Home>Instruments>Bass>How Hard Is It To Learn Bass Guitar


Bass
How Hard Is It To Learn Bass Guitar
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn bass guitar and master the art of playing this instrument with ease. Discover how to overcome the challenges and become skilled in playing the bass.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Benefits of Learning Bass Guitar
- Basic Anatomy of a Bass Guitar
- Getting Started: Choosing the Right Bass Guitar
- Understanding Notes and Chords on the Bass Guitar
- Essential Techniques for Bass Guitar
- Learning to Read Bass Guitar Tablature
- Practicing and Building Your Skills
- Common Mistakes to Avoid as a Beginner Bassist
- Resources for Learning Bass Guitar
- Conclusion
Introduction
Learning to play a musical instrument is a rewarding experience that can bring joy, self-expression, and a sense of accomplishment. If you’ve always been drawn to the deep, rhythmic pulse of music, learning to play the bass guitar may be the perfect choice for you. But just how hard is it to learn bass guitar?
The bass guitar is a vital component of any band or ensemble, providing the foundation for the rhythmic groove and anchoring the harmony. Its distinct low-end sound adds depth, power, and texture to a song. While learning any instrument requires time, effort, and dedication, the bass guitar offers unique benefits that make the learning journey both enjoyable and fulfilling.
One of the advantages of learning bass guitar is its relatively straightforward playing technique. Unlike more complex instruments like the piano or violin, the bass guitar has fewer strings and a simpler fretboard, making it easier to learn basic chords and scales. With the right guidance and practice, even a beginner can quickly develop a solid foundation and start playing their favorite songs.
Additionally, playing the bass guitar provides an immersive and rhythmic experience. As you strum the strings and feel the vibrations resonating through your body, you become one with the music. The bass guitar’s role as the rhythmic heartbeat of a band allows you to connect with the drummer and other musicians, creating a powerful sense of unity and collaboration.
Furthermore, learning to play the bass guitar opens up a world of opportunities for creativity and expression. As you become more proficient, you can experiment with different playing styles, techniques, and genres, from funky slap bass to smooth jazz lines. The versatility of the instrument allows you to adapt to various musical contexts and explore your unique musical voice.
Whether you aspire to jam with friends, play in a band, or simply enjoy the therapeutic benefits of playing music, learning bass guitar is a fulfilling and enriching endeavor. This article will guide you through the basic concepts, techniques, and resources you need to embark on your bass guitar journey. So grab your bass and let’s dive in!
Benefits of Learning Bass Guitar
Learning to play the bass guitar offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond just creating music. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced musician looking to expand your skills, here are some compelling reasons why learning bass guitar can be a rewarding and worthwhile endeavor.
- Enhances your musicality: Playing the bass guitar trains your ears to identify tones, rhythm, and harmony. As you learn to lock in with the drummer and other musicians, you develop a strong sense of timing and groove, which can significantly improve your overall musicianship.
- Builds coordination and dexterity: Mastering the bass guitar requires coordinated movements between your fretting hand and plucking hand. Regular practice improves your hand-eye coordination, finger strength, and agility, enhancing your overall dexterity.
- Strengthens your rhythmic sense: The bass guitar’s role as the foundation of the rhythm section hones your ability to maintain a steady beat and play in sync with the drummer. This rhythmic training translates to better timing and groove in all aspects of your musical endeavors.
- Boosts your confidence: As you progress and learn to play songs, your confidence as a musician soars. Being able to contribute to a band or perform in front of an audience fosters self-assurance and a sense of accomplishment.
- Fosters collaboration: The bass guitar is an integral part of any band, and learning to play it allows you to collaborate effectively with other musicians. You’ll develop communication skills, learn to listen and respond to other instruments, and experience the joy of creating music together.
- Relieves stress and enhances well-being: Playing the bass guitar can serve as a therapeutic escape from everyday stress. It allows you to channel your emotions, express yourself, and immerse yourself in the joy of making music, promoting mental well-being and relaxation.
- Expands your musical horizons: The bass guitar is a versatile instrument that transcends genres and musical styles. Learning to play opens up a world of possibilities, enabling you to explore various genres like rock, jazz, funk, blues, and more.
The benefits of learning bass guitar go far beyond the instrument itself. It enriches your musical journey, improves your cognitive abilities, and provides a platform for meaningful self-expression. Whether you’re aiming to pursue a professional career or simply seeking a fulfilling hobby, the bass guitar is a fantastic choice that can bring a lifetime of enjoyment.
Basic Anatomy of a Bass Guitar
Before diving into playing the bass guitar, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with its basic anatomy. Understanding the different parts of the instrument will not only help you properly handle and care for your bass but also enhance your playing experience. Here are the main components of a bass guitar:
- Headstock: Located at the end of the neck, the headstock houses the tuning machines or tuning pegs. These pegs are used to adjust the tension of each string, allowing you to tune your bass to the desired pitch.
- Neck: The long, slender part of the bass guitar that connects the headstock to the body. The neck is usually made of wood and contains the fretboard, which is where you press down on the strings to produce different notes.
- Fretboard: Also known as the fingerboard, this is a flat surface on the neck made of wood or other materials. It is divided into frets, which are metal bars that run across the width of the neck. Pressing down on a string behind a specific fret changes the pitch of the note played.
- Frets: The metal bars on the fretboard that divide it into different segments. By pressing down a string against a specific fret, you can alter its vibrating length and produce different pitches.
- Strings: These are the long, thin metal or nylon cables that run the length of the neck and produce sound when plucked or struck. Traditionally, a bass guitar has four strings, tuned in fourths (E, A, D, G from thickest to thinnest), but five and six-string bass guitars are also common.
- Pickups: Located underneath the strings, pickups are magnets that capture the vibrations of the strings and convert them into electrical signals. These signals are then sent to an amplifier or speaker, which produces the amplified sound of the bass guitar.
- Bridge: Positioned at the bottom end of the body, the bridge serves two purposes: it anchors the strings to the body and helps transmit the strings’ vibrations to the body, enhancing the bass guitar’s resonance.
- Controls: Bass guitars typically have a set of controls on the body, including volume knobs for each pickup and tone controls. These allow you to adjust the volume and tone of the instrument, giving you greater control over your sound.
- Body: The body of the bass guitar can come in various shapes and sizes, including classic designs like the Precision Bass and Jazz Bass. The body provides support for all the components and contributes to the overall tone and resonance of the instrument.
By understanding the basic anatomy of a bass guitar, you’ll have a solid foundation for exploring its capabilities and techniques. Familiarize yourself with each component, experiment with the controls, and get comfortable with the instrument before embarking on your musical journey as a bassist.
Getting Started: Choosing the Right Bass Guitar
Choosing the right bass guitar is a crucial step in your journey as a bassist. With a wide range of options available, it’s important to consider various factors to ensure you find an instrument that suits your playing style, budget, and musical preferences. Here are some key points to keep in mind when choosing a bass guitar:
- Consider your budget: Determine how much you’re willing to invest in a bass guitar. While there are affordable options for beginners, higher-end instruments offer superior craftsmanship and tonal qualities. Set a budget that strikes a balance between your financial capacity and your long-term commitment to playing.
- Decide on the number of strings: Bass guitars commonly come in four-string, five-string, or six-string configurations. A four-string bass is a standard choice that covers most music genres. If you’re interested in playing styles that require extended range or complex chord voicings, you may want to consider a five or six-string bass.
- Consider the body style: Bass guitars come in various shapes, such as the classic Fender Precision or Jazz Bass, as well as more modern designs. The body style can affect the instrument’s ergonomics, playability, and tone. Try different body styles to see which one feels comfortable and suits your aesthetic preferences.
- Pay attention to the neck profile: The shape and thickness of the neck can greatly influence your playing experience. Some basses have thicker necks, providing more stability and support, while others have slimmer profiles for faster playing. Try out different neck profiles to find the one that feels comfortable in your hands.
- Test and compare different models: Visit music stores and try out different bass guitars within your budget range. Play various models to get a feel for their sound, playability, and overall quality. Pay attention to the instrument’s resonance, sustain, and how well it stays in tune.
- Consider your musical preferences: Think about the musical genres you’re interested in playing and the sound you want to achieve. Different bass guitars can produce distinct tones, and some models are better suited for certain genres. Research the bassists of your favorite bands or styles to get an idea of the instruments commonly used in those contexts.
- Seek advice and guidance: Consult experienced bassists, music instructors, or knowledgeable staff at music stores. They can offer valuable recommendations and insights based on their expertise and experience.
Remember, the right bass guitar for you is one that feels comfortable to play, produces a sound you love, and fits within your budget. Take your time to research, test, and compare different models before making a decision. Once you find the perfect bass guitar, you’ll be well on your way to unlocking its potential and embarking on an exciting musical journey.
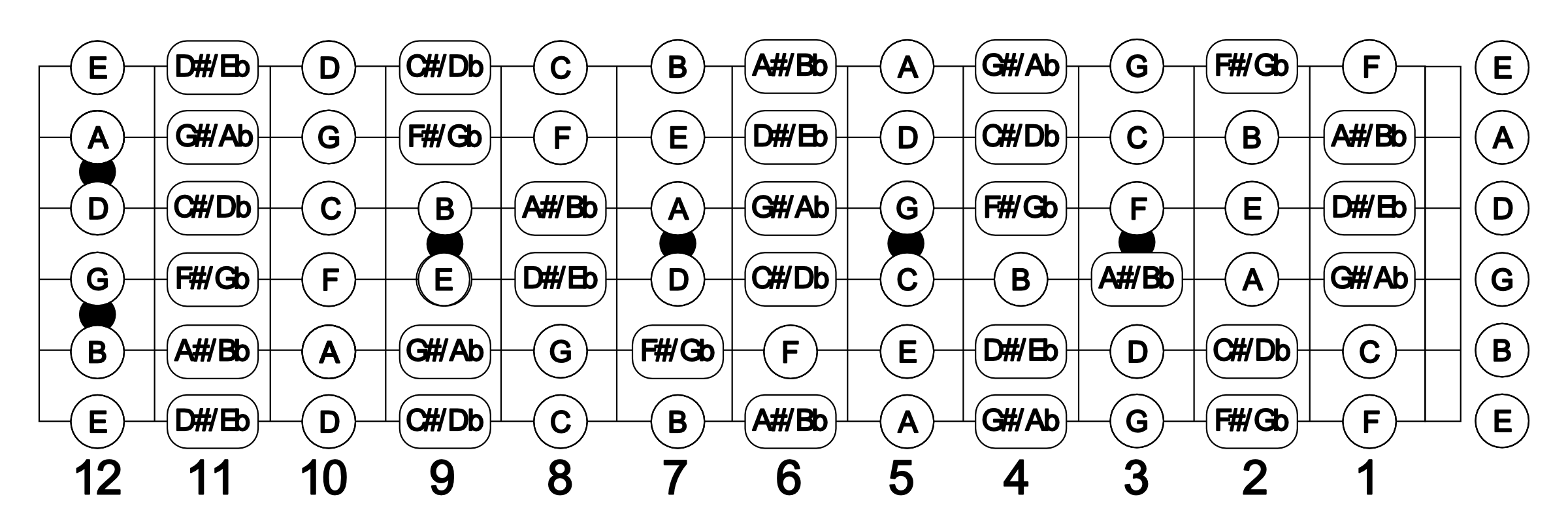
Understanding Notes and Chords on the Bass Guitar
To become proficient on the bass guitar, it’s essential to understand the system of notes and chords. This knowledge forms the foundation for creating basslines, improvising, and playing with other musicians. Let’s delve into the basics of notes and chords on the bass guitar:
Notes: The musical alphabet consists of seven basic notes: A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. These notes repeat in higher or lower octaves as you move up or down the fretboard. Each note represents a specific pitch or tone.
On the bass guitar, each string is tuned to a specific note. The standard tuning for a four-string bass is E, A, D, and G from thickest to thinnest string. Therefore, the open string notes correspond to those respective pitches.
Chords: Chords are groups of notes played together to create harmony. While chords are typically associated with guitars, bassists can also play chords to add depth and texture to their playing, especially in genres like funk, jazz, and fusion.
On the bass guitar, you can play chords by simultaneously fretting multiple notes across different strings. The most common type of chord for bassists is the power chord, which consists of the root note and the fifth interval. Power chords are often played on the lower strings to provide a solid foundation and a driving sound.
In addition to power chords, bassists can also explore extended chords, such as major, minor, and dominant chords. These chords involve playing more than two notes and can be used to embellish basslines or create melodic phrases.
To develop a strong foundation in understanding notes and chords, it’s crucial to learn and practice scales. Scales are a series of notes played in a specific pattern, which help you navigate the fretboard and create melodic basslines.
Common scales for bassists include the major scale, minor scale, pentatonic scale, and blues scale. By mastering these scales, you can begin to improvise and create your own basslines, as well as play along with other musicians.
Remember, learning and understanding notes and chords on the bass guitar is an ongoing process. Take the time to practice scales, study chord progressions, and explore different melodic patterns. The more you immerse yourself in the world of notes and chords, the more confident and versatile you’ll become as a bassist.
Essential Techniques for Bass Guitar
Mastering essential techniques is key to becoming a skilled bass guitarist. These techniques not only enhance your playing ability but also allow you to create a wide range of sounds and styles. Here are some foundational techniques that every bass player should learn:
- Fingerstyle: Fingerstyle technique involves plucking the strings with your fingers instead of using a pick. It provides greater control and a warmer tone. Practice alternating between your index and middle fingers to develop speed and accuracy.
- Slap and pop: Slapping involves striking the strings with the bony part of your thumb, creating a percussive sound. Popping involves snapping the strings with your index or middle finger to produce a punchy, bright tone. These techniques add a funk and groove element to your playing.
- Muting: Muting is essential for creating clean, tight basslines. Use both hands to lightly touch or rest on the strings to suppress unwanted noise or unwanted vibrations. Experiment with palm muting, fret-hand muting, and string damping techniques.
- Slides and Hammer-ons/Pull-offs: Sliding involves smoothly transitioning from one note to another by sliding your finger along the string. Hammer-ons and pull-offs are techniques used to create fluid legato lines by adding notes without plucking the string. Practice these techniques to add expressiveness and fluidity to your playing.
- Octaves and Double Stops: Octaves are played by simultaneously fretting the same note on two different strings. Double stops involve playing two different notes simultaneously. These techniques create a fuller sound and can be used to embellish basslines and melodies.
- Walking basslines: Walking basslines involve playing individual notes in a sequential pattern, often following the chord changes of a song. Practice playing root notes and adding passing notes in between to create rhythmic and melodic interest.
- Syncopation: Syncopation is the technique of emphasizing off-beat rhythms, creating a groove that pushes and pulls against the standard downbeat. Experiment with playing notes slightly ahead or behind the beat to add rhythmic complexity to your basslines.
- Dynamic Control: Use variations in volume, attack, and sustain to add expression and nuance to your playing. Practice using your plucking hand to control the intensity of each note, and experiment with techniques such as palm muting, ghost notes, and accents.
Remember, mastering these techniques takes time, patience, and dedication. As you practice, start slow, focusing on accuracy and control. Gradually increase your speed and experiment with incorporating these techniques into your playing. By developing a strong foundation in essential techniques, you’ll have the tools to create captivating basslines and adapt to various musical styles and genres.
Learning to Read Bass Guitar Tablature
Bass guitar tablature, or bass tab, is a simple and effective way to read and understand basslines without having to learn standard music notation. It uses a system of numbers and symbols to represent the strings and frets on the bass guitar. Learning to read bass tab is a valuable skill for any bassist. Here’s a breakdown of how bass tab works:
String Representation: Bass tab consists of horizontal lines that represent each string on the bass guitar. The thickest string (usually the E string) is at the bottom of the tab, while the thinnest string (usually the G string) is at the top.
Number System: Each number in bass tab represents a specific fret on the corresponding string. For example, if there is a “3” on the third line (A string) of the tab, it means you press down the third fret of the A string.
Open String: An open string is represented by a “0” in bass tab. It means you play the string without pressing down any frets.
Timing and Duration: In bass tab, the horizontal placement of the numbers indicates the timing of the notes. The numbers are written in sequential order from left to right, indicating the order in which the notes are played. The spacing between the numbers represents the duration of the notes – closer spacing for shorter notes and wider spacing for longer notes.
Repetitions and Structures: To indicate repeated sections or patterns, bass tab often includes brackets or lines to group notes together. This helps to make the structure of the bassline clearer and easier to follow.
While bass tab is a useful tool, it’s important to note that it doesn’t provide information about timing or rhythm as precisely as standard sheet music notation does. It’s often beneficial to listen to recordings of the song you’re learning and use your ear to determine the exact timing and feel of the bassline.
To start learning to read bass tab, begin with simple exercises and songs. Familiarize yourself with the string representation, number system, and basic timing. As you become more comfortable, gradually progress to more complex basslines and songs.
There are numerous online resources and tablature websites available where you can find a wide range of bass tabs for popular songs. These resources can help you practice reading tab and expand your repertoire.
Remember that reading bass tab is not a substitute for developing a strong foundation in music theory and ear-training. It’s essential to continue learning and growing as a musician by studying scales, chords, and musical concepts alongside reading bass tab.
By learning to read bass tab, you’ll unlock a vast library of basslines and have a valuable tool for learning songs and creating your own bass parts. Embrace the simplicity and convenience of bass tab while aiming to broaden your musical skills and knowledge.
Practicing and Building Your Skills
Practicing is the key to developing your skills as a bass guitarist. Regular, focused practice sessions will help you improve your technique, build your repertoire, and broaden your musicality. Here are some essential tips to make the most of your practice time:
- Set specific goals: Define what you want to achieve in each practice session. It could be mastering a particular technique, learning a new song, or improving your speed and accuracy. Setting clear goals will help you stay focused and measure your progress.
- Establish a consistent practice routine: Carve out dedicated time in your schedule for regular practice sessions. Consistency is key to building muscle memory and retaining what you’ve learned. Even short, focused practice sessions can be highly effective.
- Warm-up exercises: Begin each practice session with warm-up exercises to prepare your fingers and hands for playing. This could include finger stretching, scales, or simple repetitive exercises to get your muscles loosened up.
- Practice technique drills: Focus on specific techniques and drills to improve your playing. This could involve exercises such as scales, arpeggios, fingerstyle patterns, or rhythm exercises. Start slowly and gradually increase speed and difficulty.
- Learn songs you enjoy: Learning songs that you love is not only fun but also provides practical application for your skills. Start with simpler songs and gradually work your way up to more challenging pieces. Use bass tab or sheet music to guide your learning.
- Jam with others: Playing with other musicians is an excellent way to develop your musicality and adaptability. Seek opportunities to jam with friends, join a band, or participate in local music events. Collaborating with others will help you refine your rhythmic skills and learn to listen and respond in a musical context.
- Record yourself: Use a recording device or software to record yourself playing. Listening back to your playing can help you identify areas for improvement, notice subtle nuances, and track your progress over time.
- Seek feedback and guidance: Share your playing with knowledgeable musicians or seek the guidance of a bass instructor. Constructive feedback can provide invaluable insights and help you overcome challenges you may encounter in your practice.
- Stay motivated and have fun: Remember that playing the bass guitar is a journey, and progress takes time. Enjoy the process, celebrate small victories along the way, and stay motivated by playing music that inspires you.
By adopting these practice strategies and incorporating them into your routine, you’ll develop discipline, enhance your technical skills, and grow as a bassist. Consistent and focused practice will allow you to reach new levels of proficiency and enjoy the rewarding experience of playing the bass guitar.
Common Mistakes to Avoid as a Beginner Bassist
As a beginner bassist, it’s natural to make mistakes and face challenges along your musical journey. However, being aware of common mistakes can help you avoid them and progress more efficiently. Here are some crucial mistakes to avoid as a beginner bassist:
- Neglecting proper technique: Developing proper technique from the beginning is essential. Avoid bad habits like using excessive force, anchoring your thumb on the pickup, or neglecting to use correct finger placement. Take time to learn and practice proper technique to prevent injuries and ensure clean and efficient playing.
- Not using a metronome: Rhythm is a fundamental aspect of playing bass. Many beginners underestimate the importance of practicing with a metronome. It helps develop a solid sense of timing and accuracy. Incorporate metronome practice from the start and focus on playing in time with the beat.
- Ignoring music theory: While it’s possible to play bass without extensive music theory knowledge, understanding basic concepts like scales, chords, and key signatures will greatly benefit your playing. It will enhance your improvisation skills, facilitate communication with other musicians, and open up new musical possibilities.
- Practicing without a plan: Aimless practice can lead to slow progress and frustration. Instead, set specific goals and plan your practice sessions accordingly. Focus on technique, scales, songs, or specific areas you want to improve. Having a clear practice plan will keep you motivated and help you make efficient use of your practice time.
- Overlooking ear training: Developing your ear is crucial for playing bass. Train your ears to identify pitch, recognize intervals, and distinguish different chord progressions. This skill will make it easier to play by ear, improvise, and communicate with other musicians.
- Not playing with others: Playing bass in isolation can limit your musical growth. Seek opportunities to play with other musicians, whether it’s in a band, jam sessions, or online collaborations. Playing with others will improve your timing, groove, and ability to respond to different musical contexts.
- Comparing yourself to others: Each musician’s journey is unique, and progress takes time. Avoid comparing yourself to more advanced players or feeling discouraged if you don’t progress as quickly as you’d like. Celebrate your own achievements, focus on your own growth, and enjoy the process.
- Not maintaining your instrument: Regular maintenance and care for your bass guitar are essential. Keep your instrument clean, change strings when needed, and ensure proper storage and humidity control. A well-maintained instrument performs better and lasts longer.
Remember, mistakes are part of the learning process. Embrace them as opportunities to grow and improve. By avoiding these common mistakes and staying committed to your musical journey, you’ll develop a strong foundation and become a skilled and confident bassist.
Resources for Learning Bass Guitar
Learning to play the bass guitar is an exciting and fulfilling journey that requires the right resources and guidance. Whether you prefer self-study or structured lessons, there are several resources available to help you develop your skills and expand your musical horizons. Here are some valuable resources for learning bass guitar:
- Online Bass Lessons: Numerous websites offer video lessons and tutorials specifically designed for bass guitarists of all levels. Websites like StudyBass, Scott’s Bass Lessons, and BassBuzz provide comprehensive lesson plans, technique exercises, and song tutorials to guide your learning process.
- Bass Method Books: Bass method books are a great resource for self-study. Books like “Hal Leonard Bass Method” by Ed Friedland and “The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Playing Bass Guitar” by David Hodge offer structured lessons, exercises, and music theory, covering a wide range of playing styles and techniques.
- YouTube Tutorials: YouTube is a treasure trove of free bass guitar lessons. Many skilled bassists and educators share tutorials, technique tips, and play-along videos on their channels. Seek out channels like TalkingBass, Scott Devine, and MarloweDK for a variety of bass lessons and inspiration.
- In-person Lessons: Taking lessons from a qualified bass instructor can provide personalized guidance and feedback. Look for local music schools, community centers, or private instructors who specialize in teaching bass guitar. They can tailor lessons to your needs, offer valuable insights, and help you progress more efficiently.
- Music Theory Resources: Understanding music theory is beneficial for any musician. Resources like music theory books, online courses, and websites such as MusicTheory.net can help you grasp essential concepts, such as scales, chords, key signatures, and rhythmic patterns, enabling you to apply them to your bass playing.
- Jamming with Others: Playing with other musicians is an excellent way to grow as a bassist. Seek opportunities to jam with friends, join a band, or participate in local jam sessions. Collaborating with others will improve your improvisation skills, enhance your sense of timing, and expose you to different musical styles and ideas.
- Transcribing Basslines: Transcribing basslines from your favorite songs is an effective way to develop your ear, learn new techniques, and study different musical styles. Use transcription software or apps like Transcribe! or Anytune to slow down and loop difficult parts, making the learning process more manageable.
- Online Communities and Forums: Joining online communities and forums dedicated to bass guitarists can provide a wealth of information and support. Websites like TalkBass and BassChat have active forums where you can ask questions, share experiences, and connect with other bass players.
Remember, the key to progress is consistent practice and a passion for learning. Explore these resources, find what works best for you, and enjoy the process of honing your skills as a bassist. With dedication and the right resources, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a skilled and versatile bass guitarist.
Conclusion
Learning to play the bass guitar is an exciting and rewarding endeavor that can bring joy, creativity, and a deep connection to the music you love. While it may require dedication and practice, the journey is filled with incredible opportunities for growth as a musician. By avoiding common mistakes, utilizing valuable resources, and consistently honing your skills, you can become a skilled and confident bassist.
Remember to start with the basics, understanding the anatomy of the bass guitar and learning how to read tablature. As you progress, focus on building a strong foundation in technique, exploring different playing styles, and expanding your musicality. Embrace the process of practicing and seek opportunities to play with others, as collaboration and performance will enhance your playing experience.
Utilize a variety of resources such as online lessons, books, YouTube tutorials, and in-person instruction to guide your learning. Take advantage of music theory resources, transcribe basslines, and engage with online communities to deepen your understanding and connect with fellow musicians.
Remember, the most important aspect of your bass guitar journey is to enjoy the process. Celebrate your progress, stay motivated, and continuously challenge yourself to reach new heights. Whether you aspire to perform on stage, join a band, or simply play for your own pleasure, the bass guitar can provide a lifetime of musical fulfillment.
So grab your bass guitar, embrace the rhythm, and dive into the world of low-end frequencies. With perseverance, determination, and a love for music, you have the power to become a skilled bassist and make your mark in the world of music.