Home>Production & Technology>Sound>What Do Rales Sound Like


Sound
What Do Rales Sound Like
Published: December 17, 2023
Learn what rales sound like and how they can indicate a serious respiratory issue. Understand the significance of these sounds and seek medical attention if necessary.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
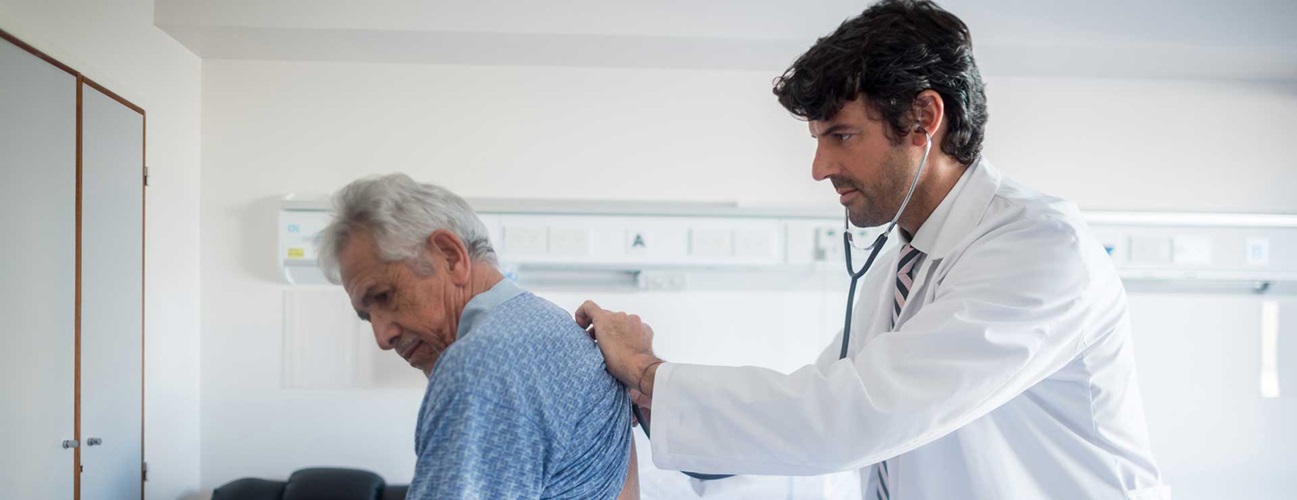
Welcome to the fascinating world of rales! If you’ve ever wondered what those crackling, rattling or bubbling sounds you hear when breathing are, you’re in the right place. Rales, also known as crackles, are abnormal lung sounds that can be heard with a stethoscope during a physical examination. These sounds can provide valuable clues about the underlying respiratory condition.
Rales are often associated with various respiratory disorders, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and pulmonary fibrosis. They occur when there is an obstruction or narrowing in the airways, leading to the turbulent flow of air. This turbulence causes the airway walls to vibrate, resulting in the characteristic crackling sounds.
In this article, we will delve into the world of rales, exploring their types, characteristics, causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. Whether you are a healthcare professional or simply curious about this topic, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of rales and their significance in respiratory health.
So, put on your stethoscope and get ready to explore the symphony of sounds that the lungs can produce. Let’s dive in!
Definition of Rales
Rales, also known as crackles, are abnormal lung sounds that can be heard during a physical examination with a stethoscope. They are characterized by crackling, rattling, or bubbling noises that occur during breathing. Rales are typically heard during inspiration, but in some cases, they may also be present during expiration.
These abnormal sounds are produced due to the disruption of the normal airflow in the lungs. The airway passages in the lungs are normally open and allow for smooth, unrestricted flow of air. However, when there is an obstruction or narrowing in the airways, such as excess fluid, inflammation, or mucus, the flow of air becomes turbulent. This turbulent flow causes the airway walls to vibrate, resulting in the characteristic crackling sounds known as rales.
Rales can vary in intensity and quality. They may be soft or loud, fine or coarse, and may have different patterns, such as fine crackles or bubbling sounds. The specific characteristics of rales can provide important diagnostic information about the underlying respiratory condition.
It is essential to distinguish rales from other lung sounds, such as wheezing and rhonchi. Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs due to narrowed airways, often associated with conditions like asthma. Rhonchi, on the other hand, are low-pitched rumbling sounds caused by the vibration of thick mucus or secretions in the larger airways.
Rales can occur in different regions of the lungs and can be unilateral (affecting one side) or bilateral (affecting both sides). They can also vary in their location within the lung, such as crackles heard over the bases (bottom) of the lungs or crackles heard over the upper lung fields.
Understanding the definition and characteristics of rales is crucial for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and managing respiratory conditions. By recognizing and interpreting these abnormal lung sounds, medical professionals can provide appropriate treatment and care to patients.
Types of Rales
Rales can be categorized into different types based on their characteristics and the underlying conditions that cause them. Here are the most common types of rales:
- Fine crackles: These are soft, high-pitched crackling sounds that are often described as similar to the sound of hair being rubbed between the fingers. Fine crackles are usually heard during late inspiration and are associated with conditions like pulmonary fibrosis, congestive heart failure, and pneumonia.
- Coarse crackles: Unlike fine crackles, coarse crackles have a lower-pitched sound, similar to the noise produced by rubbing one’s hands together. They can be heard both during inspiration and expiration and are often associated with conditions like bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary edema.
- Bubbling rales: Bubbling rales are characterized by the sound of bubbles popping, indicating the presence of fluid in the airways. They are commonly heard in conditions such as pneumonia and bronchiectasis.
- Rubbing sounds: These are dry, grating sounds that resemble the noise produced by rubbing two pieces of leather together. Rubbing sounds, also known as pleural rubs, occur when the inflamed pleural surfaces rub against each other during breathing. They are often associated with pleurisy or pleural effusion.
It is important to note that the presence of rales alone is not always indicative of a specific condition. The underlying cause needs to be evaluated through a thorough clinical examination and additional diagnostic tests. Differentiating between the types of rales can help healthcare professionals in narrowing down the potential causes and determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Characteristics of Rales
Rales exhibit certain characteristics that can provide valuable insights into the underlying respiratory condition. Understanding these characteristics can help healthcare professionals in making an accurate diagnosis and determining the appropriate course of treatment. Here are some key characteristics of rales:
- Timing: Rales are typically heard during inspiration, but in some cases, they may also be present during expiration. The timing of rales can offer clues about the nature of the underlying condition.
- Intensity: Rales can range from being soft and faint to loud and easily audible. The intensity of the rales may vary depending on factors such as the severity of the underlying condition and the location within the lungs.
- Pitch: Rales can have different pitches. Fine crackles are high-pitched, while coarse crackles are low-pitched. The pitch can provide insights into the size of the airway obstruction or the nature of the underlying lung tissue abnormality.
- Quality: Rales can be described as crackling, rattling, or bubbling sounds. The quality of the rales can help healthcare professionals differentiate them from other abnormal lung sounds.
- Distribution: Rales can occur unilaterally (affecting one side) or bilaterally (affecting both sides) of the chest. They can also vary in their location within the lungs, such as crackles heard over the bases (bottom) of the lungs or crackles heard over the upper lung fields.
- Changes with Positioning: Rales can sometimes change with changes in body positioning. For example, rales that are more prominent when laying down and decrease when sitting up can be a sign of conditions such as pulmonary edema.
- Temporal Pattern: Rales may have a specific temporal pattern, such as being predominantly present during the early inspiratory phase or being continuous throughout the respiratory cycle. This pattern can provide additional diagnostic information.
It is important to note that the characteristics of rales can vary depending on the individual and the underlying condition. Therefore, healthcare professionals must listen attentively and carefully assess the specific qualities of the rales during a physical examination.
By taking into account the timing, intensity, pitch, quality, distribution, changes with positioning, and temporal pattern of rales, healthcare professionals can use this valuable information to guide further investigations, create an accurate diagnosis, and develop a tailored treatment plan for their patients.
Causes of Rales
The presence of rales can indicate an underlying respiratory condition. These abnormal lung sounds can be attributed to various causes. Here are some common causes of rales:
- Pneumonia: Rales are frequently heard in cases of pneumonia, which is an infection of the lungs. The inflammatory response and accumulation of fluid and debris in the airways can lead to the production of crackling sounds during breathing.
- Pulmonary Fibrosis: In pulmonary fibrosis, the lung tissue becomes scarred and stiff, leading to impaired lung function. The abnormal lung tissue can cause disrupted airflow and result in the development of rales.
- Bronchitis: Acute or chronic bronchitis, characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, can be another cause of rales. Excessive mucus production and inflammation in the airways can lead to the production of crackling sounds.
- Pulmonary Edema: In conditions like congestive heart failure, fluid can accumulate in the lungs, resulting in pulmonary edema. The presence of excess fluid in the airways can lead to the development of rales.
- Asthma: While wheezing is the characteristic sound associated with asthma, rales may also be heard in severe asthma exacerbations. The presence of rales indicates further airway inflammation and mucus production.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A blood clot in the pulmonary artery, known as a pulmonary embolism, can cause rales. The clot can obstruct the blood flow and compromise oxygenation, leading to abnormal lung sounds.
- Pleurisy: Inflammation of the pleura, the membranes that line the lungs and chest cavity, can result in pleurisy. The rubbing of the inflamed pleural surfaces against each other during breathing can produce rubbing sounds or rales.
- Respiratory Infections: Other respiratory infections, such as bronchiectasis, tuberculosis, and viral respiratory infections, can also lead to the development of rales due to the accumulation of mucus and inflammation in the airways.
It is important to emphasize that these are just a few examples of the many potential causes of rales. The presence of rales should prompt further evaluation by a healthcare professional to identify the specific underlying condition and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
By understanding the potential causes of rales, healthcare professionals can narrow down the diagnostic possibilities and provide effective management for patients experiencing these abnormal lung sounds.
Diagnostic Methods for Rales
When rales are detected during a physical examination, further diagnostic methods are necessary to determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment. Here are some commonly used diagnostic methods for rales:
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can provide valuable information about the presence of any abnormalities in the lungs, such as pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis, or fluid accumulation.
- Pulmonary Function Tests: Pulmonary function tests, including spirometry and lung volume measurements, can assess lung function, airflow limitation, and the presence of any obstruction in the airways.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) and inflammatory markers, can help identify infections, inflammation, and other systemic conditions that may be contributing to the development of rales.
- Sputum Culture: Collecting and analyzing a sample of sputum can help identify any bacteria, viruses, or fungi causing respiratory infections and guide appropriate treatment.
- Chest CT Scan: A chest CT scan provides a more detailed view of the lungs and can help identify abnormalities, such as masses, lung nodules, and lymph node enlargement that may be associated with the presence of rales.
- Bronchoscopy: In cases where the cause of rales remains unclear, a bronchoscopy may be performed. This procedure involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the airways to visualize any abnormalities, collect tissue samples, or remove obstructions.
- Echocardiogram: If the presence of rales is suspected to be related to heart conditions, an echocardiogram may be performed to assess the structure and function of the heart and detect any abnormalities, such as heart failure or valve disorders.
It is important to note that the specific diagnostic methods employed will depend on the suspected underlying cause of the rales as determined by the healthcare professional. A thorough clinical evaluation and medical history, combined with the appropriate diagnostic tests, will aid in accurately diagnosing the respiratory condition causing the rales.
By utilizing these diagnostic methods, healthcare professionals can gather crucial information to establish an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan to address the underlying cause of the rales.
Treatment Options for Rales
The treatment of rales depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the respiratory condition. The goal of treatment is to address the root cause of the rales and improve respiratory function. Here are some common treatment options for rales:
- Antibiotics: If the rales are caused by a bacterial infection, such as pneumonia, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the infection and reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Bronchodilators: Bronchodilators, such as short-acting or long-acting inhalers, are commonly used to open up the airways and improve airflow. They are often prescribed for conditions like asthma, chronic bronchitis, or COPD, which can cause rales.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that can help reduce airway inflammation and alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like pulmonary fibrosis or bronchitis, which can contribute to the development of rales.
- Diuretics: In cases where rales are caused by fluid accumulation in the lungs, diuretics may be prescribed to help reduce excess fluid and relieve symptoms associated with conditions like congestive heart failure or pulmonary edema.
- Treatment of Underlying Diseases: Treating the underlying condition responsible for rales is essential. Depending on the cause, treatments may include physical therapy, oxygen therapy, antifungal medications, or lifestyle modifications, among others.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Pulmonary rehabilitation programs can help improve lung function, increase exercise tolerance, and provide education on managing respiratory conditions. These programs often involve a combination of exercise training, breathing exercises, and education on symptom management.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address underlying structural abnormalities, remove tumors, or repair damaged lung tissue contributing to the development of rales.
- Supportive Care: Along with specific treatments targeting the underlying cause, supportive care measures like staying hydrated, getting adequate rest, and maintaining overall good respiratory health can also be helpful in managing rales.
It is important to note that the treatment approach will vary depending on the individual and the specific respiratory condition causing the rales. Healthcare professionals will evaluate each case thoroughly and create a personalized treatment plan based on the underlying cause, severity, and individual needs.
By implementing appropriate treatment strategies, healthcare professionals can help alleviate symptoms, improve lung function, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals experiencing rales.
Prevention and Home Remedies
While rales are often associated with underlying respiratory conditions, there are steps you can take to prevent their occurrence or manage them at home. Here are some prevention strategies and home remedies you can consider:
- Maintain good respiratory hygiene: Practice good respiratory hygiene by covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of infections that can lead to rales.
- Quit smoking: If you are a smoker, quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to improve your respiratory health. Smoking damages the lungs and can contribute to the development of conditions like chronic bronchitis and COPD, which can cause rales.
- Avoid exposure to environmental pollutants: Minimize your exposure to environmental pollutants, such as dust, allergens, and air pollution. Use air purifiers, avoid smoking areas, and take measures to reduce indoor allergens.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eat a nutritious diet, exercise regularly, and maintain a healthy weight. Good overall health can help support respiratory function and reduce the risk of respiratory conditions that may cause rales.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to keep your respiratory system moist and help thin out mucus, making it easier to clear your airways and reduce the risk of developing rales.
- Follow prescribed medication and treatment plans: If you have a respiratory condition that can lead to rales, make sure you follow your prescribed medication and treatment plan as directed by your healthcare professional.
- Practice proper breathing techniques: Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can help improve lung capacity, promote relaxation, and enhance overall respiratory health.
- Use a humidifier: A cool mist humidifier can add moisture to the air, which can help soothe the airways and reduce the risk of dryness and irritation that can contribute to the development of rales.
- Avoid triggers: Identify any triggers that worsen your respiratory symptoms and try to avoid them. This may include allergens, strong scents, or irritants that can cause inflammation and lead to rales.
- Seek medical attention: If you notice persistent or worsening symptoms, such as increased breathlessness, chest pain, or a change in the character of rales, seek medical attention promptly for a thorough evaluation and proper management.
It is important to note that while these prevention strategies and home remedies can be beneficial, they do not replace medical advice or treatment. If you have a respiratory condition or experience persistent or concerning symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and management.
By taking proactive steps to maintain good respiratory health and managing underlying conditions effectively, you can potentially reduce the risk of rales and improve your overall respiratory well-being.
Conclusion
Rales, or crackling lung sounds, can serve as important indicators of underlying respiratory conditions. They can provide valuable diagnostic clues and assist healthcare professionals in formulating effective treatment plans. Understanding the types, characteristics, causes, and diagnostic methods for rales is essential in accurately identifying and managing the root cause of these abnormal lung sounds.
From fine crackles to coarse crackles, the quality and distribution of rales can vary depending on the specific condition affecting the respiratory system. Diagnostic methods such as chest X-rays, pulmonary function tests, and blood tests assist in identifying the underlying causes of rales.
Treatment options for rales are tailored to address the root cause and severity of the respiratory condition. These options range from antibiotics for infections to bronchodilators or corticosteroids to improve airway obstruction and inflammation. Equally important are preventive measures and home remedies, including maintaining good respiratory hygiene, quitting smoking, staying hydrated, and following prescribed medications and treatment plans.
It is crucial to note that while prevention and home remedies can be beneficial, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment. Every individual is unique, and an accurate assessment ensures appropriate management.
In conclusion, rales are not just ordinary sounds heard during breathing; they are important signs of potential respiratory issues. By understanding the various aspects of rales and collaborating with healthcare professionals, individuals can take charge of their respiratory health, leading to better outcomes and an improved quality of life.