Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>How Is Music Theory Useful For Guitar


Music Theory
How Is Music Theory Useful For Guitar
Modified: February 14, 2024
Discover the importance of music theory for guitarists and how it enhances your understanding of chords, scales, and musical composition. Unlock your full potential with music theory!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Music theory is often seen as a daunting and complex subject, especially for those who are new to learning an instrument like the guitar. However, understanding the fundamentals of music theory can greatly enhance your skills as a guitarist and open up new doors of creativity and musical expression.
At its core, music theory is a system of principles and rules that govern how music is created, organized, and performed. It provides a framework for understanding the relationships between notes, chords, scales, and rhythms. By studying music theory, you can develop a deeper understanding of how music works, enabling you to become a more skilled and versatile musician.
When it comes to playing the guitar, having a solid foundation in music theory can greatly enhance your playing ability. It allows you to navigate the fretboard with ease, understand and create complex chord progressions, improvise melodies, and compose your own music.
Whether you are a beginner guitarist or have been playing for years, incorporating music theory into your practice routine can help take your playing to the next level. In this article, we will explore some of the key aspects of music theory that are particularly relevant to guitarists, including understanding the fretboard, chord progressions, scales and improvisation, transposing and modulating, sight-reading and notation, composing and songwriting techniques, and analyzing and appreciating music.
By delving into these topics, you will gain a deeper understanding of the guitar and its role in creating music. So, let’s dive into the world of music theory and discover how it can be used to enhance your guitar playing!
What is Music Theory?
Music theory is the study of the principles and concepts that govern how music is created, organized, and understood. It provides a framework for analyzing and understanding the elements of music, such as melody, harmony, rhythm, and form. Music theory involves the study of notation, scales, chords, intervals, and the relationship between different musical elements.
At its core, music theory aims to answer questions about why certain musical sounds are appealing, how they can be combined to create meaningful compositions, and how they can be interpreted and performed. It encompasses a wide range of topics, from the basics of note naming and reading sheet music to more advanced concepts like advanced harmony, counterpoint, and orchestration.
Music theory is not just limited to one specific genre or style of music; it applies to various forms of music, including classical, jazz, rock, pop, and many others. While the specific techniques and approaches may vary across different genres, the principles of music theory remain constant.
For guitarists, understanding music theory is crucial in developing a strong foundation for playing the instrument effectively. It enables you to understand the relationship between the notes on the fretboard, how to construct chords, and how to create melodies that harmonize with the underlying chords.
By studying music theory, you gain the ability to analyze and appreciate music on a deeper level. It enhances your overall musicianship and equips you with the tools to communicate and collaborate with other musicians. Whether you want to learn to play your favorite songs, improvise solos, or compose your own music, a solid understanding of music theory is invaluable.
While learning music theory may seem intimidating at first, it is a gradual and rewarding process. Just like any new skill, it takes time and practice to become proficient. As you delve into the world of music theory, you’ll discover new ways to express yourself through the guitar and gain a deeper appreciation for the art of music.
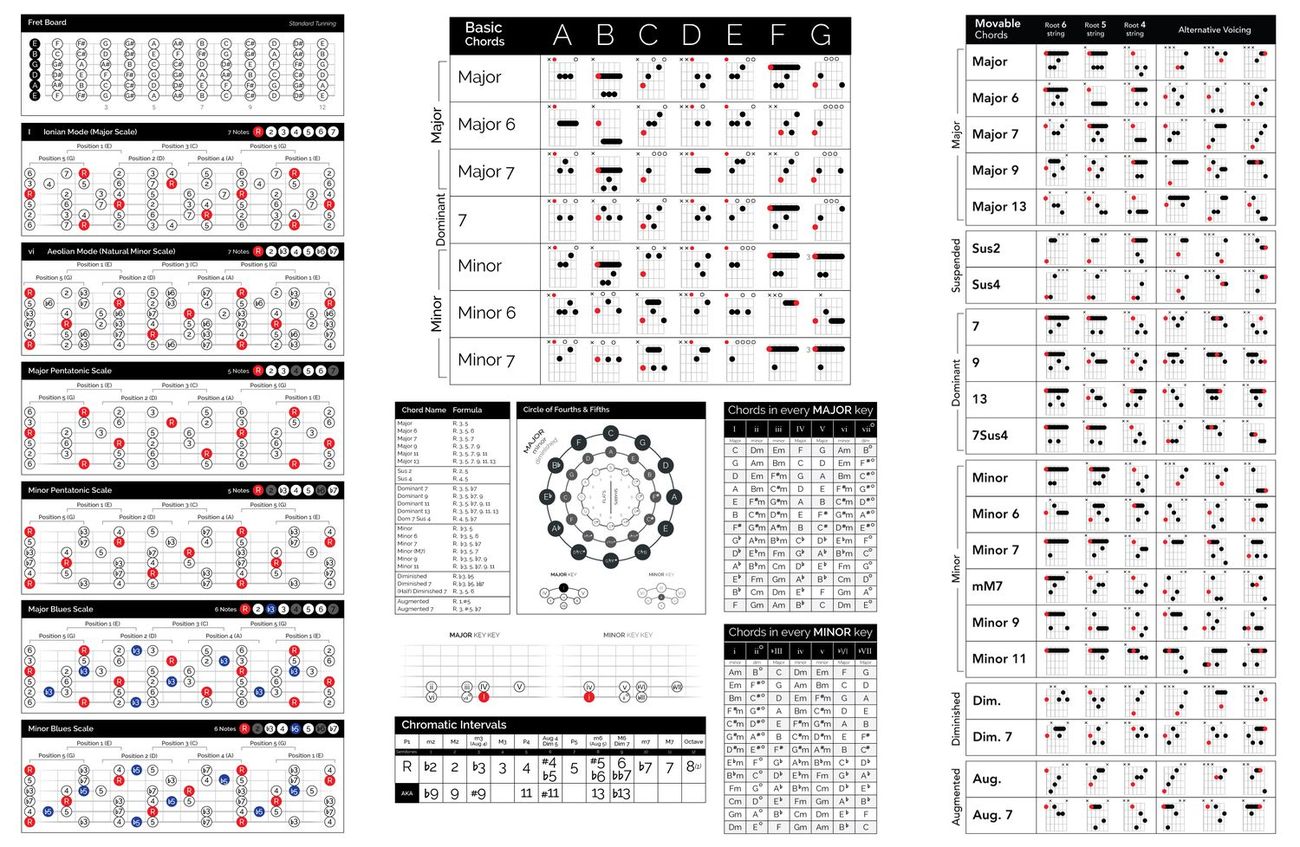
Understanding the Fretboard
One of the most important aspects of playing the guitar is understanding the fretboard. The fretboard is the part of the guitar where the strings are pressed down to produce different notes. It is divided into multiple frets and strings, each representing a specific musical pitch.
By understanding the layout of the fretboard, guitarists can easily locate and play different notes, chords, and scales. This knowledge is essential for effective playing, improvisation, and composing.
At first glance, the fretboard may seem overwhelming with its collection of metal lines and dots. However, it follows a systematic pattern that can be easily understood. The guitar is typically tuned in standard tuning, where the strings are tuned to E-A-D-G-B-E, from lowest to highest pitch.
Each fret on the guitar represents a half-step or one semitone, which is the smallest interval in Western music. Moving one fret higher increases the pitch by one semitone, while moving one fret lower decreases the pitch by one semitone. This pattern repeats throughout the entire fretboard, allowing guitarists to create melodies, chords, and scales in any key.
To navigate the fretboard effectively, it is important to familiarize yourself with the note names on each string. The open strings are E, A, D, G, B, and E, from thickest to thinnest string. As you move up the fretboard, the note names change based on the chromatic scale.
For example, when playing on the 5th fret of the low E string, you are playing an A note. Moving up two frets to the 7th fret gives you a B note. Similarly, by understanding the relationship between the different strings and the frets, you can easily play chords, scales, and melodies across the entire fretboard.
Learning the fretboard takes time and practice, but there are several techniques to make the process easier. Visual aids, such as fretboard diagrams and charts, can help you visualize the patterns and relationships between notes. Physical exercises, like playing scales and arpeggios in different positions, can also improve your familiarity with the fretboard.
Understanding the fretboard not only enhances your ability to play the guitar, but it also opens up a world of possibilities for creative expression. By knowing where each note is located, you can experiment with different chord inversions, create unique melodies, and effortlessly navigate the guitar in any musical context.
Take the time to explore and master the fretboard. It is a fundamental aspect of playing the guitar and will greatly improve your overall musicianship and versatility as a guitarist.
Chord Progressions and Harmony
Chord progressions and harmony are essential elements of music that contribute to the overall sound and emotional impact of a piece. Understanding these concepts is crucial for guitarists as they form the foundation for creating melodies, improvising solos, and composing songs.
A chord progression is a series of chords played in a specific order. It creates a sense of movement and provides a harmonic structure for a song. Common chords used in progressions include major, minor, dominant, and diminished chords.
Harmony refers to the relationship between multiple chords played together. It involves understanding how different chords interact and create tension and resolution. The study of harmony allows guitarists to choose chords that complement each other, creating a pleasing and cohesive musical experience.
When constructing chord progressions, it is important to consider the key of the song. The key determines a set of related chords that harmonize with the melody. For example, in the key of C major, common chords include C, Dm, Em, F, G, Am, and Bdim.
One popular chord progression is the I-IV-V progression, where the chords are based on the first, fourth, and fifth degrees of a major scale. For instance, in the key of G major, the chords would be G, C, and D. Many songs across different genres, such as blues, rock, and pop, utilize this progression.
Understanding chord progressions and harmony allows guitarists to create variations and add flavor to their playing. Substituting chords, using inversions, and adding extensions can dramatically alter the mood and sound of a progression.
Additionally, knowing how to identify common chord progressions in songs helps guitarists play along with their favorite tunes. By recognizing the patterns and relationships between chords, you can quickly pick up songs by ear or using chord charts.
Studying chord progressions and harmony also improves improvisation skills. As you become familiar with common progressions, you can confidently choose the appropriate scales and arpeggios to create engaging solos. This knowledge allows you to navigate the fretboard and effortlessly connect melodies to the underlying chords.
Overall, chord progressions and harmony are essential components of music theory for guitarists. They provide the tools to create compelling melodies, compose original songs, and improvise solos. By understanding and experimenting with different progressions, you can elevate your guitar playing to new heights and captivate listeners with your musicality.
Scales and Improvisation
Scales and improvisation go hand in hand in the world of guitar playing. Scales are a series of notes played in a specific order, while improvisation involves spontaneously creating melodies and solos using those scales.
There are various scales used in music, but some of the most common scales for guitarists include the major scale, minor scale, pentatonic scale, and blues scale. These scales provide a roadmap of notes that are harmonically compatible and can be used to create melodies and solos that fit within a given key or chord progression.
The major scale is a foundational scale that is widely used in many genres of music. It consists of seven notes and follows a specific pattern of whole steps and half steps. Understanding the major scale enables guitarists to create melodies and harmonies that evoke a happy and uplifting mood.
The minor scale, on the other hand, has a different pattern of whole steps and half steps, resulting in a darker and more melancholic sound. It is commonly used in genres like blues, rock, and metal to add emotional depth to guitar solos. The minor pentatonic scale, a simplified version of the minor scale, is particularly popular among guitarists and is versatile for improvisation in various musical styles.
Improvisation is the art of spontaneously creating melodies and solos on the spot. It allows guitarists to express themselves and add their unique touch to a song or musical piece. By understanding scales and how they relate to chords and progressions, guitarists can confidently improvise and create melodic lines that complement the music.
When improvising, it’s important to listen to the underlying chords and base your melodies around the notes of the corresponding scale. This creates a sense of coherence and harmony. By experimenting with different rhythms, techniques, and note choices within the scale, you can create captivating solos that stand out and convey your musical voice.
Improvisation skills are honed through practice and experimentation. By incorporating exercises and drills that focus on scale patterns, intervallic leaps, and phrasing into your practice routine, you can develop the ability to effortlessly navigate the fretboard and create melodies on the fly.
Understanding scales and being able to improvise not only enhances your ability to solo but also improves your overall musicality. It trains your ears to recognize different intervals and musical patterns, enabling you to play by ear, transcribe music, and communicate with other musicians more effectively.
Whether you want to jam along with a band, take compelling solos during live performances, or simply express yourself through your guitar playing, mastering scales and improvisation is essential. It opens up a world of creative possibilities and allows you to truly make the guitar an extension of your musical voice.
Transposing and Modulating
Transposing and modulating are techniques that guitarists use to change the key of a piece of music or transition between different keys within a song. These techniques are valuable tools for diversifying your playing and adding variety to your repertoire.
Transposing involves shifting all the notes and chords of a song by a certain interval. This allows you to change the key of the song to better suit your vocal range or to play along with other instruments. For example, if a song is originally in the key of C major, transposing it up one whole step would change it to the key of D major, shifting all the notes and chords up by two frets on the guitar.
Transposing can be done up or down in pitch, depending on the desired result. This technique is particularly useful when accompanying singers or playing in a band where the original key may not be ideal. By transposing, guitarists can ensure that they are playing in a key that fits the overall sound and feel of the music.
Modulating, on the other hand, involves smoothly transitioning from one key to another within a piece of music. This can be done to create tension and resolution or to add a sense of progression and complexity to a song. Modulation can occur through various methods, such as using chord progressions that lead to a new key or incorporating a pivot chord that functions in both the original and new keys.
Understanding how to transpose and modulate requires a solid understanding of music theory, including scales, key signatures, and chord progressions. By familiarizing yourself with the relationship between different keys and the corresponding chords, you can confidently navigate key changes and create seamless transitions.
Transposing and modulating not only enhance your versatility as a guitarist but also expand your musical horizons. By experimenting with different keys and exploring new tonalities, you can breathe new life into familiar songs and explore different musical possibilities.
Developing a proficiency in transposing and modulating can be a challenging process, but it is immensely rewarding. It allows you to adapt music to suit your preferences and collaborate with other musicians in different keys. By honing these skills, you become a more versatile and adaptable guitarist, ready to tackle a wide range of musical situations.
Sight-reading and Notation
Sight-reading is the ability to read and play music on the guitar in real-time, without prior practice or memorization. It involves quickly interpreting musical notation and translating it into sound on the instrument. Sight-reading is an important skill for guitarists, as it allows them to learn new music efficiently and perform with accuracy.
Music notation is a system of written symbols that represents musical sounds and rhythms. It consists of notes, rests, time signatures, key signatures, dynamics, and other markings that convey the composer’s intended expression of the music. By learning to read and interpret notation, guitarists gain access to a vast library of sheet music and can explore a wide range of musical styles and genres.
When sight-reading on guitar, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the notes on the fretboard, as well as the corresponding positions on the staff. Each note on the staff represents a specific pitch, and guitarists must quickly identify the corresponding fret and string to produce the correct sound.
Practicing sight-reading regularly helps develop fluency and accuracy. Start with simple melodies and gradually progress to more complex pieces. Focus on rhythm, dynamics, and phrasing as you play through the music. Over time, your reading speed and comprehension will improve, allowing you to tackle more challenging pieces.
Notation also provides valuable information about the structure and arrangement of a piece of music. Understanding time signatures, key signatures, and other symbols can help guitarists interpret the intended feel and style of the music. It enables them to accurately reproduce the composer’s intentions and communicate with other musicians when playing in an ensemble setting.
While reading music notation is an important skill, it is worth noting that many guitarists also rely on tablature as an alternative or complementary form of notation. Tablature displays the fingerings and positions on the guitar fretboard, making it easier to learn specific songs or solos. It is particularly useful for beginners or those who prefer a more visual representation of music on the guitar.
However, learning to read standard notation opens up a world of music that may not be available in tablature format. It provides a universal language that connects guitarists with a broader community of musicians, composers, and music educators.
Whether you choose to primarily read standard notation or utilize tablature, developing sight-reading skills and familiarizing yourself with music notation enhances your musicianship. It allows you to explore a wide variety of music, accurately interpret the composer’s intentions, and collaborate more effectively with other musicians.
Composing and Songwriting Techniques
Composing and songwriting are creative processes that allow guitarists to express their unique musical ideas and create original music. Whether you aspire to write your own songs or simply want to explore the art of composition, understanding various techniques can greatly enhance your abilities as a guitarist.
One important aspect of composing for the guitar is exploring different chord progressions. Experimenting with unusual or unexpected chord changes can add intrigue and freshness to your compositions. Playing around with different voicings, inversions, and extensions can also create unique harmonies and textures.
Melody plays a crucial role in songwriting. Crafting memorable and expressive melodies can greatly impact the overall emotional impact of your music. By exploring different scales, interval leaps, and rhythmic patterns, you can create melodies that are both catchy and emotionally compelling.
In addition to chords and melody, rhythm plays a vital role in songwriting. Experimenting with different strumming patterns, picking techniques, and rhythmic accents can give your compositions their own distinct flavor and groove. Don’t be afraid to break away from traditional rhythmic conventions and explore syncopation and unusual time signatures.
Lyrics are another integral part of songwriting. If you choose to incorporate vocals into your compositions, focus on writing meaningful and relatable lyrics. Explore themes and emotions that resonate with you and your audience. Consider experimenting with different rhyme schemes, metaphors, and storytelling techniques to craft lyrics that engage and connect with listeners.
Structure is a key aspect of effective songwriting. Understanding popular song structures, such as verse-chorus-bridge or AABA, can help guide your composition and create a sense of familiarity and coherence. However, don’t be afraid to deviate from traditional structures and experiment with unconventional song forms to add interest and surprise to your music.
Lastly, technology can be a valuable tool in the compositional process. Utilize recording software, virtual instruments, and digital effects to experiment with different sounds and arrangements. These tools can help you fully realize your musical ideas and bring your compositions to life.
Remember, composition and songwriting are deeply personal processes, and there are no hard and fast rules. Trust your instincts and embrace your own unique musical voice. The more you explore and experiment with different techniques, the more you will develop your own style and artistic vision.
Ultimately, composing and songwriting on the guitar allow you to express your creativity and bring your musical ideas to life. It is a rewarding journey that gives you the freedom to create music that is entirely your own, and it is a skill that will continue to evolve and grow the more you practice and explore the possibilities of the instrument.
Analyzing and Appreciating Music
Analyzing and appreciating music is a valuable skill that allows guitarists to deepen their understanding and connection with the music they play. By studying and dissecting musical compositions, guitarists can gain insights into the techniques, structures, and emotions conveyed within the music.
One aspect of analyzing music is identifying the key and chord progressions used in a song. By recognizing the harmonic structure, guitarists can better understand the relationships between chords, identify patterns, and make informed choices when improvising or creating their own compositions.
Rhythm analysis involves examining the rhythmic patterns, accents, and syncopations in a piece of music. Understanding the rhythmic nuances can help guitarists accurately replicate the feel and groove of a song. It also allows them to experiment with different rhythmic techniques and create their own unique rhythmic patterns.
Another important aspect of music analysis is studying melody and phrasing. By examining the melodic motifs, intervallic leaps, and phrasing choices, guitarists can gain insights into the melodic development and overall structure of a composition. This knowledge can be applied to their own improvisation and composition techniques.
Formal analysis involves examining the structure of a musical composition. This includes identifying sections, such as verse, chorus, bridge, and understanding their relationships to one another. By analyzing the form, guitarists can better interpret a song’s narrative and make informed decisions when arranging or performing it.
Not only does analyzing music enhance a guitarist’s technical understanding, but it also deepens their appreciation for the art form. By studying different genres, styles, and historical periods, guitarists can develop a broader perspective of music and its cultural significance.
Listening actively to a wide range of music, attending concerts, and exploring different genres and artists can further expand a guitarist’s musical appreciation. By exposing themselves to diverse musical perspectives, guitarists gain a deeper understanding of the endless possibilities and creativity inherent in music.
Analyzing and appreciating music also fosters a sense of curiosity and lifelong learning. It encourages guitarists to continuously seek out new musical experiences, challenge their musical assumptions, and grow as musicians.
By becoming skilled in music analysis and cultivating an appreciation for various musical styles, guitarists can infuse their playing with greater depth, emotion, and creativity. Whether through interpreting the genius of the great masters or exploring new and innovative sounds, analyzing and appreciating music is a lifelong journey that brings endless rewards to guitarists.