Jazz
How Would You Describe Jazz Music
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the soulful and improvisational world of Jazz music. From its origins to its modern interpretations, explore the vibrant rhythms and melodic expressions that define this iconic genre.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Jazz music is a genre that has captivated audiences around the world with its distinct sound, creative improvisation, and rich cultural history. Originating from African-American communities in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, jazz has evolved over time to encompass a wide range of styles and influences. It is a genre that celebrates individual expression, encourages musicians to push the boundaries of harmony and rhythm, and has made a lasting impact on the music industry as a whole.
With its roots in the blues, ragtime, and African musical traditions, jazz emerged as a unique form of artistic expression that defied convention and embraced innovation. From its early beginnings in the streets of New Orleans, jazz quickly spread across the United States and eventually gained international recognition. Its ability to blend different musical styles, cultural influences, and improvisation techniques set it apart from other genres of music.
At its core, jazz is characterized by its syncopated rhythms, complex harmonies, and improvisational nature. Musicians use their technical skill and artistic intuition to create spontaneous and unique musical expressions. Solo improvisation is a hallmark of jazz, allowing musicians to showcase their individual talents and interact with other players in a dynamic and collaborative way.
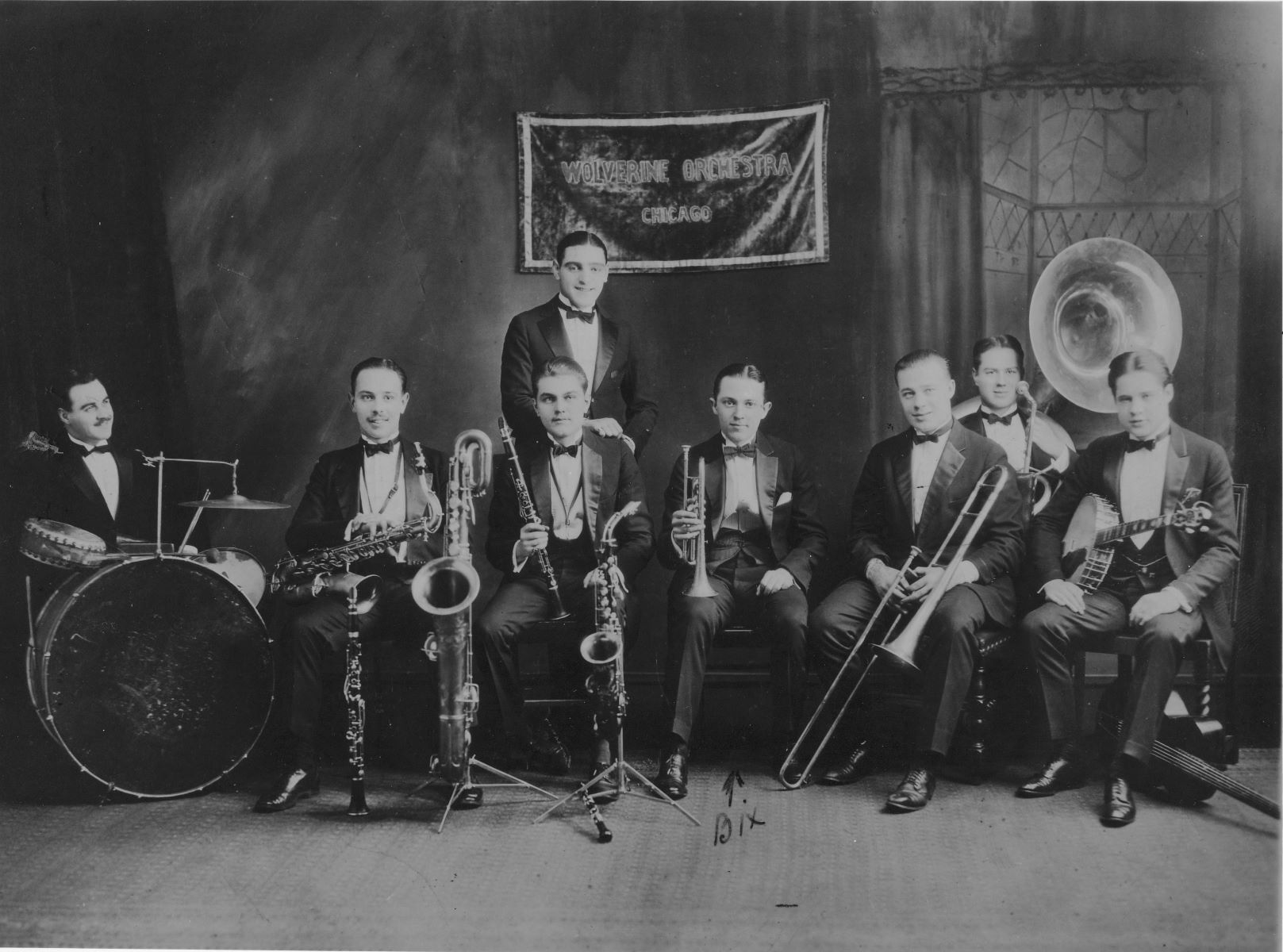
Jazz music is also known for its diverse instrumentation. Traditional jazz ensembles typically include instruments such as the trumpet, saxophone, trombone, piano, bass, and drums. However, jazz has also embraced other instruments such as the guitar, vibraphone, and even unconventional instruments like the accordion and the theremin.
Over the years, jazz has developed into various styles, each with its own unique characteristics and historical significance. From the smooth sounds of cool jazz to the energetic rhythms of bebop, each style has contributed to the evolution of the genre and has left a lasting impact on the music industry.
The influence of jazz extends beyond its own genre. It has influenced and been influenced by other musical genres such as rock, pop, and hip-hop. Many renowned musicians, from Miles Davis to John Coltrane, have seamlessly blended jazz with elements of other genres, showcasing the versatility and adaptability of this music.
Today, jazz music continues to thrive and evolve. Artists such as Kamasi Washington and Esperanza Spalding are pushing the boundaries of the genre, infusing it with elements of funk, soul, and contemporary influences. Jazz festivals around the world attract audiences of all ages, showcasing the vibrant and timeless nature of this genre.
In this article, we will explore the origins, characteristics, instruments, different styles, notable musicians, and the influence of jazz music on popular culture. Join us on this musical journey as we delve into the world of jazz and uncover why it continues to resonate with music lovers across the globe.
Origins of Jazz Music
The origins of jazz music can be traced back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana. It emerged as a fusion of various musical styles, including ragtime, blues, gospel, and African rhythms.
One of the major influences on the development of jazz was the African musical tradition brought to America by enslaved Africans. This tradition emphasized improvisation, call and response patterns, and syncopated rhythms, which are key elements in jazz music.
Another significant influence was the incorporation of European musical traditions, particularly the classical music brought by European immigrants and the brass band tradition. The combination of African and European musical elements resulted in a unique and distinct musical style.
The birthplace of jazz, New Orleans, was a melting pot of cultures, with African, European, and Caribbean influences converging in the city. The city’s vibrant and diverse music scene provided fertile ground for the development of jazz.
Early jazz musicians often played in brass bands, performing in parades, funerals, and other social gatherings. These bands laid the foundation for the improvisational and ensemble-based nature of jazz music.
One of the key figures in the early development of jazz was Buddy Bolden, a cornet player known for his powerful and expressive playing style. Bolden’s performances in the late 19th century are believed to be some of the earliest recordings of jazz music.
As jazz gained popularity, musicians from New Orleans began to spread the genre to other parts of the country. The Great Migration of African Americans to cities like Chicago, New York, and Kansas City in the early 20th century played a crucial role in the dissemination of jazz.
Jazz received widespread recognition and acclaim with the advent of the Harlem Renaissance in the 1920s. The movement, centered in Harlem, New York, celebrated African-American culture and arts, and jazz became a symbol of black cultural identity.
Notable jazz pioneers such as Louis Armstrong, Duke Ellington, and Jelly Roll Morton emerged during this time, pushing the boundaries of the genre and elevating jazz to new heights of creativity and sophistication.
Today, we can still hear the echoes of the early jazz traditions in contemporary jazz music. The undeniable influence of African music, the syncopated rhythms, the use of improvisation, and the vibrant energy that defines jazz can all be traced back to its humble origins in the neighborhoods of New Orleans.
Characteristics of Jazz Music
Jazz music is characterized by several key elements that distinguish it from other genres. These characteristics contribute to the unique and captivating sound of jazz.
Rhythm: One of the defining features of jazz is its complex and syncopated rhythms. Unlike other genres with straight and predictable rhythms, jazz often incorporates offbeat accents and unexpected rhythmic patterns. This rhythmic complexity adds a sense of excitement and unpredictability to the music.
Improvisation: Jazz is renowned for its emphasis on improvisation. Musicians have the freedom to spontaneously create melodies, harmonies, and rhythms during their performances. This artistic freedom allows for individual expression and creativity, and it is a hallmark of jazz music.
Swing: Swing is a rhythmic style often associated with jazz. It refers to the smooth and flowing feeling created by a combination of syncopation, swing eighth notes, and a relaxed groove. The swinging rhythm is what gives jazz music its infectious energy and groove.
Harmony: Jazz harmonies are often more complex and adventurous than those found in other genres. Musicians explore colorful chord progressions, extended chords, and substitutions, creating a rich and harmonically intriguing sound. This harmonic complexity contributes to the improvisational nature of jazz.
Call and Response: Call and response is a musical technique commonly found in jazz as well as African musical traditions. It involves a musical phrase or idea played by one musician or group of musicians, followed by a responsive phrase or idea played by another musician or group. This back-and-forth interaction adds a dynamic and conversational element to jazz performances.
Blue Notes: Blue notes are a distinct characteristic of jazz music. They refer to the flattened or lowered third, fifth, and seventh notes of a major scale. Blue notes add a touch of melancholy, tension, and emotional depth to the music, contributing to the expressive and soulful nature of jazz.
Syncopation: Syncopation is an integral part of jazz music. It involves emphasizing the weak beats or offbeats in a musical measure. This rhythmic displacement creates a sense of forward motion and adds excitement and unpredictability to the music.
Interaction and Collaboration: Jazz is a collaborative art form that thrives on the interaction between musicians. It encourages spontaneous musical conversations, with musicians reacting and responding to each other in real-time. This interaction creates a sense of unity and musical interplay that is unique to jazz.
Variety and Freedom: Jazz is a genre that embraces versatility and freedom. It allows for the incorporation of various musical styles, influences, and improvisational approaches. From traditional swing to avant-garde experimentation, jazz encompasses a wide range of styles and encourages musicians to explore and push the boundaries of their art.
All these characteristics combine to give jazz music its distinct and evolving sound. The versatility, improvisation, and unique rhythmic qualities of jazz continue to captivate audiences, making it a genre that remains relevant and influential to this day.
Instruments Used in Jazz Music
Jazz music is known for its diverse instrumentation, with a wide range of instruments contributing to its distinct sound. While there is no strict rule on which instruments are included in a jazz ensemble, there are several common instruments associated with the genre.
1. Trumpet: The trumpet is one of the iconic instruments in jazz music. Its bright and piercing sound is often used to play melodic lines, improvise solos, and lead the ensemble. Jazz trumpet players such as Louis Armstrong, Dizzy Gillespie, and Miles Davis have left a lasting impact on the genre.
2. Saxophone: The saxophone is another integral instrument in jazz. Its versatile and expressive nature allows it to embody the emotion and energy of jazz music. The saxophone family, including the alto, tenor, and soprano saxophones, has been prominently featured in many jazz ensembles, with legends like Charlie Parker and John Coltrane pushing the boundaries of the instrument.
3. Trombone: The trombone adds a rich and powerful sound to jazz music. Its unique slide mechanism allows for smooth glissandos and melodic phrasing. Trombonists play a crucial role in jazz ensembles, providing harmonic support, improvisational solos, and contributing to the overall texture of the music.
4. Piano: The piano serves as the harmonic foundation in jazz music. Pianists are responsible for creating complex chord voicings, improvising melodies, and providing rhythmic accompaniment. Legendary jazz pianists such as Duke Ellington, Thelonious Monk, and Herbie Hancock have made significant contributions to the genre.
5. Bass: The bass, whether acoustic or electric, provides the fundamental rhythm and harmony in jazz music. Bassists play a crucial role in establishing the groove, outlining the chord progressions, and providing melodic and rhythmic variations. Notable jazz bassists include Charles Mingus, Jaco Pastorius, and Ray Brown.
6. Drums: The drum set lays the rhythmic foundation of jazz, providing the pulse, accents, and polyrhythms. Drummers use various components of the drum set, including the snare, bass drum, hi-hat, cymbals, and toms, to create intricate rhythmic patterns and interact with other musicians. Jazz drummers like Max Roach, Art Blakey, and Elvin Jones are revered for their innovative approaches and mastery of the instrument.
7. Guitar: While not as commonly associated with jazz as other instruments, the guitar has played a significant role in shaping the genre. Jazz guitarists employ techniques such as chord voicings, improvisation, and soloing, bringing a unique melodic and harmonic element to jazz music. Legends like Django Reinhardt, Charlie Christian, and Wes Montgomery have left an indelible mark on jazz guitar.
In addition to these instruments, jazz music has seen the incorporation of various others, depending on the style and preferences of the musicians. These may include instruments such as the vibraphone, clarinet, double bass, flugelhorn, and even unconventional instruments like the accordion or the theremin. The combination of different instruments in jazz allows for endless possibilities and sonic expressions.
It is the collective interplay and creativity of these instruments that contribute to the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of jazz music. Each instrument adds a unique voice to the ensemble, allowing for individual expression, improvisation, and collaborative exploration.
Different Styles of Jazz Music
Jazz music is a genre that has evolved over time, giving rise to a rich tapestry of styles, each with its own distinct characteristics and historical importance. From the early roots of New Orleans jazz to the modern innovations of contemporary jazz, there are several notable styles that have shaped the genre.
1. New Orleans Jazz: Also known as Dixieland jazz, New Orleans jazz emerged in the early 20th century. It is characterized by its ensemble-based improvisation, collective improvisation, and lively polyphonic texture. New Orleans jazz often features front-line instruments like the trumpet, clarinet, and trombone, creating a vibrant and joyful sound.
2. Swing: Swing jazz, popular during the 1930s and 1940s, is characterized by its upbeat and danceable rhythms. Big bands with brass sections and rhythm sections were at the forefront of the swing era. Famous bandleaders, such as Benny Goodman, Count Basie, and Duke Ellington, popularized the swing style, with smooth melodies and infectious swing rhythms.
3. Bebop: Bebop emerged in the 1940s as a reaction to the commercially driven swing era. It focused on small-group improvisation and complex harmonies. Bebop musicians, including Charlie Parker, Dizzy Gillespie, and Thelonious Monk, introduced intricate melodies, lightning-fast improvisation, and unconventional harmonic progressions, pushing the boundaries of jazz.
4. Cool Jazz: Cool jazz, born in the late 1940s and 1950s, is characterized by its relaxed and subdued sound. It explores a more relaxed and introspective approach to improvisation, often featuring smaller ensembles. Musicians like Miles Davis, Chet Baker, and Dave Brubeck played a pivotal role in popularizing this style.
5. Modal Jazz: Modal jazz, popularized by Miles Davis’ seminal album “Kind of Blue,” emerged in the late 1950s and early 1960s. It focuses on improvisation over static harmonies, rather than complex chord progressions. Modal jazz often employs scales and modes as the basis for improvisation, allowing for a more open and atmospheric sound.
6. Fusion: Fusion jazz emerged in the late 1960s and combined elements of jazz with rock, funk, and other genres. Musicians such as Herbie Hancock, Weather Report, and Chick Corea embraced electric instruments, synthesizers, and funk-inspired grooves. Fusion jazz pushed the boundaries of genre classification and embraced a more experimental and eclectic approach.
7. Contemporary Jazz: Contemporary jazz is a broad term that encompasses various modern jazz styles. It incorporates influences from various genres, including pop, hip-hop, R&B, and world music. Contemporary jazz artists, such as Kamasi Washington, Snarky Puppy, and Robert Glasper, fuse traditional jazz elements with modern production techniques, creating a unique and accessible sound.
These are just a few examples of the many styles that have emerged within the realm of jazz music. Each style reflects the cultural and artistic context of its time, allowing for continuous innovation and exploration within the genre. Jazz remains a vibrant and ever-evolving art form, with musicians continually pushing the boundaries and redefining its boundaries.
The Influence of Jazz Music on Other Genres
Jazz music has had a profound influence on the development of various other genres throughout the history of popular music. Its distinct sound, improvisational nature, and innovative approaches to harmony and rhythm have left an indelible mark on the musical landscape.
One of the first genres to be influenced by jazz was swing, a style that emerged in the 1930s. Swing drew heavily from the rhythmic energy, big band arrangements, and improvisation found in jazz. Many big band leaders, like Benny Goodman and Duke Ellington, incorporated elements of jazz into their swing compositions, expanding the genre’s popularity and scope.
Jazz also played a pivotal role in the development of bebop, a subgenre that emerged in the 1940s. Characterized by fast tempos, complex harmonies, and virtuosic improvisation, bebop musicians sought to break away from the more commercial aspects of swing. Their innovative approach to melody and rhythm laid the foundation for the development of modern jazz and had a significant impact on the subsequent evolution of other genres such as cool jazz, hard bop, and modal jazz.
In the 1950s, the influence of jazz extended beyond its own genre and seeped into the world of popular music. Artists like Frank Sinatra and Ella Fitzgerald incorporated jazz phrasing and improvisation into their vocal performances, blurring the boundaries between jazz and popular music. This fusion of styles helped popularize jazz among a wider audience.
Furthermore, the advent of fusion jazz in the 1960s and 1970s brought jazz into direct contact with rock, funk, and other contemporary genres. Musicians like Miles Davis, Herbie Hancock, and Chick Corea incorporated elements of popular music, electronic instruments, and rock-inspired rhythms into their jazz compositions. This fusion of styles paved the way for the development of jazz fusion, jazz-rock, and jazz-funk, pushing the boundaries of both jazz and popular music.
Jazz’s influence continues to be felt in the realms of contemporary R&B, hip-hop, and electronic music. Artists like Robert Glasper and Kamasi Washington have seamlessly incorporated jazz elements into their compositions, creating a fresh and innovative sound that blends genres. The improvisational nature and harmonic complexity of jazz have found a new home in these genres, infusing them with a sense of sophistication and musical exploration.
Overall, the influence of jazz on other genres can be seen in the use of improvisation, complex harmonies, and rhythmic experimentation. It has acted as a catalyst for musical innovation across a wide range of styles, from swing to rock, from R&B to electronic music. Jazz’s enduring legacy as a genre that fosters individual expression and musical exploration ensures that its influence will continue to shape and inspire new generations of musicians and genres for years to come.
Notable Jazz Musicians
Jazz music has been home to countless talented and influential musicians throughout its history. These artists have pushed the boundaries of the genre, created groundbreaking compositions, and redefined what it means to be a jazz musician. Here are just a few notable jazz musicians who have left an indelible mark on the genre:
1. Louis Armstrong: Known as the “Father of Jazz,” Louis Armstrong is one of the most influential figures in jazz history. His innovative trumpet playing, charismatic stage presence, and distinctive vocal style set the standard for jazz musicians. Armstrong’s recordings, such as “West End Blues” and “What a Wonderful World,” continue to inspire and move audiences.
2. Duke Ellington: As a composer, pianist, and bandleader, Duke Ellington was a true jazz visionary. His big band compositions, such as “Take the A Train” and “Mood Indigo,” showcased his unique blend of sophisticated harmonies, memorable melodies, and lush orchestrations. Ellington’s contributions to jazz earned him the title of “America’s Composer.”
3. Charlie Parker: Known as “Bird,” Charlie Parker was one of the key architects of the bebop movement. His virtuosic saxophone playing, innovative harmonic approach, and complex improvisations revolutionized jazz. Parker’s compositions, including “Now’s the Time” and “Confirmation,” continue to be studied and performed by aspiring jazz musicians.
4. Ella Fitzgerald: Dubbed the “First Lady of Song,” Ella Fitzgerald’s velvety voice and extraordinary vocal range made her one of the greatest jazz singers of all time. Her remarkable interpretations and scat singing ability, showcased in iconic recordings like “Mack the Knife” and “A-Tisket, A-Tasket,” solidified her place in jazz history.
5. Miles Davis: Miles Davis was a visionary trumpeter, bandleader, and composer who constantly pushed the boundaries of jazz. A pioneer of cool jazz, modal jazz, and jazz fusion, Davis’ albums, including “Kind of Blue” and “Bitches Brew,” remain among the most influential and best-selling jazz recordings of all time.
6. John Coltrane: Revered for his technical prowess and groundbreaking improvisations, John Coltrane expanded the possibilities of the saxophone in jazz. His exploratory albums, such as “Giant Steps” and “A Love Supreme,” pushed the boundaries of harmonic complexity and spiritual expression in jazz.
7. Billie Holiday: With her hauntingly emotive voice and unique phrasing, Billie Holiday remains one of the greatest jazz vocalists in history. Her interpretations of songs like “Strange Fruit” and “God Bless the Child” convey raw emotion and vulnerability, making her an enduring icon of the genre.
These are just a few of the many notable jazz musicians who have made significant contributions to the genre. Their innovation, musical genius, and artistic vision have shaped the course of jazz music and continue to inspire generations of musicians.
Jazz Music in Popular Culture
Jazz music has made a significant impact on popular culture, transcending its roots as a niche genre and becoming a recognizable and influential force in various forms of media. From film soundtracks to television shows, advertisements to video games, jazz has left its mark on the cultural fabric of society.
One of the most prominent mediums through which jazz has infiltrated popular culture is film. The mesmerizing scores and soundtracks of classic films, such as “Casablanca” and “Anatomy of a Murder,” have highlighted the emotional depth and sophistication of jazz music. Jazz’s ability to evoke a wide range of moods, from melancholy to exuberance, makes it a natural fit for visual storytelling.
Television shows have also embraced jazz music as part of their soundtracks. From crime dramas like “Mad Men” and “Twin Peaks” to animated series like “Family Guy” and “The Simpsons,” jazz is often used to set the tone and create a specific atmosphere. Its smooth melodies, lush harmonies, and improvisational nature can add authenticity and an air of sophistication to any scene.
Jazz has also been utilized in the world of advertising. Brands have recognized the evocative and timeless nature of jazz music, using it in commercials to create a sense of nostalgia, class, and style. Whether it’s a luxury car advertisement or a high-end fashion campaign, jazz is often the music of choice to convey elegance and sophistication.
Furthermore, jazz has found its way into the realm of video games. Many game soundtracks incorporate jazz elements to enhance the immersive experience and set the tone for certain scenes or levels. Games such as “Bioshock,” “Fallout,” and “Civilization” feature jazz-inspired soundscapes that transport players to a different era and add depth to the overall gaming experience.
Outside of the entertainment industry, jazz festivals around the world celebrate the genre’s rich history and continuing influence. These festivals attract music lovers of all ages, showcasing talented jazz musicians from both established and emerging artists. They serve as a platform to keep the jazz tradition alive and introduce new generations to the ever-evolving sounds of the genre.
Jazz’s influence also extends to fashion, art, and design. The aesthetics of the jazz era, with its sleek suits, vibrant posters, and bold typography, have become iconic in their own right. From album covers to concert posters, the visual representation of jazz has been as influential as the music itself, leaving a lasting impact on art and design.
All of these instances exemplify how jazz music has permeated popular culture in various forms. Its expressive nature, historical significance, and timeless appeal have made it a versatile and enduring art form that continues to captivate and inspire audiences around the world.
The Future of Jazz Music
The future of jazz music holds great promise as the genre continues to evolve and adapt to the changing musical landscape. While deeply rooted in tradition, jazz has always been a genre that embraces innovation and draws inspiration from different musical styles.
One aspect that shapes the future of jazz is the exploration of new sonic possibilities and technological advancements. Jazz musicians are incorporating electronic instruments, digital effects, and production techniques into their compositions, expanding the sonic palette of the genre. This fusion of jazz with contemporary technology opens up new avenues for creativity and experimentation.
The influence of other genres, such as hip-hop, R&B, and electronic music, continues to permeate jazz. Artists like Robert Glasper and Kamasi Washington have successfully blended jazz with these genres, attracting a new generation of listeners. This cross-pollination of styles keeps jazz relevant and ensures its continued growth and popularity.
Furthermore, the diversification of voices and perspectives within the jazz community is shaping the future of the genre. Women and artists from diverse backgrounds are making significant contributions to jazz, challenging conventions and expanding the boundaries of the genre. This inclusivity is vital in keeping jazz vibrant and reflective of the evolving society it exists within.
The future of jazz also lies in the hands of emerging musicians who are pushing the boundaries and redefining what jazz can be. These artists bring fresh ideas, cultural influences, and unique approaches to the genre. Whether it’s through incorporating elements of their own heritage or exploring new ways to blend genres, these musicians are shaping the future of jazz.
Education and mentorship play a crucial role in preserving and advancing jazz music. Institutions, festivals, and programs dedicated to jazz education create opportunities for young musicians to learn and collaborate. These platforms foster the growth of new talent and ensure the continuation of the jazz tradition.
Moreover, the accessibility of jazz through digital platforms and streaming services enables a wider audience to discover and appreciate the genre. Online communities and social media provide platforms for jazz musicians to connect, collaborate, and promote their work. This connectivity strengthens the jazz community and fosters a sense of global creativity and collaboration.
The future of jazz music is bright, with its ability to adapt, innovate, and inspire. As long as there are musicians who are passionate about expanding the boundaries of the genre and audiences who are receptive to new sounds, jazz will continue to evolve and captivate listeners across the globe.
Conclusion
Jazz music is a timeless and dynamic genre that has left an indelible mark on the music landscape. Its rich history, distinct characteristics, and innovative spirit have shaped the course of music and influenced countless other genres. From its origins in the African-American communities of New Orleans to its global reach today, jazz continues to captivate audiences with its vibrant rhythms, intricate melodies, and vast improvisational possibilities.
The influence of jazz can be seen and heard across various forms of media, from film soundtracks to television shows, advertisements to video games. Its evocative and sophisticated sound has become synonymous with elegance and artistic expression.
The future of jazz holds great promise as the genre continues to evolve and adapt to the changing musical landscape. Artists are exploring new sonic territories, incorporating technology, and drawing inspiration from other genres. The diversification of voices within the jazz community ensures its relevance and vitality in reflecting the society it exists within. Jazz education and mentorship programs play a vital role in preserving the legacy and nurturing the next generation of talented musicians.
As jazz music continues to inspire and push the boundaries of creativity, it remains a beloved art form that transcends cultural boundaries and resonates with listeners across the globe. Its ability to evoke a range of emotions, encourage artistic exploration, and provide a platform for individual expression sets it apart as a truly unique and influential genre.
Join us on this musical journey as we celebrate the legacy, diversity, and future of jazz music. From the early roots of New Orleans jazz to the innovative sounds of contemporary jazz, let us embrace the beauty and power of this timeless genre.