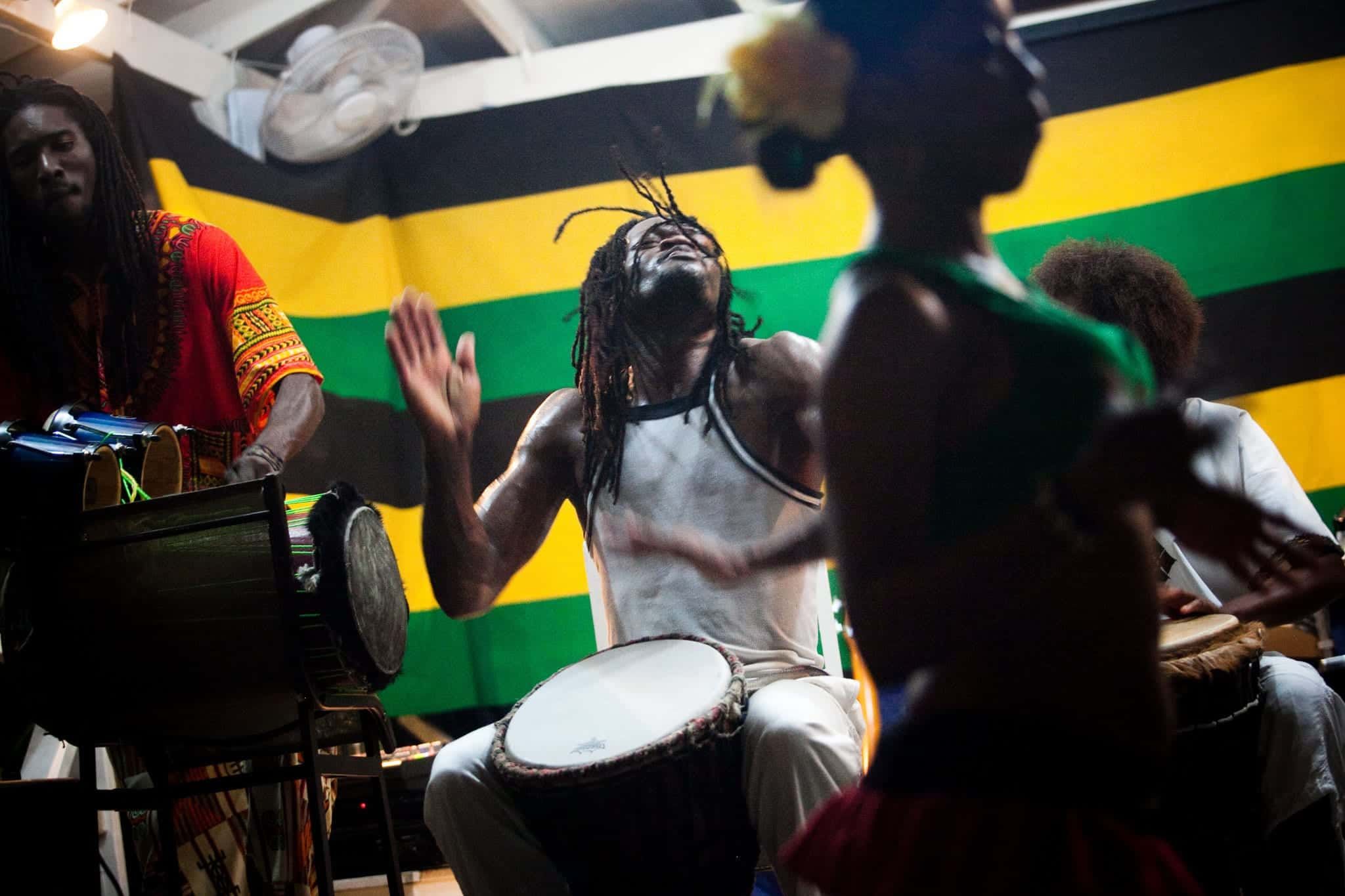
Reggae
What Are The Roots Of Reggae Music
Modified: February 15, 2024
Discover the roots and history of reggae music, its influences and iconic artists. Explore the genre's evolution and impact on popular culture.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Origins of Reggae Music
- Influences from Jamaican Folk Music
- Rastafarianism and Its Impact on Reggae
- The Role of Ska and Rocksteady in Reggae’s Development
- The Influence of African and Caribbean Musical Styles
- The Evolution of Reggae as a Global Genre
- The Social and Political Message of Reggae Music
- Reggae’s Influence on Other Music Genres
- Conclusion
Introduction
Reggae music, with its infectious rhythms and uplifting messages, has captivated audiences around the world for decades. Originating in Jamaica in the late 1960s, this genre of music has become synonymous with the island’s vibrant cultural heritage and has left an indelible mark on the global music scene.
Rooted in a rich tapestry of influences, reggae music embodies the spirit of Jamaica, reflecting the struggles and resilience of its people. It has evolved from the amalgamation of various musical styles, such as Jamaican folk music, ska, rocksteady, and African and Caribbean rhythms, to create a unique sound that is instantly recognizable.
At its core, reggae music carries a powerful social and political message, championing themes of unity, love, and resistance against oppression. It has served as a voice for the marginalized, addressing issues of poverty, racial inequality, and injustice. Through its lyrics and infectious grooves, reggae has touched the hearts and souls of millions, resonating with people from all walks of life.
In this article, we will delve into the roots of reggae music, tracing its origins and exploring its influences. We will examine the role of Jamaican folk music, the impact of Rastafarianism, the evolution of ska and rocksteady, and the influence of African and Caribbean musical styles. Furthermore, we’ll discuss reggae’s global expansion and its cross-pollination with other music genres. Lastly, we’ll explore the enduring social and political messages that continue to define reggae music today.
Join us on a journey through the history of reggae as we unravel the layers of this vibrant and captivating musical genre.
The Origins of Reggae Music
Reggae music emerged in Jamaica during the late 1960s, evolving from earlier Jamaican musical styles such as mento, calypso, and ska. Its distinctive sound can be attributed to a combination of influences from various sources, ultimately creating a genre that is both unique and deeply rooted in Jamaican culture.
Jamaican folk music played a significant role in the development of reggae. This traditional music, passed down through generations, incorporated elements of African rhythms and storytelling. It provided the foundation for the rhythmic patterns and lyrical themes that would later define reggae music.
Another pivotal factor in the origins of reggae was the rise of Rastafarianism, a religious and social movement that emerged in Jamaica in the early 20th century. Rastafarianism influenced not only the lyrics and spirituality of reggae but also its distinct vocal style and overall vibe. Reggae artists such as Bob Marley, Peter Tosh, and Burning Spear became ambassadors of Rastafarianism, spreading its ideology through their music.
Ska and rocksteady, two popular genres that preceded reggae, also played a vital role in its evolution. Ska, which originated in the 1950s, featured upbeat rhythms, catchy melodies, and a strong emphasis on the off-beat rhythm guitar. As ska evolved into rocksteady in the mid-1960s, the tempo slowed down, and the bassline became more prominent, laying the foundation for the characteristic bass-driven groove of reggae.
The influence of African and Caribbean musical styles further enriched the sound of reggae. African drumming and percussion techniques infused reggae with a hypnotic rhythm that encouraged listeners to immerse themselves in the music’s infectious groove. Caribbean musical styles such as calypso and soca brought a joyful and celebratory element to reggae, adding to its diverse musical tapestry.
With its rich blend of Jamaican folk music, Rastafarianism, ska, rocksteady, and African and Caribbean rhythms, reggae music emerged as a genre that encapsulated the spirit and struggles of the Jamaican people. It provided a platform for self-expression, cultural pride, and social commentary, giving a voice to the marginalized and oppressed.
In the next sections, we’ll explore how reggae music continued to evolve and expand beyond the shores of Jamaica, leaving an indelible mark on the global music landscape.
Influences from Jamaican Folk Music
Jamaican folk music played a pivotal role in the development of reggae music, shaping its rhythms, melodies, and lyrical themes. Rooted in the cultural traditions of Jamaica, folk music provided the foundation upon which reggae would later flourish.
Jamaican folk music, also known as “mento,” is deeply rooted in African musical traditions brought to the island during the era of slavery. It is characterized by lively rhythms, catchy melodies, and storytelling through song. The use of African musical instruments, such as the banjo and the marimba, gives mento its distinct sound.
The rhythmic patterns found in Jamaican folk music greatly influenced reggae. The syncopated beats and polyrhythms of mento provided the basis for reggae’s groove, creating a compelling and infectious rhythm that instantly resonated with listeners. Reggae’s characteristic “one-drop” rhythm, characterized by emphasizing the third beat of each bar, can be traced back to the rhythmic patterns of Jamaican folk music.
Lyrically, Jamaican folk music encompassed a wide range of themes, often reflecting the struggles and aspirations of the Jamaican people. These themes would later become central to reggae’s socially conscious lyrics. Mento songs addressed topics such as poverty, social inequality, and the desire for freedom and empowerment. Reggae artists, drawing inspiration from this tradition, continued to use their music as a platform to address these issues and advocate for social change.
Jamaican folk music’s influence on reggae can also be seen in the use of call-and-response patterns in vocals. This interactive style of singing, where a lead vocalist is followed by a chorus of voices, had its roots in African musical traditions. It adds a dynamic and participatory element to reggae performances, creating a sense of unity and collective spirit among both artists and audiences.
Furthermore, the storytelling aspect of Jamaican folk music is also prevalent in reggae. Through their lyrics, reggae artists tell stories of struggle, resilience, love, and social commentary. These narratives not only entertain but also serve as a mirror to society, shining a light on the realities and challenges faced by the Jamaican people.
Overall, the influences of Jamaican folk music on reggae are undeniable. From its rhythmic patterns to its lyrical themes, reggae owes much of its identity to the rich heritage of Jamaican folk music. This influence continues to resonate in reggae music today, reminding us of the deep connection between the past and the present in Jamaica’s musical landscape.
Rastafarianism and Its Impact on Reggae
Rastafarianism, a religious and social movement that originated in Jamaica in the early 20th century, played a profound role in shaping the identity and message of reggae music. The principles and beliefs of Rastafarianism strongly influenced reggae artists, lyrics, and the overall spirit of the genre.
Rastafarianism emerged as a response to the oppressive social and economic conditions faced by black Jamaicans, promoting a message of self-empowerment, African identity, and spiritual awakening. The movement drew inspiration from the philosophy of Marcus Garvey, a Jamaican activist advocating for black pride and liberation.
Reggae artists, such as Bob Marley, Peter Tosh, and Burning Spear, became iconic symbols of Rastafarianism and used their music as a platform to spread the movement’s ideology. With their signature dreadlocks, red, gold, and green symbolism, and spiritually charged lyrics, these artists brought Rastafarianism to the forefront of popular culture and revolutionized the reggae music scene.
Rastafarian beliefs heavily influenced reggae lyrics, infusing them with themes of spirituality, social justice, and cultural pride. The lyrics often reference biblical stories and teachings, emphasizing the connection between black people and their African roots. Songs like Bob Marley’s “Redemption Song” and Peter Tosh’s “Equal Rights” embody the Rastafarian principles of liberation and equality, rallying against the oppressions faced by marginalized communities.
Rastafarianism also influenced the vocal style and delivery of reggae artists. The distinctively soulful and emotive singing style, characterized by its melodic improvisation and powerful vocal expressions, drew inspiration from the chants and hymns of Rastafarian ceremonies. This style of singing added a spiritual depth and authenticity to reggae music.
Moreover, Rastafarianism’s reverence for nature and the natural world is reflected in reggae’s laid-back and organic sound. The use of acoustic instruments, such as the guitar and the drums, combined with the incorporation of natural sounds like birdcalls and ocean waves, creates a sense of serenity and connection to the earth.
Through its promotion of African identity, spiritual awakening, and advocacy for social justice, Rastafarianism had a transformative impact on the development of reggae music. It provided reggae artists with a powerful platform to address the struggles and aspirations of the Jamaican people, and to inspire audiences around the world.
In summary, Rastafarianism’s influence on reggae music cannot be overstated. It shaped not only the lyrical content of reggae songs but also the overall ethos and spirit of the genre. The combination of Rastafarian beliefs, powerful storytelling, and captivating melodies created a musical movement that resonates with listeners on a deep level.
The Role of Ska and Rocksteady in Reggae’s Development
Ska and rocksteady, two Jamaican music genres that preceded reggae, played a crucial role in the evolution and development of reggae music. These genres laid the foundation for the distinctive sound and rhythm that would come to define reggae’s infectious groove.
Ska emerged in Jamaica in the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was a vibrant and energetic musical style characterized by its fast tempo, upbeat rhythms, and lively horn sections. Ska’s catchy melodies and infectious beats captured the imagination of the Jamaican youth and became the soundtrack of the burgeoning independence movement in Jamaica.
Ska’s influence can be heard in later reggae music through its distinctive off-beat rhythm guitar, known as the “skank.” This guitar technique, playing chords on the upbeats, creates a rhythmic pattern that encourages dancing and adds an irresistible bounce to the music. The skank became a staple of reggae music and contributed to its infectious and unmistakable sound.
Rocksteady, which emerged in the mid-1960s, was a slower and smoother evolution of ska. It featured a more laid-back tempo, emphasized the bassline, and introduced new elements like the Hammond organ. With its soulful vocals and romantic lyrics, rocksteady became popular in the dancehalls of Jamaica.
Rocksteady’s influence on reggae is evident in the evolution of the rhythm section. The slower tempo allowed for greater emphasis on the bassline, creating a deep and pulsating groove that became a defining characteristic of reggae music. The bassline took on a more melodic role, complementing the vocal melodies and providing a solid foundation for the music.
Both ska and rocksteady provided a platform for talented Jamaican artists to showcase their skills and creativity. Legendary musicians like Toots and the Maytals, The Skatalites, Desmond Dekker, and Alton Ellis emerged during this period and made significant contributions to the Jamaican music scene.
Reggae, which emerged out of rocksteady in the late 1960s, built upon the foundations laid by ska and rocksteady. It adopted the off-beat skank guitar rhythm and the deep basslines while infusing its own unique elements. Reggae slowed down the tempo even further, creating a more relaxed and laid-back feel that allowed space for the deep and thought-provoking lyrics to shine.
Without the influence of ska and rocksteady, reggae music would not have its characteristic groove and rhythmic patterns that have captivated audiences around the world. The vibrancy and energy of ska and the soulful smoothness of rocksteady paved the way for reggae’s emergence as a distinct and powerful musical genre.
In summary, ska and rocksteady played a fundamental role in the development of reggae music. They provided the musical and rhythmic building blocks upon which reggae would build its own unique sound. The influence of ska and rocksteady can be heard in reggae’s infectious groove, its distinct guitar skank, and the prominent role of the bassline. These genres laid the groundwork for the success and global popularity of reggae music.
The Influence of African and Caribbean Musical Styles
Reggae music, with its rich and diverse sound, owes a great debt to the influence of African and Caribbean musical styles. These musical traditions brought their own unique rhythms, melodies, and instrumentation, which seamlessly blended with the Jamaican music scene to create the distinct sound of reggae.
The African roots of reggae can be heard in the hypnotic drumming and percussion techniques that infuse the music with a powerful rhythmic drive. African music is known for its polyrhythms and syncopated beats, and reggae embraced these elements, using them to create layered and infectious grooves. The steady heartbeat of the drums, the pulsating basslines, and the intricate interplay between the instruments all reflect the influence of African musical styles.
In addition to African influences, reggae music incorporates various elements from Caribbean musical traditions. Jamaican mento, a form of folk music, had roots in African and Caribbean rhythms and melodies. The catchy and lively spirit of mento served as a foundation for reggae’s rhythmic patterns and melodic sensibilities.
Furthermore, the calypso and soca music styles of the neighboring Caribbean islands also played a significant role in shaping reggae. Calypso, with its vibrant melodies and catchy hooks, brought a joyful and celebratory element to reggae. This influence can be heard in reggae’s versatile vocal melodies and the sheer exuberance that radiates from many reggae songs. Soca, born out of calypso, added a contemporary and energetic flavor to reggae, infusing it with a danceable and infectious energy.
Caribbean musical styles, including reggae’s close relative, ska, also contributed to the development of reggae. Ska, with its up-tempo rhythm and brass section, introduced a lively and upbeat energy that influenced reggae’s instrumentation and overall sound. The horn-driven melodies and the emphasis on the off-beat rhythm guitar, which define ska, can still be heard in reggae music to this day.
Overall, the influence of African and Caribbean musical styles on reggae cannot be overstated. These rich and diverse traditions provided reggae with its rhythmic foundation, melodic sensibilities, and overall vibrancy. The blending of African rhythms, Caribbean melodies, and Jamaican cultural expressions resulted in a genre that is both deeply rooted in its origins and globally resonant.
Reggae’s ability to seamlessly incorporate these musical influences is a testament to the power of music as a universal language, bridging cultural divides and connecting people across continents. It is this cross-pollination of musical styles that has made reggae a truly global phenomenon, spreading positive vibrations and inspiring people worldwide.
The Evolution of Reggae as a Global Genre
Reggae music, born out of the vibrant cultural landscape of Jamaica, has transcended its origins to become a powerful and influential global genre. From its humble beginnings in the 1960s, reggae has made its way onto the international stage, captivating hearts and minds around the world.
The global rise of reggae can be attributed to the immense talent and vision of Jamaican artists who brought the genre to the forefront. Artists like Bob Marley, Peter Tosh, Jimmy Cliff, and Burning Spear became iconic figures, their music resonating with people from all walks of life, transcending cultural and language barriers.
The breakthrough of reggae on the global stage can be traced back to the 1970s, with Bob Marley emerging as a symbol of the genre. Marley’s timeless hits, such as “One Love,” “No Woman, No Cry,” and “Redemption Song,” carried messages of peace, love, and social change, propelling reggae to new heights and capturing the hearts of listeners worldwide.
Reggae’s popularity outside of Jamaica was also fueled by the emergence of the reggae sound systems, which took the music to communities across the globe. These mobile sound systems, with their powerful speakers and DJs spinning reggae records, played a crucial role in spreading the infectious beats and positive messages of reggae music to diverse audiences.
As reggae gained popularity, artists from different countries began incorporating elements of the genre into their own music, leading to a fusion of styles and an expansion of the reggae sound. This cross-pollination allowed reggae to adapt and evolve, giving rise to subgenres like reggae fusion, reggae rock, and reggae pop.
In addition to the music itself, the imagery and symbolism associated with reggae also played a significant role in its global appeal. The iconic colors of red, gold, and green, the imagery of the Rastafarian flag, and the unmistakable sight of dreadlocked artists became synonymous with reggae and its message of unity, love, and cultural pride.
Reggae festivals and events sprouted up across the globe, showcasing local and international reggae artists and further solidifying the genre’s global reach. Festivals like Reggae Sunsplash in Jamaica, Rototom Sunsplash in Spain, and Sumfest in Montego Bay became annual gatherings for reggae enthusiasts, providing a platform for artists to showcase their talent and for fans to immerse themselves in the reggae experience.
Today, reggae continues to resonate with audiences worldwide, imbuing them with a sense of positivity, spirituality, and social consciousness. It serves as a unifying force, connecting people from different cultures, backgrounds, and languages through its universal message of love and equality.
The evolution of reggae as a global genre is a testament to the power of music to transcend boundaries and bring people together. Its influence can be felt in various music genres, from pop to hip-hop, with artists incorporating reggae elements into their own sound.
As reggae continues to evolve and adapt, its global impact remains unwavering, spreading messages of unity, justice, and the celebration of life. Reggae’s journey from the shores of Jamaica to the world stage is a testament to its enduring power and the universal appeal of its infectious rhythms and profound messages.
The Social and Political Message of Reggae Music
Reggae music has always been synonymous with social and political commentary, using its powerful lyrics and infectious rhythms to address a wide range of issues. From its earliest days, reggae artists have used their music as a platform to speak out against injustice, inequality, and oppression, making it a powerful tool for social change.
One of the defining characteristics of reggae is its ability to communicate deeply profound messages in a way that is accessible to all. Through lyrics that are often poetic and metaphorical, reggae artists shed light on the social and political realities faced by marginalized communities, inspiring listeners to question the status quo and work towards a better world.
Reggae music champions themes of unity, love, and equality. It emphasizes the importance of coming together as a global community, transcending racial, religious, and cultural boundaries. Songs like Bob Marley’s “One Love” and Burning Spear’s “Slavery Days” promote the idea of unity and advocate for a world where all people can live free from oppression and discrimination.
Reggae’s social and political messages often focus on issues such as poverty, social inequality, and systemic injustice. Artists such as Peter Tosh, known for his powerful activism, used their music to challenge authority, advocate for equal rights, and condemn the exploitation of the poor and marginalized.
Furthermore, reggae is closely linked to the Rastafarian movement, which promotes spiritual awakening and empowerment. Rastafarian beliefs, influenced by Marcus Garvey’s philosophy, advocate for black pride, self-determination, and the repatriation of African diaspora. Rastafarian-inspired reggae songs like Bob Marley’s “Redemption Song” and Peter Tosh’s “Equal Rights” are potent anthems that resonate with those fighting against racial inequality and seeking justice.
Reggae’s social and political messaging extends beyond Jamaica, impacting listeners around the world. The genre has been embraced by oppressed and marginalized communities globally as a source of hope and inspiration. It has become a soundtrack for various social justice movements, including the fight against apartheid in South Africa and the struggle for civil rights in the United States.
Reggae’s ability to blend its socially conscious message with infectious rhythms and melodies has allowed it to reach a wide audience, transcending cultural and linguistic differences. Its profound lyrics and captivating sound have become a rallying cry for those seeking social justice and a better world.
Ultimately, reggae music serves as a powerful reminder of the transformative power of art. It brings awareness to social and political issues, provides a voice for the marginalized, and inspires individuals to take action. Reggae’s continuous commitment to addressing these topics and promoting positive change is a testament to its enduring impact on society.
Reggae’s Influence on Other Music Genres
Reggae music’s impact extends far beyond its own genre, as it has influenced and shaped numerous other music genres around the world. Reggae’s distinctive rhythms, smooth melodies, and powerful messages have left an indelible mark on the global music landscape, inspiring artists from various genres to incorporate reggae elements into their own sound.
One genre that has been heavily influenced by reggae is hip-hop. In the 1970s, Jamaican-born DJ Kool Herc brought the Jamaican sound system culture to the Bronx in New York City, laying the foundation for hip-hop’s birth. The DJ’s mixing techniques and use of reggae records became integral to the development of hip-hop, influencing the use of rhythm and beats in rap music. Artists like The Notorious B.I.G., Nas, and Snoop Dogg have incorporated reggae samples and performed in a reggae-style delivery, fusing the two genres into a unique fusion.
Additionally, reggae has made a significant impact on the development of electronic music genres. Dub music, a subgenre of reggae characterized by its emphasis on instrumental versions and heavy use of effects, played a crucial role in the evolution of electronic music. The techniques and production styles used in dub music, such as echo, delay, and reverb, have been incorporated into genres like dubstep, drum and bass, and jungle, giving them a distinct atmospheric and rhythmic quality.
Reggae’s influence can also be heard in pop music. Artists like Sting, UB40, and Jason Mraz have incorporated elements of reggae into their songs, infusing their pop sound with the laid-back rhythms and catchy melodies of reggae. This fusion has broadened the appeal of reggae music, exposing it to new audiences who may not be familiar with the genre in its purest form.
Furthermore, reggae’s influence extends to rock and punk music. Bands like The Clash and Sublime have incorporated reggae elements into their music, creating a sound that combines the energy and aggression of punk with the infectious grooves of reggae. This fusion of genres has brought reggae to alternative rock audiences and helped to expand its reach even further.
Reggae’s influence on other music genres goes beyond its sound. Its socially conscious and politically charged lyrics have inspired artists across various genres to tackle similar themes in their own music. This can be seen in the emergence of protest music that addresses issues of social inequality, racism, and injustice, fueled by the spirit of reggae’s powerful messages.
Ultimately, reggae’s influence on other music genres is a testament to its universal appeal and enduring impact. From hip-hop to electronic music, pop to rock, reggae has left its mark, enriching these genres with its distinctive sound and socially conscious messages. With its infectious rhythms and powerful messages, reggae continues to inspire and influence artists around the world, carrying its positive vibrations to new audiences and generations.
Conclusion
Reggae music, with its roots deeply embedded in Jamaican culture, has evolved into a global phenomenon that resonates with people from all corners of the world. From its origins in the vibrant streets of Jamaica in the 1960s, reggae has transcended boundaries, becoming a voice for the marginalized, an anthem for social justice, and an embodiment of love and unity.
With influences ranging from Jamaican folk music to Rastafarianism, from ska and rocksteady to African and Caribbean rhythms, reggae has developed a sound that is uniquely its own. The infectious grooves, melodic sensibilities, and socially conscious lyrics have captivated audiences, eliciting a profound emotional response and a sense of connection.
Reggae’s impact goes beyond its music, influencing other genres such as hip-hop, electronic music, pop, and rock. Its rhythms, melodies, and messages have found their way into diverse musical styles, creating new fusions and expanding reggae’s reach to audiences who may not have been previously exposed to the genre.
Furthermore, reggae’s influence extends to social and political spheres, empowering listeners to challenge the status quo, advocate for equality, and strive for positive change. Its messages of unity, love, and resistance against oppression continue to inspire generations, touching hearts and sparking movements for social justice around the world.
As reggae continues to evolve, it remains deeply rooted in its Jamaican heritage while embracing the global stage. Its ability to bridge cultural divides, transcend language barriers, and unite people through music is a testament to its enduring power and resonance.
In conclusion, reggae music is a vibrant and dynamic genre that has had a profound impact on the global music landscape. It has brought the rich cultural traditions of Jamaica to the forefront, inspiring and influencing artists from various genres and spreading messages of love, unity, and social change. Reggae’s infectious rhythms, powerful lyrics, and enduring legacy continue to make it a force to be reckoned with, ensuring that its positive vibrations will continue to resonate for generations to come.