Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>Music Theory What Are Structural Voices

Music Theory
Music Theory What Are Structural Voices
Modified: February 24, 2024
Discover the importance of structural voices in music theory and how they contribute to the overall composition. Enhance your understanding of music theory concepts with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of music theory! If you’ve ever wondered what sets a great piece of music apart from the rest, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we will explore an essential concept in music theory known as structural voices.
Music theory is the study of how different elements come together to create harmony, melody, and rhythm. One of the key aspects of this study is understanding how various voices interrelate within a musical composition. These voices, also known as musical lines, contribute to the overall structure and character of a piece.
Structural voices refer to the distinct melodic lines or parts that form the foundation of a musical composition. They can be thought of as the different “characters” in a musical story, each playing their own role and contributing to the overall narrative.
As we delve into the concept of structural voices, we will explore their definition, their role in music theory, the different types of structural voices, techniques for analyzing them, and provide examples of their usage in renowned musical compositions.
Whether you’re an aspiring musician, a dedicated music student, or simply have an interest in the inner workings of music, understanding structural voices is crucial in unraveling the complex layers of musical compositions.
So, let’s embark on this musical journey together and explore the captivating world of structural voices in music theory!
Definition of Structural Voices
In music theory, structural voices are the individual melodic lines or parts that make up a musical composition. They can be thought of as the different voices or characters within a piece of music, each with its own unique melodic contour and role.
Structural voices are responsible for creating the harmonic and melodic framework on which the entire composition rests. They form the structural backbone of the music, providing depth, complexity, and cohesion to the overall piece.
Each structural voice contributes to the overall texture and character of the music, and they interact with one another to create a harmonious and coherent musical experience. By analyzing the relationship between these voices, music theorists can gain insights into the compositional techniques employed by the composer.
It is important to note that not all musical compositions have the same number of structural voices. Some may have only one or two primary voices, while others may have multiple voices interacting and intertwining with each other. The number of voices can vary depending on the composer’s artistic intent and the style of the composition.
Furthermore, structural voices can vary in terms of their range, movement, and melodic characteristics. Some voices may have a wider range, moving across multiple octaves, while others may have a narrower range, staying within a particular pitch range. The movement of the voices can also vary, ranging from smooth and flowing to angular and fragmented.
Understanding the concept of structural voices is crucial in analyzing and interpreting musical compositions. By identifying and analyzing the different voices within a piece of music, music theorists and performers can gain a deeper appreciation and understanding of the composer’s intention and the intricacies of the composition.
Now that we have a clear understanding of the definition of structural voices, let’s explore their role in music theory and how they contribute to the overall musical experience.
Role of Structural Voices in Music Theory
Structural voices play a pivotal role in music theory as they contribute to the overall structure, harmony, and form of a musical composition. They are the building blocks that give shape and coherence to the piece, allowing listeners to follow and comprehend its musical narrative.
One of the key functions of structural voices is to create harmonic progression. Each voice moves independently, often with its own distinct melodic contour, creating a rich tapestry of interweaving melodies. The interaction between these voices determines the harmonies that are formed as they simultaneously ascend, descend, or hold specific pitches.
Structural voices also provide a sense of verticality and depth to the music. By layering different melodic lines, composers can create complex chordal structures and harmonies that elicit a range of emotions and moods. These voices work together to establish the tonal center and modulations within a composition, guiding listeners through various harmonic progressions and creating tension and resolution.
Furthermore, structural voices contribute to the overall texture of the music. They create different levels of density and clarity, adding complexity and interest to the sonic landscape. The interaction between voices can result in contrapuntal textures, where multiple melodic lines are simultaneously heard, or in homophonic textures, where one voice takes the melodic lead while others provide accompaniment.
Additionally, structural voices assist in delineating the formal structure of a musical composition. They help to establish sections such as verses, choruses, and bridges, as well as provide transitions between different musical ideas. By tracking the movement and development of these voices, music theorists can analyze the structural organization and form of a piece.
Moreover, structural voices allow for expressive interpretation and performance. Musicians can bring out the nuances and dynamics of each voice, highlighting their thematic importance or emotional significance. By paying attention to the phrasing, articulation, and dynamic markings of each voice, performers can enhance the overall musical interpretation and convey the composer’s intentions.
By studying the role of structural voices in music theory, musicians, composers, and music enthusiasts gain a deeper understanding of the compositional techniques employed by different musicians throughout history. This knowledge enhances their musical literacy and enables them to appreciate the intricacies and artistry behind the creation of a musical work.
Now that we understand the important role of structural voices in music theory, let’s explore the different types of structural voices that can be found in various musical compositions.
Types of Structural Voices
In music theory, there are several types of structural voices that can be found in a variety of musical compositions. These voices can be categorized based on their function, range, and role within the overall musical structure.
1. Melodic Voice: This is the primary voice that carries the main melody of the composition. It is often the most prominent and memorable voice that listeners recall. The melodic voice is responsible for conveying the main thematic material and can be found in various instruments or vocal parts.
2. Bass Voice: The bass voice provides the foundation and stability to the harmonies and serves as the lowest-pitched voice. It often supports the harmonic progression and provides a sense of grounding. The bass voice can be found in instruments such as double bass, cello, or bass guitar.
3. Inner Voices: These voices fill the space between the melodic and bass voices. They provide harmonic support and contribute to the overall texture of the music. Inner voices can be found in various instruments or vocal parts, such as violas, horns, or alto singers.
4. Counterpoint: Counterpoint refers to the simultaneous sounding of multiple melodic voices. It involves the interplay of independent voices, each with its own melodic character and rhythmic pattern. Counterpoint can be heard in compositions from the Baroque era, where composers like J.S. Bach mastered this technique.
5. Ostinato: Ostinato is a repeated melodic or rhythmic pattern that remains consistent throughout a composition. It provides a sense of continuity and can be found in various voices, either as a supporting element or as a central theme.
6. Choral Voices: In vocal music, choral voices refer to the different vocal sections, such as soprano, alto, tenor, and bass. Each choral voice has its own range and role within the composition, and they often weave together to create intricate harmonies and textures.
7. Orchestral Voices: Orchestral voices pertain to the different sections of the orchestra, including strings, woodwinds, brass, and percussion. Each section contributes to the overall sound and adds its own unique color and timbre to the composition.
These are just a few examples of the types of structural voices that can be found in music compositions. It is important to note that the number and combination of voices can vary greatly depending on the genre, style, and artistic intent of the composer.
By understanding the different types of structural voices, music theorists and performers can better analyze and interpret the interplay between these voices and gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies and richness of a musical composition.
Now that we have explored the types of structural voices, let’s move on to the techniques used for analyzing these voices in music theory.
Techniques for Analyzing Structural Voices
Analyzing structural voices in music theory involves studying the interplay between different melodic lines and understanding how they contribute to the overall composition. By employing various techniques, music theorists can gain insights into the harmonic progression, voice-leading, and formal structure of a piece. Here are some commonly used techniques for analyzing structural voices:
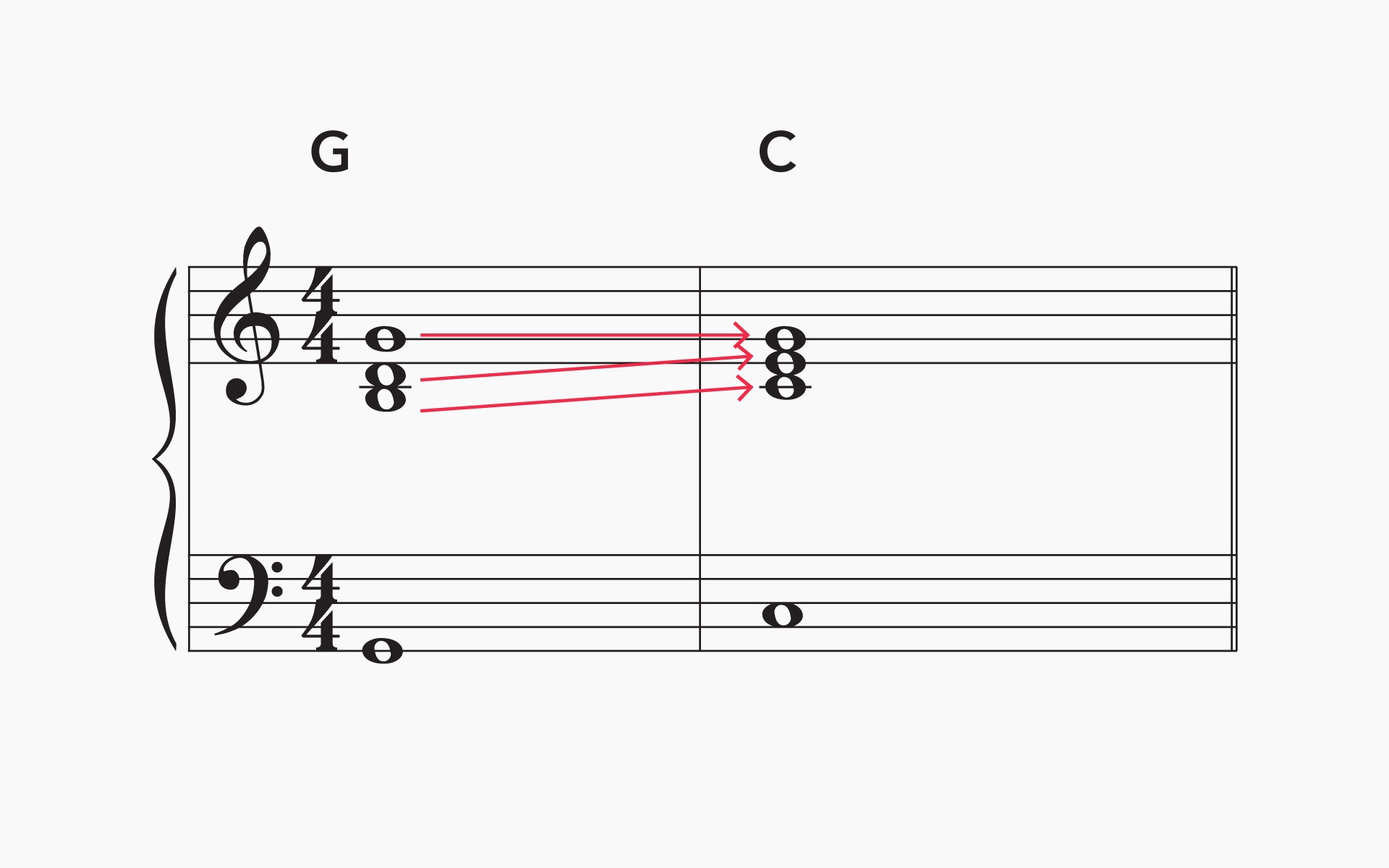
1. Voice-leading analysis: Voice-leading analysis focuses on the smooth and logical movement of each voice. It examines how individual voices move from one note to another, considering factors such as intervals, leaps, and melodic contour. By studying the voice-leading, analysts can identify patterns, chord progressions, and contrapuntal techniques employed by the composer.
2. Harmonic analysis: Harmonic analysis involves identifying and interpreting the underlying harmonic structure of a composition. It examines the chords and progressions created by the interaction of different voices. By analyzing the harmonic language and chordal relationships, theorists can gain insights into tonal centers, modulations, and the overall harmonic flow of the piece.
3. Phrase and formal analysis: Phrase and formal analysis delve into the larger-scale structure and organization of a composition. It examines how structural voices contribute to the creation of phrases, sections, and overall form. By examining the repetition, contrast, and development of melodic and harmonic material, analysts can identify the various sections and their relationships within the composition.
4. Texture analysis: Texture analysis focuses on the density, layering, and interaction of different voices in a composition. It considers the balance between melody, harmony, and accompaniment, as well as the use of contrapuntal techniques and textural changes throughout the piece. By examining the texture, theorists can understand the overall sonic landscape and how structural voices contribute to it.
5. Motivic analysis: Motivic analysis explores the recurring melodic or rhythmic motives within a composition. It involves identifying and tracking the development and transformation of these motives across different voices. By analyzing motives, analysts can identify thematic connections and their role in the overall structure of the piece.
6. Score analysis: Score analysis involves studying the written musical notation of a composition. It allows theorists to examine the specific instructions, markings, and indications provided by the composer. By analyzing the score, theorists can gain a comprehensive understanding of the composer’s intentions and the specific interactions between different voices.
These techniques provide a foundation for analyzing structural voices in music theory. By applying these methods, music theorists can unravel the complexities of a musical composition and gain deeper insights into the artistic choices made by the composer.
Now, let’s explore some examples of structural voices in well-known music compositions.
Examples of Structural Voices in Music Compositions
Structural voices play a crucial role in shaping the sound and structure of music compositions. Let’s explore some examples of how different types of structural voices are utilized in well-known pieces:
1. Johann Sebastian Bach – Brandenburg Concerto No. 3: In this renowned concerto, Bach showcases the interplay of multiple structural voices. The first movement features a rich contrapuntal texture with independent melodic lines in the violins, violas, and cellos, creating a lively and intricate musical dialogue. The bass voice provides a solid foundation, while the upper voices weave together in intricate counterpoint.
2. Ludwig van Beethoven – Symphony No. 5: Beethoven’s Symphony No. 5 is known for its memorable opening motif. The melodic voice in the iconic da-da-da-daaa rhythm is presented by the orchestral instruments, particularly the violins. The bass voice provides a steady, driving force, while the inner voices adding depth and complexity to the composition. The interplay between these voices creates a powerful and dramatic symphonic experience.
3. Johannes Brahms – Symphony No. 3: Brahms masterfully employs structural voices in his Symphony No. 3. The melodic voice is shared among different instruments, each contributing to the thematic development. The bass voice provides a foundation, while the inner voices add richness and harmonic support. Brahms skillfully intertwines the voices, creating beautiful and intricate melodies and harmonies.
4. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart – Piano Sonata No. 16: Mozart’s Piano Sonata No. 16 showcases the use of structural voices in a solo piano composition. The melodic voice is carried by the right hand, while the left hand provides the bass voice. The interplay between the hands creates a sense of conversation and musical dialogue. Mozart’s careful balancing of these voices creates a balanced and harmonious sonata.
5. Gioachino Rossini – Overture to “The Barber of Seville”: Rossini’s lively and energetic overture is a prime example of the use of structural voices. The melodic voice is divided among various instrumental sections, including strings, woodwinds, and brass, creating a vibrant and playful texture. The bass voice provides a strong and driving rhythm, while the inner voices add depth and color to the orchestration.
These examples demonstrate the diverse ways in which structural voices are employed in different musical genres and styles. Whether it’s in orchestral works, chamber music, or solo compositions, understanding the role and interaction of these voices enhances our appreciation and understanding of the musical composition.
As we conclude this exploration of structural voices, it becomes clear that they are the essential building blocks that give life, depth, and coherence to music compositions.
Now, armed with an understanding of structural voices, their role in music theory, and their presence in various compositions, you can embark on your own musical journey and further explore the captivating world of music theory.
Conclusion
Structural voices are the foundation of music compositions, providing depth, harmony, and structure. Through the interplay of different melodic lines, structural voices create a captivating musical narrative that captivates listeners. Understanding the role and analysis of these voices in music theory allows us to appreciate the intricacies and artistry behind a musical piece.
In this article, we have explored the definition of structural voices and their essential role in music theory. We have examined different types of structural voices, such as melodic voices, bass voices, inner voices, and choral voices, and discussed how they contribute to the overall texture and character of a composition. We have also highlighted techniques for analyzing structural voices, including voice-leading analysis, harmonic analysis, and phrase and formal analysis.
Moreover, we have delved into examples of structural voices in famous compositions, showcasing the interplay of voices in works by composers such as Bach, Beethoven, Brahms, Mozart, and Rossini. These examples demonstrate the diverse ways in which structural voices are utilized to create powerful melodies, harmonies, and textures.
By understanding and analyzing structural voices, we gain deeper insights into the compositional techniques, harmonic progressions, and formal structures employed by composers throughout history. This knowledge enhances our ability to interpret and appreciate musical compositions, whether as performers, theorists, or avid listeners.
As you continue your exploration of music theory, always remember the importance of structural voices in shaping the essence and impact of a musical work. They are the threads that weave together to create dynamic, emotive, and memorable compositions.
So, let the beauty of music and the intricacies of structural voices guide you on your journey of discovery and appreciation of this timeless art form.