Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>How To Identify Intervals In Music Theory


Music Theory
How To Identify Intervals In Music Theory
Published: January 29, 2024
Learn how to identify intervals in music theory with this comprehensive guide. Understanding the fundamentals of music theory is essential for any musician or songwriter.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What are intervals in music theory?
- The importance of identifying intervals
- Steps to identify intervals in music theory
- Understand the concept of half steps and whole steps
- Learn the names of the intervals
- Identify the interval with the help of a keyboard or instrument
- Recognize common interval patterns
- Practice interval identification with exercises and examples
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the realm of music theory, intervals play a crucial role in understanding the relationship between musical notes. An interval refers to the distance between two pitches, whether they are played simultaneously or sequentially. It is essential for musicians, composers, and music enthusiasts to be able to identify intervals in order to develop a deeper understanding of melodies, harmonies, and overall musical structure.
Identifying intervals is like deciphering a secret code that unlocks the hidden language of music. By recognizing the distance between notes, musicians can build chords, create harmonies, and compose melodies that captivate listeners. It is a skill that can be honed with practice, and it provides a solid foundation for musicians to explore the nuances of music composition and performance.
In this article, we will delve into the world of interval identification in music theory. We will explore the importance of identifying intervals and walk you through the steps to master this skill. Whether you are an aspiring musician, a seasoned composer, or simply a music lover looking to deepen your understanding of the art form, this article will provide you with the tools and knowledge necessary to identify intervals confidently.
What are intervals in music theory?
In music theory, an interval refers to the distance between two musical pitches. It is the relationship between the frequencies, or vibrations, of two notes. Intervals are the building blocks of melody, harmony, and musical structure, and understanding them is essential for any musician.
An interval is typically measured in terms of the number of steps (or half steps) between two pitches. A half step (also known as a semitone) is the smallest distance between two adjacent notes on a keyboard or fretboard, while a whole step (also known as a tone) consists of two half steps. These steps serve as the foundation for identifying and classifying intervals in music theory.
Intervals are named based on the combination of their step distance and their position within the musical scale. They can be classified as either melodic intervals or harmonic intervals. A melodic interval is the distance between two notes played sequentially, while a harmonic interval is the distance between two notes played simultaneously.
Each interval has its own unique sound and character, providing a distinct musical color to melodies, harmonies, and chords. For example, a minor second interval creates a dissonant and tense sound, while a perfect fifth interval produces a strong and stable sound. By understanding intervals and their unique qualities, musicians can create evocative harmonies, build complex chord progressions, and compose melodies that evoke specific emotions.
Intervals are not only fundamental to the study of music theory but also play a significant role in ear training. By training their ears to recognize intervals, musicians can develop a strong sense of pitch, improve their ability to reproduce melodies, and enhance their overall musicality.
In the next section, we will explore the importance of identifying intervals and how it can benefit musicians in their musical journey.
The importance of identifying intervals
Identifying intervals in music theory is of utmost importance for several reasons:
- Enhances musical understanding: Understanding and recognizing intervals allows musicians to comprehend the structure and relationships within a piece of music. By identifying intervals, musicians can analyze melodies, harmonies, and chords, enabling them to better appreciate the music’s composition and intricacies.
- Facilitates sight-reading: For musicians who sight-read sheet music, interval identification skills are invaluable. Being able to quickly identify interval patterns enables musicians to efficiently read and play music in real-time, without having to rely solely on memorized notes.
- Aids in composition and improvisation: Identifying intervals empowers composers and improvisers to create captivating melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions. By understanding the unique characteristics of different intervals, musicians can strategically use them to evoke specific emotions and create musical tension or resolution.
- Strengthens ear training: Developing the ability to identify intervals by ear is fundamental to ear training. By training their ears to recognize the distinctive sound of each interval, musicians can improve their pitch accuracy, replicate melodies more easily, and develop a heightened sense of musicality.
- Fosters collaboration: When working with other musicians, being able to communicate interval names and relationships facilitates efficient collaboration. It allows musicians to discuss musical ideas, harmonies, and chord progressions using a common language, promoting effective communication during rehearsals, jam sessions, and performances.
Overall, identifying intervals in music theory opens up a world of possibilities for musicians. It enhances their understanding of music, improves their technical skills, and expands their creative potential. By honing their interval identification skills, musicians can deepen their musicality and take their performances to new heights.
Steps to identify intervals in music theory
Identifying intervals in music theory is a skill that can be developed with practice and training. Here are the steps to help you improve your interval identification abilities:
- Understand the concept of half steps and whole steps: Familiarize yourself with the concept of half steps (semitones) and whole steps (tones). A half step is the smallest distance between two adjacent notes on a keyboard or fretboard, while a whole step consists of two half steps.
- Learn the names of the intervals: Study and memorize the names of the different intervals. Start with the basics, such as seconds, thirds, fourths, fifths, and octaves. Then progress to larger intervals like sixths and sevenths. Understanding the naming conventions will help you identify intervals more efficiently.
- Identify the interval with the help of a keyboard or instrument: Utilize a keyboard or instrument to visually and audibly identify intervals. Start by playing the two notes of the interval simultaneously and listen to the sound they create. Then, compare this sound to your knowledge of intervals to determine the correct name.
- Recognize common interval patterns: Familiarize yourself with common interval patterns and their distinctive sounds. For example, a major third has a recognizable and uplifting quality, while a minor seventh carries a sense of tension and dissonance. By recognizing these patterns, you can quickly identify intervals in music.
- Practice interval identification with exercises and examples: Engage in regular practice exercises to improve your interval recognition skills. Use various resources, such as interval identification apps, online quizzes, and music theory textbooks, to test yourself and reinforce your knowledge. Additionally, listen to a wide variety of music and try to identify intervals by ear, further honing your abilities.
Remember that interval identification is a skill that takes time and dedication to develop. Be patient with yourself and continue practicing regularly. With consistent effort, you will gradually improve your ability to identify intervals accurately and confidently.
Understand the concept of half steps and whole steps
Before diving into interval identification, it is essential to have a solid understanding of half steps and whole steps. These terms refer to the smallest units of distance between two adjacent notes on a keyboard or fretboard.
A half step, also known as a semitone, is the smallest distance between two notes. In Western music, a half step corresponds to moving one key or one fret up or down on a keyboard or stringed instrument. For example, going from C to C# (or Db) is a half step.
A whole step, also known as a tone, consists of two half steps. It is equivalent to moving two keys or two frets up or down on a keyboard or stringed instrument. For example, going from C to D is a whole step.
Understanding the concept of half steps and whole steps is crucial because intervals are described in terms of these steps. When identifying an interval, you need to determine the number of half steps or whole steps between two notes.
It is helpful to visualize these steps on a keyboard or a diagram of the musical staff. By practicing and familiarizing yourself with the patterns of half steps and whole steps, you can quickly identify intervals in music.
Take the time to study and internalize the concept of half steps and whole steps. Practice moving up and down the keyboard or fretboard, paying attention to the distance between each note. With time, you will develop a keen sense of the step distances and be ready to move onto the next step of interval identification.
Learn the names of the intervals
Once you have a solid understanding of half steps and whole steps, the next step in identifying intervals is to learn the names associated with each interval. Learning the names of intervals is crucial because it allows you to communicate and label the distance between two notes accurately.
Intervals are named based on their position in the musical scale and the number of steps they encompass. The most common intervals are seconds, thirds, fourths, fifths, sixths, and sevenths. Additionally, the interval of an octave represents a complete cycle of the scale and is equivalent to the distance between two notes of the same name.
Here are the names of some common intervals:
- Unison: The distance between two identical notes.
- Second: The distance of a whole step or a half step.
- Third: The distance of two whole steps or a whole step and a half step.
- Fourth: The distance of three whole steps or two whole steps and a half step.
- Fifth: The distance of four whole steps or two whole steps and two half steps.
- Sixth: The distance of five whole steps or three whole steps and a half step.
- Seventh: The distance of six whole steps or three whole steps and two half steps.
- Octave: The distance between two notes with the same name, representing a complete cycle of the scale.
Study and memorize the names of the intervals, understanding their order and relationships. Practicing interval naming exercises can help reinforce this knowledge and improve your ability to identify intervals accurately.
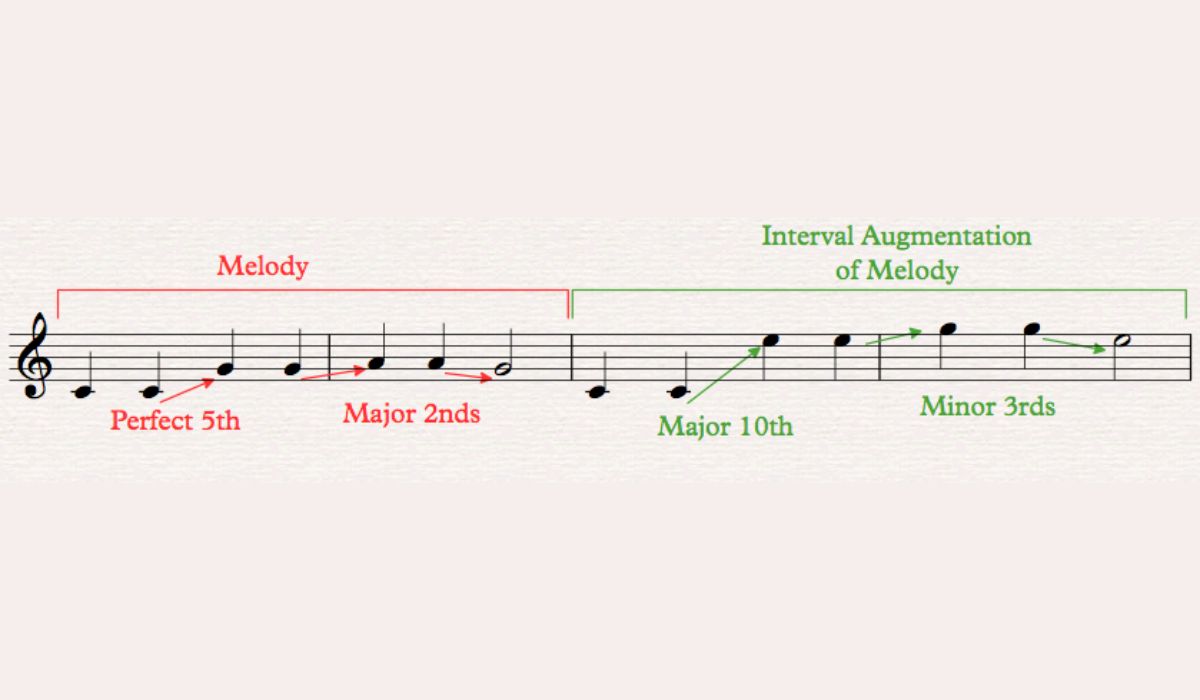
As you become more proficient in identifying intervals, you can also explore compound intervals, which are larger intervals spanning more than one octave.
By learning the names of intervals and understanding how they relate to the musical scale, you will develop a solid foundation for identifying intervals in music theory.
Identify the interval with the help of a keyboard or instrument
One effective way to identify intervals in music theory is by utilizing a keyboard or instrument. The visual and auditory cues provided by these tools can greatly assist in accurately identifying intervals.
Begin by selecting two notes that form the interval you want to identify. Play these notes simultaneously to hear the interval’s sound. Listen closely to the relationship between the two notes and try to discern any distinct qualities or characteristics.
Using a keyboard, you can easily visualize the distance between the two notes. Count and identify the number of keys or steps between the two notes, taking note of whether they are half steps or whole steps.
For example, if you play C and E together, you will hear a major third interval. On a keyboard, you can see that there are two whole steps (C -> D -> E) between these two notes, confirming that it is indeed a major third.
If you don’t have access to a keyboard, you can use other instruments, such as a guitar or a virtual instrument on a computer or mobile app, to play the notes and identify the interval. The important aspect is to be able to hear and visualize the distance between the two notes.
By repeatedly practicing interval identification using a keyboard or instrument, you will gradually develop the ability to quickly recognize and name different intervals by their sound and visual relationship.
It is worth noting that this method is particularly useful for immediate interval recognition. However, as you progress in your musical journey, aim to develop your ear training skills to identify intervals solely by their sound, without the need for an instrument as a reference. This will further enhance your musical abilities and overall musicianship.
Recognize common interval patterns
Recognizing common interval patterns can significantly enhance your ability to identify intervals in music theory. By familiarizing yourself with these patterns, you can quickly and accurately identify intervals based on their distinct characteristics and sound.
Here are some common interval patterns to become familiar with:
- Perfect Unison and Octave: These intervals have a unique characteristic of the notes sounding the same. They create a sense of unity and stability in a melody or harmony.
- Major and Minor Thirds: Major thirds have a bright and uplifting quality, while minor thirds carry a more mellow and melancholic tone.
- Perfect Fourth, Perfect Fifth, and Octave: These intervals are often referred to as the “power intervals” due to their strong and stable sounds. They form the backbone of many melodies and chords in various musical genres.
- Major and Minor Sixths: Major sixths have a warm and positive feel, while minor sixths possess a more somber and introspective quality.
- Major and Minor Sevenths: Major sevenths convey a sense of tension and anticipation, while minor sevenths evoke a darker and more dissonant mood.
Learning to recognize these interval patterns by ear and being able to associate them with their corresponding names will greatly aid in interval identification. Practice listening to examples of music that highlight these intervals and train your ear to differentiate between them.
In addition to the intervals mentioned above, there are many other interval patterns that you will come across in your musical journey. By actively listening to music and analyzing the intervals used, you will gradually become more adept at identifying these patterns and subsequently naming the intervals.
Remember, interval recognition is an acquired skill that improves with practice and exposure. The more you listen to and engage with different musical pieces, the better equipped you will be to identify intervals and appreciate the unique qualities they bring to a composition.
Practice interval identification with exercises and examples
To strengthen your interval identification skills, regular practice is key. Engaging in exercises and examples specifically designed to challenge your ability to recognize intervals will greatly enhance your proficiency. Here are some strategies to help you practice interval identification:
- Interval recognition exercises: Utilize online interval identification tools, ear training apps, or music theory textbooks that provide exercises for interval identification. These resources typically present you with a series of intervals and prompt you to identify each one. Gradually increase the difficulty level as you become more comfortable.
- Interval comparison exercises: Practice comparing intervals side by side. Play two intervals consecutively and determine whether they are the same or different. This exercise helps sharpen your ability to distinguish between similar intervals and strengthens your memory of their distinctive sounds.
- Interval singing: Singing intervals is an effective way to internalize their sounds and develop your ear training skills. Start by singing familiar melodies and identifying the intervals within them. Then progress to singing intervals without any melodic context, challenging yourself to accurately reproduce their pitches.
- Listening to interval examples: Actively listen to music and focus on identifying the intervals being played. Seek out songs or compositions that prominently feature specific intervals and try to name them as you hear them. You can also find interval recognition exercises online that play intervals for you to identify.
- Practical application: Apply your interval identification skills while playing an instrument. Incorporate interval recognition exercises in your regular practice routine, playing intervals on your instrument and identifying them by ear. This helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical musicianship.
Consistency is key in practicing interval identification. Set aside dedicated time regularly to work on improving your skills. As you progress, challenge yourself with more complex intervals and patterns.
Remember to be patient with yourself during the learning process. Developing strong interval identification skills takes time and practice. Celebrate your successes along the way and stay motivated to continue improving.
By incorporating these practice strategies into your musical routine, you will gradually become more proficient in identifying intervals and further hone your ear for music.
Conclusion
Identifying intervals in music theory is a fundamental skill that empowers musicians to understand, analyze, and create captivating melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions. By recognizing the distance between two pitches, musicians can navigate the vast landscape of music with confidence and creativity.
In this article, we explored the concept of intervals, the importance of identifying them, and the steps to improve your interval identification skills. Understanding the concepts of half steps and whole steps, learning the names of intervals, and utilizing a keyboard or instrument for reference are all crucial aspects of interval identification.
Recognizing common interval patterns and practicing interval identification through exercises and examples are key strategies in honing your skills. By consistently exposing yourself to intervals in music and actively engaging in practice, you will strengthen your ability to identify intervals accurately and efficiently.
As you progress in your musical journey, aim to cultivate your ear training skills to identify intervals solely by their sound, further enhancing your musicality and overall musicianship.
Remember, interval identification is not just an intellectual exercise; it allows you to connect with the emotional and expressive aspects of music. Embrace the process and enjoy the journey of discovering the unique beauty and power behind each interval.
So, take your time, practice diligently, and immerse yourself in the rich tapestry of intervals. With knowledge, practice, and a trained ear, you will unlock the secrets of intervals and unlock your full potential as a musician.