E-F-G-A-B) and start on the third degree, which is E, and play all the notes until the next E, we would have the E Phrygian mode (E-F-G-A-B-C-D).
The defining characteristic of the Phrygian mode is its flattened second scale degree. In the E Phrygian mode, the second degree, F, is lowered by a half step to F♭. This gives the mode its unique, dark, and mysterious sound.
In addition to the flattened second degree, the Phrygian mode also features a minor third, perfect fourth, perfect fifth, minor sixth, and minor seventh. The interval pattern can be summarized as follows:
Root – ♭2 – ♭3 – 4 – 5 – ♭6 – ♭7 – Root
The Phrygian mode can be transposed to any key by starting on the corresponding note of the major scale. For example, if we start on the fifth degree of the C major scale, which is G, we would have the G Phrygian mode (G-A♭-B♭-C-D-E♭-F-G).
Now that we have a basic understanding of the Phrygian mode, let’s explore how chords are constructed within this mode and how we can use them to create captivating musical progressions.
Chord Construction Basics
Understanding the basics of chord construction is essential for creating harmonically rich and melodically pleasing music in any mode, including the Phrygian mode. In music theory, a chord is a combination of three or more notes played together to create a harmonious sound. These notes are selected from the corresponding scale or mode to form a specific chord type.
Chords are built using intervals, which are the distances between two notes. The two most fundamental intervals in chord construction are the third and the fifth. The third determines whether the chord is major or minor, while the fifth adds stability and richness to the chord.
In the Phrygian mode, we use the notes of the mode to construct chords. Taking the E Phrygian mode as an example (E-F-G-A-B-C-D), let’s build some basic chords:
- E Minor (Em) chord: The root note of the chord is E, and we add the minor third (G) and the perfect fifth (B) from the Phrygian mode. So, the E minor chord in the Phrygian mode is E-G-B.
- F Major (F) chord: The root note of the chord is F, and we add the major third (A) and the perfect fifth (C) from the Phrygian mode. So, the F major chord in the Phrygian mode is F-A-C.
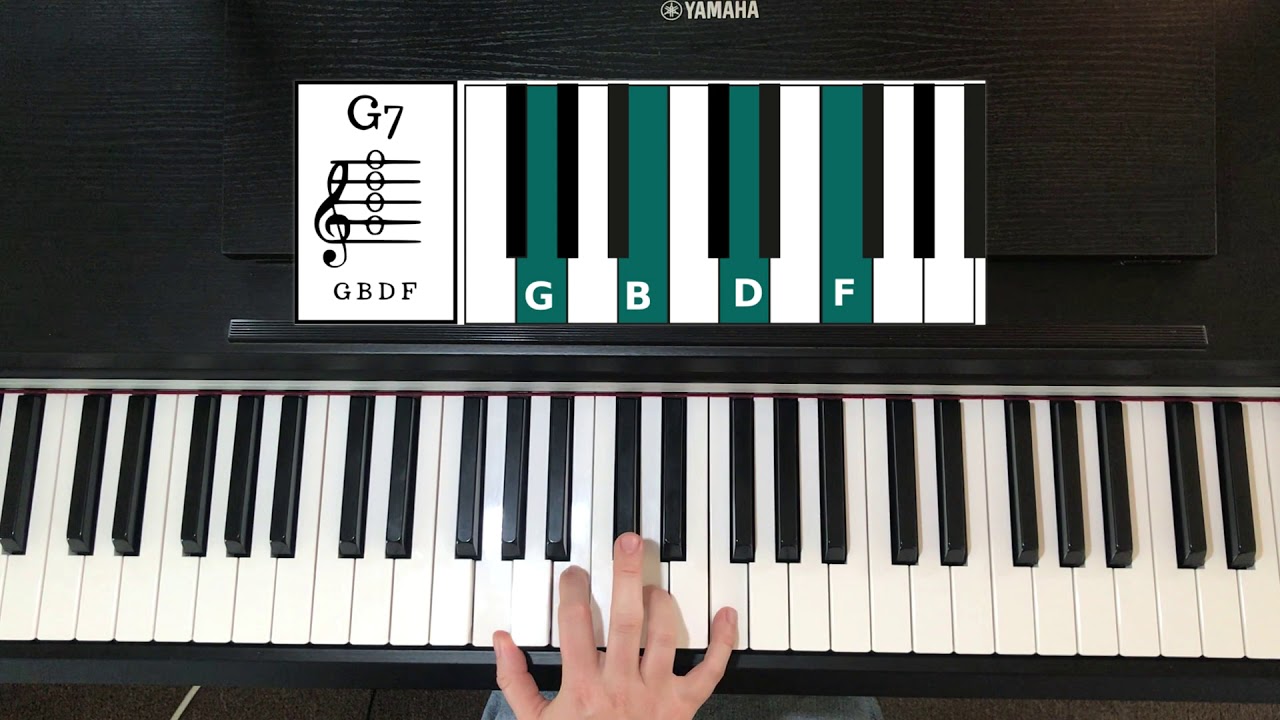
- G Major (G) chord: The root note is G, and we add the major third (B) and the perfect fifth (D) from the Phrygian mode. So, the G major chord in the Phrygian mode is G-B-D.
These are just a few examples of the chords that can be constructed within the Phrygian mode. By applying the same principles and using the appropriate intervals, you can build chords on any note of the mode to create your own unique harmonies.
Now that we know the basics of chord construction, let’s move on to exploring how to build chords specifically in the Phrygian mode.
Building Chords in the Phrygian Mode
Building chords in the Phrygian mode involves selecting notes from the mode’s scale and combining them in different combinations. By understanding the intervals and characteristics of the Phrygian mode, we can create chords that emphasize its unique tonality and create captivating musical progressions.
One common chord in the Phrygian mode is the Phrygian chord itself, which is a minor triad with a flattened second. Using the E Phrygian mode as an example (E-F-G-A-B-C-D), the Phrygian chord would consist of the root note (E), the minor third (G), and the perfect fifth with a flattened second (B♭). So, the Phrygian chord in the E Phrygian mode would be E-G-B♭.
Another frequently used chord is the dominant Phrygian chord, also known as the Phrygian dominant chord. It combines the Phrygian mode with a major third, creating a more tense and dramatic sound. In the E Phrygian mode, the dominant Phrygian chord would be E-G-B♭-D♭.
Moving further, we can explore extended chords in the Phrygian mode. These chords include additional notes, such as the seventh or ninth, to create more complexity and richness in the sound. For example, the E Phrygian mode could have an E minor seventh chord (E-G-B-D) or an E minor ninth chord (E-G-B-D-F).
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of the chords that can be built within the Phrygian mode. Experimentation and creativity are key when building chords in any musical mode. By combining different intervals and selecting notes from the mode’s scale, you can create your own unique and captivating chord progressions.
When building chords in the Phrygian mode, it’s also important to consider how they function within the overall musical context. Chord progressions and harmonic movement play a crucial role in creating engaging and dynamic music. Understanding common chord progressions within the Phrygian mode can help you create more coherent and compelling musical compositions.
Now that we have a solid understanding of how to build chords in the Phrygian mode, let’s move on to exploring some common chord progressions used in this mode.
Common Chord Progressions in Phrygian
Understanding common chord progressions in the Phrygian mode is essential for creating melodies and harmonies that capture the distinct character and mood of this unique musical mode. These chord progressions can serve as a foundation for your compositions or as a starting point for improvisation.
One of the most common chord progressions in the Phrygian mode is the Phrygian cadence. The Phrygian cadence is a minor chord progression that adds tension and resolution to the musical phrase. In the key of E Phrygian, a typical Phrygian cadence would involve the chords E minor (Em) and F major (F). This progression creates a dark and melancholic atmosphere, characteristic of the Phrygian mode.
Another commonly used chord progression in the Phrygian mode is the Phrygian dominant progression. This progression is often found in flamenco and jazz fusion music, adding a flair of intensity and exoticism. In the key of E Phrygian, the Phrygian dominant progression would involve the chords E7, F, and G major. The dominant seventh chord (E7) provides a strong sense of tension that resolves to the F and G major chords, creating a compelling musical journey.
Additionally, you can experiment with different chord extensions to add complexity and depth to your chord progressions in the Phrygian mode. For example, you can incorporate chords like E minor seventh (Em7), F major seventh (Fmaj7), or G major ninth (G9) to create more intricate harmonic textures.
Remember, these are just a few examples of common chord progressions in the Phrygian mode. As a composer or musician, you have the freedom to explore and create your own unique progressions based on your artistic vision and musical taste. Don’t be afraid to experiment and let your creativity guide you.
When using chord progressions in the Phrygian mode, it is important to consider the overall musical context and the emotional impact you want to convey. The Phrygian mode is known for its mysterious and captivating sound, so it’s crucial to use the chord progressions in a way that enhances these qualities.
Now that we have explored common chord progressions in the Phrygian mode, let’s summarize what we have learned and conclude our journey into the realm of music theory and the enchanting chords of the Phrygian mode.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have embarked on a journey into the fascinating world of music theory and delved into the captivating chords of the Phrygian mode. By understanding the basics of chord construction and exploring the unique characteristics of the Phrygian mode, you have gained valuable insights into building harmonies that capture its distinct tonality.
Through chord construction basics, you learned how to build chords in the Phrygian mode by selecting notes from its corresponding scale and combining them in different combinations. You discovered chords such as the Phrygian chord and the dominant Phrygian chord, which serve as the foundation for creating captivating musical progressions.
Furthermore, by exploring common chord progressions in the Phrygian mode, you gained the knowledge of how to create melodies and harmonies that capture the mood and character of this unique musical mode. Whether it’s the Phrygian cadence or the Phrygian dominant progression, these progressions provide a starting point for your musical compositions and improvisations.
Remember that while understanding the theory is important, music is ultimately an expression of creativity and emotion. Use your newfound knowledge to experiment, explore, and create your own unique chord progressions and musical compositions in the Phrygian mode.
As you continue on your musical journey, keep in mind that the Phrygian mode is just one of many tools in your musical arsenal. Don’t hesitate to explore other modes, scales, and chord progressions to expand your musical versatility and create an even more diverse range of compositions.
So, grab your instrument, unleash your creativity, and immerse yourself in the enchanting world of the Phrygian mode. Let the captivating chords you’ve learned guide you to explore new soundscapes and express your musical voice in a unique and compelling way.
Happy creating, and may your musical ventures be filled with harmonies that resonate with the hearts and souls of your listeners!