Home>Devices & Equipment>Streaming>What Format Do Streaming Sites Convert Your Music To?


Streaming
What Format Do Streaming Sites Convert Your Music To?
Published: March 8, 2024
Learn about the music format conversion process on streaming sites. Understand how streaming services convert your music files for optimal playback. Discover the impact of streaming format on audio quality.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When you hit play on your favorite streaming platform, have you ever wondered what happens behind the scenes to deliver your music seamlessly? The answer lies in the intricate process of converting audio files into specific formats that can be streamed across various devices. This conversion is crucial for ensuring that your music sounds just as captivating as the artist intended, regardless of the device you're using.
Streaming sites utilize a range of audio formats to cater to the diverse needs of their users. Understanding these formats and the conversion process sheds light on the technology that underpins our modern music consumption. From the widely used MP3 to the high-fidelity FLAC, each format has its own unique characteristics that impact the quality of the audio you hear.
In this article, we will delve into the world of audio formats and explore how streaming sites convert your music to make it accessible across different platforms. We will also examine the implications of these conversions on the sound quality, providing insights that can help you appreciate the intricacies of the music streaming experience. So, let's embark on a journey through the digital realm of audio formats and unravel the magic that brings your favorite tunes to life on your chosen streaming service.
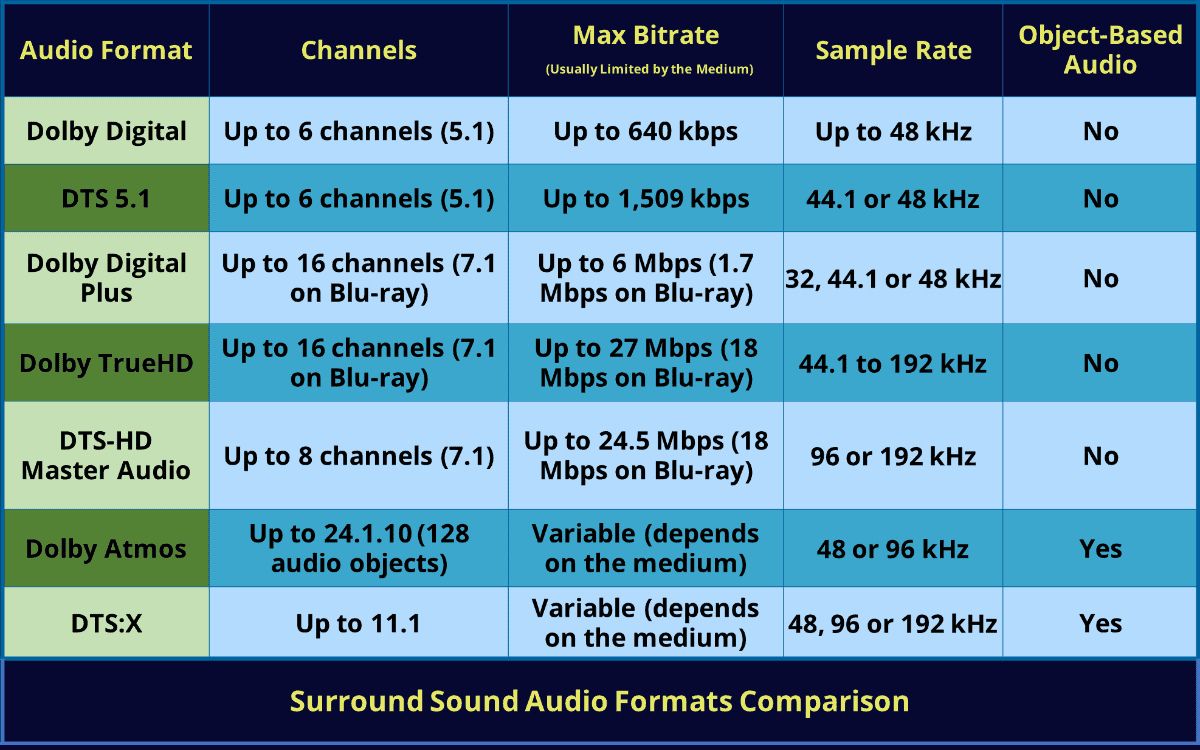
The Most Commonly Used Formats
When it comes to streaming music, several audio formats have emerged as the industry standards, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these formats is essential for comprehending the nuances of audio quality and compatibility across different devices and platforms. Here are some of the most commonly used formats in the realm of music streaming:
1. MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer III)
MP3 is arguably the most well-known and widely used audio format for streaming music. Its popularity stems from its efficient compression algorithm, which significantly reduces file sizes without compromising audio quality. This makes MP3 files easy to stream and download, even on devices with limited storage and bandwidth. While MP3 is known for its widespread compatibility, it is considered a lossy format, meaning that some audio data is permanently discarded during compression, potentially affecting the overall sound quality.
2. AAC (Advanced Audio Coding)
Developed as the successor to MP3, AAC offers improved sound quality and greater efficiency in compression. This format is favored by many streaming platforms due to its ability to deliver high-quality audio at lower bitrates, making it ideal for mobile streaming and storage-constrained devices. AAC is known for its ability to reproduce audio more accurately than MP3 at similar bitrates, resulting in a more immersive listening experience.
3. FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec)
For audiophiles and music enthusiasts who prioritize uncompromised audio fidelity, FLAC has become the format of choice. Unlike MP3 and AAC, FLAC is a lossless format, meaning that it retains all the original audio data without sacrificing quality for file size. This results in pristine, studio-quality sound reproduction, making FLAC an ideal format for streaming high-resolution audio on premium audio equipment and high-fidelity playback systems.
4. OGG (Ogg Vorbis)
OGG is an open-source audio format that offers a balance between efficient compression and high-quality audio. It is particularly popular among streaming platforms that prioritize open standards and flexibility. OGG files can deliver impressive sound quality at lower bitrates, making them suitable for streaming on a wide range of devices while minimizing data usage and storage requirements.
5. WAV (Waveform Audio File Format)
WAV is a widely recognized uncompressed audio format known for its broad compatibility and support for high-resolution audio. While WAV files are not as space-efficient as compressed formats like MP3 and AAC, they are favored for their ability to preserve the full audio fidelity without any lossy compression. This makes WAV an ideal format for streaming high-definition audio on platforms that cater to audiophiles and professional audio production.
6. AIFF (Audio Interchange File Format)
Similar to WAV, AIFF is an uncompressed audio format commonly used in professional audio production and high-fidelity streaming. It is known for its ability to retain the full audio quality without compression, making it a preferred format for streaming platforms that prioritize uncompromised sound reproduction and support for studio-grade audio equipment.
In the diverse landscape of music streaming, these formats play a pivotal role in delivering an immersive and tailored listening experience to users across various devices and preferences. Understanding the characteristics and applications of these formats provides valuable insights into the intricate process of converting and streaming music in the digital age.
How Streaming Sites Convert Your Music
Streaming sites employ sophisticated algorithms and encoding processes to convert audio files into formats that can be seamlessly streamed across a wide range of devices. The conversion of music files involves several key steps, each aimed at optimizing the audio for efficient delivery and playback. Here's a detailed look at how streaming sites convert your music:
-
Format Detection: When you upload a music file to a streaming platform, the system first detects the format of the file. This step is crucial for identifying the specific encoding parameters and characteristics of the audio, which will inform the subsequent conversion process.
-
Compression and Encoding: Once the format is identified, the audio undergoes compression and encoding to prepare it for streaming. For lossy formats like MP3 and AAC, the compression process involves removing non-essential audio data while retaining the perceptually important elements. This results in smaller file sizes optimized for streaming without significant loss in audio quality. In the case of lossless formats such as FLAC, the encoding process focuses on packaging the audio data in a format that preserves its original quality without compression.
-
Bitrate Optimization: Streaming sites often optimize the bitrate of the audio based on the user's device and network capabilities. This involves adjusting the amount of data transmitted per unit of time to ensure smooth playback while conserving bandwidth. Lower bitrates are typically used for mobile streaming to accommodate varying network conditions, while higher bitrates are employed for premium audio streaming on high-fidelity devices.
-
Adaptive Streaming: Many streaming platforms utilize adaptive streaming techniques to dynamically adjust the audio quality based on the user's network speed and device capabilities. This involves encoding the audio in multiple bitrates and allowing the platform to switch between them in real time to deliver the best possible listening experience without interruptions or buffering.
-
Metadata Integration: As part of the conversion process, streaming sites integrate metadata such as track information, album art, and artist details into the audio files. This metadata enhances the user experience by providing context and visual elements alongside the music, enriching the overall streaming experience.
-
Multi-Format Support: To cater to diverse user preferences and device compatibility, streaming sites often convert and store music in multiple formats simultaneously. This allows users to access their favorite tunes in the format best suited to their devices, ensuring seamless playback across a wide array of hardware and software platforms.
By understanding the intricacies of how streaming sites convert music, users can gain a deeper appreciation for the technology that enables them to enjoy their favorite tunes anytime, anywhere. The careful orchestration of format detection, compression, bitrate optimization, and adaptive streaming culminates in a seamless and immersive music streaming experience that transcends the boundaries of devices and platforms.
The Impact on Sound Quality
The conversion of music files into different formats for streaming has a profound impact on the sound quality experienced by listeners. The choice of audio format and the encoding process directly influence the fidelity, richness, and overall listening experience of the music. Understanding the implications of these conversions on sound quality is essential for discerning listeners and music enthusiasts who seek the best possible audio reproduction.
Compression and Lossy Formats
In the case of lossy formats such as MP3 and AAC, the compression process involves discarding certain audio data to reduce file sizes. While this enables efficient streaming and downloading, it can lead to a loss of subtle nuances and details in the music. The impact of compression is most noticeable in complex musical passages, where artifacts and distortions may become perceptible, particularly on high-end audio equipment. However, for casual listening on mobile devices and in environments with ambient noise, the difference in sound quality may be less discernible.
Lossless and High-Fidelity Formats
On the other hand, lossless formats like FLAC, WAV, and AIFF preserve the original audio data without any loss in quality. This results in a more faithful reproduction of the music, capturing the full spectrum of sound as intended by the artists and producers. The impact on sound quality is particularly evident when streaming high-resolution audio on premium audio systems, where the nuances of the music are rendered with exceptional clarity and depth. For audiophiles and discerning listeners, the choice of lossless formats can significantly enhance the immersive and authentic nature of the listening experience.
Bitrate and Adaptive Streaming
The bitrate at which audio is streamed also plays a crucial role in determining sound quality. Lower bitrates, commonly used for mobile streaming, may result in some loss of audio fidelity, especially in intricate passages and dynamic ranges. However, adaptive streaming techniques, which dynamically adjust the bitrate based on network conditions, help mitigate these effects by optimizing the audio quality in real time. This ensures that listeners receive the best possible sound quality without interruptions or buffering, regardless of their network speed and device capabilities.
Device and Environment Considerations
The impact of format conversions on sound quality is further influenced by the playback device and listening environment. High-fidelity audio equipment and acoustically treated spaces can reveal the subtle differences between various formats, allowing listeners to appreciate the nuances of lossless audio. Conversely, casual listening on earphones or speakers in noisy environments may minimize the perceptible differences between formats, making the choice of format less critical for everyday listening.
In essence, the impact of format conversions on sound quality is multifaceted, influenced by the choice of format, compression techniques, bitrate optimization, and the playback environment. While lossy formats offer convenience and efficiency, they may compromise certain aspects of sound quality. On the other hand, lossless formats cater to audiophiles and enthusiasts who prioritize uncompromised audio fidelity. By considering these factors, streaming sites strive to balance efficiency and quality, ensuring that users can enjoy their favorite music with the best possible sound reproduction across a diverse range of devices and listening scenarios.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of audio formats and the conversion processes employed by streaming sites offer a fascinating glimpse into the intricate technology that underpins our modern music consumption. As users, understanding the nuances of these formats and their impact on sound quality enriches our appreciation for the music streaming experience.
The diverse landscape of audio formats, ranging from the widely used MP3 and AAC to the high-fidelity FLAC and uncompressed WAV and AIFF, caters to the varied needs and preferences of music enthusiasts. Each format brings its own set of advantages and considerations, influencing the way music is streamed and enjoyed across different devices and platforms.
The conversion of music files involves a carefully orchestrated series of steps, including format detection, compression, bitrate optimization, adaptive streaming, and metadata integration. This process ensures that music is delivered seamlessly and optimally across a wide range of devices, networks, and listening environments, enhancing the accessibility and convenience of music streaming for users worldwide.
The impact of format conversions on sound quality is a critical consideration, with lossy formats offering efficiency and convenience while potentially compromising certain nuances, and lossless formats delivering uncompromised audio fidelity for discerning listeners. The interplay of compression techniques, bitrate optimization, and adaptive streaming techniques shapes the listening experience, highlighting the balance between efficiency and quality that streaming sites strive to achieve.
Ultimately, the conversion of music files into streaming formats represents a harmonious fusion of technology and artistry, enabling users to immerse themselves in the world of music with unparalleled convenience and accessibility. By recognizing the intricacies of format conversions and their implications for sound quality, we can approach our music streaming experiences with a deeper understanding and an enhanced ability to savor the richness of our favorite tunes.
As we continue to embrace the digital realm of music streaming, the evolution of audio formats and conversion technologies will undoubtedly shape the future of how we experience and enjoy music. With a blend of innovation, creativity, and a commitment to delivering exceptional sound quality, streaming sites are poised to continue captivating audiences and enriching the global music landscape for years to come.