Home>Events & Info>Music History>Why Is Haydn Significant In Music History


Music History
Why Is Haydn Significant In Music History
Published: December 28, 2023
Discover the significance of Haydn in music history with our in-depth exploration. From his innovative compositions to his influence on future generations, learn why Haydn is a key figure in the evolution of music.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Early Life and Career of Haydn
- Haydn’s Influence on Classical Music
- Haydn’s Contribution to the Development of the Symphony
- Haydn’s String Quartets and Chamber Music
- Haydn’s Impact on Musical Form and Structure
- Haydn’s Influence on Mozart and Beethoven
- Haydn’s Legacy in Music History
- Conclusion
Introduction
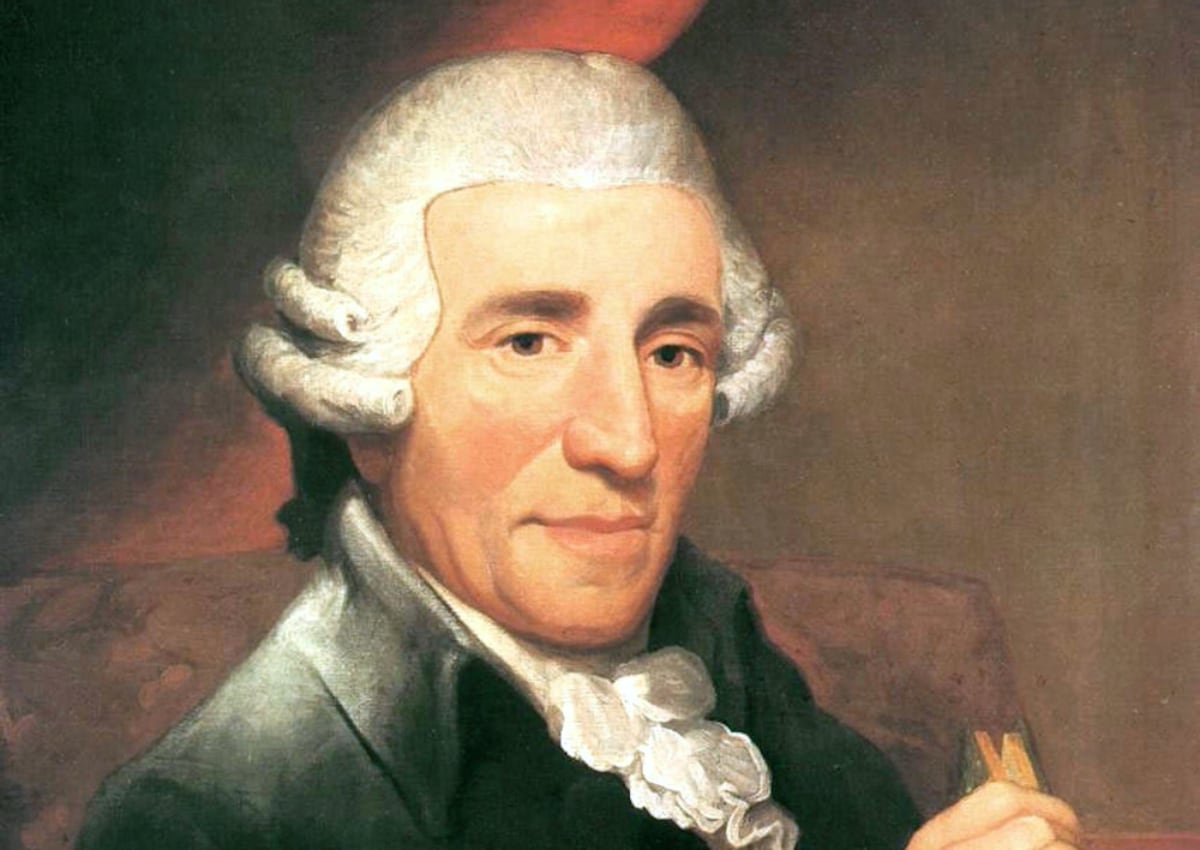
Welcome to the fascinating world of music history! In this article, we will delve into the life and significance of one of the most influential composers in classical music – Franz Joseph Haydn. Often referred to as the “Father of the Symphony” and the “Father of the String Quartet,” Haydn’s contributions to music have left an indelible mark on the musical landscape.
Born on March 31, 1732, in Rohrau, Austria, Haydn led a remarkable life that spanned the transition from the Baroque to the Classical era of music. He came from humble beginnings, displaying his musical talents from an early age. His musical education began as a choirboy at St. Stephen’s Cathedral in Vienna, where he honed his skills as a singer and violinist. It was during this time that he started composing and developing his unique style.
Haydn’s career truly took off when he became the court composer for Prince Nikolaus Esterházy in 1761. As the Kapellmeister, or music director, Haydn was responsible for composing music for the court and overseeing performances. This position provided Haydn with the artistic freedom to experiment and innovate, leading to breakthroughs in musical form and structure.
Haydn’s influence on classical music cannot be overstated. His compositions and innovations paved the way for future generations of composers, including his protégé, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and Ludwig van Beethoven. Haydn’s impact can be felt through his symphonies, string quartets, chamber music, and vocal compositions.
Throughout this article, we will explore Haydn’s remarkable contributions to classical music and how his influence has shaped the course of musical history. We will delve into his early life and career, examine his impact on the symphony and string quartet genres, and explore his influence on musical form and structure. By the end, you will have a deep appreciation for the musical genius that is Franz Joseph Haydn.
Early Life and Career of Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn was born on March 31, 1732, in the small village of Rohrau, Austria. He was the second of twelve children in a musical family, and it was clear from a young age that he possessed a natural musical talent. His parents recognized his potential and encouraged his musical pursuits.
At the age of eight, Haydn was sent to live with Johann Matthias Frankh, a relative in Hainburg, where he received his early musical training. Frankh recognized Haydn’s exceptional abilities and provided him with lessons in singing, keyboard, and violin. This solid foundation enabled Haydn to develop his skills and set the stage for his future success.
After completing his training with Frankh, Haydn embarked on a journey to Vienna in his late teens in search of musical opportunities. He faced numerous challenges and financial hardships during this period but persevered with his dedication to music.
Haydn’s breakthrough came when he caught the attention of composer and impresario Karl Joseph von Fürnberg. Fürnberg recognized Haydn’s talent and offered him a place to stay and opportunities to perform. This support allowed Haydn to establish himself within the Viennese musical community and gain recognition for his compositions.
In 1761, Haydn’s career took a significant turn when he was appointed as the Vice-Kapellmeister to the Esterházy family, one of the wealthiest and influential noble families in Austria. The position required him to compose music for the family’s court and oversee musical performances.
Haydn’s association with the Esterházy family became instrumental in his career development. In 1766, he was promoted to the prestigious position of Kapellmeister, giving him full artistic control over the court’s music. This newfound freedom allowed Haydn to experiment with different musical forms and styles.
During his time with the Esterházys, Haydn composed an immense volume of music, showcasing his versatility and mastery of various genres. He composed symphonies, string quartets, operas, choral works, and keyboard sonatas, continually pushing the boundaries of musical expression.
Haydn’s works gained widespread acclaim, and his reputation as a composer grew throughout Europe. His music was admired for its elegance, creativity, and emotional depth. He became a celebrated figure in the musical community, attracting the attention of notable composers and musicians of the time.
Haydn’s early life and career paved the way for his later achievements and established him as a prominent figure in the world of music. His determination, talent, and dedication to his craft allowed him to rise above humble beginnings and leave an enduring legacy in the annals of music history.
Haydn’s Influence on Classical Music
Franz Joseph Haydn’s impact on classical music is immeasurable. As one of the most important figures in the Classical era, his innovations and contributions laid the groundwork for the development and evolution of the genre.
One of Haydn’s notable influences on classical music was his role in expanding the symphony. Prior to Haydn, the symphony was a relatively modest and uncomplicated form. Haydn transformed it into a grand and expressive genre, incorporating intricate melodic lines, harmonic richness, and dynamic contrasts. He expanded the symphony from a three-movement structure to a four-movement form, introducing the concept of the “symphony cycle” that remains prevalent to this day.
Haydn was also a trailblazer in developing the string quartet. He is often referred to as the “Father of the String Quartet” due to his remarkable contributions to the genre. Haydn’s string quartets showcased his mastery of combining four independent voices into a harmonious whole. He elevated the status of the string quartet, transforming it from a simple entertainment format into a profound and intellectually demanding chamber music genre.
Furthermore, Haydn’s influence extended to his exploration of musical form and structure. Through his compositions, he introduced new concepts such as thematic development, elaborate codas, and unexpected harmonic progressions. Haydn’s innovative approach to musical structure pushed the boundaries of convention and inspired future composers to experiment and push the limits of musical expression.
Haydn’s impact on classical music is not limited to his own compositions. His influence on composers who came after him, such as Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Ludwig van Beethoven, cannot be overstated. Mozart, in particular, held Haydn in high regard and considered him a mentor and a source of inspiration. Beethoven also greatly admired Haydn’s work and learned from his innovative techniques.
Haydn’s influence can be heard in the symphonies, string quartets, concertos, and chamber music of Mozart and Beethoven. His artistic vision and musical language laid the foundation for the development of the Classical style and provided a starting point for composers who followed in his footsteps.
Overall, Franz Joseph Haydn’s influence on classical music is profound and far-reaching. Through his groundbreaking compositions and innovative techniques, he transformed the symphony and string quartet genres, expanded the boundaries of musical form, and inspired generations of composers. His legacy is not only evident in his own works but also in the music of the great composers who came after him.
Haydn’s Contribution to the Development of the Symphony
Franz Joseph Haydn’s impact on the development of the symphony is monumental. Often referred to as the “Father of the Symphony,” Haydn played a pivotal role in transforming this genre and elevating it to new heights.
Prior to Haydn, the symphony was a relatively straightforward and limited form, typically consisting of three movements. Haydn recognized the potential for expansion and experimentation within the symphonic form, and he took it upon himself to push its boundaries.
One of Haydn’s most significant contributions was his expansion of the symphony from a three-movement structure to a four-movement format. By adding a minuet and trio as the third movement, Haydn brought a sense of elegance and balance to the symphony, creating a more cohesive and satisfying musical experience.
Haydn’s four-movement symphony structure became the foundation for symphonic compositions that followed, including those of his protégé Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and later masters like Ludwig van Beethoven.
Additionally, Haydn introduced the concept of the “symphony cycle,” which refers to a collection of symphonies that are cohesive in their musical style and thematic material. He composed numerous symphony cycles throughout his career, with each cycle showcasing his growth as a composer and his mastery of the symphonic form.
Haydn’s symphonies were characterized by their rich harmonic language, inventive thematic development, and careful attention to orchestration. He explored a variety of musical styles and moods within his symphonies, from the energetic and lively to the lyrical and introspective.
His use of dynamic contrasts, unexpected harmonic progressions, and intricate melodic lines added depth and complexity to his symphonic works. Haydn’s symphonies were known for their ability to captivate audiences and take them on an emotional journey.
Moreover, Haydn’s symphonies served as a bridge between the Baroque and Classical eras of music. While still rooted in the formal structures of the Baroque period, Haydn infused his compositions with the spirit of innovation and experimentation that would define the Classical era.
Haydn’s influence can be heard not only in his own symphonic works but also in the symphonies composed by his successors. His innovations laid the groundwork for the symphonic masterpieces of Mozart, Beethoven, and countless other composers who followed in his footsteps.
Overall, Franz Joseph Haydn’s contribution to the development of the symphony is immeasurable. Through his groundbreaking four-movement structure, symphony cycles, and innovative musical techniques, he revolutionized the genre and set the stage for future symphonic compositions. His symphonies continue to be admired and performed to this day, solidifying his legacy as one of history’s greatest symphonists.
Haydn’s String Quartets and Chamber Music
Franz Joseph Haydn is often hailed as the “Father of the String Quartet” due to his significant contributions to this genre of chamber music. His string quartets, along with his other chamber music compositions, showcase his mastery of musical craftsmanship and his ability to create deeply expressive and intimate works.
Haydn’s string quartets revolutionized the genre, elevating it from a simple entertainment format to a profound and intellectually demanding form of chamber music. Composed for two violins, a viola, and a cello, his string quartets showcase the ensemble’s ability to create a dialogue and interplay among the individual voices.
One of Haydn’s notable achievements in string quartet composition was his ability to balance the individual voices while creating a cohesive whole. Each instrument had its distinct role and contributed to the overall musical texture, resulting in a harmonious blend of four distinct voices.
Haydn composed a staggering number of string quartets throughout his career, including the famous Opus 33 and Opus 76 quartets. These works display his innovative spirit, experimentation with form, and ability to capture a wide range of emotions.
Within his string quartets, Haydn explored various musical techniques and forms, including intricate counterpoint, inventive melodies, and unexpected harmonic twists. His use of thematic development, where a melody is transformed and varied throughout a composition, added depth and complexity to his works.
Haydn’s chamber music extends beyond string quartets. He composed numerous trios, sonatas, and other chamber works, showcasing his versatility as a composer and his ability to create intimate and expressive musical conversations.
His chamber music compositions were often performed in small private settings, such as Salons, allowing for a close interaction between the performers and the audience. This intimate nature of chamber music allowed for a deeper emotional connection and a more nuanced musical experience.
Haydn’s contributions to the string quartet and chamber music genres laid the foundation for future composers, including his students Mozart and Beethoven. Mozart, in particular, was heavily influenced by Haydn’s mastery of chamber music and incorporated these principles into his own compositions.
Haydn’s string quartets and chamber music represent a pinnacle of musical expression and remain significant milestones in the history of classical music. Their enduring popularity and influence continue to inspire and captivate musicians and audiences to this day.
Haydn’s Impact on Musical Form and Structure
Franz Joseph Haydn’s contributions to musical form and structure have forever altered the landscape of classical music. Through his groundbreaking compositions and innovative techniques, Haydn pushed the boundaries of convention and laid the groundwork for future generations of composers.
One of Haydn’s notable impacts on musical form was his development of thematic development. This technique involves the transformation and variation of a musical theme throughout a composition. Haydn’s skillful manipulation of melodies allowed him to create unity and coherence within his works, as well as introduce new and unexpected musical ideas.
Haydn also developed the concept of the sonata form, which became a cornerstone of classical music composition. This form consists of three main sections: exposition, development, and recapitulation. Haydn’s sonatas and symphonies exemplified the use of this form, with clear and distinct sections that showcased his mastery of musical structure.
In addition to the sonata form, Haydn’s compositions also incorporated the rondo form. The rondo features the repeated return of a main theme interspersed with contrasting musical material. Haydn’s use of the rondo form added a sense of familiarity and symmetry to his works, providing a satisfying and memorable listening experience.
Moreover, Haydn’s compositions often featured elaborate codas, which are passages at the end of a musical piece used to bring closure and add a final flourish. Haydn’s codas were renowned for their creativity, often containing unexpected twists and turns that added excitement and surprise to the overall structure of his compositions.
Haydn’s exploration of musical form and structure was not confined to his instrumental compositions. His vocal works, such as his masses and oratorios, also showcased his innovative approach. By incorporating choral sections, solo arias, and recitatives, Haydn created a multi-dimensional musical experience that enhanced the expressive power of his compositions.
Haydn’s impact on musical form and structure extended beyond his own compositions. His techniques and innovations influenced a new generation of composers, most notably his younger contemporaries Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Ludwig van Beethoven.
Mozart, in particular, admired Haydn’s mastery of form and structure and incorporated these principles into his own compositions. Beethoven, though initially influenced by Haydn’s work, would eventually break free from conventional forms and forge his own path, pushing the boundaries even further.
Overall, Haydn’s impact on musical form and structure cannot be overstated. His innovative techniques, development of sonata and rondo forms, and exploration of thematic development left an indelible mark on classical music composition. His influence reverberates through the works of composers who followed in his footsteps, solidifying his legacy as a trailblazer in musical form and structure.
Haydn’s Influence on Mozart and Beethoven
Franz Joseph Haydn’s influence on the musical world extended beyond his own compositions. As a mentor and inspiration to many, his impact on two of the greatest composers in history, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Ludwig van Beethoven, cannot be overstated.
Mozart and Haydn enjoyed a close friendship and professional collaboration. Mozart greatly admired Haydn’s work, recognizing him as a master of form, structure, and expressiveness. The two composers shared ideas, engaged in friendly competition, and exchanged musical manuscripts. This close relationship deeply influenced Mozart’s own compositions.
Haydn’s influence on Mozart can be seen in the meticulous craftsmanship of Mozart’s music, as well as the complexity and depth of his compositions. Mozart adopted Haydn’s use of thematic development, incorporating it into his symphonies, string quartets, and other works. Additionally, Mozart incorporated Haydn’s mastery of form and structure, creating works with greater complexity and musical maturity.
Beethoven, although initially influenced by Haydn, would eventually forge his own musical path. However, Haydn laid the groundwork for Beethoven’s development as a composer. Beethoven first studied under Haydn in Vienna, benefiting from his guidance and learning from his innovative techniques.
Haydn’s influence on Beethoven is evident in the younger composer’s early works, such as his early symphonies and piano sonatas. Beethoven adopted Haydn’s classical style and expanded upon it, injecting his unique and innovative approach. As Beethoven’s career progressed, he would depart from conventions and break new ground, pushing the boundaries of classical music.
Haydn’s influence on Beethoven can be seen in their shared commitment to form and structure. Both composers valued the importance of compositional craftsmanship and carefully planned musical architecture. This emphasis on structure allowed Beethoven to create works with a sense of cohesiveness and emotional impact.
Haydn’s influence was not limited to specific musical techniques or forms, but rather in his ability to inspire and ignite the creative spark in both Mozart and Beethoven. His dedication to his craft, his innovative spirit, and his musical versatility served as inspiration for the younger generation of composers that followed.
Haydn’s impact on Mozart and Beethoven extends beyond their individual musical achievements. He played a critical role in shaping classical music as we know it today, and his influence on these two great composers helped to pave the way for the evolution of music in the years to come.
Ultimately, Haydn’s influence on Mozart and Beethoven cannot be understated. Through his mentorship, collaboration, and groundbreaking compositions, Haydn left an indelible impact on the musical world, nurturing the genius of Mozart and inspiring the revolutionary spirit of Beethoven.
Haydn’s Legacy in Music History
Franz Joseph Haydn’s legacy in music history is as significant as it is enduring. As one of the most influential composers of the classical era, Haydn’s innovative compositions and contributions continue to shape the landscape of music to this day.
One of Haydn’s most profound legacies is his role as the “Father of the Symphony” and the “Father of the String Quartet.” Through his symphonies and string quartets, Haydn expanded the possibilities of these genres, creating a more sophisticated and expressive art form. His development of the four-movement symphony structure, the exploration of thematic development, and the integration of intricate counterpoint within the string quartet revolutionized the classical music canon.
Moreover, Haydn’s impact is felt in his influence on his contemporaries and future generations of composers. His close relationship with Mozart and his mentorship of Beethoven helped shape the music of these two legendary figures. Mozart admired Haydn’s mastery of form and structure, while Beethoven built upon Haydn’s innovations and pushed the boundaries of musical expression even further. Countless composers who followed, such as Schubert, Brahms, and even into the 20th century, drew inspiration from Haydn’s works.
Haydn’s legacy also lies in his exploration of musical form, including the development of the sonata and rondo forms. He pushed the boundaries of conventional structures, introducing unexpected harmonic progressions, thematic variations, and inventive codas. These innovations laid the foundation for the development of musical form in the classical era and beyond.
Furthermore, Haydn’s contributions to chamber music and vocal music are equally significant. His chamber music compositions, including his numerous trios and sonatas, showcased his ability to create intimate and expressive musical conversations. His vocal works, such as masses and oratorios, demonstrated his skill in crafting emotionally captivating and spiritually profound pieces.
Haydn’s legacy also extends to his impact on the development of the Viennese classical style, with its emphasis on clarity, elegance, and balance. His compositions bridged the gap between the Baroque and Classical eras, while laying the foundation for the Romantic era. His music exemplified the ideals of the Enlightenment, combining intellectual depth with emotional expression.
Overall, Haydn’s legacy as a composer and musical innovator is truly remarkable. His contributions to the symphony, string quartet, chamber music, and musical form continue to inspire and captivate audiences around the world. Through his groundbreaking compositions and his influence on future generations of composers, Haydn has secured his place as one of the greatest figures in the history of music.
Conclusion
Franz Joseph Haydn’s immense contributions to music history have solidified his status as one of the most influential composers of all time. As the “Father of the Symphony” and the “Father of the String Quartet,” Haydn revolutionized these genres and left an indelible mark on the classical music canon.
From his early life and career to his impact on musical form and structure, Haydn’s legacy is seen in his groundbreaking compositions and his influence on other renowned composers such as Mozart and Beethoven. Through his exploration of thematic development, the expansion of symphonic and chamber music forms, and his meticulous attention to musical craftsmanship, Haydn pushed the boundaries of what was thought possible in music.
Haydn’s influence on musical history extends beyond his own compositions and reaches into the future. His innovative techniques and dedication to musical excellence inspired generations of composers who followed in his footsteps.
Haydn’s immense catalogue of symphonies, string quartets, chamber music, and vocal compositions continues to captivate audiences worldwide, and his music remains influential and cherished. His legacy as a pivotal figure in music will forever be linked to the evolution of classical music and the development of musical form and structure.
So, as we explore the pages of music history, let us never forget the immense contributions of Franz Joseph Haydn, a musical visionary and pioneer whose legacy will continue to inspire generations to come.