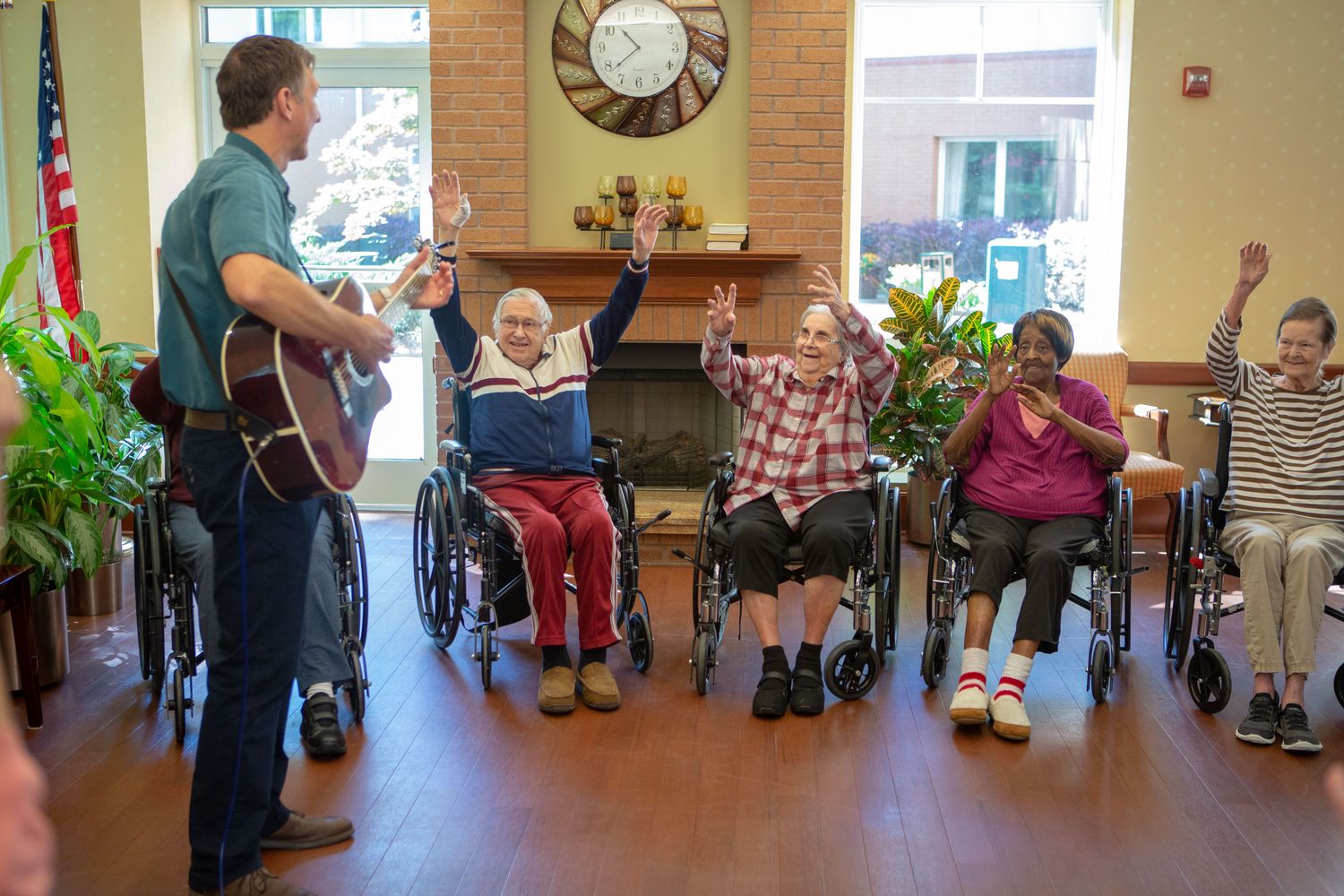
Home>Events & Info>Music Therapy>How Music Therapy Benifits Alzheimers


Music Therapy
How Music Therapy Benifits Alzheimers
Published: February 1, 2024
Discover the powerful benefits of music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer's. Harnessing the healing power of music, this therapy offers a unique approach to improving cognitive function and enhancing overall well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
- What is Music Therapy?
- The Role of Music Therapy in Alzheimer’s Care
- Benefits of Music Therapy for Alzheimer’s Patients
- Enhancing Cognitive Function
- Reducing Agitation and Anxiety
- Stimulating Memory Recall
- Promoting Emotional Well-being
- Improving Communication and Social Interaction
- Implementing Music Therapy in Alzheimer’s Care
- Music Therapy Techniques for Alzheimer’s Patients
- Creating a Personalized Music Playlist
- Incorporating Rhythmic Activities
- Singing and Vocal Exercises
- Conclusion
Introduction
Music has always played a powerful role in our lives. It has the ability to evoke emotions, bring back memories, and uplift our spirits. But did you know that music can also have incredible therapeutic effects on the mind and body? This is where music therapy comes in.
Music therapy is a specialized field that utilizes music as a therapeutic tool to improve physical, emotional, cognitive, and social well-being. It involves working with a trained music therapist who uses specific techniques and interventions to address individual needs and goals.
One area where music therapy has shown remarkable results is in the care and treatment of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurological disorder that affects memory, cognition, and behavior. It poses significant challenges for both the person afflicted and their caregivers.
Music therapy provides a unique approach to Alzheimer’s care that bypasses cognitive decline and taps into the emotional and musical memories stored deep within the brain. The power of music to engage the brain and elicit responses makes it an effective tool for improving cognitive function, reducing agitation and anxiety, stimulating memory recall, promoting emotional well-being, and improving communication and social interaction for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
In this article, we will delve into the world of music therapy and explore its benefits for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. We will also discuss the different techniques used in music therapy and how they can be implemented in the care and treatment of Alzheimer’s patients. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and uncover the transformative power of music therapy for Alzheimer’s care.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Before delving into the role of music therapy in Alzheimer’s care, it is important to have a basic understanding of the disease itself. Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects older adults. It is the most common form of dementia, accounting for about 60-80% of all cases.
The hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease is the gradual decline in cognitive function, including memory loss, difficulty with language and problem-solving, confusion, and changes in behavior. As the disease progresses, individuals may struggle with everyday tasks, lose the ability to recognize loved ones, and experience changes in mood and personality.
Alzheimer’s disease is caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Abnormal protein deposits, known as plaques and tangles, develop in the brain, disrupting communication between nerve cells and leading to cell damage and death. The exact cause of these plaques and tangles is still not fully understood.
As the disease advances, it places a significant burden on both the individuals living with Alzheimer’s and their caregivers. It can be emotionally and physically exhausting to witness the gradual decline of a loved one’s cognitive abilities and witness the impact it has on their quality of life.
While there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, research has shown that certain interventions can help slow down the progression of symptoms and improve the overall well-being of those affected. One such intervention is music therapy, which offers a unique approach to engage and stimulate the brain, creating moments of clarity and connection for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Now that we have a better understanding of Alzheimer’s disease, let’s explore how music therapy can play a pivotal role in the care and treatment of individuals living with this condition.
What is Music Therapy?
Music therapy is a specialized discipline that harnesses the power of music to promote healing and enhance well-being. It is an evidence-based practice that involves a qualified music therapist using music-based interventions to address the physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs of individuals.
A music therapist is a trained professional who possesses a deep understanding of music and its therapeutic applications. They work closely with clients to develop individualized treatment plans that incorporate various music therapy techniques tailored to their specific needs and goals.
Music therapy is based on the belief that music has the ability to elicit profound physiological and psychological responses in individuals. It taps into the universal language of music to facilitate communication, expression, and engagement.
Music therapy sessions can involve a wide range of activities such as listening to music, singing, playing musical instruments, improvising, composing, and even dancing. These activities are carefully chosen and adapted by the music therapist to address specific therapeutic goals.
The therapeutic benefits of music therapy are vast and can be experienced by individuals of all ages and abilities. It can aid in reducing stress, promoting relaxation, improving mood, enhancing cognitive skills, and facilitating personal growth and self-awareness.
In the context of Alzheimer’s care, music therapy offers a unique approach to engage individuals who may have limited verbal communication and cognitive abilities. It taps into the emotional and musical memories stored deep within the brain, creating moments of connection, joy, and empowerment.
Now that we have a better understanding of what music therapy entails, let’s explore the remarkable role it can play in Alzheimer’s care and how it can benefit individuals living with the condition.
The Role of Music Therapy in Alzheimer’s Care
Music therapy plays a vital role in the care and treatment of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. It offers a unique approach to engage and stimulate the brain, bypassing cognitive decline and tapping into the emotional and musical memories stored deep within.
One of the key aspects of music therapy is its ability to reach individuals on an emotional level. Music has the power to evoke strong emotions and can elicit responses even in individuals who may have difficulty with verbal communication or expression. This emotional connection can create a sense of calm, joy, and comfort for individuals living with Alzheimer’s.
Music therapy also helps to enhance cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. The structured nature of music prompts the brain to engage in various cognitive processes including attention, memory, and problem-solving. It stimulates different regions of the brain and can improve overall cognitive abilities, providing moments of mental clarity for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Additionally, music therapy helps to reduce agitation and anxiety, which are commonly experienced by individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. The soothing and familiar sounds of music can help to calm and relax individuals, reducing their stress levels and creating a more peaceful and conducive environment for care.
One of the most remarkable aspects of music therapy in Alzheimer’s care is its ability to stimulate memory recall. Music has a unique way of evoking memories and triggering associations. Even individuals with severe memory loss can often remember and respond to familiar songs from their past. This can lead to moments of connection and reminiscence, allowing individuals to engage in meaningful interactions and experiences.
Furthermore, music therapy promotes emotional well-being for individuals with Alzheimer’s. It provides an outlet for self-expression and can help individuals process and manage their emotions. It can uplift mood, provide a sense of comfort, and offer opportunities for individuals to connect with their identity and sense of self.
Lastly, music therapy improves communication and social interaction for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Music has a way of bridging communication barriers and fostering connections. It can facilitate verbal and non-verbal communication, encourage participation in group activities, and promote social engagement among individuals with Alzheimer’s and their caregivers or peers.
In summary, music therapy plays a multifaceted role in Alzheimer’s care. It enhances cognitive function, reduces agitation and anxiety, stimulates memory recall, promotes emotional well-being, and improves communication and social interaction. By harnessing the power of music, individuals with Alzheimer’s can experience moments of joy, connection, and empowerment, ultimately improving their overall quality of life.
Benefits of Music Therapy for Alzheimer’s Patients
Music therapy offers a wide range of benefits for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. From promoting cognitive function to improving emotional well-being, music therapy has a transformative effect on the lives of those living with this condition.
Here are some of the key benefits of music therapy for Alzheimer’s patients:
- Enhancing Cognitive Function: Music therapy stimulates various cognitive processes such as attention, memory, and problem-solving. Engaging in music-based activities can help individuals with Alzheimer’s to maintain and improve cognitive abilities, creating moments of mental clarity and heightened awareness.
- Reducing Agitation and Anxiety: The calming and familiar sounds of music can have a soothing effect on individuals with Alzheimer’s. Music therapy helps to decrease feelings of agitation and anxiety, promoting a sense of relaxation and emotional well-being.
- Stimulating Memory Recall: Music has a remarkable ability to evoke memories and trigger associations. Listening to familiar songs can help individuals with Alzheimer’s to remember and connect with past experiences, leading to moments of reminiscence and enhanced memory recall.
- Promoting Emotional Well-being: Music therapy provides individuals with Alzheimer’s with opportunities for self-expression and emotional release. It can uplift mood, provide comfort, and create a positive and enjoyable atmosphere, enhancing overall emotional well-being.
- Improving Communication and Social Interaction: Music has a universal language that transcends verbal communication. Music therapy facilitates communication and social interaction among individuals with Alzheimer’s, their caregivers, and peers. It encourages participation in group activities, fosters connections, and promotes a sense of belonging.
These benefits of music therapy have been observed in numerous studies and research findings. Music therapy has shown to positively impact the quality of life for individuals with Alzheimer’s, improving their cognitive abilities, emotional state, and overall well-being.
It is important to note that the benefits of music therapy may vary from person to person. Each individual responds differently to music-based interventions, and the effectiveness of music therapy may depend on various factors such as personal preferences, musical background, and the stage of Alzheimer’s disease.
Nevertheless, the power of music to engage the brain and evoke emotional and physical responses makes music therapy an invaluable tool in the care and treatment of Alzheimer’s patients. By incorporating music therapy into Alzheimer’s care plans, individuals can experience improved cognitive function, reduced agitation, enhanced memory recall, emotional well-being, and enhanced social connections.
Enhancing Cognitive Function
One of the remarkable benefits of music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease is its ability to enhance cognitive function. Cognitive decline is a hallmark symptom of Alzheimer’s, affecting memory, attention, problem-solving, and other cognitive skills. However, music has the power to engage and stimulate the brain, creating moments of mental clarity and improving cognitive abilities.
Music therapy utilizes various techniques and interventions to target specific cognitive areas and promote cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s. Here are a few ways in which music therapy enhances cognitive function:
- Arousing Attention: Music has a unique ability to capture and sustain attention. Engaging with music can help individuals with Alzheimer’s to focus and concentrate, providing a structured and stimulating activity for their brain.
- Stimulating Memory Retrieval: Music has a powerful association with memory. Listening to familiar songs can trigger memories and encourage the retrieval of information stored in the brain. This can improve memory recall and help individuals with Alzheimer’s connect to their personal histories.
- Improving Executive Functioning: Executive functions, such as planning, organizing, and problem-solving, can be challenging for individuals with Alzheimer’s. Music therapy activities that involve improvisation or playing musical instruments can help exercise these executive functions and improve cognitive flexibility.
- Promoting Language Skills: Music is closely linked to language processing in the brain. Singing along to songs or engaging in songwriting can enhance language skills, including verbal expression, vocabulary, and rhythmic speech.
- Boosting Mental Processing Speed: Music therapy activities often involve rhythmic patterns, which can improve mental processing speed in individuals with Alzheimer’s. Rhythmic activities, such as drumming or clapping, require individuals to synchronize their movements and thoughts, enhancing cognitive processing abilities.
These music therapy techniques not only stimulate specific cognitive areas but also create a stimulating and enriching environment for individuals with Alzheimer’s. Regular engagement with music therapy can strengthen neural connections, increase brain plasticity, and improve overall cognitive abilities.
While the benefits of music therapy on cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients are well-documented, it is important to note that the extent of improvement may vary from person to person. The stage of Alzheimer’s disease, individual preferences, and the specific goals of the music therapy intervention can all influence the outcomes. However, even small improvements in cognitive function can have a significant impact on the quality of life for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Music therapy offers a unique and enjoyable approach to enhance cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. By engaging in music-based activities and interventions, individuals can experience improved attention, memory retrieval, executive functioning, language skills, and mental processing speed, ultimately improving their cognitive abilities and overall well-being.
Reducing Agitation and Anxiety
Agitation and anxiety are common symptoms experienced by individuals with Alzheimer’s disease, which can significantly impact their quality of life. However, music therapy has shown to be a powerful tool in reducing these symptoms and creating a sense of calm and relaxation.
Music has a profound impact on our emotions and can elicit strong emotional responses. The soothing and familiar sounds of music can have a calming effect on individuals with Alzheimer’s, helping to alleviate feelings of agitation and anxiety. Here are a few ways in which music therapy reduces agitation and anxiety:
- Promoting Relaxation: Listening to calming music or engaging in rhythmic activities can induce a state of relaxation in individuals with Alzheimer’s. Music therapy sessions often incorporate slow-tempo and melodic music to create a tranquil and peaceful environment, helping to ease feelings of agitation and anxiety.
- Eliciting Positive Emotions: Music has the power to evoke positive emotions and uplift mood. By playing upbeat or joyful music, music therapists can help individuals with Alzheimer’s experience positive emotions and shift their focus away from feelings of agitation or anxiety.
- Providing Predictability and Structure: Music therapy activities often follow familiar structures such as song verse-chorus patterns or rhythmic sequences. This predictability can provide a sense of comfort and security for individuals with Alzheimer’s, reducing feelings of uncertainty and anxiety.
- Creating a Therapeutic Environment: Music therapy sessions are designed to be supportive and non-threatening. The presence of a trained music therapist who provides a safe and nurturing environment can help alleviate anxiety in individuals with Alzheimer’s and foster a sense of trust and relaxation.
- Encouraging Distraction and Diversion: Engaging in music therapy activities can serve as a distraction from distressing thoughts or situations, allowing individuals with Alzheimer’s to focus on the pleasurable and engaging aspects of music. This diversionary effect can help reduce agitation and anxiety.
Music therapy has been found to have a significant impact on reducing agitation and anxiety in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. It provides a non-pharmacological approach to managing these symptoms, allowing for a more holistic and person-centered care approach.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of music therapy in reducing agitation and anxiety may vary among individuals. Personal preferences, individual music triggers, and the specific techniques used in music therapy can all influence the outcomes. However, the overall benefits of music therapy in promoting relaxation, evoking positive emotions, and providing a structured and supportive environment make it a valuable intervention for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
By incorporating music therapy into the care plan for individuals with Alzheimer’s, caregivers can witness a reduction in agitation and anxiety, creating a more peaceful and harmonious environment for both the individuals and their caregivers.
Stimulating Memory Recall
One of the remarkable benefits of music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease is its ability to stimulate memory recall. Memory loss is a key characteristic of Alzheimer’s, making it challenging for individuals to remember and connect with their past experiences. However, music has a unique way of bypassing cognitive decline and tapping into the emotional and musical memories stored deep within the brain.
Music therapy utilizes the powerful association between music and memory to help individuals with Alzheimer’s retrieve and connect with memories. Here are several ways in which music therapy stimulates memory recall:
- Evoking Emotional Memories: Music has a strong connection to our emotions and can evoke powerful emotional responses. By playing music that is associated with specific events or emotions in an individual’s life, music therapists can stimulate the retrieval of related memories, bringing back vivid recollections and emotional connections.
- Using Familiar Songs: Listening to familiar songs from the past can trigger memories and associations. Familiarity provides a cognitive anchor, enabling individuals with Alzheimer’s to connect with specific moments and experiences. Singing along or engaging in movements associated with the songs can further enhance memory recall.
- Encouraging Verbal Expression: Listening to music can elicit verbal responses and encourage individuals to sing along or share memories related to the songs. This verbal expression not only helps individuals to exercise their language skills but also serves as a pathway to accessing and retrieving memories.
- Engaging Multisensory Experiences: Music therapy often incorporates multiple senses, such as hearing, movement, and touch. These multisensory experiences can create a rich and immersive environment that stimulates memory recall. For example, dancing to music can evoke memories of social events or past celebrations.
- Promoting Personalized Playlists: Creating personalized music playlists based on an individual’s musical preferences and history can be a powerful memory recall tool. Listening to songs that hold personal significance and meaning can unlock memories and spark conversations about past experiences.
The impact of music therapy on memory recall in individuals with Alzheimer’s is truly remarkable. Even individuals with severe memory loss can often remember and respond to familiar songs, providing moments of connection and reminiscence.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of music therapy in stimulating memory recall may vary among individuals. The personal significance of specific songs, the emotional connection to music, and the stage of Alzheimer’s disease can all influence the outcomes. However, the overall benefits of music therapy in retrieving memories, fostering connections, and facilitating communication make it an invaluable tool in Alzheimer’s care.
By incorporating music therapy into the care plan for individuals with Alzheimer’s, caregivers can provide them with opportunities to reconnect with their past, evoke memories, and create meaningful and engaging experiences.
Promoting Emotional Well-being
Music therapy plays a significant role in promoting emotional well-being for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. The evocative power of music can have a profound impact on emotions, providing comfort, joy, and a means of expression for those living with this condition.
Here are some ways in which music therapy promotes emotional well-being for individuals with Alzheimer’s:
- Uplifting Mood: Music has the ability to uplift mood and evoke positive emotions. Listening to favorite songs or engaging in musical activities can bring about feelings of happiness, joy, and nostalgia, creating a positive emotional experience for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
- Providing Comfort and Soothing: The soothing and familiar sounds of music can bring comfort and alleviate distress. Music therapy sessions often incorporate calming melodies and rhythms, creating a peaceful and nurturing environment that can reduce anxiety and provide emotional relief for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
- Fostering Self-expression: Music therapy provides a means of self-expression for individuals who may have difficulty with verbal communication. Through music, individuals with Alzheimer’s can express their emotions, thoughts, and desires, empowering them to communicate and be understood in a meaningful way.
- Creating Positive Associations: Memories associated with music are often linked to positive experiences and emotions. By engaging with music that holds personal significance and positive associations, individuals with Alzheimer’s can relive those moments and experience the associated emotions, promoting a sense of happiness and well-being.
- Providing Validation and Identity: Music therapy acknowledges and validates the individuality and identity of individuals with Alzheimer’s. By incorporating personal musical preferences and history, music therapists create a sense of belonging and a space where individuals can connect with their sense of self, promoting emotional well-being.
Emotional well-being is a crucial aspect of overall quality of life, and music therapy provides a unique and powerful avenue for individuals with Alzheimer’s to experience and express their emotions. By engaging in music therapy, individuals can find solace, joy, and a renewed sense of self, enhancing their emotional well-being despite the challenges of the disease.
It is important to note that the emotional responses to music therapy may vary among individuals. Personal preferences, individualized music triggers, and the overall therapeutic relationship with the music therapist can influence the emotional experiences. However, by tailoring music therapy interventions to the unique needs and preferences of individuals with Alzheimer’s, caregivers can provide them with opportunities for emotional expression, comfort, and joy.
Incorporating music therapy into the care plan for individuals with Alzheimer’s can have a profound impact on their emotional well-being, fostering a sense of happiness, comfort, and connection even in the face of the disease.
Improving Communication and Social Interaction
Communication and social interaction can become increasingly challenging for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. However, music therapy has been shown to be a powerful tool in improving communication and facilitating meaningful social interactions for individuals living with this condition.
Here are several ways in which music therapy improves communication and social interaction for individuals with Alzheimer’s:
- Bypassing Speech Limitations: Music has its own language that transcends the need for verbal communication. Listening to music or engaging in musical activities allows individuals with Alzheimer’s to connect and communicate without relying solely on spoken words.
- Encouraging Verbal Expression: Singing along to songs, participating in group singing, or engaging in discussions about music can prompt individuals with Alzheimer’s to express themselves verbally. The rhythmic and melodic nature of music helps stimulate language skills and encourages communication.
- Facilitating Non-Verbal Communication: Music therapy provides opportunities for individuals with Alzheimer’s to communicate non-verbally through movements, gestures, and body language. Dancing, playing instruments, or engaging in rhythmic activities can serve as a means of expression and connection.
- Promoting Group Interactions: Music therapy sessions often involve group activities, creating a supportive and inclusive environment for individuals with Alzheimer’s to interact with their peers. Participating in music-making or singing in a group setting fosters a sense of belonging, encourages social interaction, and promotes shared experiences.
- Creating Emotional Connections: Music has a unique ability to evoke emotional responses. By engaging with music together, individuals with Alzheimer’s and their caregivers or peers can forge emotional connections and shared experiences, fostering social bonds and enhancing communication.
Music therapy creates a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals with Alzheimer’s to communicate and connect with others. It provides opportunities for self-expression, emotional sharing, and engagement in a meaningful way, even for those who may struggle with verbal communication.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of music therapy in improving communication and social interaction may vary among individuals. The stage of Alzheimer’s disease, individual preferences, and the specific techniques used in music therapy can all influence the outcomes. However, overall, music therapy offers a valuable avenue for individuals with Alzheimer’s to engage in meaningful interactions, enhance communication, and maintain social connections.
By incorporating music therapy into Alzheimer’s care plans, caregivers can provide individuals with opportunities to express themselves, connect with others, and experience the joy of shared musical experiences, thereby improving their communication skills and fostering social interaction.
Implementing Music Therapy in Alzheimer’s Care
Implementing music therapy in the care of individuals with Alzheimer’s involves careful planning and collaboration between caregivers, healthcare professionals, and trained music therapists. By incorporating music therapy as part of the care plan, individuals with Alzheimer’s can experience the transformative benefits that music therapy provides.
Here are important considerations for implementing music therapy in Alzheimer’s care:
- Consulting with a Music Therapist: Engage the services of a qualified music therapist with experience in working with individuals with Alzheimer’s. Music therapists have the expertise to assess individual needs, customize interventions, and guide the implementation of music therapy in a safe and effective manner.
- Individualized Treatment Plan: Each individual with Alzheimer’s has unique needs and preferences. A music therapist will develop an individualized treatment plan, taking into account the individual’s musical background, preferences, cognitive abilities, and therapeutic goals.
- Collaboration with Caregivers: Caregivers play a vital role in the successful implementation of music therapy. Collaborate with the music therapist to understand the goals of the therapy and learn strategies to integrate music-based activities into daily caregiving routines.
- Creating a Music-Rich Environment: Surround the individual with Alzheimer’s with music by playing familiar songs throughout the day. Consider incorporating background music during meals, daily activities, or relaxation periods to create a stimulating and supportive environment.
- Personalized Playlists: Develop personalized playlists for individuals with Alzheimer’s based on their musical preferences and history. Include songs that hold personal significance and have the potential to evoke positive emotions and memories.
- Encouraging Active Participation: Encourage active participation in music-based activities such as singing, playing instruments, movement, and improvisation. This active engagement maximizes the therapeutic benefits of music therapy and promotes a sense of empowerment and enjoyment for the individual.
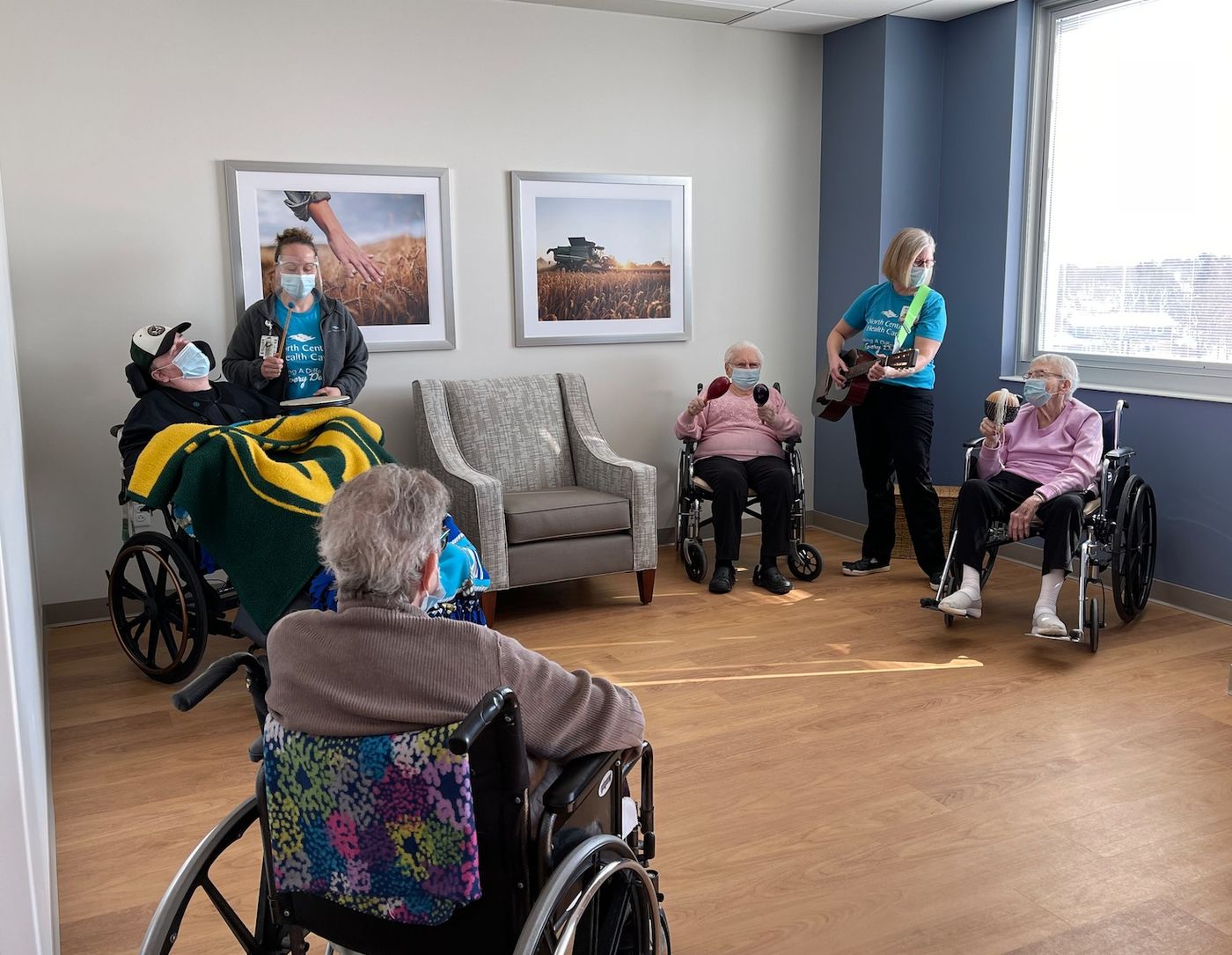
- Engaging in Group Sessions: Incorporate group music therapy sessions into the care plan. Group sessions provide opportunities for social interaction, emotional connection, and a sense of community for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: Regularly assess the progress and response to music therapy interventions. The music therapist can provide insights and make adjustments as needed to ensure the most effective and meaningful experience for the individual with Alzheimer’s.
It is important to note that music therapy should not replace other standard forms of care for individuals with Alzheimer’s, but rather complement and enhance the overall care plan. The collaborative effort between caregivers, healthcare professionals, and music therapists is crucial in providing holistic and person-centered care for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
By implementing music therapy in Alzheimer’s care, caregivers can tap into the therapeutic power of music to improve cognitive function, reduce agitation and anxiety, stimulate memory recall, promote emotional well-being, and enhance communication and social interaction. Music becomes a powerful and transformative tool in creating meaningful and engaging experiences for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease.
Music Therapy Techniques for Alzheimer’s Patients
Music therapy offers a variety of techniques and interventions that are specifically tailored to the unique needs and abilities of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. These techniques harness the power of music to engage the brain, stimulate memory recall, and promote overall well-being. Here are some commonly used music therapy techniques for Alzheimer’s patients:
- Creating a Personalized Music Playlist: Develop personalized playlists that include familiar songs from the individual’s past. Choose songs that hold personal significance and evoke positive emotions. These playlists can be played during different times of the day to improve mood, reduce anxiety, and create a sense of familiarity and comfort.
- Incorporating Rhythmic Activities: Engage individuals with Alzheimer’s in rhythmic activities such as drumming, clapping, or using handheld percussion instruments. Rhythmic activities stimulate sensorimotor coordination and provide opportunities for physical engagement and self-expression.
- Singing and Vocal Exercises: Encourage individuals with Alzheimer’s to sing along to familiar songs. Singing exercises the vocal muscles, stimulates breath control, and aids in verbal expression. Group singing can also foster a sense of community and social connection.
- Musical Improvisation: Engage individuals with Alzheimer’s in spontaneous musical improvisation using simple instruments or their own voices. This technique encourages creative expression, promotes emotional release, and provides a safe space for exploration and freedom of musical expression.
- Music-Assisted Relaxation: Use calming and soothing music to induce a state of relaxation. This technique can involve guided imagery exercises, deep breathing techniques, and progressive muscle relaxation while listening to tranquil music. It helps promote relaxation, reduce stress, and create a sense of calm.
- Music and Movement: Combine music with movement activities to promote physical coordination, motor skills, and balance. Engage individuals with Alzheimer’s in gentle exercises, dancing, or chair-based movements that are synchronized with the rhythm and tempo of the music.
- Reminiscence and Song Discussion: Utilize songs as a catalyst for reminiscing and facilitating verbal communication. Discuss the memories associated with specific songs, encouraging individuals with Alzheimer’s to share personal stories, emotions, and experiences that the music evokes.
Music therapy techniques for Alzheimer’s patients are adapted to suit individual preferences, cognitive abilities, and therapeutic goals. Music therapists will carefully select and customize interventions based on assessments and ongoing observations of the individual’s response to music.
By implementing these techniques, music therapy aims to enhance cognitive function, reduce agitation and anxiety, stimulate memory recall, promote emotional well-being, improve communication, and facilitate social interaction for individuals with Alzheimer’s. The power of music engages the brain, creates connections, and offers individuals a sense of joy, comfort, and self-expression.
Creating a Personalized Music Playlist
One of the key techniques in music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease is the creation of a personalized music playlist. This technique involves selecting and compiling a collection of familiar and meaningful songs that resonate with the individual’s past experiences, preferences, and emotional connections.
Here are the steps involved in creating a personalized music playlist for individuals with Alzheimer’s:
- Gather Information and Preferences: Start by gathering information about the individual’s musical background, cultural heritage, and personal preferences. Consult with family members, caregivers, or the individual themselves to learn about the songs and genres that hold significance and evoke positive emotions.
- Assess and Observe the Individual’s Response to Music: Observe the individual’s reaction to different types of music or specific songs. Pay attention to their facial expressions, body language, and any changes in mood or behavior when listening to particular songs. This assessment will help guide the selection process.
- Select Familiar Songs: Choose songs that the individual is likely to recognize and have an emotional connection to. This may include popular songs from their youth, songs from significant life events, or music associated with religious or cultural traditions. Aim to create a diverse playlist that reflects different moods and genres.
- Incorporate Music Triggers: Consider incorporating songs that have specific memories or associations for the individual. These “music triggers” can evoke personal stories, emotions, and experiences. By including these songs, you create opportunities for reminiscing and engaging in meaningful conversations.
- Consider Musical Preferences: Take into account the individual’s musical preferences, such as favorite artists, genres, or instruments. Include songs that align with their taste and reflect their musical identity. This personalization enhances the individual’s emotional connection to the playlist.
- Organize the Playlist: Arrange the songs in a logical and coherent order. Consider the flow of the songs and how the playlist may progress from more calming or slow-tempo tunes to more uplifting or energetic tracks. This arrangement can help create a cohesive and engaging musical experience.
- Use Technology or Physical Media: Depending on the individual’s access and comfort with technology, create the playlist using a portable music player, a smartphone, or a computer. Alternatively, you can create a physical media collection, such as a CD or a USB drive, for easy playback.
A personalized music playlist taps into the emotional and musical memories stored deep within the brain, creating a profound connection and enhancing the therapeutic benefits of music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer’s. Listening to familiar songs can evoke memories, uplift mood, reduce anxiety, and foster a sense of comfort and familiarity.
Regularly engage the individual with Alzheimer’s in listening sessions with their personalized music playlist. Observe their responses, engage in conversation about the songs, and encourage singing or movement. This personalized approach enhances the individual’s emotional well-being, promotes cognitive engagement, and enhances the overall quality of life.
Incorporating Rhythmic Activities
Rhythmic activities are a valuable component of music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. They involve engaging individuals in various rhythmic movements or interactions with percussion instruments to stimulate sensorimotor coordination, provide physical engagement, and promote self-expression. Incorporating rhythmic activities in music therapy sessions can have numerous benefits for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Here are some ways to incorporate rhythmic activities in music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer’s:
- Clapping and Tapping: Encourage individuals to clap their hands or tap their fingers to the rhythm of the music. This simple rhythmic activity not only engages the motor skills but also helps to enhance coordination and focus.
- Playing Percussion Instruments: Provide individuals with Alzheimer’s a variety of handheld percussion instruments, such as drums, shakers, or tambourines. Encourage them to play along with the music, following the rhythm and tempo. This activity stimulates sensorimotor coordination and offers a creative outlet for self-expression.
- Body Percussion: Guide individuals to use their bodies as instruments, incorporating rhythmic movements like clapping, stomping, or patting different body parts. Body percussion can help individuals connect with the rhythm on a deeper level and engage their entire body in the rhythmic experience.
- Chair Drumming: For individuals with limited mobility, encourage them to drum on the arms of their chair or use drumsticks on a pad or pillow. Chair drumming allows them to actively participate in rhythmic activities and experience the joy of creating percussive sounds.
- Rhythm-based Exercises: Combine rhythmic activities with simple movements or exercise routines. For example, instruct individuals with Alzheimer’s to march or walk in time with the beat of the music, emphasizing the rhythmic component of the movement. This integrates physical exercise with rhythm, providing a fun and engaging experience.
- Call and Response: Engage individuals in call and response activities, where you play a rhythmic pattern on a percussion instrument, and they respond by echoing the pattern back to you. This interactive technique not only fosters engagement but also promotes communication and attention to rhythmic patterns.
Incorporating rhythmic activities in music therapy sessions provides individuals with Alzheimer’s an opportunity for physical engagement, self-expression, and cognitive stimulation. The rhythmic elements of music create a structured and predictable environment, offering comfort and a sense of control. Rhythmic activities can also help to regulate the heartbeat, reduce stress, and create a positive and joyful atmosphere.
When incorporating rhythmic activities, observe and adjust the level of complexity based on the individual’s abilities and comfort. Pay attention to their responses and adapt the activities to ensure an enjoyable and accessible experience.
In summary, incorporating rhythmic activities in music therapy sessions for individuals with Alzheimer’s adds a dynamic and interactive element to the therapeutic process. It engages motor skills, enhances cognitive engagement, and promotes self-expression and overall well-being.
Singing and Vocal Exercises
Singing and vocal exercises are highly beneficial components of music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. The act of singing engages various cognitive, physical, and emotional processes, making it an effective tool for communication, cognitive stimulation, and emotional expression. Incorporating singing and vocal exercises into music therapy sessions can have a profound impact on individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Here are some ways to incorporate singing and vocal exercises in music therapy for individuals with Alzheimer’s:
- Sing-Along Sessions: Encourage individuals to participate in sing-along sessions where they can join in singing familiar songs. Provide lyric sheets or use visual aids, such as a projector or a large print book, to assist with following along. Singing familiar songs triggers memory recall, stimulates cognitive processes, and fosters a sense of connection and engagement.
- Solo Singing: Offer individuals the opportunity to sing solo, expressing their emotions and memories through their voice. Encourage them to choose songs that have personal significance or meaning to them. Solo singing promotes self-expression, boosts confidence, and can bring about a sense of joy and accomplishment.
- Vocal Exercises: Guide individuals with Alzheimer’s through vocal exercises that focus on breath control, articulation, and vocal range. Simple vocal warm-ups, such as humming, lip trills, or tongue exercises, can help strengthen vocal muscles and improve vocal clarity.
- Rhythmic Vocal Patterns: Engage individuals in rhythmic vocal patterns or chants. This involves repeating rhythms, syllables, or short phrases with rhythmic precision. Rhythmic vocal patterns help improve timing, coordination, and working memory, stimulating cognitive function and promoting communication.
- Improvisation and Vocal Play: Encourage individuals to engage in vocal improvisation, exploring different sounds, pitches, and vocal techniques. This creative expression allows freedom of vocal exploration and promotes emotional release. Vocal play can also include using sounds and non-linguistic vocalizations to express emotions or communicate.
- Group Singing and Harmonizing: Create opportunities for group singing and harmonizing. Invite individuals with Alzheimer’s to sing together, harmonizing their voices. Group singing fosters a sense of community, enhances social interaction, and encourages cooperation and shared experiences.
When incorporating singing and vocal exercises, it is essential to create a supportive and non-judgmental environment. Focus on the enjoyment and personal expression rather than achieving perfect pitch or vocal technique. Adapt the activities to the abilities and comfort level of each individual, allowing for flexibility and individualized expression.
Singing and vocal exercises offer a range of benefits for individuals with Alzheimer’s. Singing stimulates cognitive processes such as memory recall, language skills, and attention. It also promotes emotional expression, social engagement, and overall well-being. The act of using the voice in music therapy can provide individuals with Alzheimer’s a means of self-expression when other forms of communication may be challenging.
In summary, incorporating singing and vocal exercises in music therapy sessions for individuals with Alzheimer’s provides a platform for self-expression, cognitive stimulation, and emotional connection. Singing taps into the power of the voice, inviting individuals to engage in a creative and joyful experience.
Conclusion
Music therapy has emerged as a powerful and effective intervention for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. It harnesses the therapeutic potential of music to address the unique needs and challenges faced by individuals living with this condition. By engaging individuals in personalized music therapy sessions, caregivers and healthcare professionals can tap into the transformative power of music and enhance the overall well-being of individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of music therapy and its benefits for individuals with Alzheimer’s. Music therapy offers a range of advantages, including enhancing cognitive function, reducing agitation and anxiety, stimulating memory recall, promoting emotional well-being, improving communication, and fostering social interaction. It provides a holistic approach to care that goes beyond the limitations of cognitive decline.
Through techniques such as creating personalized music playlists, incorporating rhythmic activities, engaging in singing and vocal exercises, and more, individuals with Alzheimer’s can experience the profound effects of music therapy. The familiarity and emotional connections evoked by music provide a sense of comfort, joy, and self-expression.
It is important for caregivers, healthcare professionals, and music therapists to collaborate in implementing music therapy as part of Alzheimer’s care plans. By tailoring interventions to the individual’s preferences and needs, monitoring their responses, and adapting as necessary, the power of music can be harnessed to its fullest potential.
In conclusion, music therapy offers a unique and impactful approach to support individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. By integrating music therapy into their care, we can enhance cognitive abilities, reduce stress and anxiety, foster emotional well-being, improve communication, and foster connections. Let us embrace the therapeutic power of music and enrich the lives of individuals with Alzheimer’s through the transformative and universal language of music.