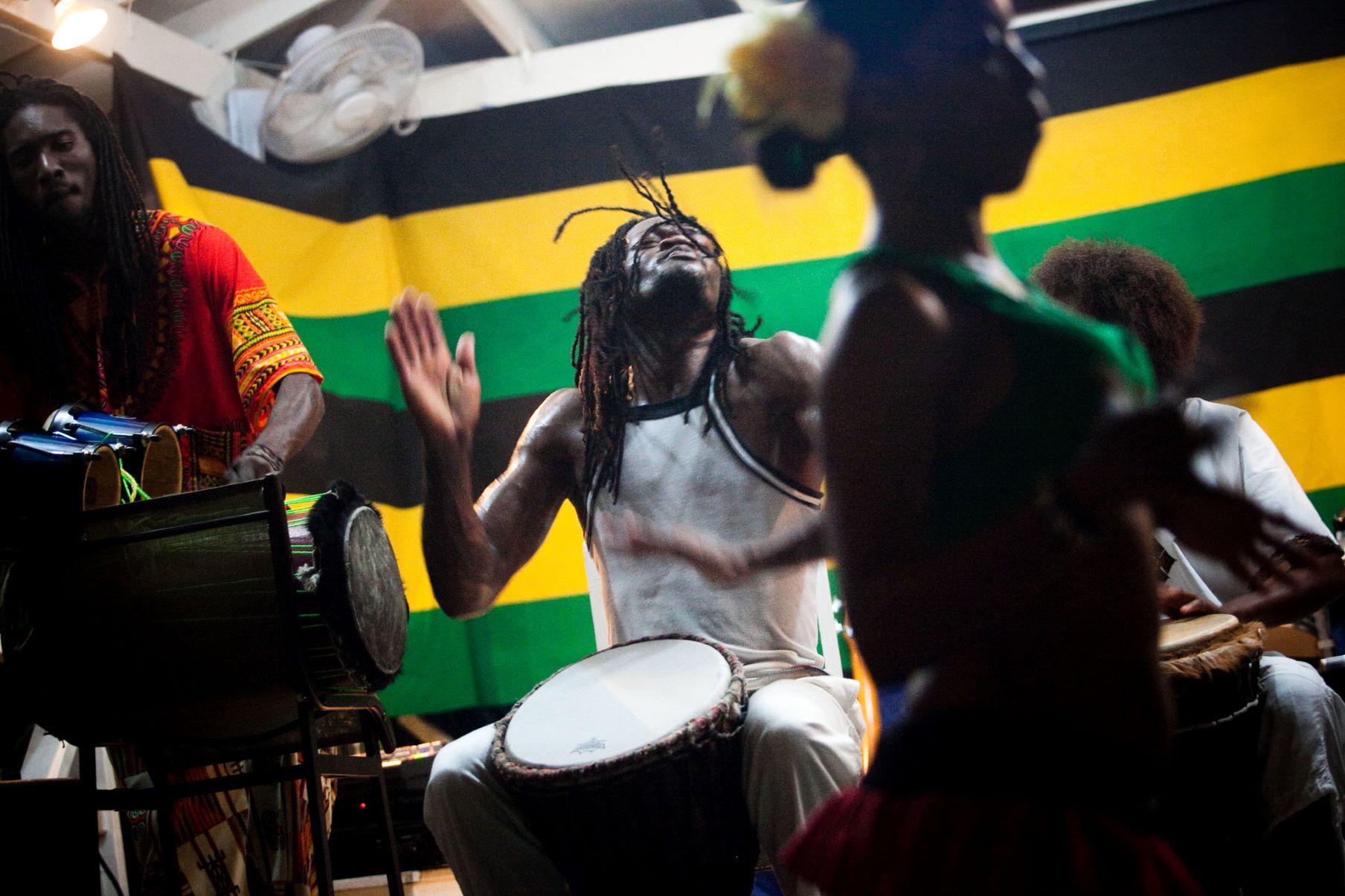Home>Genres>Reggae>What Genre Does The Music Genre Reggae Go Into


Reggae
What Genre Does The Music Genre Reggae Go Into
Modified: March 3, 2024
Discover the genre that Reggae music falls under and explore its unique sound and influences. Learn more about the origins and characteristics of Reggae.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Reggae music is a genre that has captivated audiences worldwide with its infectious rhythms, soulful melodies, and powerful messages. Originating in Jamaica in the late 1960s, reggae quickly gained popularity and became a symbol of cultural identity and social activism. It has since spread its roots globally, influencing various music genres and artists across the globe.
Reggae is more than just a style of music; it represents a way of life, embracing themes of love, unity, and social justice. The unique sound of reggae is characterized by its distinctive offbeat rhythm, often referred to as the “one drop” rhythm, and the prominent use of bass guitar and drums.
Reggae music is deeply rooted in the cultural and historical context of Jamaica. It emerged as a fusion of different music genres, such as ska, rocksteady, and mento, to create a fresh and vibrant sound that reflected the struggles and aspirations of the Jamaican people. It became a powerful form of expression for artists, who used their music to address social issues, advocate for peace and unity, and celebrate their cultural heritage.
Over the years, reggae music has continued to evolve and diversify, giving rise to subgenres such as dancehall, roots reggae, and dub. These subgenres add their own unique elements and flavors to the reggae sound, expanding its reach and appeal to different audiences.
Reggae’s impact on popular music cannot be underestimated. Its influence can be heard in genres ranging from hip-hop to pop, and it has inspired countless artists and musicians around the world. From Bob Marley and Peter Tosh to UB40 and Ziggy Marley, reggae has produced iconic figures who have left an indelible mark on the music industry.
This article delves into the background and characteristics of reggae music, explores its influences on other genres, and examines the debate over its classification within the broader music landscape. Additionally, it explores the various subgenres within reggae and highlights some notable artists and songs that have shaped the genre.
Background of Reggae Music
Reggae music emerged in Jamaica in the late 1960s, evolving from genres such as ska and rocksteady. Its roots can be traced back to the urban music scene in Kingston, where young musicians experimented with blending different musical styles to create a fresh sound that reflected the social and political climate of the time.
One of the key figures in the development of reggae was the legendary musician Bob Marley. Alongside his band, The Wailers, Marley played a pivotal role in popularizing reggae music and bringing it to an international audience. His songs, infused with messages of peace, love, and equality, resonated deeply with listeners around the world.
Reggae’s popularity grew rapidly in the 1970s, becoming synonymous with the Rastafarian movement and its philosophy. The Rastafarian influence is prominent in reggae lyrics, with themes of spirituality, social justice, and African diaspora resonating throughout the music.
At its core, reggae music is driven by a deep sense of rhythm. The rhythmic pattern known as the “one drop” is a key element in reggae, characterized by an emphasis on the third beat of each measure. This distinctive rhythm, combined with the use of syncopation and the pulsating bassline, creates a hypnotic and infectious groove that is instantly recognizable.
Reggae also places a strong emphasis on the bass guitar and drums, which provide the backbone of the music. The bassline, often played using a technique called “stopping,” adds a melodic and rhythmic element to the songs, while the drums create a steady heartbeat that drives the music forward.
In addition to its musical elements, reggae is known for its vocal style. Many reggae artists incorporate elements of call-and-response and improvisation in their performances, allowing for an interactive and dynamic experience with the audience.
Reggae music has always been closely tied to the socio-political climate of Jamaica. In the 1970s, it served as a voice for the marginalized and oppressed, addressing issues such as poverty, inequality, and racial discrimination. Songs like “Get Up, Stand Up” by Bob Marley and “Many Rivers to Cross” by Jimmy Cliff became anthems of resistance and empowerment for generations.
Today, reggae continues to evolve and adapt, incorporating influences from various musical styles such as hip-hop, EDM, and pop. It remains a powerful and influential genre, with its messages of love, unity, and social consciousness continuing to resonate with audiences globally.
Characteristics of Reggae Music
Reggae music is characterized by a unique blend of musical elements that come together to create its distinctive sound. Here are some of the key characteristics that define reggae:
- Offbeat Rhythm: Reggae is known for its offbeat rhythm, often referred to as the “one drop” rhythm. This rhythm emphasizes the third beat of the measure, creating a syncopated and laid-back feel that is instantly recognizable.
- Bassline and Drum Groove: The bass guitar and drums play a crucial role in reggae music. The bassline, often played using a technique called “stopping,” adds a melodic and rhythmic element to the music. The drums provide a steady and pulsating groove that drives the song forward.
- Soulful Melodies: Reggae melodies are soulful and emotive, often delivered with smooth and heartfelt vocals. These melodies create a sense of warmth and connection, adding to the overall emotional impact of the music.
- Lyrics with Social Commentary: Reggae lyrics often address social and political issues, conveying messages of unity, love, and social justice. Many reggae songs are a form of protest against inequality, poverty, and injustice, championing the rights and struggles of the marginalized and oppressed.
- Instrumentation: In addition to the bass guitar and drums, reggae music incorporates a wide range of instruments. These can include guitars, keyboards, horns, percussion, and even traditional Jamaican instruments such as the nyabinghi drums.
- Improvisation and Call-and-Response: Reggae performances often involve elements of improvisation and call-and-response interactions between the lead vocalist and the audience. This creates a sense of participation and engagement, making every performance a unique and memorable experience.
- Dub Effects: Dub, a subgenre of reggae, introduced the use of studio effects and techniques to manipulate the music. These techniques include echoes, delays, reverbs, and the manipulation of individual instrument tracks, resulting in a distinctive and experimental sound.
These characteristics combine to form the foundation of reggae music, creating a sound that is both captivating and uplifting. The rhythm, melodies, and lyrics come together to create a powerful and transformative musical experience that continues to resonate with audiences worldwide.
Influences on Reggae Music
Reggae music is a genre that has been shaped by a diverse range of influences, both musical and cultural. The roots of reggae can be traced back to various music genres and cultural developments that have had a significant impact on its evolution. Here are some of the key influences on reggae music:
- African Rhythms: The rhythms and musical traditions of Africa played a crucial role in shaping reggae music. The African diaspora in Jamaica brought with it a rich and diverse musical heritage that fused with local Jamaican styles to create the foundation for reggae’s rhythmic patterns and grooves.
- Mento: Mento, a traditional Jamaican folk music style, heavily influenced the early development of reggae. Mento’s upbeat and lively rhythms, as well as its use of acoustic instruments like banjos and maracas, can be heard in the early ska and rocksteady rhythms that laid the groundwork for reggae.
- Ska and Rocksteady: Reggae evolved from the popular music styles of ska and rocksteady. Ska music, characterized by its energetic offbeat rhythms, formed the bridge between mento and reggae. Rocksteady followed ska and brought a slower, more soulful sound, with emphasis on the bassline and vocal harmonies.
- American Rhythm and Blues: Jamaican musicians of the 1950s and 1960s were heavily influenced by American rhythm and blues artists such as Fats Domino, Ray Charles, and Sam Cooke. The soulful melodies, vocal techniques, and lyrical themes of these artists found their way into the early reggae sound.
- Political and Social Climate: The political and social climate of Jamaica in the 1960s and 1970s had a profound impact on the development of reggae music. The struggles and aspirations of the Jamaican people, as well as the influence of the Rastafarian movement, infused reggae with a strong sense of social consciousness and empowerment.
- Sound System Culture: Sound system culture, which emerged in Jamaica in the 1950s, played a significant role in the development and dissemination of reggae music. Sound systems were mobile DJ setups that played records at parties and events, and they served as a platform for showcasing new music and influencing the sound of reggae.
- Global Influences: As reggae gained popularity worldwide, it began to incorporate influences from different musical styles. Artists and producers from the United Kingdom, the United States, and other countries added their own flavors to the reggae sound, resulting in diverse subgenres like dancehall, reggae fusion, and lovers rock.
These influences have contributed to the rich and varied nature of reggae music, giving it a global appeal and allowing it to transcend cultural boundaries. The fusion of diverse musical traditions and the incorporation of social and political themes are what make reggae such a powerful and influential genre.
Classification of Reggae within Music Genres
Classifying music into specific genres can often be a subjective and complex task, as genres tend to evolve and overlap over time. Reggae, with its unique blend of musical elements and cultural influences, has sometimes been a subject of debate regarding its classification within the broader spectrum of music genres.
While reggae is commonly recognized as a distinct music genre, it is also considered a subgenre of Jamaican popular music. It emerged from the fusion of various music styles such as ska, rocksteady, and mento, which were prevalent in Jamaica during the 1960s. The incorporation of African rhythms, American Rhythm and Blues, and political themes helped shape reggae into its own identifiable style.
Reggae’s defining characteristics, such as the offbeat rhythm, soulful melodies, and emphasis on bass and drums, set it apart from other music genres. However, reggae has also influenced and been influenced by several other genres, blurring the boundaries and creating hybrid styles.
One notable genre that has been heavily influenced by reggae is dub. Dub music emerged in Jamaica in the late 1960s and early 1970s, featuring remixes of existing reggae tracks with added emphasis on the rhythm section and studio effects. Dub became a genre in its own right, characterized by its experimentation with sound manipulation and spacious, echo-laden production techniques.
Reggae has also influenced the development of other music genres, including dancehall, reggae fusion, and lovers rock. Dancehall, which originated in the late 1970s, blended reggae rhythms with elements of hip-hop, electronic music, and Caribbean influences. Reggae fusion incorporates elements of reggae with genres like pop, rock, and R&B, resulting in a more commercial and mainstream sound.
Lovers rock, on the other hand, is a subgenre of reggae known for its romantic and soulful sound. It became popular in the 1970s in the United Kingdom, particularly among the British-Jamaican community. Lovers rock features smooth melodies and romantic lyrics, focusing on love and relationships.
While reggae has influenced and been influenced by other genres, it still maintains its unique identity as a genre rooted in Jamaican culture and history. Its profound impact on music worldwide and its strong association with social activism and cultural identity set it apart from many other genres.
In the broader classification of music genres, reggae is often categorized under world music or as a subgenre of popular music. However, it is important to acknowledge that reggae’s influence and global reach have made it a significant genre in its own right, with a dedicated following and a distinct musical and cultural legacy.
Ultimately, the classification of reggae within music genres is subjective, and different individuals and experts may have varying opinions. Regardless of its classification, reggae’s enduring popularity and its ability to resonate with people from diverse backgrounds are a testament to its universal appeal and its unique place in the musical landscape.
Debate over Reggae’s Genre Classification
The genre classification of reggae music has been a topic of debate and discussion among music enthusiasts, critics, and scholars. Due to its diverse influences and unique characteristics, reggae’s classification within the broader music landscape has sometimes proven to be a challenge.
One point of contention is whether reggae should be considered a standalone genre or a subgenre of Jamaican popular music. Some argue that reggae is distinct enough in its style, rhythm, and lyrical themes to be classified as a separate genre. They highlight the distinct offbeat rhythm, soulful melodies, and social commentary that define reggae music as its own entity.
Others argue that reggae should be seen primarily as a subgenre of Jamaican music, derived from earlier genres such as ska and rocksteady. They believe that reggae’s roots in these pre-existing styles make it a natural progression and evolution of Jamaican popular music rather than a wholly separate genre.
Additionally, the influence of reggae on other music genres and its ability to adapt and blend with different styles has further fueled the debate. While reggae has undeniably influenced genres like dub, dancehall, and reggae fusion, some argue that these subgenres should be considered distinct from reggae itself. They argue that reggae is the foundation from which these subgenres have emerged, but each subgenre has its own distinct characteristics and evolutionary trajectory.
The cultural and political associations of reggae have also played a role in the debate. Reggae is closely tied to the Rastafarian movement and has often been used as a platform for social activism and cultural expression. The genre’s focus on social justice, spirituality, and African diaspora has led some to argue that reggae should be more broadly classified as a form of world music, highlighting its global significance and transcultural appeal.
Ultimately, the debate over reggae’s genre classification highlights the complex nature of music genres and the difficulty of categorizing a genre that is constantly evolving and influencing other styles. While it can be useful to assign labels and categories to music for the purpose of organization and understanding, it is important to recognize that these classifications are subjective and can vary depending on cultural perspectives and individual interpretations.
Regardless of the debate, reggae’s impact on popular music and its enduring legacy cannot be ignored. Its powerful rhythms, soulful melodies, and socially conscious lyrics have made it a genre that resonates with audiences worldwide. Whether classified as a standalone genre or a subgenre, reggae’s cultural significance and influence on music make it a genre that continues to captivate and inspire listeners across the globe.
Different Subgenres of Reggae
Reggae, as a genre, has given rise to various subgenres that have added their own unique flavors and styles to the music. These subgenres have emerged over time, incorporating influences from different musical genres and cultures. Here are some of the notable subgenres of reggae:
- Dancehall: Dancehall is a subgenre of reggae that emerged in the late 1970s and early 1980s. It is characterized by its faster tempo, electronic sounds, and often explicit lyrical content. Dancehall puts more emphasis on the DJ or “toaster,” who delivers rhythmic and catchy verses over looping beats.
- Roots Reggae: Roots reggae is the foundation of reggae music. It emerged in the 1970s and is characterized by its conscious lyrics, uplifting messages, and spiritual themes. Roots reggae often addresses social issues and promotes cultural and political awareness.
- Dub: Dub is a subgenre of reggae that developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s. It focuses on instrumental versions of reggae tracks, with heavy use of effects such as echoes, reverbs, and delays. Dub emphasizes the role of the producer, who manipulates tracks and creates sonic landscapes.
- Lovers Rock: Lovers rock originated in the 1970s in the United Kingdom. It is a romantic and smooth subgenre of reggae that focuses on love, relationships, and emotional connections. Lovers rock often features melodic harmonies and soulful vocals.
- Nyabinghi: Nyabinghi is a spiritual and ceremonial style of reggae that is deeply rooted in the Rastafarian faith. It incorporates traditional African drumming patterns, chants, and hymns. Nyabinghi music is often associated with Rastafarian gatherings and is considered sacred by adherents.
- Reggae Fusion: Reggae fusion incorporates elements of reggae with other musical styles such as pop, rock, hip-hop, and electronic music. It often features collaborations with artists from different genres, resulting in a fusion of sounds and influences.
- Rockers: Rockers is a subgenre of reggae that emerged in the 1970s. It is characterized by its heavy basslines, driving rhythms, and guitar-driven sound. Rockers often addresses socio-political issues and showcases the instrumental prowess of the musicians.
These subgenres within reggae reflect the versatility and adaptability of the genre. Each subgenre brings its own unique elements, allowing reggae to continuously evolve and resonate with diverse audiences. These subgenres have expanded the musical landscape of reggae, showcasing its ability to blend with other genres and create new sounds.
Artists such as Chronixx, Buju Banton, Sean Paul, and Shaggy have contributed to the popularity of reggae and its subgenres, pushing the boundaries and reaching new audiences around the world. The influence of these subgenres can be seen in contemporary reggae and the broader music scene, demonstrating the ongoing relevance and impact of reggae music.
Conclusion
Reggae music, with its infectious rhythms, soulful melodies, and powerful messages, has become a globally recognized and beloved genre. Its roots in Jamaica, the fusion of various musical styles, and its ability to address social issues have made reggae a powerful form of cultural expression.
Throughout its history, reggae has continuously evolved and diversified, giving rise to subgenres like dancehall, dub, lovers rock, and reggae fusion. Each subgenre brings its own unique elements and influences, expanding the reach and appeal of reggae to different audiences around the world.
While there may be debate over the genre classification of reggae, its distinctive characteristics, cultural significance, and influential presence within the music industry cannot be denied. Reggae has made an indelible mark on popular music, influencing artists across various genres and captivating listeners with its infectious rhythms, soulful melodies, and socially conscious lyrics.
From its roots in African rhythms and Jamaican folk music to its global impact and fusion with other genres, reggae has proven to be a genre that transcends cultural boundaries. Its messages of love, unity, social justice, and spirituality have resonated with people from all walks of life, making it a powerful force for positive change and cultural unity.
In conclusion, reggae music stands as a testament to the power of music as a form of expression, connection, and social activism. Its legacy continues to thrive, with new artists and subgenres pushing the boundaries of the genre and spreading its influence to new frontiers. Whether it is Bob Marley’s iconic anthems or the infectious beats of dancehall, reggae’s impact and influence will continue to be felt for generations to come.