Home>Devices & Equipment>Radio>What Frequency Is Ham Radio


Radio
What Frequency Is Ham Radio
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the frequency range of ham radio and explore the world of amateur radio enthusiasts. Stay tuned for tips, resources, and frequencies to enhance your radio experience.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Radio technology has revolutionized the way we communicate. From AM/FM stations to satellite radio, there are numerous ways to tune in and listen to our favorite music or catch up on the latest news. However, there is another world of radio enthusiasts who go beyond just listening and embrace the world of ham radio.
Ham radio, also known as amateur radio, is a hobby that allows individuals to communicate with others using designated radio frequencies. Unlike commercial radio stations, ham radio operators have the flexibility to experiment, build their own equipment, and engage in two-way communication with fellow enthusiasts around the world.
In the world of ham radio, understanding frequency is crucial. It forms the backbone of communication, determining how signals travel through the airwaves and reach their intended destinations. Whether you’re an aspiring ham radio operator or simply curious about the subject, this article will delve into the importance of frequency in ham radio and explore the various frequency bands available for use.
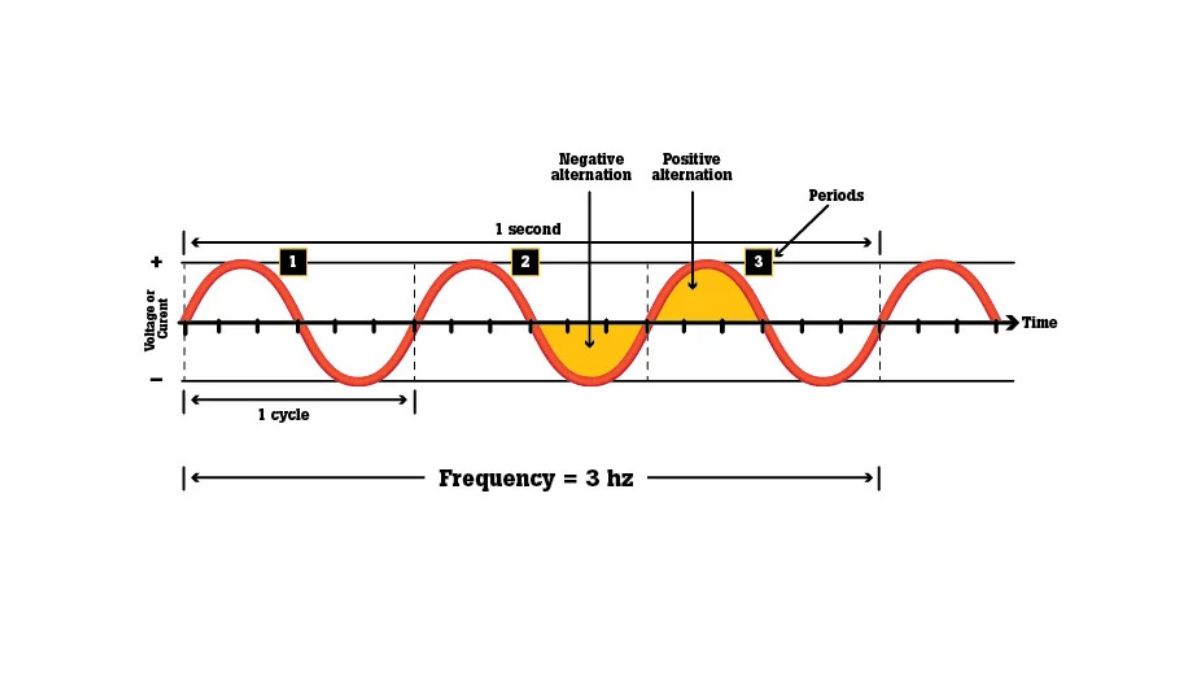
So, what exactly is frequency? In simple terms, frequency refers to the number of times a signal oscillates or cycles per second. It is typically measured in hertz (Hz) and plays a fundamental role in radio communication. Different frequency ranges are allocated for various transmission purposes, ensuring smooth and efficient communication among ham radio operators.
Understanding frequency is like having a knack for tuning into your favorite radio station. Just as turning the dial to different frequencies changes the station you’re listening to, adjusting your ham radio’s frequency settings allows you to connect with different operators and explore new horizons of communication.
In the following sections, we will explore the different frequency bands available for ham radio operation, the factors that can affect frequency performance, and the licensing requirements to operate within specific frequency ranges. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of ham radio frequency and discover the endless possibilities it offers for communication and experimentation.
Understanding Frequency
Before we dive into the specifics of ham radio frequency bands, it’s important to have a basic understanding of what frequency is and how it relates to radio communication.
Frequency is a measure of how often a wave oscillates, or completes a cycle, in a given amount of time. In the context of radio waves, frequency refers to the number of cycles per second, also known as hertz (Hz). The higher the frequency, the more cycles occur in a second.
Radio waves propagate through the air, carrying information in the form of electromagnetic waves. These waves have different properties depending on their frequency. Lower frequency waves, such as those used in AM radio, can travel longer distances but have lower information-carrying capacity. On the other hand, higher frequency waves, like those used in FM radio, have a shorter range but can transmit more data.
In the world of ham radio, operators utilize a wide range of frequency bands to communicate. These bands are designated by regulatory authorities and offer different advantages and limitations. By understanding the different ham radio frequency bands, operators can choose the most suitable one for their communication needs.
When operating a ham radio, you will come across terms like HF (High Frequency), VHF (Very High Frequency), and UHF (Ultra High Frequency). These terms refer to different ranges of frequencies that are allocated for ham radio communication.
HF bands, typically ranging from 1.8 MHz to 30 MHz, are known for their long-distance propagation capabilities. Ham radio operators utilize HF bands for worldwide communication, bouncing signals off the ionosphere to reach distant locations. These bands offer unique opportunities for long-range contacts and are popular for amateur radio contests and emergency communication.
VHF and UHF bands, on the other hand, operate at higher frequencies, ranging from 30 MHz to 300 MHz (VHF) and 300 MHz to 3 GHz (UHF). These bands are well-suited for short-range communication, often referred to as line-of-sight communication. VHF and UHF radios are commonly used for local communication within a limited geographical area, such as within a neighborhood or city.
Understanding frequency is essential for ham radio operators, as it enables them to choose the appropriate frequency band for their intended communication range and goals. By selecting the right frequency, operators can maximize the effectiveness and efficiency of their radio communication.
With a basic understanding of frequency and its relevance in ham radio communication, let’s explore the specific frequency bands available for ham radio operation and their respective advantages and limitations.
What is Ham Radio?
Ham radio, also known as amateur radio, is a fascinating hobby that allows individuals to explore the world of radio communication. It is a non-commercial form of radio operation that enables enthusiasts to experiment, build their own equipment, and engage in two-way communication with other ham radio operators.
The term “ham” originates from the early days of wireless communication when amateur operators were often considered “ham-fisted” or inexperienced compared to professional telegraphers. However, over time, the term has evolved to become a well-respected label for those involved in the hobby.
Ham radio operators, known as hams, have the opportunity to communicate across the globe using a wide variety of technologies and modes. From simple voice communication to digital data transmission, hams can connect with fellow operators near and far, sharing information, experiences, and building lasting friendships.
One of the unique aspects of ham radio is the ability to build and modify equipment. Unlike commercial radio services, hams have the freedom to design and construct their own radios and antennas, delving into the technical aspects of radio communication. This hands-on approach not only enhances their understanding of the technology but also allows for personalized and customized setups.
Furthermore, ham radio serves a vital role in emergency communication. During natural disasters or other emergencies that disrupt regular communication channels, ham radio operators can establish a vital link for relaying messages and assisting in rescue operations. The decentralized and independent nature of ham radio allows for communication when conventional methods fail.
To operate a ham radio legally, individuals are required to obtain a license from their respective regulatory authorities. The licensing process typically includes passing an examination that tests the operator’s knowledge of radio regulation, operating procedures, safety practices, and technical aspects of radio communication. Licenses are specific to certain frequency bands and determine the privileges granted to operators.
Ham radio is not just a hobby but a community of individuals passionate about radio communication. Through radio clubs, contests, on-air nets, and online forums, hams come together to exchange ideas, share experiences, and promote the growth and advancement of the hobby.
Whether it’s a hobbyist exploring the technical aspects of radio, an adventurer seeking global communication, or an emergency responder providing critical communication during times of crisis, ham radio offers a world of possibilities. It combines the thrill of exploration, the satisfaction of building, and the joy of connecting with fellow enthusiasts worldwide.
In the next sections, we will delve into the different frequency bands allocated for ham radio operation and discuss their specific characteristics and applications. So, stay tuned as we uncover the exciting world of ham radio frequencies!
Frequency Bands for Ham Radio
The world of ham radio is governed by a diverse range of frequency bands that are allocated for amateur radio use. These bands span different frequency ranges and offer various advantages and limitations for communication. Understanding these frequency bands is crucial for ham radio operators to make informed decisions about their communication setup and goals.
Ham radio frequency bands are categorized into different bands, such as HF (High Frequency), VHF (Very High Frequency), and UHF (Ultra High Frequency). Each band has its own unique characteristics and applications. Let’s explore some of the commonly used ham radio frequency bands:
- HF Bands: HF bands encompass frequencies between 1.8 MHz and 30 MHz. These bands excel in long-distance communication, as the radio waves bounce off the ionosphere and cover vast distances. The most popular HF bands used by ham radio operators include the 80-meter band (3.5-4.0 MHz), 40-meter band (7.0-7.3 MHz), and 20-meter band (14.0-14.350 MHz). HF bands are suitable for worldwide communication, making them ideal for DXing (long-distance contacts) and participating in amateur radio contests.
- VHF and UHF Bands: VHF bands cover frequencies between 30 MHz and 300 MHz, while UHF bands range from 300 MHz to 3 GHz. These bands are commonly used for local communication within a shorter range, typically referred to as line-of-sight communication. VHF and UHF frequencies are well-suited for handheld radios and are often utilized for activities such as local repeater usage, club nets, and community events. Popular VHF and UHF bands for ham radio include the 2-meter band (144-148 MHz) and the 70-centimeter band (420-450 MHz).
- SHF and EHF Bands: Super High Frequency (SHF) and Extremely High Frequency (EHF) bands operate at even higher frequencies, extending into the microwave range. These bands, ranging from 3 GHz to 300 GHz, are used for specialized communication purposes such as satellite operations, microwave link experimentation, and amateur radio television (ATV) transmissions. These bands require specialized equipment and antenna systems due to their higher frequencies and shorter wavelength.
Each ham radio frequency band has its own unique propagation characteristics, advantages, and limitations. Factors such as antenna size, atmospheric conditions, and terrain can affect signal propagation and range for different frequency bands. It is essential for ham radio operators to be familiar with these factors and choose the appropriate frequency band based on their communication requirements and objectives.
As technology continues to advance, additional frequency bands may become available for ham radio use. For example, the 630-meter band (472-479 kHz) and 2200-meter band (135.7-137.8 kHz) have been allocated for amateur radio use in some regions. These bands offer new opportunities for experimentation and long-distance communication at lower frequencies.
Having a good understanding of the available frequency bands allows ham radio operators to select the most suitable band for their intended communication range, terrain, and propagation conditions. It enables them to effectively utilize the strengths of each band and maximize their communication capabilities.
Now that we have explored the different frequency bands available for ham radio operation, let’s delve into why frequency is so important in ham radio and how it impacts communication.
Why Frequency is Important in Ham Radio
Frequency plays a crucial role in ham radio communication, determining how signals propagate through the airwaves and reach their intended destinations. Understanding why frequency is important in ham radio is essential for operators to effectively communicate and make the most of their equipment and capabilities.
Here are a few reasons why frequency is important in ham radio:
- Signal Propagation: Different frequencies behave differently when it comes to signal propagation. Lower frequency bands, such as those in the HF range, have the ability to travel long distances by bouncing off the ionosphere. This makes them ideal for long-range communication, especially for DXing (contacting distant stations). On the other hand, higher frequency bands like VHF and UHF are more prone to line-of-sight propagation, which limits their range to shorter distances. By choosing the appropriate frequency band, ham radio operators can optimize their communication based on their intended reach.
- Spectrum Usage: The radio frequency spectrum is a limited resource, and each frequency band is allocated for specific purposes. By adhering to the designated frequency bands, ham radio operators can ensure that their communication does not interfere with other users or services. Understanding the frequency allocations and operating within these bands is essential for responsible and legal ham radio operation.
- Noise and Interference: Different frequency bands are susceptible to varying levels of noise and interference. For example, HF bands are prone to atmospheric noise, while VHF and UHF bands can be affected by local interference sources like electrical devices or buildings. By selecting the appropriate frequency band, ham radio operators can mitigate the impact of noise and interference, ensuring clearer and more reliable communication.
- Equipment and Antenna Requirements: The choice of frequency band determines the equipment and antenna requirements for ham radio operation. Lower frequency bands, such as HF, often require larger antennas due to their longer wavelengths. Higher frequency bands, like VHF and UHF, can be utilized with smaller antennas, making them more suitable for handheld or mobile operations. Understanding the antenna requirements for different frequency bands allows operators to select or design the appropriate antenna system for optimal performance.
- Specialized Communication: Certain frequency bands are designated for specific communication purposes. For example, some bands are allocated for satellite communication, digital modes, or radio experiments. By familiarizing themselves with these specialized frequency bands, ham radio operators can explore new avenues of communication and engage in unique activities within the amateur radio community.
Frequency selection in ham radio requires a balance between available bandwidth, desired communication range, and regulatory compliance. It is important for operators to consider their communication goals, equipment capabilities, and local regulations when choosing a frequency band for their operations.
By understanding the importance of frequency in ham radio, operators can make informed decisions regarding frequency band selection, optimize their communication range and capabilities, and enjoy the exciting world of amateur radio to the fullest.
Now that we have explored why frequency is important in ham radio, let’s discuss some of the factors that can affect ham radio frequency and signal performance.
Factors Affecting Ham Radio Frequency
Several factors can affect ham radio frequency and influence the performance of signals. Understanding these factors is crucial for ham radio operators to optimize their communication range, minimize interference, and ensure reliable transmission. Here are some key factors that can impact ham radio frequency:
- Atmospheric Conditions: The Earth’s atmosphere plays a significant role in signal propagation. Changes in atmospheric conditions, such as solar activity, ionospheric storms, or weather patterns, can affect signal strength and propagation characteristics. For instance, during periods of increased solar activity, HF bands may experience enhanced propagation conditions, allowing for long-distance communication. Monitoring and adjusting for these atmospheric conditions can greatly influence the reach and quality of ham radio communication.
- Antenna Characteristics: The design, height, and orientation of the antenna can also impact the performance of the radio signal. Antennas are highly frequency-dependent, and choosing the appropriate antenna for the intended frequency band is crucial. Factors such as gain, radiation patterns, and impedance matching influence the efficiency of the antenna system. Careful consideration and optimization of antenna characteristics are essential for maximizing signal strength and minimizing interference.
- Interference: Interference can significantly affect ham radio frequency and degrade the quality of communication. Interference can come from both natural and man-made sources. Natural interference includes atmospheric noise, static, and electromagnetic disturbances caused by lightning and weather conditions. Man-made interference can originate from nearby electrical devices, power lines, or other radio transmissions. Selecting a frequency band with minimal interference and utilizing proper filtering techniques and shielding can help mitigate these disruption sources.
- Geographical and Terrain Factors: The geographical location and terrain can impact the propagation of radio signals. Mountains, buildings, and other obstacles can create shadow zones or block communication in certain directions. Additionally, the composition of the terrain, such as soil conductivity or proximity to large bodies of water, can affect signal propagation. By considering the geographical features and terrain characteristics, operators can optimize antenna placement and overcome potential signal challenges.
- Transmitter and Receiver Quality: The quality and performance of the transmitter and receiver equipment used in ham radio operations can significantly impact frequency and signal performance. High-quality equipment with good sensitivity, selectivity, and low noise can help achieve clearer and more reliable communication. Regular maintenance and calibration of equipment are also crucial for optimal performance.
Ham radio operators should be aware of these factors and continually monitor and adapt their setup for optimal performance. By considering and addressing these factors, operators can enhance the reach, clarity, and reliability of their ham radio communication.
Understanding the factors that can affect ham radio frequency is essential for troubleshooting and optimizing the system. With this knowledge, operators can effectively overcome challenges, minimize interference, and ensure successful communication in the ever-changing world of ham radio.
Now that we have explored the factors that can impact ham radio frequency, let’s move on to discuss the importance of ham radio licenses and the frequency privileges they provide.
Ham Radio Licenses and Frequency Privileges
Operating a ham radio legally requires obtaining a license from the respective regulatory authorities. Ham radio licenses ensure that operators have the necessary knowledge and skills to operate safely, responsibly, and within the guidelines set by the regulatory bodies. These licenses also grant operators certain frequency privileges, allowing them to transmit within specific frequency bands. Let’s explore the importance of ham radio licenses and the frequency privileges they provide:
Licensing Process: The licensing process for ham radio operators typically involves passing an examination that tests their knowledge of radio regulations, operating procedures, safety practices, and technical aspects of radio communication. The specific requirements and examination formats may vary between countries, but the aim is to ensure that operators have a solid understanding of the principles and practices of amateur radio.
Legal Compliance: Ham radio licenses are essential for legal compliance and adherence to the regulations set by the regulatory authorities. These regulations help ensure the orderly and efficient use of the radio spectrum, prevent interference with other radio services, and maintain the integrity of the amateur radio community as a whole. By operating with a valid license, ham radio operators contribute to the responsible and lawful operation of the hobby.
Frequency Privileges: One of the key benefits of holding a ham radio license is the frequency privileges it provides. Each license class grants operators access to specific frequency bands or portions within those bands. These frequency privileges determine the range of frequencies that operators can legally transmit on. Higher-level licenses often come with expanded frequency privileges, allowing operators to enjoy a wider range of communication options. Frequency privileges can vary between countries and may be subject to local regulations.
Bandwidth and Mode Limitations: Along with frequency privileges, ham radio licenses often specify the permissible bandwidth and modes of communication within those frequency ranges. For example, certain frequency bands may be designated for voice communication, while others may be reserved for digital modes or specific types of experimentation. It is important for operators to understand and adhere to these limitations to ensure compliance with their license requirements.
Advancement Opportunities: Ham radio licenses provide a framework for operators to advance their skills and knowledge within the hobby. Many licensing systems offer multiple levels or classes of licenses, allowing operators to progress from entry-level licenses to higher levels as they gain experience and demonstrate competence. Advancing to higher license classes not only provides expanded frequency privileges but also encourages continuous learning and engagement within the amateur radio community.
Obtaining a ham radio license and understanding the frequency privileges it affords is a vital step for anyone wanting to actively participate in the world of amateur radio. It provides the foundation for legal and responsible operation, allowing operators to make the most of the available frequency bands and enjoy the exciting opportunities for communication and experimentation within the hobby.
Now that we have explored the importance of ham radio licenses and frequency privileges, let’s conclude our journey through the fascinating world of ham radio frequency!
Conclusion
Ham radio, with its diverse frequency bands and unique communication capabilities, offers a captivating world for radio enthusiasts to explore. Understanding the importance of frequency and its impact on ham radio communication is essential for operators to maximize their communication range, optimize equipment, and ensure reliable transmission.
This article has provided an overview of the significance of frequency in ham radio, from its role in signal propagation to the allocation of frequency bands for different communication purposes. We have explored the various ham radio frequency bands, such as HF, VHF, UHF, and specialized bands like SHF and EHF. Each band offers its own advantages and limitations, allowing operators to adapt their communication strategies according to their needs and goals.
We have also discussed the factors that can affect ham radio frequency, such as atmospheric conditions, antenna characteristics, interference, geographical factors, and equipment quality. Understanding and addressing these factors are crucial for operators to maintain clear and reliable communication, particularly in challenging environments.
Furthermore, we have highlighted the importance of obtaining a ham radio license and understanding the frequency privileges it provides. Licenses ensure legal compliance, promote responsible operation, and grant operators access to specific frequency bands and communication modes. By acquiring higher-level licenses, operators can enjoy expanded privileges and explore a wider range of communication possibilities.
Ham radio offers endless opportunities for communication, experimentation, and community building. It serves as a platform for lifelong learning, technological innovation, and emergency communication. Whether you are interested in DXing, local networking, contesting, or contributing to emergency preparedness, ham radio provides an avenue for individuals to connect with like-minded enthusiasts across the globe.
So, if you are intrigued by the world of radio communication and eager to explore the possibilities that ham radio offers, take the first step by obtaining your ham radio license. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of ham radio frequencies, learn the ropes, connect with fellow operators, and embark on an exciting journey of exploration and connectivity.
Remember, the ham radio community is a welcoming and vibrant one, always ready to support newcomers and share their knowledge and experiences. So tune in to the frequencies, join the conversations, and let the world of ham radio open up new horizons for you!