Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>What Is A Pitch Collection Music Theory

Music Theory
What Is A Pitch Collection Music Theory
Published: January 31, 2024
Learn about pitch collections in music theory and how they can be used to enhance your understanding and composition skills. Explore the intricacies of music theory and its relevance in creating harmonious melodies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of music theory, where understanding the fundamental concepts behind music can unlock a whole new level of appreciation and creativity. One key aspect of music theory is the concept of pitch collections. In this article, we will delve into the definition, purpose, and application of pitch collections, as well as explore notable examples that showcase their significance in music.
Pitch collections refer to groups or sets of pitches that are organized and utilized in the composition and analysis of music. With pitch collections, composers can create melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions that evoke different emotions and convey unique musical ideas. They serve as the building blocks of musical compositions, providing a framework within which musicians can explore and express their artistic vision.
The concept of pitch collections is rooted in the fundamental properties of sound. Pitch, often described as the perceived frequency of a sound wave, is the primary element upon which melody and harmony are built. By organizing pitches into collections, musicians can create tonal relationships and explore the interplay between different notes and chords.
Pitch collections offer a variety of functionalities in music theory. They can be used to establish tonality, create tension and resolution, and modulate between different keys. They provide composers with a palette of musical colors, allowing them to craft unique and evocative pieces.
Understanding the different types of pitch collections and how they can be manipulated is essential in music analysis. By examining the pitch collections used in a composition, music theorists can gain insights into the structure, tonality, and expressive intent of the piece. This analysis can provide a deeper understanding and appreciation of the musical work at hand.
In the following sections, we will explore the various types of pitch collections, including set classes, modes, and scales, and discuss their applications in music composition. We will also highlight notable examples of compositions that showcase the power and versatility of pitch collections. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and unravel the fascinating world of pitch collections in music theory.
Definition of Pitch Collection in Music Theory
In music theory, a pitch collection refers to a group or set of pitches that are organized and utilized in the composition and analysis of music. These pitch collections play a fundamental role in constructing melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions, giving musicians a framework to create and express their musical ideas.
A pitch collection can be thought of as a toolbox of pitches, where composers have a range of options to choose from when building their composition. This collection of pitches provides the raw material from which melodies, harmonies, and chords are constructed.
When we talk about pitch collections, we are not referring to individual notes, but rather the organized groupings of those notes. This organization can be based on various factors such as the specific set of pitches used, the relationship between the pitches, or the properties of the collection itself.
One of the key aspects of pitch collections is their ability to establish tonality and create musical tension and resolution. For example, the use of a specific pitch collection can evoke a certain mood or convey a particular emotional quality. Composers can strategically select pitch collections to create a desired effect on the listener.
The concept of pitch collections also relates to the different scales and modes used in music. Scales such as major and minor scales are specific types of pitch collections that follow a particular pattern of whole and half steps. Modes, on the other hand, are variations of scales that use the same pitches but start on different degrees of the scale.
Overall, pitch collections provide a framework for understanding the organization and relationships between pitches in music. They allow composers to create coherence and unity within a composition, while also providing a means for exploration and experimentation. By understanding the concept of pitch collections, musicians can enhance their understanding of music theory and apply it to their own compositions and performances.
Purpose of Pitch Collections
Pitch collections serve a variety of purposes in music composition and analysis. They provide composers with a rich palette of pitches to choose from and enable the creation of melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions that convey specific emotions and aesthetic qualities. Let’s explore the main purposes of using pitch collections in music:
1. Establishing tonality:
Pitch collections play a crucial role in establishing tonality within a musical composition. Tonality refers to the sense of a central pitch or key center that the composition revolves around. By selecting a specific pitch collection, such as a major or minor scale, composers can establish a tonal center and create a sense of stability and resolution.
2. Creating tension and resolution:
Pitch collections can evoke a wide range of emotions in music. By utilizing certain pitches or combinations of pitches, composers can create tension and release within a composition. Dissonant pitches or chord progressions build tension, while consonant pitches or resolutions provide a sense of release and resolution.
3. Providing musical colors:
Pitch collections offer a vast array of pitch combinations and possibilities, allowing composers to create different moods and atmospheres through their choice of pitches. Whether it is the bright and cheerful sounds of a major scale, the melancholic feel of a minor scale, or the exotic tones of modes like the Dorian or Phrygian scale, pitch collections provide a diverse range of musical colors to work with.
4. Enhancing melodic and harmonic development:
Pitch collections provide a framework for developing melodies and harmonies. By using the pitches within a specific collection, composers can create coherent and structured melodies that flow harmonically. Additionally, pitch collections offer a foundation for exploring and experimenting with chord progressions, allowing composers to create interesting harmonic movements within their compositions.
5. Enabling modulation:
Pitch collections facilitate modulation, which is the process of changing from one key or tonal area to another within a composition. By utilizing different pitch collections, composers can smoothly transition from one tonal center to another, creating a sense of variety and musical journey within their music.
Overall, pitch collections serve as a fundamental tool for composers to express their musical ideas and create compositions that resonate with the listener. They provide structure, tonal relationships, and a versatile palette of pitches to work with, enabling composers to convey different emotions, establish tonality, and develop melodies and harmonies. The purpose of pitch collections is to enhance the depth, complexity, and artistic expression in music.
Building Blocks of Pitch Collections
At the core of pitch collections in music theory are the individual pitches that make up the collection. These pitches are the building blocks with which composers construct melodies, harmonies, and chords. Understanding the properties and relationships of these pitches is essential in working with pitch collections. Let’s explore the building blocks of pitch collections:
1. Pitches:
Pitches are the individual musical tones that make up a pitch collection. They are typically represented by letter names, such as C, D, E, and so on, and can be further defined by their octave position. Pitches can be natural, sharp, or flat, representing different intervals or steps in the musical scale.
2. Intervals:
Intervals refer to the distance or relationship between two pitches. They are the foundation of melody and harmony construction. Different intervals create different feelings and moods in music. For example, a minor second interval may sound dissonant and tense, while a perfect fifth interval sounds consonant and stable.
3. Scales:
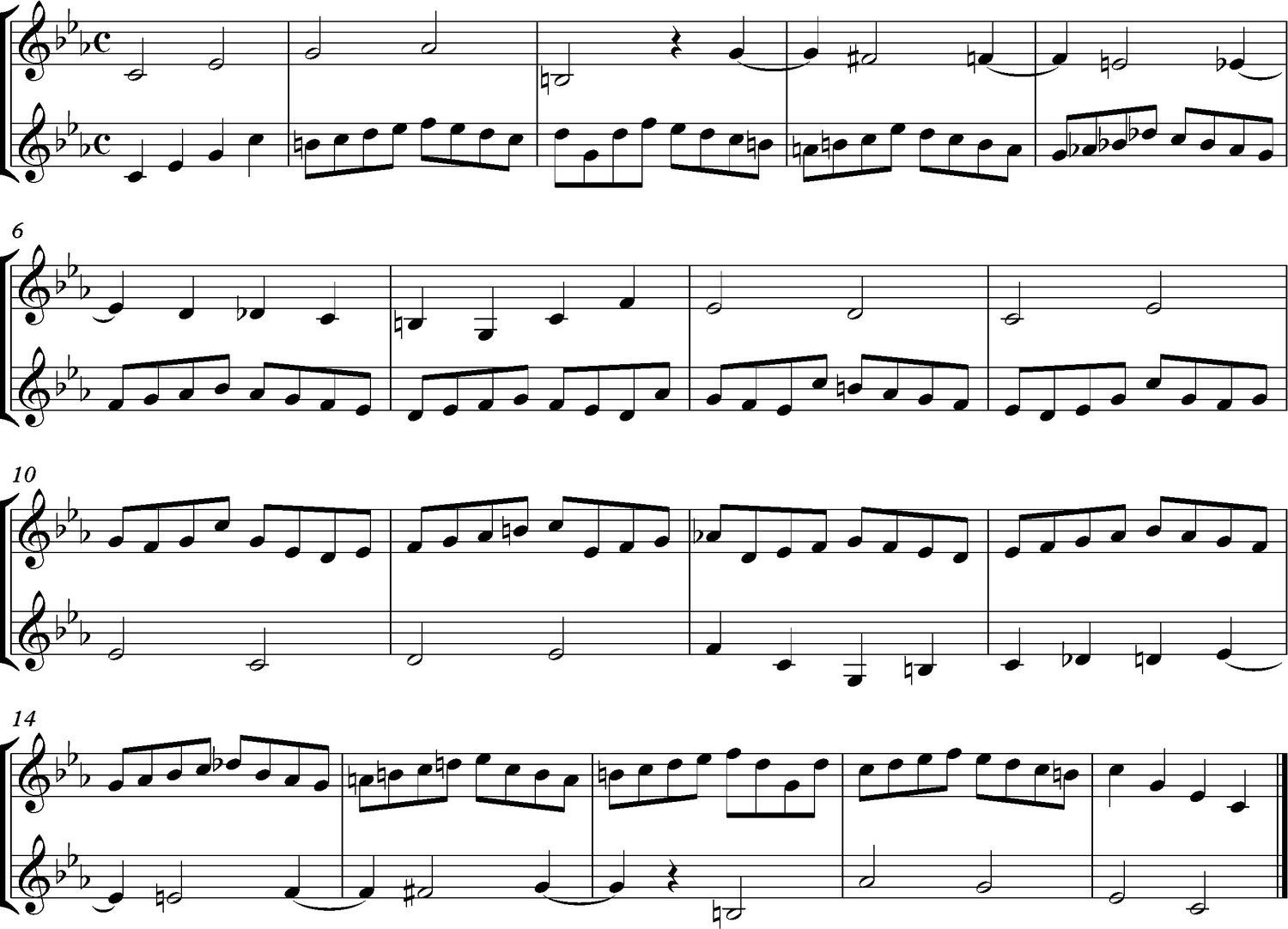
Scales are a set sequence of pitches arranged in ascending or descending order, usually following a specific pattern of whole and half steps. They serve as the basis for melody and harmony construction and form the backbone of many pitch collections. Example scales include the major scale, minor scale, pentatonic scale, and blues scale.
4. Modes:
Modes are variations of scales. They use the same pitches as the scale but start on a different degree of the scale, creating a different tonal center and characteristic sound. Modes offer composers a wide range of tonal colors and can be used to evoke different moods and emotions. Examples of modes include the Ionian, Dorian, Phrygian, and Mixolydian modes.
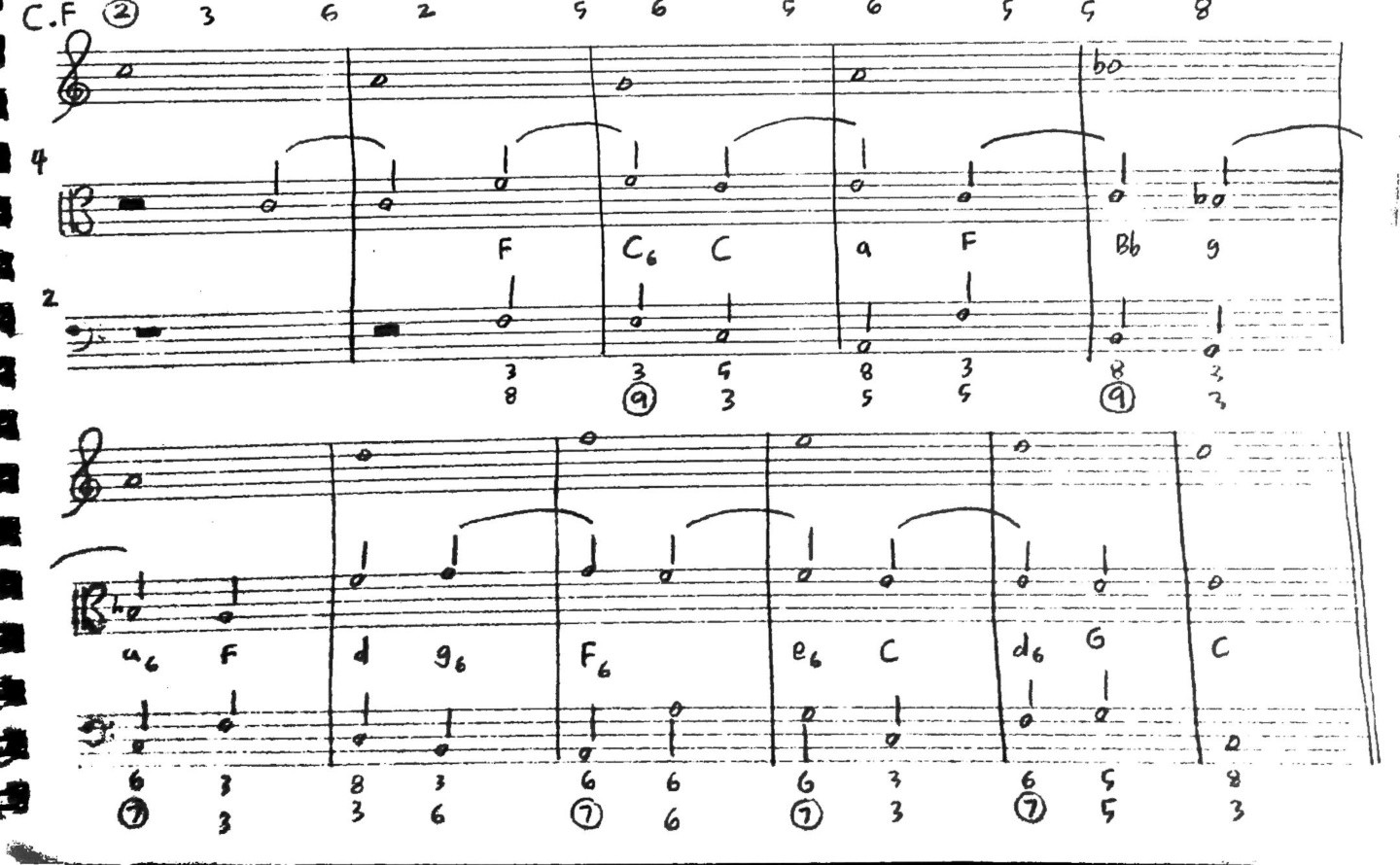
5. Chords:
Chords are harmonies made up of multiple pitches played simultaneously. They are formed by selecting specific pitches from a pitch collection and stacking them in thirds. Chords add depth, harmony, and color to a composition and play a significant role in supporting and enhancing melodies.
These building blocks, as well as their relationships and combinations, form the foundation of pitch collections. Composers use these elements to construct cohesive and expressive musical compositions. By understanding and harnessing the power of individual pitches, intervals, scales, modes, and chords, musicians can create captivating and meaningful musical experiences.
Types of Pitch Collections
Pitch collections come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and applications in music. Understanding the different types of pitch collections is essential for composers and musicians to create rich and diverse compositions. Let’s explore some of the main types of pitch collections:
1. Set Classes:
Set classes are a type of pitch collection that groups together all possible transpositions and inversions of a particular pitch collection. In set theory, the concept of set classes allows for the analysis and comparison of different pitch collections based on their intervallic content. Set classes can be useful in understanding relationships between different melodies and chord progressions.
2. Modes:
Modes are a type of pitch collection that is derived from a specific scale. Modes use the same pitches as the parent scale but start on a different degree, resulting in a distinct tonal center and characteristic sound. Examples of modes include the Ionian mode (major scale), Dorian mode, Phrygian mode, and Mixolydian mode. Modes offer composers a palette of tonal colors and can be used to evoke different moods and emotions.
3. Named Scales:
Named scales are pitch collections that have specific names and patterns. They often have cultural or historical significance and are widely used across different musical genres. Examples of named scales include the major scale, minor scale, pentatonic scale, blues scale, and whole-tone scale. Named scales provide composers with established frameworks for melody and harmony construction.
4. Serialism:
Serialism is a compositional technique that involves organizing pitches into predetermined series or rows. These rows can be used to generate melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions throughout a composition. Serialism allows composers to create cohesive and structured musical works with a deliberate arrangement of pitches.
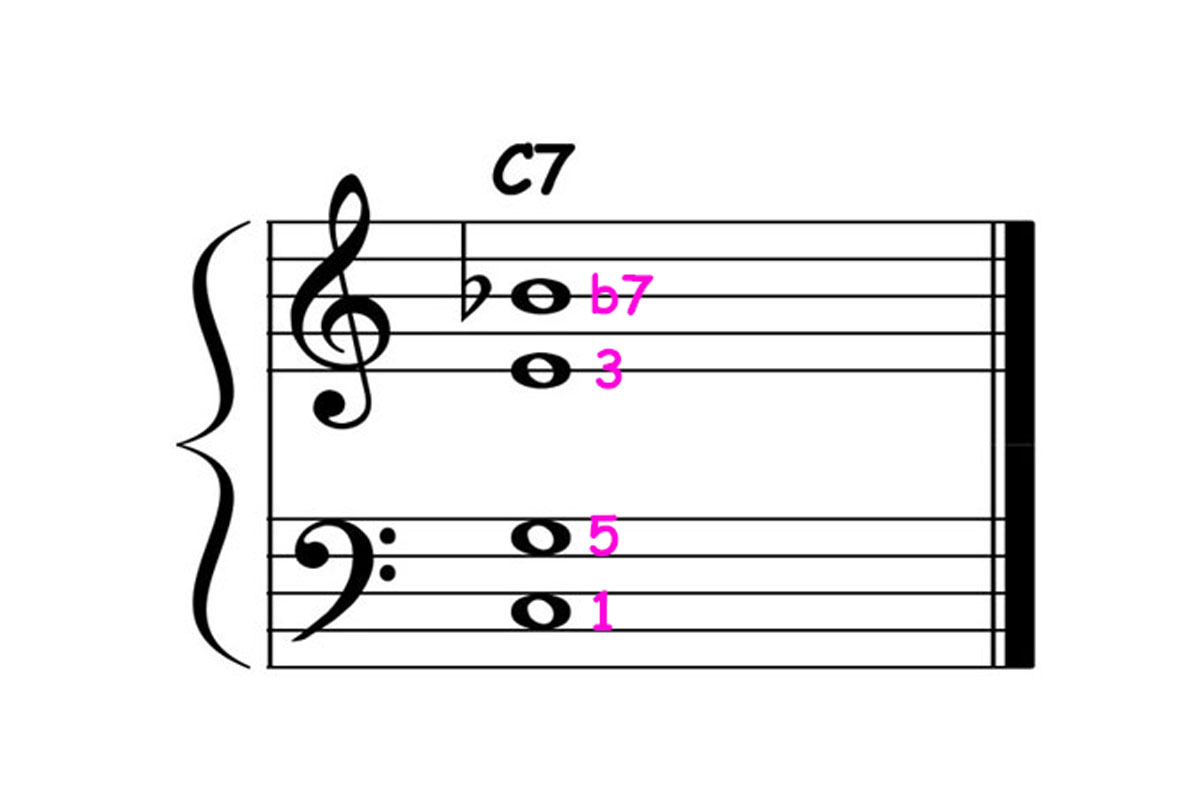
5. Altered and Extended Chords:
Altered and extended chords are pitch collections that go beyond traditional triads and seventh chords. They incorporate additional tones, such as altered or extended notes, to create unique and complex harmonies. Altered chords involve modifying the pitch content of a basic chord, while extended chords add tension and richness by including tones beyond the basic triads and seventh chords.
These are just a few examples of the types of pitch collections in music. By exploring and experimenting with the various types of pitch collections, composers can expand their musical vocabulary, create diverse compositions, and express their artistic vision in unique and dynamic ways.
Analysis and Application of Pitch Collections
The analysis and application of pitch collections play a vital role in music theory and composition. By examining the structure, relationships, and characteristics of pitch collections, musicians can gain insights into the tonality, form, and emotional impact of a composition. Let’s explore how the analysis and application of pitch collections contribute to the creation and understanding of music:
1. Analysis:
In music analysis, pitch collections are carefully examined to uncover patterns, tonal relationships, and structural elements within a composition. By analyzing the pitch collections used, music theorists can unravel the musical language employed by the composer, discern the tonal center, and identify harmonic progressions and melodic motifs. This analysis helps deepen our understanding of the composition, revealing its inner workings and compositional choices.
2. Harmonic Progressions:
Pitch collections provide the foundation for constructing harmonic progressions. By selecting specific pitches from a collection, composers can create chords that form the harmonic backbone of a composition. Analyzing the pitch collections used in a progression allows musicians to identify common chord progressions, explore tonal movement, and understand the harmonic tension and release within the piece.
3. Melodic Development:
Pitch collections shape the melodic development within a composition. By working with specific pitch collections, composers can create melodies that are cohesive and unified. Analyzing the pitch collections used in a melody helps identify recurring melodic motifs, understand intervallic relationships, and explore the overall shape and contour of the melodic line.
4. Expressive Interpretation:
Pitch collections contribute to the emotional and expressive quality of music. Different pitch collections evoke distinct moods and emotions. Analyzing the selection of pitch collections in a composition helps us understand the intended emotional impact of the music. This knowledge can guide performers in their interpretation, allowing them to effectively convey the composer’s intent and connect with the audience on a deeper level.
5. Composition and Arrangement:
For composers, an understanding of pitch collections opens up a vast array of creative possibilities. By exploring different pitch collections and their properties, composers can craft unique melodies, harmonies, and progressions that convey their artistic vision. They can experiment with the tension and resolution of different pitch collections, create contrasting sections by modulating between collections, or even combine multiple collections to create complex and rich musical textures.
Through the analysis and application of pitch collections, musicians can gain a deeper appreciation of the structure, emotion, and artistic choices behind a composition. This knowledge enhances the composition and performance of music, allowing for more nuanced interpretations and creative explorations.
Notable Examples of Pitch Collections in Music
Throughout the history of music, pitch collections have played a significant role in shaping the sound and character of compositions. Many notable examples demonstrate the diversity and creative potential of pitch collections. Let’s explore some of these notable examples:
1. The Diatonic Scale:
The diatonic scale is one of the most commonly used pitch collections in music. It consists of seven pitches arranged in a specific pattern of whole and half steps. The diatonic scale forms the foundation for Western classical music and is widely utilized in various genres such as pop, rock, and jazz. Its versatile nature allows composers to explore different tonalities, melodic lines, and harmonies.
2. The Twelve-Tone Technique:
In the early 20th century, composer Arnold Schoenberg introduced the twelve-tone technique, which involved the use of a specific pitch collection called a tone row. The tone row consists of all twelve pitches of the Western chromatic scale, arranged in a predetermined order. Composers then manipulate this pitch collection to create melodies, harmonies, and even entire compositions. The twelve-tone technique revolutionized music composition, challenging traditional tonal systems and opening doors to new avenues of expression.
3. The Pentatonic Scale:
The pentatonic scale is another widely recognized pitch collection that consists of five pitches. It is prevalent in many musical traditions worldwide and is particularly associated with traditional folk music. The pentatonic scale’s simplicity and distinctive sound have made it a popular choice for composing catchy melodies, improvisation, and soloing in a variety of genres, including blues, rock, and world music.
4. Modal Jazz:
Modal jazz is a style that emerged in the 1950s and 1960s, emphasizing the use of different modes or pitch collections derived from scales. Musicians like Miles Davis, John Coltrane, and Herbie Hancock incorporated modal approaches into their compositions, departing from traditional chord progressions and exploring modal improvisation. Modal jazz compositions often feature extended periods of modal harmony, allowing for unique and often atmospheric musical experiences.
5. Indian Classical Music:
Indian classical music, with its rich and ancient traditions, utilizes pitch collections known as melodic modes or ragas. Ragas are specific sets of pitches, each with its own unique melodic structure and emotional character. Indian classical musicians utilize ragas to improvise, compose, and evoke specific emotions or moods in their performances. The precise selection and expression of ragas are central to the aesthetic beauty and depth of Indian classical music.
These notable examples highlight the influence and versatility of pitch collections in shaping the musical landscape. From the familiar diatonic scale to the groundbreaking twelve-tone technique and the evocative ragas of Indian classical music, pitch collections continue to inspire and guide composers across various genres and traditions.
Conclusion
Pitch collections are the building blocks of music, providing composers with a rich palette of pitches to create melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions. They establish tonality, evoke emotions, and shape the overall structure and character of a composition. Through the analysis and application of pitch collections, musicians gain a deeper understanding of the compositional choices, tonal relationships, and expressive intent of a piece of music.
By exploring different types of pitch collections, such as set classes, modes, and named scales, composers can unlock endless possibilities for creative expression. They can utilize pitch collections to establish tonal centers, create tension and resolution, and develop cohesive melodies and harmonies. Pitch collections also allow for modulation, adding variety and interest to compositions.
The analysis of pitch collections reveals patterns, tonal relationships, and structural elements within a composition. It helps uncover the composer’s intention, guiding performers in their interpretation and conveying the emotional impact to listeners. Additionally, pitch collections serve as a foundation for harmonic progressions and melodic development, bringing depth and coherence to musical works.
Notable examples of pitch collections in music, such as the diatonic scale, the twelve-tone technique, the pentatonic scale, and ragas in Indian classical music, showcase the diverse ways in which pitch collections shape the sound and character of compositions across different genres and traditions.
In conclusion, understanding pitch collections in music theory provides musicians with a powerful tool for composition, analysis, and performance. Whether exploring the vast possibilities of set classes and modes or delving into the intricacies of harmonic progressions and melodic development, the world of pitch collections opens up a world of creativity and expression in music.