Home>Production & Technology>Sound>What Sound Do Coyotes Make


Sound
What Sound Do Coyotes Make
Published: December 17, 2023
Discover what sound coyotes make in this comprehensive guide. Learn about the various vocalizations and calls of coyotes and how they communicate.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
There’s something mystical and haunting about the sound of a coyote’s howl piercing the night. For many, it invokes a sense of mystery and a connection to the wild. But what exactly do coyotes sound like? In this article, we will explore the vocalizations of coyotes and dive into the various sounds they make.
As highly adaptable creatures, coyotes have managed to thrive in a wide range of habitats, from forests to deserts and even urban areas. They are known for their intelligence, agility, and remarkable ability to communicate with each other through a diverse repertoire of vocalizations.
Understanding the sounds of coyotes can provide valuable insights into their behaviors, social structures, and even their emotional states. By deciphering their vocalizations, scientists and researchers have been able to gain a deeper understanding of these elusive creatures.
So, if you’ve ever wondered about the different sounds that coyotes make and what they mean, you’re in the right place. From howling to yipping, barking to growling, we will cover it all in this comprehensive exploration of coyote sounds.
Basic Characteristics of Coyotes
Before diving into their vocalizations, let’s start with a brief overview of the basic characteristics of coyotes. Coyotes (Canis latrans) are medium-sized canines native to North and Central America. They are part of the same genus as wolves and domestic dogs, and they share many physical and behavioral traits with their relatives.
On average, adult coyotes weigh between 20 to 50 pounds and measure about 3 to 4 feet long, including their tail. They have a slender build with a pointed snout, erect ears, and a bushy tail. Coyotes also possess excellent vision, hearing, and sense of smell, which aid them in hunting and navigating their surroundings.
Coyotes are primarily crepuscular and nocturnal animals, meaning they are most active during the twilight hours and nighttime. They are highly adaptable and can survive in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, mountains, and even urban areas. Their diet is omnivorous, consisting of small mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, fruits, and vegetation.
These intelligent predators are known for their social structure, typically living in family groups called packs. A typical pack usually consists of a breeding pair, their offspring, and sometimes unrelated individuals. Within the pack, there is a hierarchy with an alpha male and female that lead and make important decisions for the group.
Now that we have a better understanding of the basic characteristics of coyotes, let’s delve into their vocalizations to uncover the intriguing world of coyote sounds.
Vocalizations of Coyotes
Coyotes are known for their wide range of vocalizations, which they use to communicate with each other, establish territory, and convey their intentions. Their vocal repertoire includes howling, yipping, yapping, barking, whining, growling, and various combinations of these sounds.
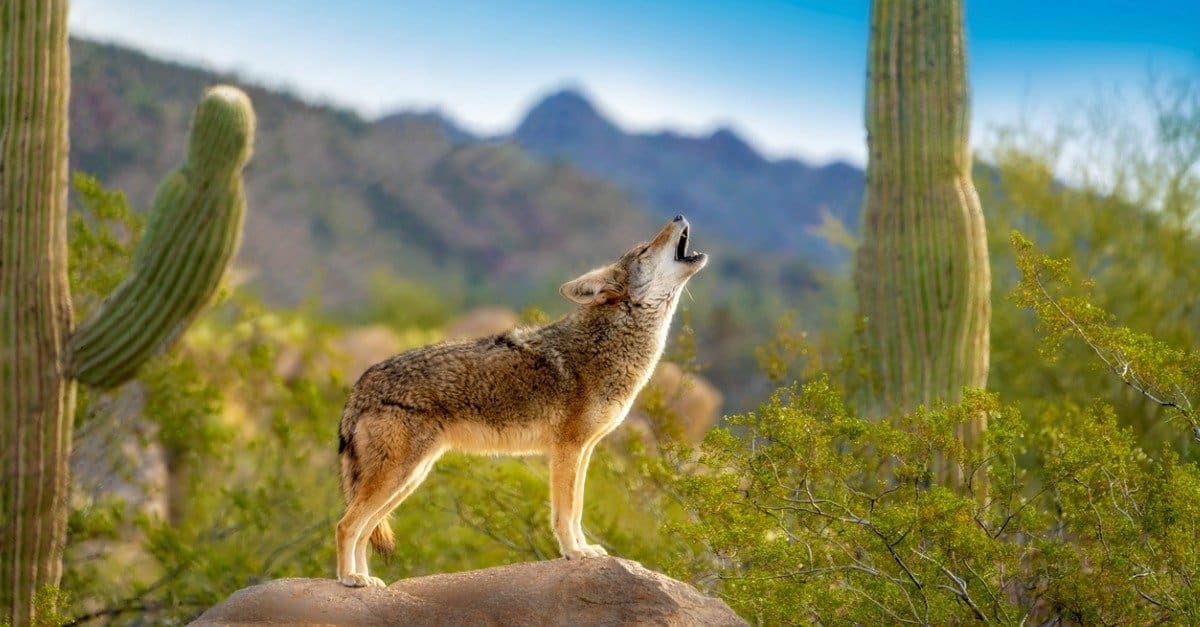
Howling is perhaps the most iconic coyote sound. It is a long, high-pitched vocalization that can carry for miles. Howling serves several purposes for coyotes, including communication with other pack members, territorial marking, and as a way to locate each other over long distances. It is also believed to serve as a declaration of presence, warning potential intruders to stay away.
Yipping and yapping are short, sharp barks or shrieks that coyotes often emit when excited or alarmed. These sounds are typically higher in pitch compared to howling and are often heard during social interactions or when coyotes are chasing prey. Yipping and yapping can also be an indication of the coyote’s playfulness or aggression.
Barking is another sound that coyotes utilize in their vocal repertoire. Unlike the deep and booming barks of larger canids like wolves, coyote barks are higher-pitched and have a distinct cadence. They are often employed as a means of communication within the pack, alerting others to potential danger or signaling their presence.
Whining and growling are vocalizations that coyotes use to convey different emotions. Whining is a softer, plaintive sound that can express submission or a need for attention. Growling, on the other hand, is a warning or defensive sound that suggests aggressiveness and a desire to protect territory or resources.
In addition to these common vocalizations, coyotes can produce other sounds such as huffing, squealing, and even a series of low-pitched woofs. These variations in sounds highlight the complexity of their communication and the rich variety of vocal expressions that coyotes are capable of.
Now that we’ve explored the different sounds coyotes make, let’s delve deeper into the reasons behind their vocalizations.
Howling
When it comes to coyote vocalizations, the haunting sound of their howl often comes to mind. Howling is an iconic and integral part of coyote communication, serving various important functions for these canines.
One primary purpose of howling is to establish and maintain territory. By vocalizing their presence, coyotes can communicate to other nearby packs about the boundaries of their territory, preventing conflicts and minimizing the chances of encounters between rival groups.
Howling is also used as a means of social bonding within the pack. It helps to strengthen the familial ties between individuals and reinforce their sense of unity. Pack members often join in a chorus of howling, with each individual contributing their unique vocalizations, creating a symphony of voices that resonate across the landscape.
Furthermore, howling enables coyotes to communicate their location and coordinate their movements. Since coyotes have large home ranges, howling helps them stay connected with their pack members when they are dispersed over a wide area. It serves as a way of calling each other back together, ensuring that the group remains cohesive.
During the breeding season, howling takes on an additional significance. It acts as a vocal advertisement for potential mates, allowing males and females to locate each other and establish breeding partnerships. The pitch, duration, and complexity of a coyote’s howl can provide indicator their age, health, and vitality, influencing the choice of a mate.
It is also important to note that howling is not limited to territorial purposes and social bonding. Coyotes may howl in response to certain environmental stimuli or events. For example, they may howl in celebration after successfully catching prey or to alert pack members of the presence of a predator or a potential threat in the area.
The captivating sound and soulful nature of coyote howls have long fascinated humans and played a role in folklore and legends. They evoke a sense of the wild and hold a certain beauty that is deeply ingrained in our imaginations.
Now that we’ve explored the significance of howling, let’s move on to the next vocalization: yipping and yapping.
Yipping and Yapping
Besides howling, coyotes are also known for their distinctive yipping and yapping sounds. These short, sharp vocalizations serve different purposes and often indicate the coyotes’ level of excitement or agitation.
Yipping and yapping are commonly heard during social interactions among coyotes, especially during playtime. Young coyotes, known as pups, are particularly known for their playful nature and high-pitched yips. These vocalizations help in strengthening bonds and maintaining social harmony within the pack. It’s not uncommon to hear a chorus of yips and yaps as the coyote pups engage in romping and mock hunting, honing their physical and social skills.
Yipping and yapping can also serve as alarm calls. When coyotes sense danger or encounter potential threats, they emit rapid, sharp barks or shrieks to alert other members of the pack. These vocalizations can signify a warning and prompt a coordinated response, allowing the coyotes to either defend their territory or retreat to safety. It’s their way of communicating that there’s potential danger nearby and that caution should be exercised.
In addition, yipping and yapping can be heard during hunting activities. Coyotes have a diverse diet that includes small mammals, birds, and even insects. When a group of coyotes is in pursuit of prey, their excitement and adrenaline can manifest in these high-pitched vocalizations. The yips and yaps serve as a way to synchronize their efforts, communicate their intentions, and possibly even confuse and disorient their prey.
It’s important to note that the pitch, intensity, and rhythm of yipping and yapping can vary depending on the individual coyote and the specific situation. For instance, a lone coyote may yip and yap in a different manner compared to a group of coyotes engaging in play or hunting activities.
The distinct sounds of yipping and yapping add an energetic and dynamic element to the coyotes’ vocal repertoire. They reveal the social nature of these canines and highlight their ability to communicate and coordinate with each other in various contexts.
Now let’s move on to another vocalization: barking.
Barking
Barking is a vocalization commonly associated with dogs, but coyotes are also known to use barking as a means of communication. However, coyote barks have distinct characteristics that set them apart from the deep and resonant barks of larger canids like wolves.
Coyotes use barking as a way to communicate within their pack and with other coyotes in their vicinity. The barks can vary in pitch and duration, and they serve different purposes depending on the context. One of the primary functions of barking is to alert pack members to potential dangers or threats in the area. When a coyote senses something unusual or perceives a possible threat, it will emit a series of rapid and repetitive barks to signal the situation. This helps the rest of the pack to stay vigilant and respond accordingly.
Barking can also serve as a vocalization to establish dominance or assert territorial boundaries. When two rival packs of coyotes come into contact with each other, barking can be used as a form of vocal confrontation. The intensity and duration of the barks may indicate the coyotes’ willingness to defend their territory and discourage intruders. It serves as a territorial declaration, letting other coyotes know that this particular area is already claimed and should be avoided.
In some cases, barking can be a form of communication between pack members, especially during social interactions or when coordinating hunting activities. Barks can signify a variety of messages, such as signaling the presence of potential prey, indicating a change in direction during a chase, or simply expressing excitement or eagerness to engage in a particular activity.
It’s worth noting that coyote barks can also have a more playful tone. When engaging in playful behaviors, such as chasing each other or engaging in mock hunting, coyotes may intersperse their play with playful barks. These barks are typically shorter, higher-pitched, and accompanied by enthusiastic body language.
Barking is just one of the many vocalizations that coyotes employ, showcasing their ability to communicate and convey different messages within their social groups and to other coyotes in their environment. It adds yet another fascinating layer to the rich vocal repertoire of these intelligent canines.
Now, let’s explore the vocalizations of whining and growling.
Whining and Growling
Whining and growling are two distinct vocalizations that coyotes use to convey various emotions and intentions, showcasing the complexity of their communicative abilities. These sounds provide insights into the emotional states and social dynamics within coyote packs.
Whining is a softer and more plaintive vocalization, often expressing submission or a need for attention. Coyotes may whine when they are seeking reassurance or when they are in a subordinate position within the pack’s hierarchy. It can be a form of communication to elicit empathy and support from other pack members. Whining can also occur during social interactions, such as during greetings or when soliciting food from dominant individuals.
Growling, on the other hand, is a warning or defensive vocalization. When a coyote growls, it is expressing aggression or a desire to protect its territory, resources, or pack members. Growling is often accompanied by other body language cues, such as bared teeth and a stiff posture. It serves as a clear signal to potential threats or intruders to back off or face the consequences. Growling can occur during territorial disputes between rival coyote packs or when defending food sources.
Both whining and growling can be heard during social interactions within the pack. Whining and growling can be part of the intricate social dynamics of coyote packs as individuals establish and maintain their roles within the group. It helps to reinforce the social hierarchy and ensure cooperation and order among pack members.
It’s important to note that the context in which whining and growling occur can influence their meaning. Whining, for example, can also serve as a form of communication between adult coyotes and their young pups, expressing care and nurturing. Growling can range in intensity from a low warning growl to a more aggressive and confrontational growl, depending on the perceived threat level.
Understanding the various vocalizations, including whining and growling, provides valuable insights into the communication and social dynamics of coyotes. It underscores their ability to convey complex emotions and maintain social harmony within their pack.
Now, let’s explore some other intriguing sounds that coyotes produce.
Other Coyote Sounds
In addition to howling, yipping, yapping, barking, whining, and growling, coyotes are capable of producing a range of other intriguing sounds. These sounds further showcase the versatility and complexity of their vocalizations.
One notable sound that coyotes commonly make is a series of low-pitched woofs. These woofs are often heard during social interactions within the pack and serve as a way to communicate with one another. They can indicate a range of emotions, such as excitement, camaraderie, or even a gentle warning to maintain distance.
Coyotes can also emit a huffing sound, which is a short, sharp exhalation of breath. Huffing can signify a sense of curiosity or alertness. It is often heard when a coyote encounters something unfamiliar or interesting in its environment.
Another sound that coyotes may produce is a high-pitched squeal or scream. This sound is typically heard during intense territorial disputes or aggressive encounters with other animals. It is a vocalization that signifies a heightened state of agitation or distress and is often accompanied by aggressive posturing and body language.
Furthermore, coyotes can make various vocalizations in combination, creating unique and complex sequences of sounds. For example, they may combine howling with yipping or yapping, resulting in a symphony of vocal expressions that carry different meanings depending on the context and situation.
Each individual coyote may have its own unique vocal style, contributing to the diversity of sounds within a pack. This individuality allows for differentiation and recognition among pack members, further enhancing their communication and social bonds.
Exploring the variety of sounds that coyotes can produce highlights their adaptability and ability to convey different messages depending on their circumstances. These sounds add depth and intrigue to their vocal repertoire, and studying them provides valuable insights into their behavior and social dynamics.
Now, let’s uncover some of the reasons behind coyote vocalizations.
Reasons for Coyote Vocalizations
Coyotes are highly vocal animals, utilizing a wide array of vocalizations to communicate with each other and convey important information. These vocalizations serve various purposes and play a crucial role in the social dynamics and survival of coyote packs.
One key reason for coyote vocalizations is territorial communication. Howling, barking, and other vocalizations are used to establish and defend their territory. By marking their presence audibly, coyotes communicate to other packs or individuals that a particular area is already claimed, reducing the likelihood of confrontations. This territorial communication helps maintain boundaries and avoids unnecessary conflicts.
Coyote vocalizations also facilitate social cohesion within the pack. Howls, yips, and yaps are used for pack coordination, allowing individual members to locate each other, especially when they are dispersed over a wide area during hunting or exploration. Vocalizations serve as a means of calling pack members back together, ensuring unity and facilitating cooperative behaviors.
Breeding partnerships and mate selection are other important reasons for vocalizations. During the breeding season, coyotes use vocalizations to attract potential mates. Howls and other sounds help individuals locate each other and indicate their availability and reproductive fitness. The pitch, intensity, and duration of vocalizations can convey important information about an individual’s age, health, and genetic quality.
Specific vocalizations, such as barks, growls, and even aggressive screams, function as defensive and aggressive signals. Coyotes use these vocalizations to warn off intruders, protect their territory, or defend valuable resources like food or den sites. Aggressive vocalizations communicate a willingness to engage in confrontation, providing a clear warning to other animals to keep their distance.
Additionally, vocalizations play a role in social bonding and maintaining social harmony within the pack. Whining, huffing, and other softer vocalizations can convey submission or a need for attention, strengthening the social bonds between individuals. These vocalizations help establish and reinforce the hierarchy within the pack and promote cooperation and cooperation.
Overall, vocalizations are essential for communication and coordination among coyotes. They allow these intelligent canines to convey information about their presence, intentions, emotions, and social dynamics. By vocalizing, coyotes can navigate their social and ecological landscapes more effectively and increase their chances of survival.
Now, let’s summarize our findings on coyote vocalizations.
Conclusion
Coyotes, with their diverse vocal repertoire, demonstrate their ability to communicate, coordinate, and convey a range of emotions and messages. From the iconic howling to the playful yipping and yapping, the warning barks, and the submissive whines, coyote vocalizations serve essential purposes in their social dynamics and survival.
Through vocalizations, coyotes establish and defend their territories, coordinate movements within packs, and attract potential mates during the breeding season. They also use vocalizations to express submission, aggression, excitement, playfulness, and distress.
Understanding coyote vocalizations provides valuable insights into their behaviors, social structures, and emotional states. It allows us to appreciate the intricate communication methods of these highly adaptable canines and underscores the importance of vocalizations in maintaining social cohesion within their pack.
Moreover, coyote vocalizations reflect their adaptability to various habitats, from forests to deserts and even urban areas. These vocalizations enable them to thrive and survive in diverse environments, helping them navigate their surroundings, find food, protect their territory, and avoid potential threats.
As we listen to the haunting howls, the energetic yips, and the commanding barks of coyotes, we are reminded of their place in the natural world and the important role they play in maintaining ecological balance.
So, the next time you hear the captivating sound of a coyote’s call, take a moment to appreciate the intricate complexity and beauty of their vocalizations—nature’s symphony in motion.