Home>Production & Technology>Sheet Music>How To Remember Notes On Sheet Music


Sheet Music
How To Remember Notes On Sheet Music
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn how to easily remember notes on sheet music with these proven techniques. Enhance your music reading skills and master sheet music notation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Sheet music is the universal language of musicians. It is the written representation of musical notes, rhythms, and other musical elements that allows musicians to read and interpret a piece of music. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced musician, understanding and being able to read sheet music is crucial.
However, one of the challenges many musicians face is memorizing the notes on sheet music. It can be intimidating to see a page filled with musical symbols and try to decipher them quickly. But fear not! In this article, we will explore effective techniques and exercises to help you remember notes on sheet music with ease.
To start, it’s important to have a basic understanding of how sheet music works. Sheet music consists of a set of horizontal lines and spaces called the staff. Each line and space represents a different note. The placement of the note on the staff indicates its pitch, while the shape of the note head indicates its duration.
There are two clefs commonly used in sheet music: the treble clef and the bass clef. The treble clef is typically used for higher-pitched instruments, such as the piano, violin, and flute. The bass clef, on the other hand, is used for lower-pitched instruments, like the cello, bass guitar, and tuba.
Now that we have a basic understanding of sheet music, let’s delve into the techniques and exercises that will help you remember notes more effectively. By incorporating these strategies into your practice routine, you’ll be able to read and play sheet music fluently, making your musical journey more enjoyable and fulfilling.
Understanding Sheet Music
Before diving into memorizing notes on sheet music, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of the basic components and symbols used in sheet music. This knowledge will provide a foundation for your learning journey and help you decipher the musical language more effectively.
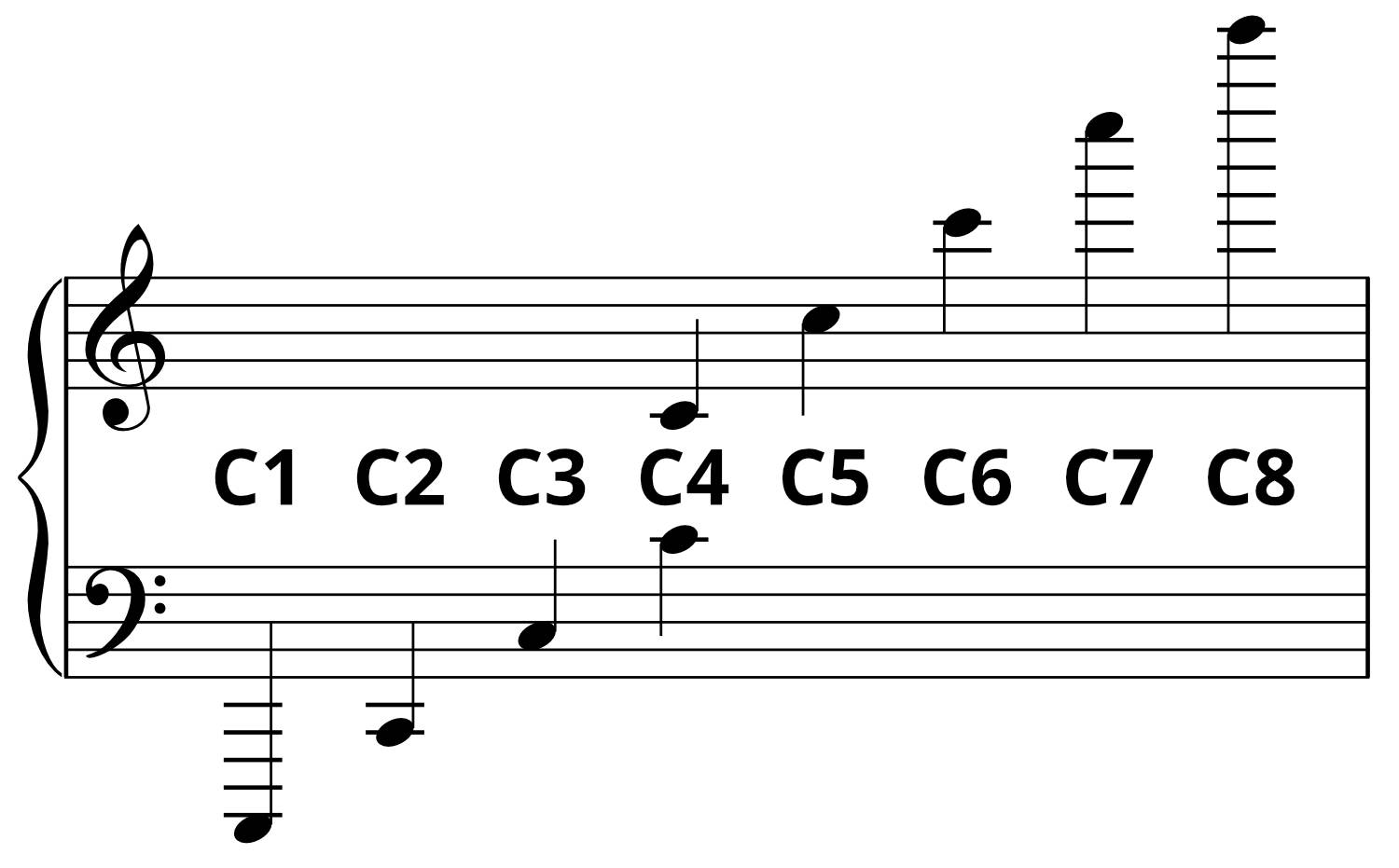
Let’s start with the staff. The staff consists of five horizontal lines and four spaces, with each line and space representing a different pitch. The lines, from bottom to top, are E, G, B, D, and F, while the spaces spell out FACE. The specific note placement on the staff signifies its pitch. For example, a note placed on the second line from the bottom represents the note G.
To determine the duration of a note, you need to look at the shape of the note head. The most common types of notes are whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, and eighth notes. A whole note is an open circle, while a half note has an open circle with a stem. A quarter note has a filled-in note head with a stem, and an eighth note has a filled-in note head with a stem and a flag.
Two essential symbols in sheet music are the treble clef and the bass clef. The treble clef is also known as the “G clef” because it wraps around the second line from the bottom, indicating that this line represents the note G. The treble clef is commonly used for instruments that have higher pitches, such as the piano, violin, and flute.
Conversely, the bass clef, also known as the “F clef,” wraps around the fourth line from the top, indicating that this line represents the note F. The bass clef is typically used for instruments that have lower pitches, like the cello, bass guitar, and tuba.
In addition to notes, sheet music also includes other symbols, such as rests, accidentals, dynamics, and articulations. Rests indicate periods of silence in the music, and their durations coincide with the values of their corresponding notes. Accidentals, such as sharps (#), flats (♭), and naturals (♮), alter the pitch of a note. Dynamics indicate the volume at which a phrase or section should be played, while articulations specify how a note should be played, such as staccato (short and detached) or legato (smooth and connected).
By familiarizing yourself with the components and symbols of sheet music, you’ll be better equipped to understand and interpret the music you encounter. This understanding will serve as a solid foundation for memorizing the notes and playing them with confidence.
Familiarizing Yourself with the Notes
Once you have a basic understanding of sheet music and its symbols, the next step is to familiarize yourself with the different notes. Knowing the names and locations of the notes on the staff is crucial for reading and interpreting sheet music accurately.
Start by memorizing the notes on the lines and spaces of the staff. Remember that the lines, from bottom to top, represent the notes E, G, B, D, and F, while the spaces spell out FACE. To help you remember this, you can come up with mnemonic devices or visual associations. For example, you can create a saying like “Every Good Boy Deserves Fudge” to remember the notes on the lines of the treble clef.
It’s also helpful to practice identifying and naming the notes on the staff. You can use flashcards, online quizzes, or even write out notes randomly and challenge yourself to name them quickly. Consistent practice will reinforce your knowledge and make note identification more intuitive.
Additionally, familiarize yourself with ledger lines. Ledger lines are short horizontal lines that extend the staff beyond its usual range. They are used when the notes go above or below the standard staff notation. Take the time to learn the positions of the ledger lines so that you can quickly identify the higher or lower notes when they appear on sheet music.
Another useful approach is to study the musical intervals between the notes. This involves understanding the distance or pitch difference between two consecutive notes. For example, the interval between two adjacent lines or spaces is called a second, while skipping one note in between is called a third. Learning these intervals will enable you to recognize patterns and intervals in the music, helping you to read the notes more fluently.
It’s important to note that learning the notes on one clef (either treble or bass) is a good starting point, but it’s beneficial to become proficient in reading both treble and bass clefs. This will expand your musical versatility and enable you to play a wider range of music.
By regularly practicing note identification and familiarizing yourself with the positions of the notes on the staff, you will develop a strong foundation for reading sheet music. This familiarity with the notes will make the process of memorizing and decoding sheet music more accessible and enjoyable.
Memorization Techniques
Memorizing notes on sheet music requires practice and repetition. By implementing effective memorization techniques, you can enhance your ability to recall the notes quickly and accurately. Here are some techniques to help you commit the notes to memory:
- Flashcards: Create flashcards with the note names and their positions on the staff. Review the flashcards regularly and challenge yourself to identify the notes quickly. This visual reinforcement will reinforce your memory and improve your note recognition skills.
- Associations: Form associations between the notes and familiar objects or words. For example, you can associate the note G on the treble clef with the word “Giraffe” or the note F on the bass clef with the word “Fish.” These associations create mental connections that make it easier to recall the notes during sight-reading.
- Repetition and Rote Learning: Practice identifying and playing the notes repeatedly. By consistently exposing yourself to the notes, you’ll gradually internalize their positions on the staff. Rote learning involves repetition without the aid of visual cues, such as covering the staff and playing or naming the notes from memory.
- Musical Mnemonics: Develop musical mnemonics or catchy phrases to remember the notes. For example, you can create a phrase like “All Cows Eat Grass” to recall the notes on the spaces of the bass clef (A, C, E, G). These mnemonic devices can be memorable and entertaining, making the learning process more enjoyable.
- Chunking: Instead of trying to memorize individual notes, group them into small chunks or patterns. By recognizing common sequences of notes, such as scales, intervals, or chord progressions, you can reduce the cognitive load and accelerate your note identification skills.
Remember, everyone learns differently, so it’s essential to find the techniques that work best for you. Experiment with different approaches and adapt them to suit your learning style.
Additionally, make sure to practice regularly and consistently. Dedicate a portion of your practice sessions specifically to note memorization exercises. Gradually increase the difficulty of the exercises and challenge yourself with different musical pieces to continually expand your knowledge of the notes.
Ultimately, the key to successful memorization is persistence and patience. With time and practice, you’ll become more proficient at recognizing, remembering, and playing the notes on sheet music.
Practice Exercises
To reinforce your note memorization skills, incorporating specific practice exercises into your routine can be highly beneficial. These exercises will not only help you solidify your understanding of the notes but also improve your overall sight-reading ability. Here are some practice exercises to consider:
- Note Naming: Create a sheet with randomly placed notes on the staff. Challenge yourself to name each note as quickly as possible. Start with a small set of notes and gradually increase the number and complexity. Repeat this exercise regularly to strengthen your note recognition skills.
- Note Identification: Practice identifying the notes on the staff by playing them on your instrument. Start with simple melodies and gradually move on to more complex pieces. This exercise will help you associate the visual representation of the note with the sound it produces, further enhancing your note memorization.
- Sight-Reading: Take advantage of sight-reading exercises or sheet music that provides a good balance of familiar and unfamiliar notes. Use a timer to set a specific duration for each piece or exercise, challenging yourself to identify and play the notes accurately within that time frame. This exercise will improve your ability to quickly process and interpret sheet music on the spot.
- Rhythm and Note Combination: Combine rhythm practice with note identification. Create rhythmic patterns and play them while identifying the corresponding notes. This exercise will enhance your ability to read rhythmically complex passages and reinforce your note memorization simultaneously.
- Interval Training: Focus on practicing intervals between notes. Play intervals on your instrument and try to identify them by their distance and sound. Gradually increase the difficulty of the intervals to challenge yourself further. This exercise will sharpen your ability to recognize and interpret the distance between notes, allowing you to read sheet music more efficiently.
Remember to approach these exercises with patience and persistence. Start with simpler exercises and gradually progress to more complex ones as your skills improve. Regularly incorporate these exercises into your practice routine, allocating dedicated time to specifically work on note memorization and sight-reading.
Additionally, consider using technology-based tools and apps that provide interactive note recognition exercises. These resources can add an element of gamification to your practice, making the learning process more engaging and enjoyable.
By consistently practicing these exercises, you will enhance your note memorization skills and become a more proficient reader of sheet music. The goal is to develop a solid foundation that allows you to approach any musical piece with confidence and ease.
Tips for Effective Note Memorization
Memorizing notes on sheet music can be a challenging task, but with the right approach, it becomes much more achievable. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your note memorization process:
- Consistency: Dedicate regular practice sessions specifically for note memorization. Consistency is key when it comes to reinforcing your memory and developing automaticity in recognizing notes.
- Break it Down: Instead of overwhelming yourself with a large amount of notes, break down the learning process into smaller, manageable segments. Focus on mastering a few notes at a time before moving on to additional ones.
- Use Mnemonics: Create mnemonic devices or associations to help you remember the notes. Whether it’s a phrase, a visual image, or a word association, finding ways to connect the notes with something memorable will enhance your recall abilities.
- Practice with Purpose: Instead of mindlessly practicing, approach your note memorization exercises with intention and concentration. Be present in the moment and actively engage with the notes on the staff.
- Visualize the Notes: Picture the notes in your mind’s eye as you read them on the sheet music. Visualizing the notes can reinforce your memory and make it easier to recall them when playing.
- Engage Multiple Senses: Incorporate multiple senses in your practice. Speak the note names out loud, clap the rhythms, and play the notes on your instrument. Engaging different senses strengthens the connections in your brain, making the memorization more effective.
- Create a Study Schedule: Set aside dedicated time each day or week specifically for note memorization. Consistency and regularity in your practice schedule will yield better results than irregular and sporadic practice sessions.
- Record Yourself: Record yourself playing a piece or a note identification exercise, and then listen back to it. Hearing your own performance can help reinforce the memory of the notes and give you valuable feedback for improvement.
- Seek Feedback: Ask for feedback from a teacher, mentor, or fellow musician. They can provide guidance on note recognition and help point out any areas that need improvement.
- Patience and Perseverance: Remember that memorizing notes on sheet music is a gradual process. Stay patient and persevere through any challenges or setbacks you encounter. With time and consistent effort, your note memorization skills will improve.
Keep in mind that everyone has their own unique learning style and strategies that work best for them. Explore and experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you. Stay motivated, and enjoy the process of unlocking the musical language of sheet music.
Conclusion
Memorizing notes on sheet music is an essential skill for any musician. It allows you to read and interpret musical compositions accurately and fluently. By understanding the basic components of sheet music, familiarizing yourself with the notes, and implementing effective memorization techniques, you can improve your note recognition and reading abilities.
Start by gaining a solid understanding of the staff, clefs, notes, and other symbols used in sheet music. Familiarize yourself with the positions of the notes on the staff and practice identifying them through various exercises and techniques. Incorporate note memorization practice into your regular routine, focusing on repetition, associations, and visualizations to reinforce your memory. Additionally, utilize mnemonic devices, practice chunking, and engage multiple senses to enhance your note memorization process.
Remember that effective note memorization requires consistency, patience, and perseverance. Break down the learning process into manageable chunks, practice with purpose, and create a study schedule that suits your needs. Seek feedback and record yourself to monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments. Embrace the process, stay motivated, and enjoy the journey of learning and mastering the language of sheet music.
With time and dedication, you will enhance your note memorization skills, becoming a more proficient musician capable of reading and playing sheet music with confidence and ease. So, don’t be intimidated by the multitude of musical symbols on the page. Embrace the challenge, practice diligently, and unlock the beauty of sheet music through your ability to remember and interpret the notes.