Home>Production & Technology>Metronome>How Many Beats Does A Metronome Play In A Minute


Metronome
How Many Beats Does A Metronome Play In A Minute
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover how many beats a metronome plays in just one minute. Gain a better understanding of this essential musical tool with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is a Metronome?
- How Does a Metronome Work?
- Understanding Beats per Minute (BPM)
- Factors Affecting Beats per Minute
- Setting the Metronome for Different Musical Styles
- The Importance of Practicing with a Metronome
- Common Misconceptions about Metronomes
- How to Use a Metronome Effectively
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of music and rhythm! Whether you are a professional musician, an aspiring artist, or simply a music lover, you have likely come across the term “metronome.” But what exactly is a metronome, and why is it so important in the realm of music?
A metronome is a device that musicians use to keep time and maintain a consistent beat. It serves as a reliable guide for tempo, ensuring that the music is played at the desired speed. Whether you’re playing the piano, guitar, drums, or any other instrument, the metronome is an indispensable tool that helps you stay in sync and develop your sense of timing.
But how does a metronome work, and what do those numbers on the dial mean? Fear not, as we explore the intricacies of this fascinating device and delve into the world of beats per minute (BPM) and how they relate to musical performance.
So, whether you are a beginner who wants to learn the basics or an experienced musician looking to refine your skills, this article will provide a comprehensive guide to understanding and utilizing the power of the metronome.
What is a Metronome?
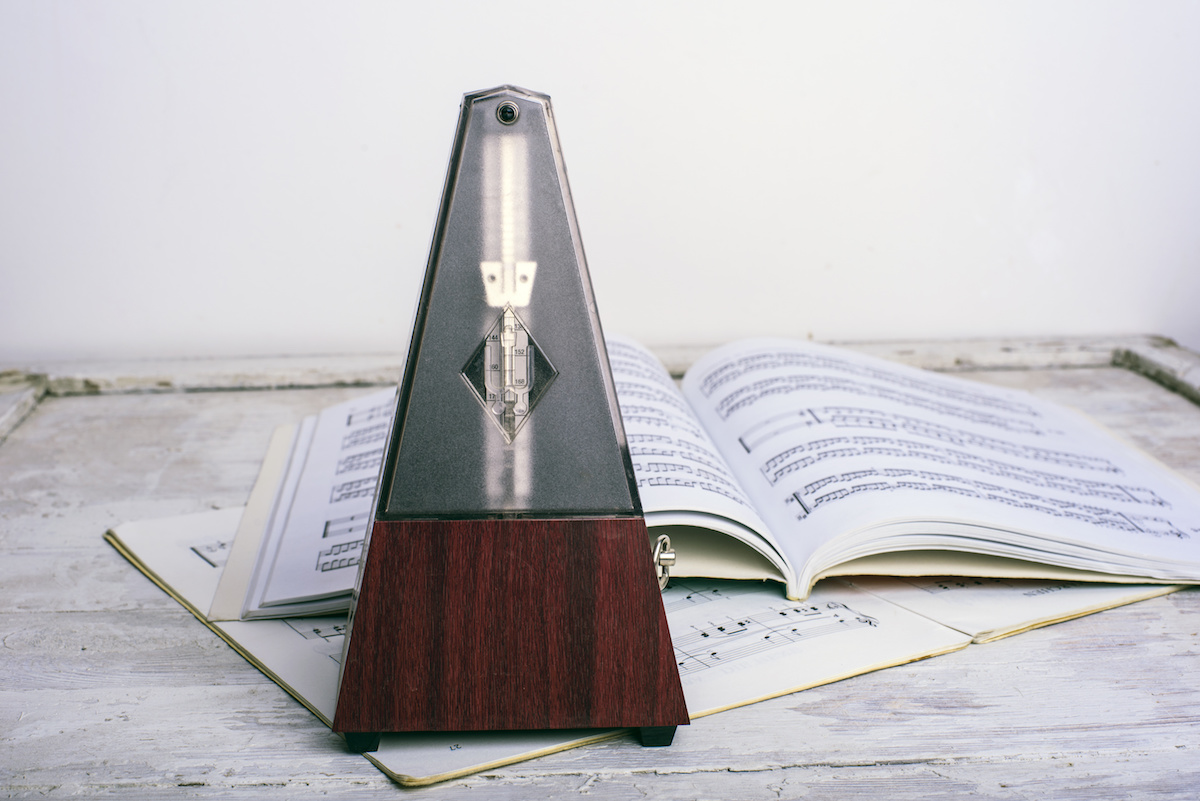
A metronome is a device that produces a rhythmic sound or visual signal at a consistent tempo. It is used by musicians to aid in keeping a steady beat and maintaining the correct tempo while playing or practicing music.
Historically, metronomes were mechanical devices with a pendulum or a weighted arm that swung back and forth, producing audible clicks. However, with the advancements in technology, electronic metronomes have become more popular. These digital metronomes typically have a small screen that displays the tempo and produce sound or visual cues through speakers or LED lights.
The primary purpose of a metronome is to help musicians develop a strong sense of timing and rhythm. By providing a constant beat, it allows musicians to practice playing in synchrony with the desired tempo, which is crucial for ensemble performances and maintaining a cohesive sound.
Metronomes are widely used in various musical genres, including classical music, jazz, rock, pop, and more. They are especially helpful for practicing difficult passages, improving speed and accuracy, and developing a solid internal sense of rhythm.
Besides its role in music practice, a metronome is also used in music composition and recording. Composers often specify the desired tempo using the BPM (beats per minute) marking, which is then translated into the corresponding metronome setting to ensure consistent timing throughout the piece. In the studio, a metronome is frequently used to provide a reference beat for recording instruments or vocals separately, ensuring precise synchronization during the mixing and editing process.
Overall, a metronome is a invaluable tool for musicians of all levels. It helps improve timing, develop a strong sense of rhythm, and elevate the quality of musical performances. So whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned musician, exploring the world of metronomes and incorporating them into your practice routine can greatly enhance your musical abilities.
How Does a Metronome Work?
While the concept of a metronome may seem simple, the inner workings of this device are quite fascinating. So, how does a metronome actually work?
In a mechanical metronome, the core mechanism consists of a pendulum or a weighted arm attached to a controlled mechanism. The weight at the end of the arm swings back and forth, creating a ticking sound with each swing. The speed at which the pendulum moves is determined by the position of a weight on the pendulum, which can be adjusted to set the desired tempo. As the weight is moved up or down, it alters the length of the pendulum, thereby changing the time it takes for each swing.
On the other hand, electronic metronomes use advanced technology to replicate the same functionality in a compact and convenient package. These digital metronomes typically have a small screen that displays the tempo and provide audible or visual cues. The tempo is controlled by buttons or knobs that enable you to adjust the beats per minute (BPM) to your desired tempo.
Regardless of the type of metronome, the fundamental principle remains the same – the metronome generates a rhythmic output to help musicians maintain a steady beat. This consistent beat serves as a guide for musicians to stay on track with the tempo and maintain a consistent rhythm.
Some modern metronomes even offer additional features such as different sounds or visual cues to accommodate various preferences. This includes options like different sounds for the downbeat and the offbeat or the ability to accentuate specific beats within a measure. These features allow musicians to further customize their practice sessions and adapt to different musical styles.
Overall, the mechanics of a metronome may vary, but the purpose remains the same – to provide a reliable and consistent beat for musicians to follow. By utilizing this essential tool, musicians can master the art of playing in time, improve their sense of rhythm, and become more confident performers.
Understanding Beats per Minute (BPM)
Beats per minute (BPM) is a measurement used to quantify the tempo or speed of music. It indicates the number of beats or pulses that occur in one minute. The BPM value serves as a reference point for musicians to play or practice music at a consistent tempo.
A higher BPM signifies a faster tempo, while a lower BPM indicates a slower tempo. For example, a piece of music with a BPM of 120 would have twice as many beats per minute as a piece with a BPM of 60.
The BPM of a musical piece is typically indicated at the beginning of the sheet music or displayed on a metronome. It acts as a guide for musicians to ensure that they maintain the desired speed and rhythm throughout the performance.
Understanding BPM is crucial for musicians in various scenarios. It allows them to synchronize with other musicians in an ensemble, maintain a consistent tempo during live performances, and accurately interpret the composer’s intentions in terms of tempo.
When practicing with a metronome, musicians often start with a slower BPM and gradually increase the tempo as they become more comfortable with the piece. This progressive approach helps in building muscle memory and allows for precision in playing complicated passages.
In addition to providing a steady beat, metronomes also display the BPM value as a visual reference. This helps musicians track their progress and ensure they are adhering to the desired tempo.
It’s important to note that while the BPM value is a helpful reference, the interpretation of tempo can vary depending on the musical style and context. For example, a classical piece may have a lower BPM compared to a fast-paced rock song.
Overall, a solid understanding of BPM is essential for musicians to maintain consistency, improve timing, and create a cohesive musical performance. Whether you’re a pianist, guitarist, drummer, or any other instrumentalist or vocalist, incorporating BPM into your practice routine will contribute to your overall musical growth and proficiency.
Factors Affecting Beats per Minute
While the beats per minute (BPM) value provides a standard measure of tempo, several factors can influence the choice of an appropriate BPM for a musical piece. These factors should be considered to ensure that the tempo aligns with the desired style, mood, and musical context.
1. Musical Style: Different musical genres have distinct conventions for tempo. For example, classical music often adheres to specific tempo markings, while popular music genres like rock or EDM may have a wider range of BPM possibilities. Understanding the style of music you are playing will guide you in selecting an appropriate BPM range.
2. Mood and Expression: The desired mood and expression of a musical piece can be enhanced or hindered by the choice of tempo. A slower tempo may evoke a sense of tranquility or introspection, while a faster tempo can generate excitement or energy. Consider the emotional impact you wish to convey when determining the BPM.
3. Instrumentation: The instruments being played can also impact the choice of BPM. Some instruments may require more time to execute complex passages at higher tempos, whereas others might excel in faster-paced sections. It’s important to consider the technical limitations and capabilities of the instruments involved in order to select an appropriate BPM.
4. Physicality: The physical demands of playing an instrument or singing can influence the BPM. Instruments like the piano or guitar may have certain limitations in terms of how quickly and accurately the musician can move their fingers. Similarly, singing intricate melodies or rapid vocal runs may require adjustments to the BPM to accommodate breath control and vocal agility.
5. Audience Engagement and Danceability: If your music is intended for dancing or engaging a specific audience, the BPM plays a crucial role. Dance music genres, such as disco or techno, often have higher BPMs to facilitate movement and create a lively atmosphere. Consider the expectations and preferences of the listeners when selecting the BPM for dance or performance-based music.
6. Interpretation and Artistic Vision: Ultimately, the choice of BPM can be a matter of interpretation and artistic vision. Musicians and composers may choose to deviate from traditional BPM guidelines to convey a unique expression or create a distinct musical experience. The artistic vision and individual creativity play an important role in shaping the final decision regarding BPM.
By considering these factors, musicians can make informed choices about the BPM that will enhance the musicality, expressiveness, and overall impact of their performances. It’s essential to experiment, listen, and adapt to find the ideal BPM that best suits the specific musical piece and artistic intent.
Setting the Metronome for Different Musical Styles
When using a metronome, it’s important to set the tempo (beats per minute or BPM) according to the specific musical style you are playing. Different genres have their own characteristic tempos, and understanding these guidelines can contribute to a more authentic and engaging performance.
Here are some common musical styles and their respective recommended BPM ranges:
- Classical: Classical music spans a wide range of styles and periods, but generally, it is known for its adherence to precise tempo indications. The BPM can vary based on the specific composition, but classical pieces often fall within a range of 60 to 140 BPM.
- Rock and Pop: Rock and Pop music encompass various subgenres and can have diverse tempos. However, a general guideline is to set the metronome between 100 and 180 BPM for most rock and pop songs. Slower rock ballads may have a BPM range of 60 to 100, while faster punk or metal tunes can reach BPM values above 180.
- Jazz: Jazz music is known for its flexibility and improvisation, which allows for a wide range of tempos. The BPM can vary based on the jazz style and specific song, but a typical range is between 100 and 200 BPM. Swing music often falls within the 120 to 140 BPM range.
- Electronic Dance Music (EDM): EDM genres like techno, house, and trance have strong emphasis on rhythm and danceability. The BPM for EDM can range from 120 to 140 BPM for genres like house, 125 to 150 BPM for techno, and 130 to 160 BPM for trance. However, faster subgenres such as drum and bass or hardcore can exceed 170+ BPM.
- Country and Folk: Country and folk music tend to have moderate tempos, reflecting the storytelling nature of the genre. The BPM for these styles often ranges from 80 to 120 BPM, with ballads falling on the lower end and more upbeat songs on the higher end.
These ranges are just general guidelines, and there can be variations within each style. It’s important to listen to the specific song and use your artistic judgment when setting the metronome. Pay attention to the feel and groove of the music to ensure that it aligns with the intended style and captures the essence of the genre.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that complexity within a song can affect the chosen BPM. Certain sections or passages may require adjustments to facilitate intricate rhythms or rapid technical execution, especially for more challenging instrumental or vocal parts.
Remember, the metronome is a tool to assist you in keeping a steady beat, but it’s also important to allow room for musical interpretation and expression. Experiment with different tempos within the recommended ranges to find the tempo where the music feels most comfortable and natural to you, and where it best resonates with the intended musical style.
The Importance of Practicing with a Metronome
Practicing with a metronome is a crucial aspect of music education and development. It serves as an essential tool that aids in improving timing, rhythm, and overall musicality. Here are some of the key reasons why practicing with a metronome is so important:
1. Establishing a Solid Sense of Timing: A metronome provides a consistent beat, allowing musicians to develop a strong internal sense of timing. By practicing with a metronome, you learn to play precisely in sync with the given tempo and develop a reliable internal pulse that stays steady even in complex musical passages.
2. Building Technique and Accuracy: Playing with a metronome helps in building technical proficiency and accuracy. It exposes any inconsistencies or timing issues in your playing, highlighting areas that require improvement. Practicing with a metronome can also enhance your hand-eye coordination and enable you to execute challenging passages with precision.
3. Enhancing Musical Ensemble Skills: Playing in an ensemble requires musicians to synchronize with one another to create a cohesive sound. Practicing with a metronome trains you to listen and play in sync with other musicians, which is essential for successful ensemble performances. It helps develop the discipline of following a unified tempo and staying together as a group.
4. Developing Dynamic Control: The metronome provides a reference point that allows you to experiment with different dynamics and articulations. By varying the intensity or volume level while staying in time, you learn to control and shape your musical phrases effectively, resulting in a more expressive and nuanced performance.
5. Improving Tempo Transitions: Many musical pieces include sections with different tempos or tempo changes. Practicing with a metronome helps in smoothly transitioning between different tempos, ensuring that you maintain a consistent sense of timing and rhythm throughout the piece.
6. Polishing Performance Skills: When preparing for a performance, practicing with a metronome ensures that you are confident and consistent in your execution. It helps reduce the chances of rushing or slowing down during the excitement of live performance, allowing you to deliver a polished and professional rendition.
Whether you are a beginner or an advanced musician, incorporating regular metronome practice into your routine is invaluable. It not only enhances your technical skills but also nurtures your musicality and overall musicianship. Practicing with a metronome cultivates discipline, precision, and a deep understanding of rhythm, leading to improved performances and musical growth.
Common Misconceptions about Metronomes
While metronomes are highly beneficial tools for musicians, there are some common misconceptions surrounding their usage. Let’s take a look at these misconceptions and debunk them:
1. Metronomes Make Music Mechanical: One misconception is that using a metronome can make music sound robotic or mechanical. However, this is not true. The purpose of a metronome is to provide a steady beat and rhythm, but it is up to the musician to infuse the music with emotion, expression, and phrasing. The metronome serves as a guide, and when used effectively, it can actually enhance a musician’s sense of timing and musicality.
2. You Must Always Practice with a Metronome: While practicing with a metronome is highly recommended, it is not necessary for every practice session. There may be times when you want to explore different interpretations or focus on specific technical aspects without the constraints of a steady beat. It’s important to strike a balance between using a metronome and practicing without one to develop a well-rounded approach to your music.
3. Playing with a Metronome Limits Creativity: Some musicians worry that practicing with a metronome can stifle their creativity. However, the metronome is a tool that helps you develop a strong foundation of timing and rhythm, which in turn allows you to explore more complex and creative musical ideas. It provides a solid framework that you can build upon and expand your musical expression.
4. The Metronome Must Be Followed Strictly: While it is important to follow the metronome’s beat, musicians can also learn to play with expressive rubato or slight variations in timing. The metronome is not a substitute for musical interpretation and expression. It serves as a guide, but musicians should feel free to add subtle fluctuations and nuances to bring the music to life.
5. Metronomes Are Only for Beginners: Another misconception is that metronomes are only useful for beginners. However, musicians of all levels can benefit from using a metronome. It helps beginners develop a sense of timing and rhythm, while more advanced musicians can use it to refine their technique, improve synchronization, and enhance their overall musicality.
6. Metronomes Are Only for Classical Music: While metronomes have long been associated with classical music, they are beneficial for musicians in all genres. From rock to jazz to electronic music, the metronome can help in maintaining a consistent tempo and improving precision in any style of music.
Understanding these common misconceptions about metronomes helps us appreciate the true value and versatility of this essential tool. By using a metronome effectively and with an open mind, we can harness its power to enhance our musicality, improve our performances, and unlock our full potential as musicians.
How to Use a Metronome Effectively
Using a metronome effectively is key to maximizing its benefits and enhancing your musical abilities. Here are some tips on how to use a metronome effectively:
- Start Slowly: When practicing a new piece or technique, start with a slower tempo on the metronome. This allows you to focus on accuracy and precision. Gradually increase the tempo as you become more comfortable and confident.
- Set Clear Goals: Determine specific goals for each practice session. This could be focusing on a particular section or passage, working on evenness of rhythm, or improving speed. Setting goals helps keep practices structured and productive.
- Practice Subdivisions: Many metronomes have the option to subdivide the beats. Utilize this feature to work on tricky rhythmic patterns or to improve your internal pulse. Practice playing along with the subdivisions to develop a stronger sense of timing.
- Experiment with Accents: Some metronomes allow you to accentuate specific beats within a measure. Experiment with different accents to improve your phrasing and accentuation skills. This adds a dynamic element to your playing and helps shape musical phrases more effectively.
- Practice Tempo Transitions: If a piece requires a change in tempo, practice transitioning smoothly between different tempos with the help of the metronome. Focus on maintaining a steady beat during the transition to ensure a seamless and controlled tempo change.
- Practice with Different Click Sounds: Many metronomes offer different click sounds, such as woodblock, cowbell, or handclaps. Experiment with different click sounds to add variety and make practicing more enjoyable.
- Record and Assess: Record your practice sessions with the metronome and critically listen back. Pay attention to any timing discrepancies or areas that need improvement. This allows you to assess your progress and make necessary adjustments.
- Integrate Musicianship: While a metronome provides a steady beat, don’t forget to incorporate your musicality. Allow for expressive variations in dynamics, phrasing, and interpretation even when playing in time. The metronome is a tool, but you bring the music to life with your artistic expression.
- Use Visual Cues: If using a digital or app-based metronome, take advantage of visual cues like blinking lights or bouncing balls that accompany the audio click. This can provide an additional layer of visual guidance to complement the auditory beat.
Remember, the metronome is a practice tool meant to enhance your musicality and technical skills. It is not a substitute for musical expression or creativity. Use it as a guide to develop a strong sense of timing, improve accuracy, and build a solid foundation of rhythm. By incorporating these tips into your practice routine, you can harness the full potential of the metronome and take your musical abilities to new heights.
Conclusion
The metronome is a powerful tool that plays a vital role in the development of musicians. Its consistent beats and precise tempo provide a solid foundation for practicing and performing music. By practicing with a metronome, musicians can improve their timing, rhythm, accuracy, and overall musicality.
Throughout this article, we have explored what a metronome is, how it works, and its significance in various musical styles. We have also addressed common misconceptions and provided tips for using a metronome effectively.
From classical music to rock, jazz, and electronic music, the metronome is a versatile tool that benefits musicians in all genres. It helps establish a strong sense of timing, aids in developing technique, promotes ensemble skills, and enhances performance quality.
While the metronome provides a steady beat, it’s important to remember that it is a tool, not a musical dictator. Musicians should feel free to add their own artistic flair, variations, and expression to the music even when practicing with a metronome.
Incorporating regular metronome practice into your routine can greatly accelerate your progress as a musician. As you build a solid foundation of timing and rhythm, you will find that your performances become more confident and expressive.
So, whether you’re a beginner starting your musical journey or an experienced musician looking to refine your skills, embrace the power of the metronome. Use it effectively, practice with intention, and discover the transformative effects it can have on your musical abilities. With the metronome as your faithful guide, you can unlock your full potential and create music that is precise, engaging, and full of emotion.