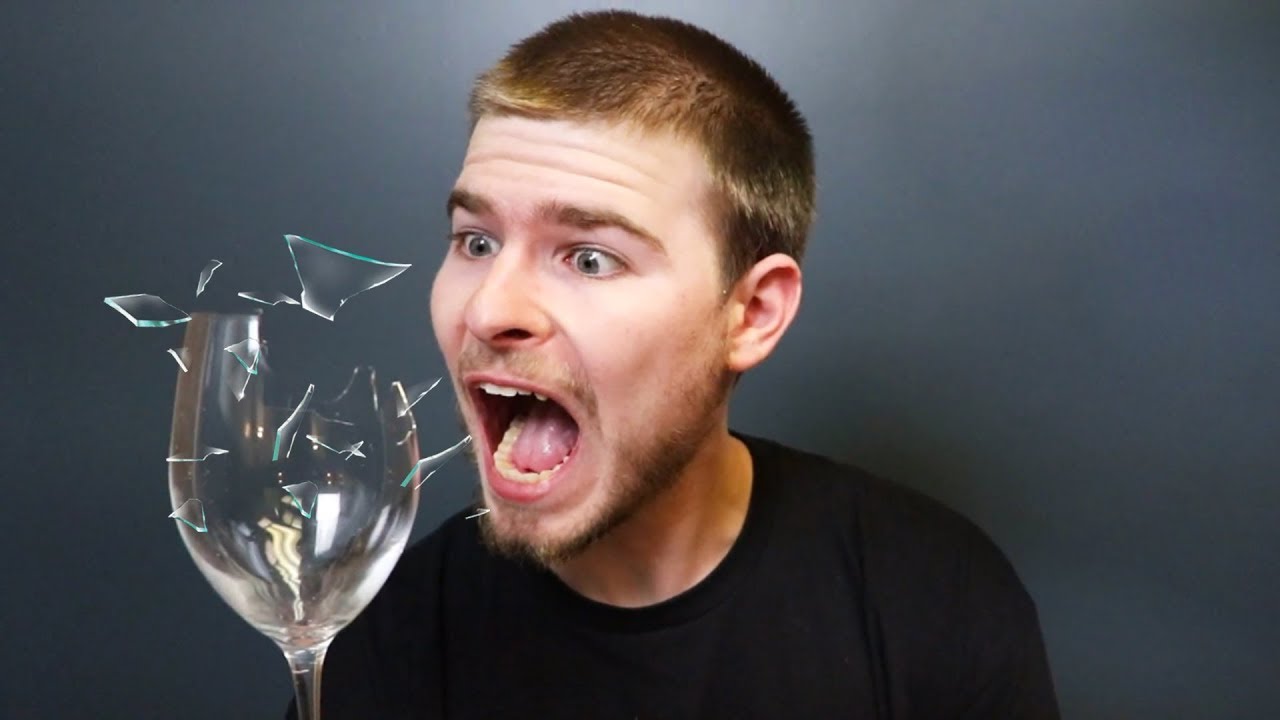
Home>Events & Info>Frequency>At What Frequency Does Glass Break


Frequency
At What Frequency Does Glass Break
Published: February 18, 2024
Discover the frequency at which glass breaks and learn about the factors that influence its susceptibility to shattering. Find out how frequency affects the strength and resilience of glass.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Glass, a material known for its transparency and versatility, has been a fundamental component in architecture, interior design, and various industries for centuries. Its fragility and strength make it a subject of fascination and curiosity. The frequency at which glass breaks is a topic that intrigues many, prompting questions about the underlying factors and mechanisms involved. Understanding the frequency of glass breakage requires a comprehensive exploration of the material's properties, the conditions it is subjected to, and the impact of external forces.
Glass is not a homogenous material; it exhibits variations in composition, thickness, and manufacturing processes, all of which contribute to its susceptibility to breakage. Whether it's a delicate glass figurine or a robust window pane, the potential for breakage exists, and the frequency of such events is influenced by a myriad of factors.
In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted nature of glass breakage, exploring the factors that influence its susceptibility to break, and shedding light on the frequency at which glass succumbs to fractures. By unraveling the science behind glass breakage and examining real-world scenarios, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this captivating phenomenon. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the mysteries of glass breakage and gain insights into the frequency at which this remarkable material meets its fragility.
Factors Affecting Glass Breakage
Several factors contribute to the propensity of glass to break under specific circumstances. Understanding these influential elements is crucial in comprehending the frequency of glass breakage. Here are some key factors that play a pivotal role in determining the susceptibility of glass to breakage:
- Material Composition: The composition of glass, including the ratio of silica, soda ash, and lime, significantly impacts its strength and resilience. Variations in the chemical composition can lead to differences in the frequency of breakage.
- Thickness: Thicker glass tends to be more resistant to breakage than thinner counterparts. The thickness of the glass directly affects its ability to withstand external forces, thereby influencing the frequency of breakage.
- Surface Flaws: Microscopic imperfections on the surface of glass, such as scratches or chips, can serve as stress concentrators, making the glass more prone to breakage. The presence of surface flaws can elevate the frequency of spontaneous breakage.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Glass expands and contracts in response to temperature variations. Rapid or extreme changes in temperature can induce thermal stress, potentially leading to breakage. The frequency of glass breakage is often heightened in environments with significant temperature differentials.
- Impact and Pressure: External forces, such as impact from objects or pressure exerted on the glass, can trigger fractures. The frequency of glass breakage is influenced by the magnitude and duration of these forces.
- Manufacturing Processes: The methods employed in the production of glass, including annealing and tempering, can profoundly impact its structural integrity. Variations in manufacturing processes can contribute to differences in the frequency of glass breakage.
By considering these factors in conjunction with real-world scenarios, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities surrounding glass breakage and the diverse range of circumstances that can influence its frequency.
Frequency of Glass Breakage
The frequency at which glass breaks is influenced by a myriad of factors, as discussed in the previous section. Understanding the occurrence of glass breakage in various contexts provides valuable insights into the material’s behavior and susceptibility to fractures.
Spontaneous glass breakage, a phenomenon characterized by the sudden fracturing of glass without apparent external causes, occurs with a certain frequency in architectural and automotive applications. This type of breakage is often attributed to internal stresses within the glass, which can lead to unexpected fractures. The frequency of spontaneous glass breakage is influenced by the quality of the glass, its manufacturing history, and the environmental conditions to which it is exposed.
In architectural settings, such as high-rise buildings with expansive glass facades, the frequency of glass breakage is a critical consideration. Factors such as wind loads, temperature differentials, and building movement can contribute to the stress experienced by the glass, affecting its propensity to break. Understanding the frequency of glass breakage in these contexts is essential for implementing effective design and maintenance strategies to mitigate potential risks.
Similarly, in the automotive industry, the frequency of glass breakage in the form of windshield damage is a significant concern. Environmental factors, road debris, and structural vibrations can all impact the likelihood of windshield breakage. By examining the frequency of glass breakage in vehicular applications, manufacturers and engineers can develop advanced safety measures and durable glass solutions to enhance vehicle resilience.
Furthermore, the frequency of glass breakage in household and commercial settings, such as windows, doors, and glass partitions, is influenced by a combination of environmental factors, material properties, and human interactions. Understanding the patterns and frequency of glass breakage in these everyday contexts is crucial for implementing preventive measures and selecting appropriate glass types to ensure safety and longevity.
By examining the frequency of glass breakage across diverse applications and environments, we gain valuable insights into the material’s vulnerabilities and strengths. This understanding serves as a foundation for developing innovative solutions, enhancing safety standards, and advancing the durability of glass products across various industries.
Conclusion
The frequency of glass breakage is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon influenced by a diverse array of factors. From the material composition and manufacturing processes to environmental conditions and external forces, the susceptibility of glass to breakage varies across different applications and contexts. By exploring the intricate dynamics of glass breakage, we gain valuable insights into the material’s behavior and the mechanisms that govern its fragility.
Understanding the frequency of glass breakage is essential for architects, engineers, manufacturers, and consumers alike. It enables the implementation of proactive measures to enhance safety, durability, and performance in architectural, automotive, and everyday applications. By identifying the influential factors and patterns associated with glass breakage, stakeholders can develop innovative solutions and best practices to mitigate risks and elevate the resilience of glass products.
Moreover, the frequency of glass breakage serves as a catalyst for advancements in material science, engineering, and design. It propels the exploration of novel glass compositions, manufacturing techniques, and protective technologies aimed at reducing breakage occurrences and enhancing the overall reliability of glass in diverse settings.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of glass breakage, it is imperative to recognize the interplay of scientific principles, real-world observations, and technological innovations in shaping the frequency and impact of glass fractures. By fostering a deeper understanding of glass breakage and its frequency, we pave the way for a future where glass products exhibit heightened resilience, safety, and longevity across a spectrum of applications.