Home>Production & Technology>Tempo>How To Write Tempo In Music 8 Timer


Tempo
How To Write Tempo In Music 8 Timer
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the essential techniques for writing tempo in music with our comprehensive 8 timer guide. Master the art of controlling speed and rhythm for captivating compositions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of music, where rhythm and melody come together to create beautiful harmonies. One crucial element that drives the energy and flow of a piece of music is tempo. Tempo refers to the speed at which a musical composition is performed, dictating the pace and rhythm of the notes.
Understanding tempo is essential for musicians, composers, and music lovers alike. It provides structure, emotion, and dynamics to a piece of music, allowing the performers to convey the intended mood and message effectively. Whether you are a beginner learning an instrument, a composer composing a new piece, or simply a listener appreciating the sounds, understanding tempo will greatly enhance your musical experience.
In this article, we will explore the concept of tempo in music, its importance, and how it is written and notated. We will also offer some practical guidelines and common tempo markings to help you accurately convey the desired tempo in your music. So, let’s dive in and unravel the fascinating world of tempo in music!
Understanding Tempo in Music
Tempo, in music, refers to the speed at which a musical composition is performed. It determines how fast or slow a piece of music is played, providing a sense of rhythm and pulse. The tempo of a song sets the overall mood and energy, influencing the emotions and impact it has on the listener.
Tempo is typically measured in beats per minute (BPM), which represents the number of beats or pulses occurring within a minute. The higher the BPM, the faster the tempo, and vice versa. For example, a fast-paced dance track may have a BPM of 120 or more, while a slow ballad might have a BPM of 60.
Understanding tempo goes beyond just knowing the speed of a song. It involves recognizing the relationship between the different elements of a piece and how they contribute to its overall feel and expression. Tempo affects the timing and duration of notes, the dynamics and phrasing of a performance, and the interaction between musicians.
Tempo is also closely related to the concept of rhythm. While tempo refers to the speed, rhythm refers to the pattern of different note durations and their placement within a musical composition. The tempo establishes the overall framework, while the rhythm fills it with intricacy and variation.
When listening to music, you can perceive the tempo by tapping your foot or nodding your head along with the beat. This physical response to the music is a natural way of connecting with the tempo and feeling its pulse. By paying attention to the tempo, you can better appreciate the artistic intention of the composer and the musicians interpreting the piece.
Next, let’s explore why tempo is such a vital element in the world of music.
Importance of Tempo in Music
Tempo plays a crucial role in music, affecting the overall feel, mood, and impact of a composition. It is the driving force that sets the pace, rhythm, and energy, allowing musicians and listeners to connect with the music on a deeper level. Here are some key reasons why tempo is important in music:
- Expressing Emotion: Tempo is a powerful tool for expressing emotions in music. A fast tempo can create a sense of excitement, energy, and exhilaration, while a slow tempo evokes feelings of calmness, introspection, and melancholy. By manipulating the tempo, composers and performers can effectively convey a specific mood or emotional message to the audience.
- Creating Intensity: The tempo of a piece can greatly impact its intensity. A fast and relentless tempo can create a sense of urgency and intensity, while a slow and steady tempo builds tension and anticipation. The manipulation of tempo throughout a composition can enhance dramatic moments, build climaxes, and create moments of release.
- Establishing Groove and Feel: Tempo is vital for establishing the groove and feel of a piece of music. Different genres have their own characteristic tempos that define their unique styles and rhythms. For example, a lively salsa relies on a fast tempo to create its infectious dance rhythms, while a slow blues tune thrives on a relaxed and laid-back tempo.
- Aiding Performance: Tempo acts as a guide for musicians during a performance. It provides a common reference point, ensuring that all performers stay in sync and maintain a cohesive musical experience. It helps musicians establish the correct timing, dynamics, and phrasing, allowing for a seamless and polished performance.
- Enhancing Listening Experience: Understanding tempo can greatly enhance the listening experience for music enthusiasts. By appreciating the tempo of a piece, listeners can connect more deeply with the rhythm and flow of the music. It allows them to tap into the emotions and intentions of the composer, resulting in a richer and more engaging musical experience.
Overall, tempo is an essential element in music, influencing the emotional impact, intensity, and overall effectiveness of a composition. It adds depth, character, and movement to the music, making it an integral part of the artistic expression and communication between the composer, performers, and listeners.
Different Notation Systems for Tempo
When it comes to notating tempo in sheet music, various systems have been developed over the years to provide composers and performers with a standardized way of indicating the desired speed. These notation systems help to ensure consistency and clarity in communicating tempo instructions. Here are some of the commonly used notation systems for tempo:
- Italian Terms: The Italian language has been traditionally used in music notation to indicate tempo. Terms like “adagio” (slow), “allegro” (fast), and “presto” (very fast) give a general idea of the tempo to be followed. Italian terms are descriptive, conveying the overall character and mood of the piece.
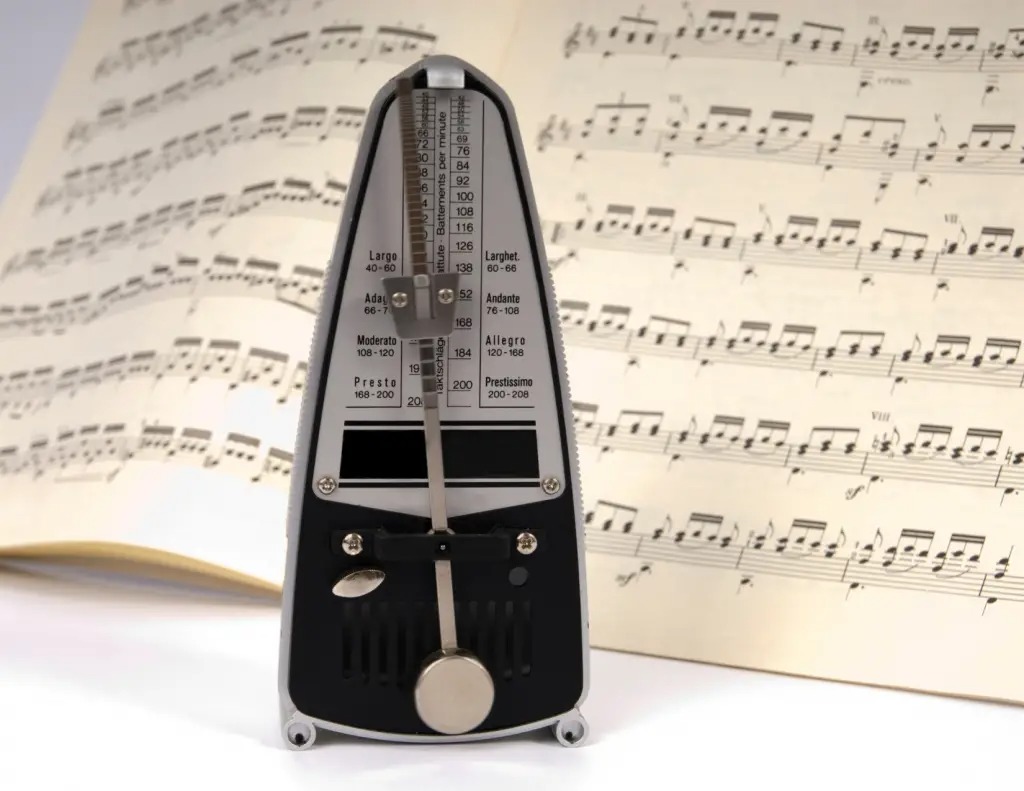
- Metronome Markings: Metronome markings provide a more precise indication of tempo by specifying the number of beats per minute (BPM). A metronome is a device that produces a consistent audible beat, helping musicians maintain a steady tempo. For example, a metronome marking of 120 BPM indicates that there should be 120 beats in one minute.
- Beats Per Minute (BPM): The BPM system is commonly used for electronic music production and modern genres where precise synchronization is important. It indicates the number of beats or pulses occurring in one minute. BPM values can range from very slow (e.g., 60 BPM) to extremely fast (e.g., 200 BPM) depending on the style and genre of music.
- Tempo Text Instructions: In addition to Italian terms and metronome markings, composers may also provide text instructions to convey the desired tempo. For example, “Moderato” suggests a moderate tempo, while “Largo” indicates a slow and broad tempo. These text instructions provide further context and interpretation for the desired speed.
- Tempo Modifications: Sometimes, composers may include additional markings to modify the tempo within a piece. These include terms like “rallentando” (gradually becoming slower) or “accelerando” (gradually becoming faster). These modifications allow for subtle shifts in tempo, adding expressiveness and shaping the musical phrases.
It is important to note that different notation systems may be used in combination, depending on the composer’s preference and the specific requirements of the musical piece. Composers and performers should be familiar with these systems to accurately interpret and convey the intended tempo.
Next, let’s explore some guidelines for effectively writing tempo indications in music notation.
How to Write Tempo in Music
Writing tempo in music notation requires clear and concise indications to guide the performer’s interpretation. Here are some guidelines to consider when notating tempo:
- Italian Terms: When using Italian terms, choose a term that best conveys the desired speed and character of the music. For example, “andante” suggests a moderate walking tempo, while “presto” indicates a very fast tempo. Familiarize yourself with commonly used Italian terms and their corresponding tempos.
- Metronome Markings: If precise tempo indications are required, consider using metronome markings with the BPM value listed above the staff. This provides a specific and measurable indication of the desired tempo, ensuring consistency across performances.
- Text Instructions: In addition to Italian terms and metronome markings, you can provide textual instructions to offer more context and guidance. For instance, you may use phrases like “with energy” or “slow and mournful” to further convey the desired musical expression and interpretation.
- Consider the Style and Genre: The tempo should be appropriate for the style and genre of the music. Different genres, such as classical, jazz, or rock, have their own conventions for tempo markings. Consider studying the tempo markings commonly used in the specific genre you are working with.
- Expressive Markings: Use additional expressive markings to convey subtle changes in tempo. Terms like “ritardando” (gradually slowing down) or “accelerando” (gradually speeding up) can be incorporated to shape the phrasing and add nuance to the performance.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in tempo indications throughout the composition. Clearly establish the initial tempo marking and ensure subsequent tempo changes are clearly and accurately indicated to avoid confusion for the performer.
When writing tempo in music, it is important to consider the intentions of the composer and provide clear guidance to the performer. By using a combination of Italian terms, metronome markings, text instructions, and expressive markings, you can effectively convey the desired tempo and enhance the musical interpretation.
Now let’s explore some common tempo markings used in music notation.
Guidelines for Writing Tempo
When it comes to writing tempo in music notation, it’s important to follow certain guidelines to ensure clarity and consistency. Here are some guidelines to consider when indicating tempo:
- Choose the Right Notation: Determine the appropriate notation system for indicating tempo in your music. This could be Italian terms, metronome markings, or a combination of both. Consider the style, genre, and intention of the piece to select the most suitable notation.
- Specify BPM Range: When using metronome markings, provide a suggested BPM range if you want to allow for some flexibility in interpretation. This range can guide the performer without restricting the natural musical expression.
- Be Clear and Concise: Use clear and concise tempo indications to avoid confusion. Avoid using ambiguous terms or symbols that might be open to interpretation, as this can lead to inconsistencies in performance.
- Consider the Performer: Keep in mind the capabilities and limitations of the performer and choose a tempo that is appropriate for their comfort and skill level. While challenging tempos can push boundaries, it’s important to strike a balance that allows for a confident and controlled performance.
- Use Contextual Phrasing and Markings: Provide additional musical instructions or markings to help convey the desired expression and interpretation. These could include dynamics, articulation, or mood-related instructions that complement the indicated tempo.
- Check for Consistency: Ensure consistency in tempo indications throughout the music. Double-check that tempo changes are clearly marked and that they align with the musical context. Inconsistencies can lead to confusion and disrupt the flow of a performance.
- Consider Revisions: Be open to revising tempo indications after hearing the music performed. Sometimes the intended tempo might not translate well in practice, and adjustments may be necessary to facilitate a more natural and effective performance.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively communicate the desired tempo to performers and ensure a cohesive and expressive musical interpretation. Remember that tempo indications should provide guidance without overly restricting the artistic freedom of the performer.
Now let’s explore some common tempo markings used in music notation.
Common Tempo Markings
In music notation, various tempo markings are used to indicate the desired speed of a composition. These markings help performers understand the intended tempo and interpret the music accordingly. Here are some of the most common tempo markings:
- Grave: Very slow and solemn, often performed around 40-50 BPM.
- Largo: Very slow and broad, typically around 50-60 BPM.
- Adagio: Slow and leisurely, usually between 60-80 BPM.
- Andante: Moderately slow, suggesting a walking pace, commonly around 80-100 BPM.
- Moderato: Moderate tempo, neither too slow nor too fast, around 100-120 BPM.
- Allegro: Fast and lively, typically around 120-168 BPM.
- Vivace: Lively and quick, usually between 168-176 BPM.
- Presto: Very fast, often performed around 176-200 BPM.
- Accelerando: Gradually increasing the tempo.
- Ritardando: Gradually slowing down the tempo.
- Tempo Primo: Return to the original tempo after a tempo change.
These tempo markings provide a general indication of the desired speed, but keep in mind that they can be open to interpretation depending on the style and context of the music. It’s important to use your judgment and consider other musical expressions and markings to provide a more accurate interpretation of the desired tempo.
It’s worth noting that composers may go beyond these common tempo markings and provide more specific instructions or use unique terms to convey their intent. As a musician or performer, it’s crucial to fully understand the composer’s indications and follow their guidance to bring the music to life.
Now that we’ve explored common tempo markings, let’s move on to some tips for writing accurate tempo markings.
Tips for Writing Accurate Tempo Markings
When writing tempo markings in music notation, it’s important to provide clear and accurate indications that effectively communicate the desired speed of the composition. Here are some tips to help you write accurate tempo markings:
- Listen and Feel the Music: Immerse yourself in the music and listen carefully to understand the natural flow and tempo. Pay attention to the rhythmic patterns, melodic phrases, and overall character of the piece. This will help you accurately capture and convey the intended tempo.
- Consider the Context: Take into account the style, genre, and mood of the music. Different musical genres have their own conventions and expectations for tempo. Consider how the tempo affects the overall musical expression and align it with the intended emotion and atmosphere.
- Use Descriptive Language: If using Italian terms or other descriptive notations, choose words that vividly convey the desired tempo. Consider the connotations associated with different terms and select the one that best represents the character and pace of the music.
- Consult a Metronome: Utilize a metronome to accurately measure the tempo and provide specific BPM markings. Practice playing or conducting the music with the metronome to ensure the indicated tempo is realistic and achievable.
- Consider Technical Ability: Take into account the technical abilities of the performers or musicians who will be interpreting the music. Ensure that the chosen tempo allows for a comfortable and controlled performance without sacrificing musicality.
- Use Additional Descriptors: Supplement the tempo markings with descriptive phrases or instructions to provide more context and guidance. This can include adjectives like “briskly” or “with a relaxed feel” that help shape the interpretation of the tempo.
- Double-Check for Consistency: Review the entire composition for consistency in tempo markings. Make sure that tempo changes are clear and accurately indicated, avoiding sudden shifts that might confuse performers. Consistency will help maintain the overall flow and coherence of the music.
- Consider the Performer’s Interpretation: Trust that performers will bring their own artistic interpretation to the music. While providing tempo markings is important, allow room for performers to infuse their own musical expression within the given parameters.
By following these tips, you can effectively write accurate tempo markings that enable performers to understand and embody the desired speed and character of the music. Clear and precise tempo indications contribute to a cohesive and engaging performance.
Now that you’re equipped with these tips, you’ll be able to confidently notate the tempo in your music and guide performers to bring your compositions to life.