Home>Production & Technology>Tempo>How To Read Tempo Of Sheet Music
Tempo
How To Read Tempo Of Sheet Music
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn how to read the tempo of sheet music and understand the pace and speed of a musical piece. Enhance your musical knowledge with our helpful guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to reading sheet music, one crucial element that musicians need to understand is tempo. Tempo refers to the speed of a musical piece or the pace at which it is performed. It plays a crucial role in conveying the mood, feel, and emotion of a composition.
Understanding tempo is essential for musicians of all levels, whether you’re a beginner just starting to read sheet music or an advanced player looking to fine-tune your performance. By grasping the concept of tempo and how it is represented in sheet music, you can enhance your musical interpretation and create a more captivating performance.
This article will guide you through the basics of tempo and how to read it accurately in sheet music. We will explore the different types of tempo markings, techniques for counting beats, and using tools like a metronome to stay on tempo. Additionally, we’ll provide helpful tips for practicing and reading tempo effectively.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to read and interpret tempo in sheet music, enabling you to bring your musical performances to life with precision and expression.
Understanding Tempo
Tempo is a fundamental element in music that determines the speed and rhythmic feel of a musical piece. It sets the pace for musicians and serves as a guide for the overall timing and expression of the music.
Tempo is indicated in sheet music through various markings, symbols, and words that convey the desired speed of the piece. These markings give musicians a clear indication of how fast or slow they should play the music.
Understanding tempo goes beyond simply knowing the indicated speed. It involves capturing the essence and character of the piece, expressing the intended emotion, and conveying the composer’s initial vision.
Tempo is subjective and can be interpreted differently by different musicians. It is not just about playing the notes at a specific speed but also about the controlled execution, dynamics, and nuances that bring out the essence of the music.
As a musician, it is important to have a good sense of time and rhythm and to be able to internalize the tempo. This allows you to stay in sync with other musicians and create a cohesive and well-coordinated performance.
By understanding tempo, you can effectively communicate and collaborate with other musicians, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and playing in sync.
Tempo also plays a crucial role in the overall structure and interpretation of a piece. It influences the phrasing, articulation, and emphasis given to certain musical passages, creating a dynamic and expressive performance.
To fully grasp and interpret the tempo of a piece, it is important to consider other musical elements such as the time signature, note values, and markings like accents and dynamics. These elements work together to create a cohesive musical experience.
By developing a deep understanding of tempo, musicians can bring out the essence and emotion of a piece, captivating listeners and creating memorable performances.
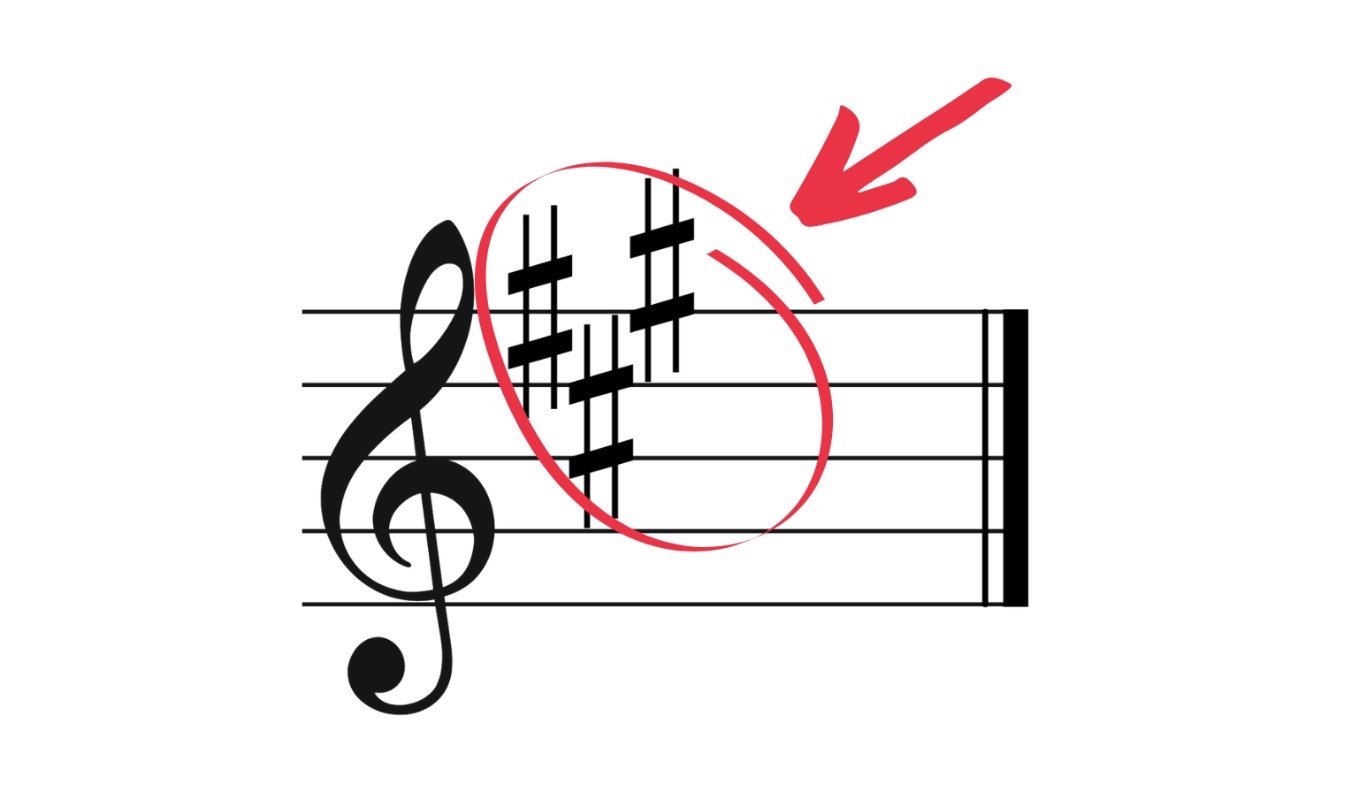
Types of Tempo Markings
Tempo markings are notated in sheet music using various symbols, words, or abbreviations to indicate the desired speed of the music. These markings give musicians a clear indication of the tempo they should follow when performing the piece. Here are some of the most commonly used tempo markings:
- Grave: This marking indicates a very slow and solemn tempo. It is often used for more serious and introspective pieces.
- Largo: Largo signifies a broad and slow tempo. It is slower than adagio and is often associated with expressive and lyrical music.
- Adagio: Adagio represents a slow tempo. It encourages a relaxed and unhurried approach to the music, allowing for expressive phrasing and emotional depth.
- Andante: Andante refers to a moderately slow tempo. It suggests a walking pace and is often associated with flowing and lyrical music.
- Moderato: Moderato signifies a moderate tempo. It is a versatile marking that can be applied to a wide range of musical styles.
- Allegro: Allegro indicates a brisk and lively tempo. It is a common marking for energetic and joyful music.
- Presto: Presto represents a very fast and spirited tempo. It requires technical agility and precision in execution.
In addition to these primary tempo markings, there are also variations and combinations that further define the speed and character of the music. For example:
- Accelerando: This means gradually increasing the tempo of the music.
- Ritardando: Ritardando denotes gradually slowing down the tempo of the music.
- Rallentando: Rallentando is similar to ritardando as it implies a gradual decrease in speed.
- Poco a poco: This means “little by little” and is often used to indicate a gradual change in tempo or dynamic level.
It’s important to remember that tempo markings are not precise measurements of BPM (beats per minute). They serve as general guidelines, giving musicians a sense of the desired speed and character of the music.
By paying attention to these tempo markings and using them as a reference, musicians can correctly interpret the feel and mood intended by the composer, resulting in a more cohesive and engaging musical performance.
Counting Beats in Sheet Music
When reading sheet music, one of the key skills for musicians is the ability to accurately count the beats. Counting beats helps to maintain a steady rhythm, stay in sync with other musicians, and accurately interpret the tempo of the music. Here are some tips on how to effectively count beats:
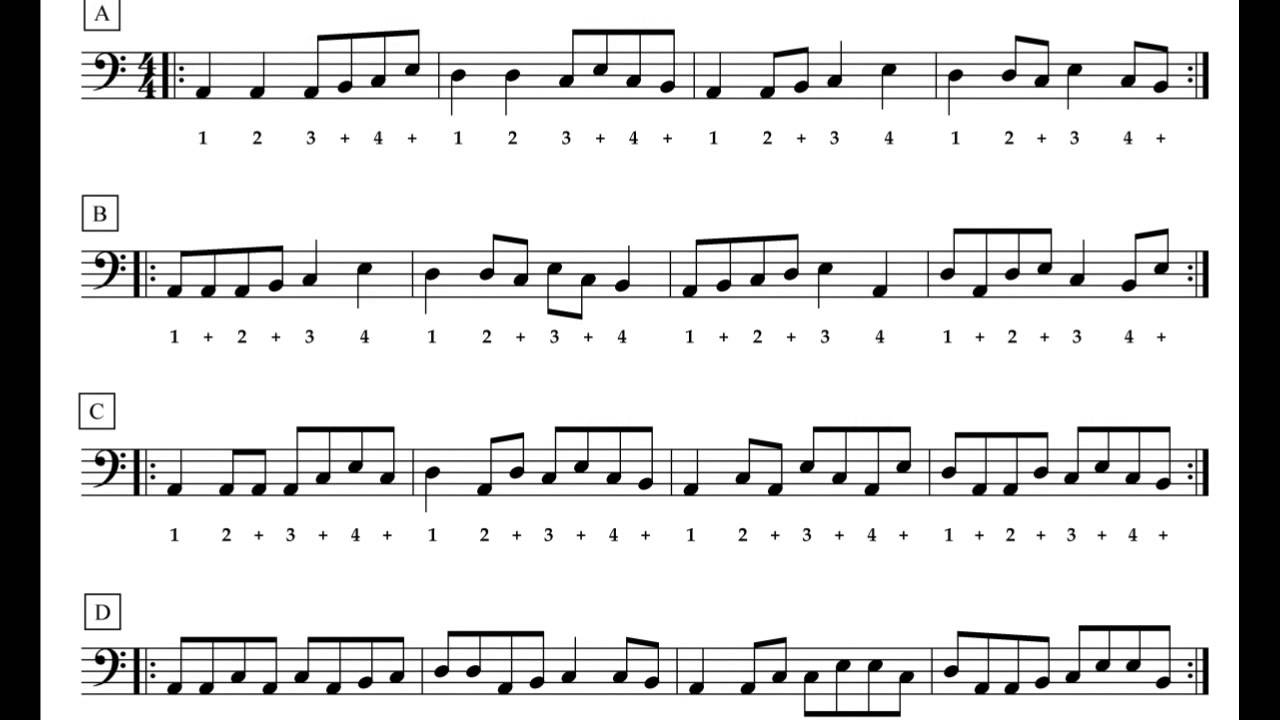
- Understand the time signature: The time signature is indicated at the beginning of the piece and represents the number of beats per measure and which note value receives one beat. For example, a 4/4 time signature indicates four beats per measure, with the quarter note receiving one beat.
- Identify the strong beats: In most time signatures, the first beat of each measure is considered the strongest beat. It usually receives an accent or emphasis. Recognizing these strong beats can help you maintain a steady rhythm throughout the piece.
- Subdivide the beats: To accurately count beats, it is helpful to subdivide them into smaller note values. For example, if the time signature is 4/4, and the quarter note receives one beat, you can further divide each beat into two eighth notes, counting “1 and 2 and 3 and 4 and” for each measure.
- Tap or clap along: Physically tapping or clapping along with the music can reinforce the sense of rhythm and help you internalize the beats. This tactile feedback can enhance your ability to count beats and maintain a steady tempo.
- Use a metronome: A metronome is a valuable tool for practicing and counting beats accurately. It provides a consistent and precise beat to follow, helping you develop a sense of timing and control. Set the metronome to the desired tempo indicated in the sheet music and practice counting along with it.
- Practice slowly: When learning a new piece, start by practicing at a slower tempo. This allows you to focus on counting the beats accurately and developing a strong sense of rhythm. Gradually increase the tempo as you become more comfortable.
- Listen to recordings: Listening to professional recordings of the piece you are learning can provide valuable insight into how the beats are counted and interpreted. Pay attention to how the musicians emphasize certain beats and phrases, and try to emulate their rhythmic accuracy.
By mastering the skill of counting beats in sheet music, you can improve your timing, precision, and overall musicality. It will enable you to navigate complex rhythms, play in sync with other musicians, and accurately convey the intended tempo of the piece.
Using a Metronome
A metronome is a valuable tool for musicians when it comes to practicing and maintaining a steady tempo. It provides a consistent and precise beat, helping musicians develop rhythm, timing, and precision in their performance. Here are some tips on how to effectively use a metronome:
- Select the appropriate tempo: Set the metronome to the desired tempo indicated in the sheet music. Start at a comfortable tempo and gradually increase it as you become more proficient.
- Start with a simple rhythm: If you’re new to using a metronome, begin with a simple rhythm. For example, set the metronome to a steady quarter-note beat and practice playing along with it. Focus on staying in sync with the metronome and maintaining a consistent rhythm.
- Be aware of accents and dynamics: Pay attention to any accents or dynamic markings in the sheet music. Adjust your playing to emphasize these markings while following the beat of the metronome. This will enhance the musical expression and add dynamic variation to your performance.
- Subdivide the beats: If the music has complex rhythms, use the metronome to help you subdivide the beats and maintain accuracy. Set the metronome to a faster tempo and count or play along with the subdivisions, ensuring that you stay in sync with the beat.
- Experiment with different subdivisions: Some metronomes offer the option to change the subdivision, allowing you to practice different rhythmic patterns. Use this feature to challenge yourself and improve your rhythmic versatility.
- Gradually increase the tempo: As you become more comfortable with a particular tempo, gradually increase the speed on the metronome. This will help you build speed and agility while maintaining control and accuracy.
- Practice with different time signatures: Use the metronome to practice different time signatures by adjusting the beats per minute and note values. This will enhance your ability to read and interpret sheet music in various rhythmic contexts.
- Record and review your practice: Record yourself practicing with the metronome and listen back to identify any areas where you might be rushing or dragging. This will help you pinpoint rhythmical inaccuracies and make necessary adjustments in your playing.
Using a metronome consistently in your practice sessions will strengthen your sense of time, improve your rhythmic accuracy, and enhance your overall musicality. Incorporate it as a regular practice tool and see the positive impact it has on your performance.
Tips for Practicing and Reading Tempo
Mastering the art of reading and interpreting tempo in sheet music requires practice and attention to detail. Here are some valuable tips to help you improve your tempo reading skills:
- Start with a clear understanding of the tempo marking: Before diving into the piece, take a moment to fully grasp the tempo marking indicated in the sheet music. Understand the specific speed and character that the composer intended.
- Listen to recordings: Listening to professional recordings of the piece can provide valuable insight into how the tempo should be interpreted. Pay attention to the subtle nuances and dynamic changes in the performance, and try to replicate them in your own playing.
- Practice with a metronome: Using a metronome can help strengthen your sense of timing and accuracy. Set the metronome to the indicated tempo and practice playing along with it. This will help you develop a precise internal clock and maintain a consistent tempo throughout the piece.
- Focus on the relationship between the melody and the accompaniment: Pay attention to the interplay between the melody and the accompanying parts. Understand how the tempo affects the dynamics and balance between these elements, and strive to achieve a cohesive and expressive performance.
- Use visual cues in the sheet music: Look for visual cues in the sheet music that can help guide you through the tempo changes. This could include tempo markings, metronome markings, or words that describe the desired feel or mood of the music. Use these cues as a reference point to stay on track with the tempo.
- Practice slow and deliberate movements: When learning a new piece, start by practicing at a slower tempo. This allows you to focus on accuracy and understanding the tempo markings. As you become more comfortable, gradually increase the speed while maintaining control and precision.
- Internalize the pulse: As you practice, aim to internalize the pulse and feel of the tempo. This will allow you to flow with the music naturally and maintain a consistent interpretation throughout the piece.
- Experiment with different interpretations: While it’s important to understand and follow the indicated tempo, don’t be afraid to experiment with different interpretations. Play around with subtle variations in tempo, emphasizing different beats or phrases to bring out your own musicality and expression.
Remember, reading tempo in sheet music is not just about playing at a specific speed. It involves understanding the character, feel, and emotion of the music, and conveying that through your playing. With consistent practice and attention to detail, you can master the art of reading tempo and deliver captivating performances.
Conclusion
Understanding and reading tempo in sheet music is a crucial skill for musicians of all levels. By grasping the concept of tempo and how it is represented in sheet music, you can bring out the essence and emotion of a musical piece, enhancing your musical interpretation and performance.
In this article, we have explored the fundamentals of tempo, delving into the different types of tempo markings and how to accurately count beats in sheet music. We have also discussed the importance of using a metronome and provided tips for practicing and reading tempo effectively.
Remember, tempo is not just about playing at a specific speed; it is about capturing the mood, feel, and expression of the music. As you develop your tempo reading skills, seek to internalize the rhythm, pay attention to the nuances in the sheet music, and incorporate your own musicality into your performances.
Consistent practice, attention to detail, and active listening to professional recordings will help you become proficient in reading and interpreting tempo. Embrace the challenges and enjoy the journey of discovering how tempo creates depth and meaning in your musical performances.
So, continue exploring different pieces, counting the beats, experimenting with interpretations, and immerse yourself in the world of tempo. With time and dedication, you will develop a strong sense of rhythm and an instinctive ability to bring out the true essence of the music.











