Home>Instruments>Drums>How To Write For Drums


Drums
How To Write For Drums
Modified: February 20, 2024
Learn how to write engaging and effective drum music with our expert tips and techniques. Improve your drumming skills and create powerful rhythms.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Writing for drums is an essential skill for any musician or composer. Whether you’re a songwriter, arranger, or producer, understanding how to write drum parts effectively can elevate the overall impact of your music. Drum notation is a specialized form of musical notation that communicates the rhythmic and percussive elements of a piece of music. It provides drummers with a clear roadmap for their performances and ensures consistency across different interpretations of a composition.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of drum notation, the tools and software available for writing drum parts, techniques for creating dynamic and expressive drum scores, and valuable tips for honing your drum writing skills. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to write for drums and be equipped with the knowledge to craft compelling and engaging drum parts for your musical projects.
Writing for drums is a unique endeavor that requires a nuanced understanding of rhythm, dynamics, and the capabilities of the drum set. Whether you’re crafting a drum score for a rock band, jazz ensemble, orchestral piece, or electronic music production, the principles of effective drum writing remain consistent. By delving into the intricacies of drum notation and exploring the creative possibilities within this domain, you will expand your musical toolkit and enrich your compositions with powerful rhythmic foundations.
Whether you’re a seasoned composer or a novice musician, mastering the art of drum writing will open up new avenues for creativity and collaboration. Throughout this guide, we will delve into the nuances of drum notation, explore the diverse approaches to writing for drums, and provide practical insights to enhance your drum writing skills. Let’s embark on this rhythmic journey and uncover the art of crafting compelling and impactful drum parts.
Understanding the Basics of Drum Notation
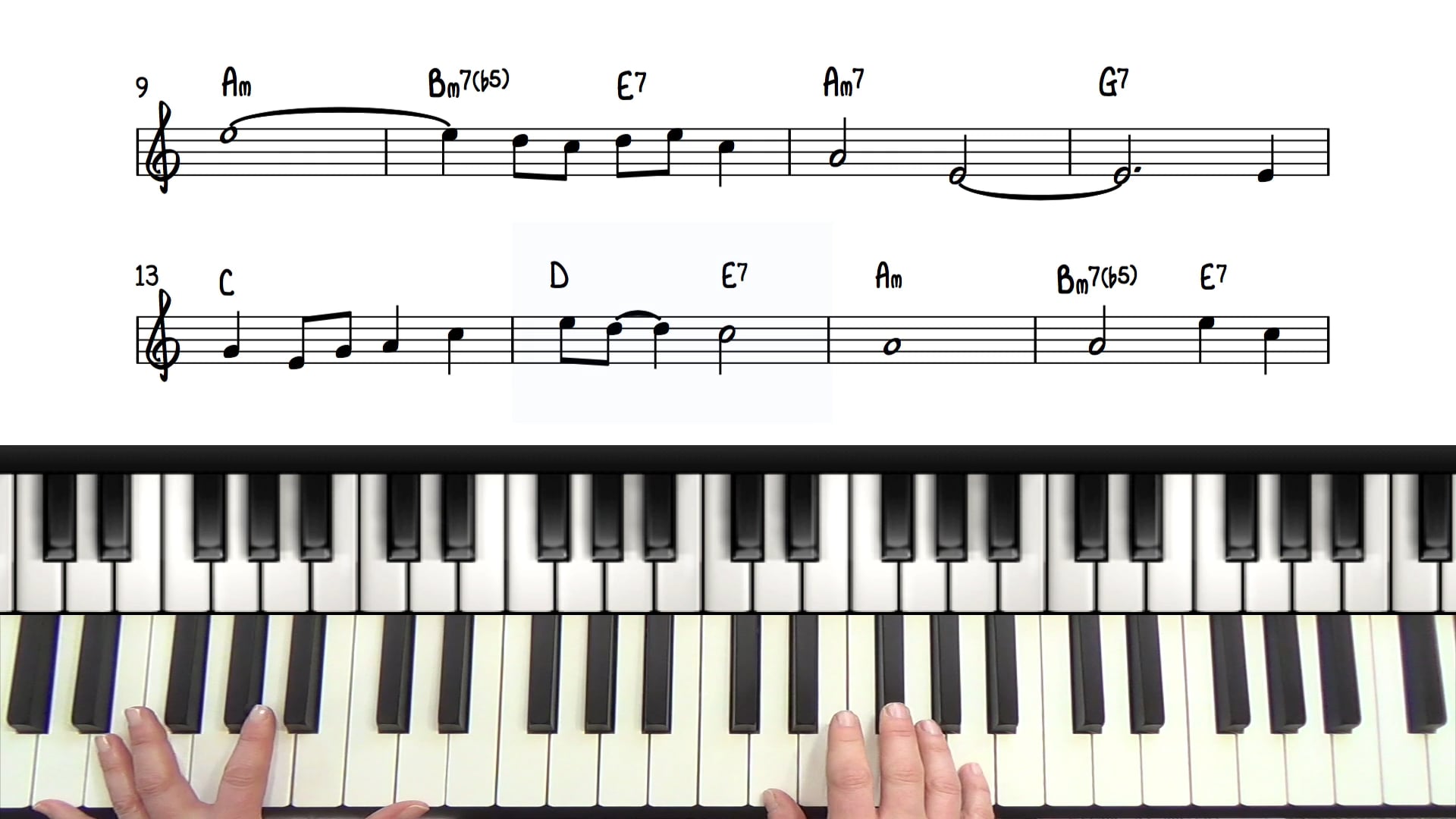
Drum notation is a symbolic representation of percussive elements within a musical composition. Unlike traditional musical notation, which primarily focuses on pitch and duration, drum notation conveys rhythmic patterns, accents, and specific techniques used in drumming. Understanding the fundamentals of drum notation is crucial for accurately communicating drum parts to performers and achieving the desired rhythmic feel in a piece of music.
At the core of drum notation are rhythmic values and symbols that denote different types of drum strokes and articulations. Common rhythmic values include whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, eighth notes, and sixteenth notes, each representing a specific duration within a musical measure. Additionally, drum notation employs various symbols to indicate drum hits, such as slashes, X’s, and note heads placed on specific lines and spaces of the staff, corresponding to different drums and percussion instruments.
Drum notation also encompasses dynamic markings, accent notations, and specific instructions for techniques like rimshots, flams, and rolls. These elements provide drummers with detailed guidance on how to execute each rhythm with precision and expression. Furthermore, drum notation accounts for the unique characteristics of different drum set components, including the snare drum, bass drum, hi-hat, cymbals, and toms, allowing composers and arrangers to tailor their drum parts to the specific capabilities of the instrument.
Aspiring drum writers can benefit from familiarizing themselves with the standard conventions of drum notation, including the layout of the drum staff, the interpretation of rhythmic symbols, and the integration of articulation markings. By mastering the basics of drum notation, composers and arrangers can effectively communicate their musical ideas to drummers and percussionists, fostering clear and cohesive performances.
Whether you’re transcribing drum parts for an existing song, composing original drum scores, or arranging percussion accompaniments for various musical genres, a solid grasp of drum notation lays the foundation for creating impactful and engaging drum parts. As we delve deeper into the realm of drum writing, the nuances of drum notation will continue to shape our understanding of rhythm and percussive expression.
Choosing the Right Notation Software
When it comes to writing drum parts, utilizing the appropriate notation software can significantly streamline the composition process and enhance the clarity of your musical ideas. Notation software offers a range of tools and features tailored to the specific requirements of drum notation, empowering composers and arrangers to create professional-quality drum scores with ease and precision.
Several leading notation software options cater to the needs of drum writers, providing intuitive interfaces, comprehensive percussion palettes, and robust playback capabilities. These programs enable users to input drum parts using specialized drum notation tools, assign specific sounds to different percussion instruments, and customize the visual layout of drum scores to align with industry standards.
One key consideration when choosing notation software for drum writing is the availability of percussion-specific symbols, articulations, and notation styles. The software should offer a diverse range of drum notation elements, including rudiment symbols, ghost notes, rim clicks, and other percussive techniques essential for accurately representing drum performances. Additionally, the ability to customize drum set configurations and assign unique playback sounds to individual drum voices can greatly enhance the authenticity and realism of the written drum parts.
Furthermore, playback functionality is a crucial aspect of notation software for drum writers. The software should support realistic playback of drum parts, allowing composers to audition their scores and assess the rhythmic and dynamic nuances of the percussion arrangements. This feature facilitates the fine-tuning of drum parts and provides valuable insight into how the written rhythms will translate into live performances.
Integration with digital audio workstations (DAWs) and compatibility with MIDI controllers are also desirable attributes of notation software for drum writing. Seamless integration with DAWs enables composers to incorporate their drum scores into larger musical productions, while MIDI controller compatibility allows for intuitive input of drum parts using electronic percussion pads or MIDI keyboards.
Ultimately, the right notation software for drum writing should align with your specific workflow preferences, musical objectives, and technical requirements. By carefully evaluating the features, usability, and compatibility of different notation software options, you can select a tool that empowers you to articulate your rhythmic ideas with clarity and precision, ultimately enhancing the impact of your drum compositions.
Techniques for Writing Drum Parts
Effective drum writing involves employing a variety of techniques to craft compelling and dynamic drum parts that enhance the overall musical experience. Whether you’re creating drum scores for a specific genre, collaborating with other musicians, or composing original percussion arrangements, mastering essential techniques for writing drum parts is essential for achieving rhythmic cohesion and expressive impact.
1. Rhythmic Layering: Incorporating rhythmic layering in drum parts involves crafting patterns that interlock and complement each other, creating a cohesive rhythmic tapestry. By assigning distinct rhythmic motifs to different drum voices and cymbals, composers can add depth and complexity to their drum arrangements, enhancing the overall rhythmic drive of the music.
2. Dynamic Markings: Utilizing dynamic markings in drum notation is crucial for conveying the varying intensity and volume of drum performances. By incorporating crescendos, decrescendos, accents, and other dynamic indicators, composers can guide drummers in delivering nuanced and expressive performances that heighten the emotional impact of the music.
3. Articulations and Techniques: Incorporating specific articulations and techniques, such as rimshots, flams, drags, and mallet rolls, adds texture and personality to drum parts. These articulations provide drummers with detailed instructions for executing intricate and expressive rhythmic embellishments, enriching the sonic palette of the percussion ensemble.
4. Groove Development: Crafting engaging grooves that drive the rhythmic pulse of the music is a fundamental aspect of effective drum writing. Experimenting with different rhythmic subdivisions, syncopated patterns, and groove variations allows composers to infuse their drum parts with infectious energy and rhythmic vitality, enhancing the overall musical feel.
5. Instrumentation and Orchestration: Tailoring drum parts to the specific capabilities and timbral characteristics of different percussion instruments is essential for achieving balanced and sonically rich drum arrangements. Understanding the sonic properties of the snare drum, bass drum, hi-hat, cymbals, and toms enables composers to orchestrate their drum parts with precision and creativity.
By incorporating these techniques into their drum writing process, composers and arrangers can elevate the rhythmic dimension of their compositions, infusing their music with captivating rhythms and expressive percussive performances. Mastering these techniques empowers drum writers to create impactful and memorable drum parts that resonate with listeners and enhance the overall musical narrative.
Tips for Effective Drum Writing
Writing compelling and effective drum parts requires a combination of technical proficiency, creative insight, and an understanding of rhythmic dynamics. Whether you’re embarking on your first drum composition or seeking to refine your existing drum writing skills, the following tips will guide you in crafting impactful and engaging drum arrangements.
1. Understand Drum Set Anatomy: Familiarize yourself with the components of the drum set, including the snare drum, bass drum, hi-hat, cymbals, and toms. Understanding the sonic characteristics and playing techniques associated with each drum and cymbal will inform your orchestration and enhance the authenticity of your drum arrangements.
2. Study Rhythmic Styles: Explore diverse rhythmic styles and genres to expand your rhythmic vocabulary. Whether it’s jazz, rock, funk, Latin, or world music, immersing yourself in various rhythmic traditions will enrich your rhythmic sensibilities and inspire innovative drum patterns and grooves.
3. Emphasize Musicality: Approach drum writing with a focus on musicality and expression. Consider the role of the drums in serving the song, supporting melodic and harmonic elements, and contributing to the overall musical narrative. Strive to create drum parts that enhance the emotional impact and energy of the music.
4. Collaborate with Drummers: Engage in collaborative exchanges with drummers to gain insight into their creative process and performance preferences. Understanding the perspectives and artistic sensibilities of drummers will inform your approach to writing drum parts, fostering a collaborative and empathetic mindset.
5. Experiment with Textures and Timbres: Explore the sonic possibilities of the drum set by experimenting with different playing techniques, mallet choices, and drum tuning. By incorporating a diverse range of textures and timbres, you can imbue your drum arrangements with depth and sonic richness.
6. Balance Complexity and Clarity: Strive to strike a balance between rhythmic complexity and clarity in your drum arrangements. While intricate rhythmic patterns can add interest, it’s essential to ensure that the rhythmic motifs are communicated clearly and intuitively, facilitating effective performance interpretation.
7. Leverage Notation Software: Take advantage of notation software equipped with percussion-specific features and playback capabilities. Utilizing notation software streamlines the process of inputting drum parts, facilitates realistic playback, and provides visual clarity for performers.
8. Embrace Creativity: Cultivate a spirit of creativity and experimentation in your drum writing process. Don’t be afraid to push boundaries, explore unconventional rhythmic ideas, and infuse your drum arrangements with your unique artistic voice.
By integrating these tips into your drum writing practice, you can refine your approach to crafting compelling and effective drum parts, enriching your musical compositions with vibrant and expressive percussive elements.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of drum writing is a transformative journey that empowers composers and arrangers to infuse their musical creations with captivating rhythmic energy and expressive percussive performances. By delving into the intricacies of drum notation, exploring diverse techniques for crafting dynamic drum parts, and embracing the creative possibilities within the realm of drum writing, musicians can elevate the impact of their compositions and engage listeners on a profound rhythmic level.
Understanding the basics of drum notation lays the foundation for clear and effective communication of rhythmic ideas, enabling composers to articulate intricate drum patterns and percussive nuances with precision. Choosing the right notation software tailored to the specific requirements of drum writing streamlines the composition process and enhances the clarity and authenticity of drum scores, empowering composers to bring their rhythmic visions to life.
Techniques such as rhythmic layering, dynamic markings, and groove development enrich drum arrangements with depth and vitality, while tips for effective drum writing provide valuable insights for honing rhythmic sensibilities and fostering collaborative exchanges with drummers. By embracing a holistic approach to drum writing, musicians can create drum parts that not only serve the rhythmic foundation of their compositions but also contribute to the overall musical narrative with artistry and expression.
As composers and arrangers continue to explore the diverse rhythmic traditions and sonic possibilities of the drum set, the art of drum writing evolves as a dynamic and ever-expanding domain of creative expression. By embracing the tips, techniques, and insights shared in this guide, musicians can embark on a rhythmic journey filled with innovation, collaboration, and the transformative power of percussive storytelling.
Ultimately, the art of drum writing transcends technical proficiency, inviting composers to channel their creativity and rhythmic intuition into compelling and impactful drum arrangements. Through the mastery of drum notation, the utilization of advanced notation software, and the application of diverse techniques, composers and arrangers can unlock the rhythmic potential of their musical visions, crafting drum parts that resonate with depth, emotion, and rhythmic vitality.