Home>Instruments>Bass>Amp Shuts Off When Bass Hits


Bass
Amp Shuts Off When Bass Hits
Published: November 27, 2023
Experiencing amp shut offs when bass hits? Find out how to solve this common issue and enjoy uninterrupted bass with these helpful tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Causes of Amp Shutting Off
- Common Problems with Amps
- Troubleshooting Steps
- Checking Power Source
- Inspecting Speaker Connections
- Verifying Grounding Issues
- Examining Amplifier Settings
- Assessing Speaker Specifications
- Evaluating Speaker Impedance
- Analyzing Bass Boost Settings
- Preventive Measures
- Conclusion
Introduction
Have you ever experienced the frustration of your amp shutting off unexpectedly when the bass hits? It can be a buzzkill for any music enthusiast or DJ trying to groove to their favorite beats. This issue not only interrupts your listening experience but also raises concerns about potential damage to your amplifier and speakers.
Understanding the causes behind an amp shutting off when the bass hits is essential for troubleshooting and resolving the problem effectively. In this article, we will explore the common issues that can lead to this frustrating occurrence and provide some troubleshooting steps to help you rectify the situation.
Before we delve into the causes and solutions, it’s important to note that amplifiers vary in their design, specifications, and features. Thus, the troubleshooting steps provided here may not apply to every specific amplifier model. Nevertheless, they offer a starting point for troubleshooting and may guide you toward resolving the issue.
So, let’s dive into this bass-filled journey and find out why your amp might be shutting off when the bass hits!
Causes of Amp Shutting Off
There are several potential causes for an amp shutting off when the bass hits. Understanding these causes can help you narrow down the issue and find an appropriate solution. Here are some common culprits:
- Power overload: One of the primary causes of an amp shutting off is a power overload. When the bass hits hard, it can draw a significant amount of power, overwhelming the amplifier’s capacity. This overload triggers the amp’s protective circuitry, causing it to shut off to prevent damage.
- Overheating: Amplifiers generate heat during operation, and excessive heat can cause them to shut down. When you crank up the bass, it increases the workload on the amplifier, leading to higher temperatures. If the amplifier’s cooling system is inadequate or if it is placed in a confined space, it can easily overheat and shut off.
- Short circuits: A short circuit in the speaker wires or the amp’s internal components can cause the amplifier to shut off. When the bass hits, it can create a momentary surge of electricity that triggers a protection mechanism, cutting off power to prevent further damage.
- Speaker impedance mismatch: Impedance mismatch occurs when the speaker’s impedance rating does not match the amplifier’s output impedance capability. This mismatch can cause excessive current flow, forcing the amplifier to shut down to protect itself.
- Grounding issues: Poor grounding can lead to various problems, including amp shut off. When the bass hits, it can create electrical noise or interference, which disrupts the amplifier’s performance and may cause it to shut off.
- Safety features: Some amplifiers have built-in safety features that automatically shut off the power when they detect certain irregularities, such as excessive distortion or voltage fluctuations. These features are designed to protect the amp from potential damage and prevent it from operating in suboptimal conditions.
It’s worth noting that these causes can overlap, and multiple factors may contribute to an amp shutting off when the bass hits. In the next section, we will discuss some troubleshooting steps to help you pinpoint and resolve the issue.
Common Problems with Amps
Amplifiers are complex electronic devices, and they can encounter various issues that can lead to them shutting off when the bass hits. Understanding these common problems can help you identify the underlying cause and take appropriate measures to resolve them. Here are a few frequently encountered problems with amps:
- Insufficient power supply: Inadequate power supply is a notorious issue that can cause an amp to shut off. If the power source is unable to provide sufficient electrical current, especially when the bass hits, the amplifier may not receive the necessary power to operate effectively, leading to a shutdown.
- Faulty wiring or connections: Loose or damaged wiring and connections can disrupt the flow of electrical signals and cause the amp to shut off. When the bass hits, the amplifier demands a significant amount of power, and any issues with the wiring or connections can interrupt the signal flow and trigger a shutdown.
- Overheating: Amplifiers generate heat during operation, and if they are unable to dissipate it properly, they can overheat and shut down. This often occurs when the amp is pushed to its limits due to intense bass levels, insufficient ventilation, or improper placement.
- Clipping and distortion: Clipping occurs when the amplifier is pushed beyond its maximum output capability, resulting in distorted sound. Excessive bass levels can easily cause clipping, leading to a shutdown as the amplifier’s protection circuitry kicks in to prevent damage to the speakers.
- Grounding issues: Poor grounding can introduce electrical noise or interference into the amplifier’s circuitry. When the bass hits, this interference can disrupt the amplifier’s performance and trigger a shutdown. Ensuring proper grounding is crucial to avoid such issues.
- Defective components: Amplifiers are made up of various intricate components, and if any of these components are defective, it can result in unexpected shutdowns. Defective capacitors, transistors, or other internal components can malfunction when the bass hits hard, causing the amp to shut off.
Remember, these are just a few common problems that can lead to an amp shutting off when the bass hits. Each amplifier model can have its own unique issues, so it’s important to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek professional assistance for troubleshooting and resolving specific problems.
Troubleshooting Steps
Experiencing an amp shutting off when the bass hits can be frustrating, but don’t worry! There are several troubleshooting steps you can take to identify and resolve the issue. Here are some steps you can follow:
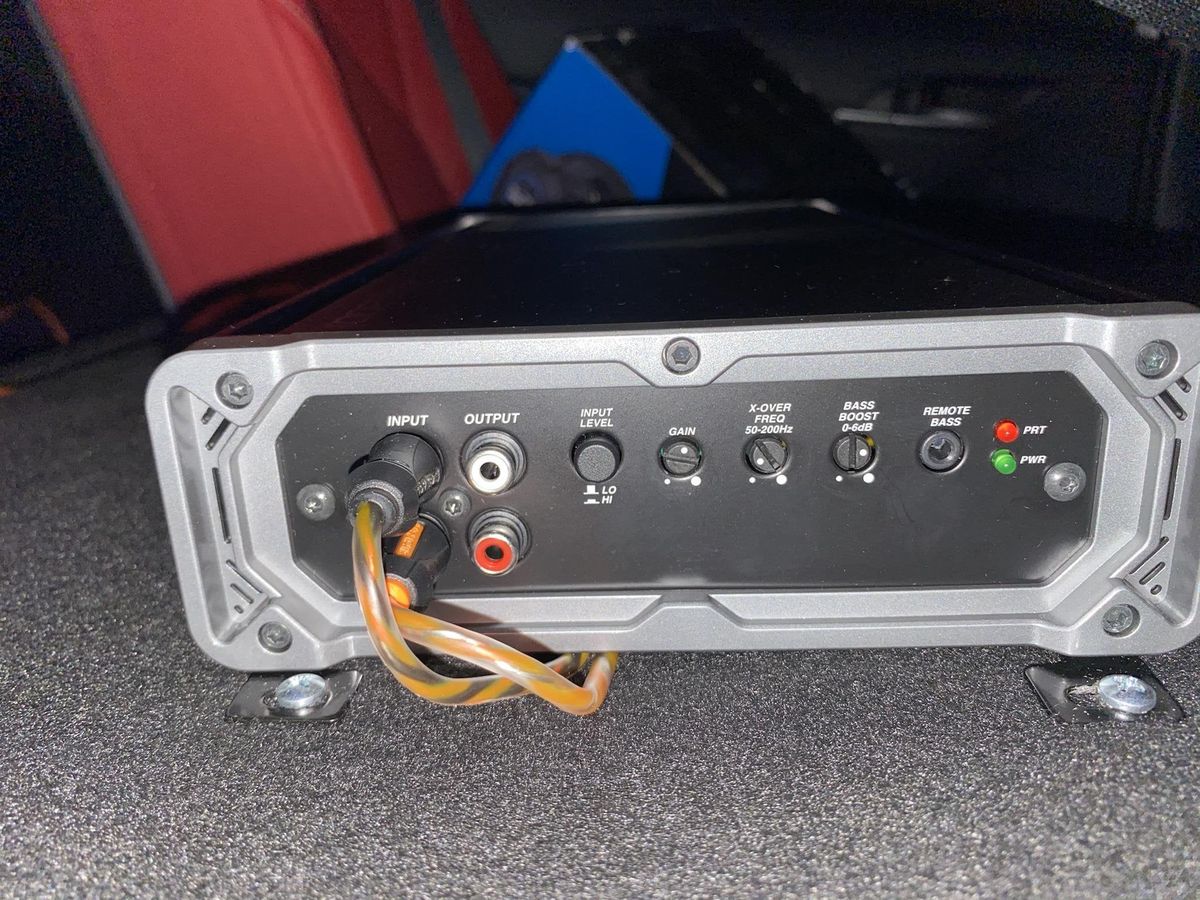
- Checking the power source: Ensure that the amplifier is receiving adequate power from the power source. Check if the power outlet is functioning correctly and that the power cable is securely plugged in. Consider using a dedicated circuit or a power conditioner to ensure a stable power supply.
- Inspecting speaker connections: Examine the speaker connections for any loose or damaged wires that could be causing interruptions. Make sure the connections are secure and properly matched between the amplifier and speakers.
- Verifying grounding issues: Check the grounding of the amplifier and speakers. Ensure that all grounding connections are secure and free of corrosion. Examine the grounding wires and connections for any damage or loose fittings.
- Examining amplifier settings: Review the amplifier settings, including bass levels, EQ settings, and gain controls. Make sure they are properly adjusted and not set to extreme levels that could cause distortion or clipping.
- Assessing speaker specifications: Verify that the amplifier and speakers are compatible in terms of power handling and impedance. Ensure that the amplifier can adequately drive the speakers without overloading or overheating.
- Evaluating speaker impedance: Confirm that the impedance of the speakers matches the amplifier’s rated impedance. Mismatched impedance can result in excessive current flow and trigger the amp’s protection mechanism.
- Analyzing bass boost settings: If your amplifier has a bass boost or subwoofer level control, adjust it to a reasonable level. Excessive bass boost can put additional strain on the amplifier and cause it to shut off.
If the above troubleshooting steps do not resolve the issue, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or contact a professional technician for further assistance. They can provide specialized guidance and diagnostics to help identify and rectify the problem.
Remember, troubleshooting an amp can be a process of elimination. Take your time, be methodical, and don’t hesitate to seek expert help if needed. By following these troubleshooting steps, you’ll be one step closer to resolving the issue and enjoying uninterrupted bass-filled music!
Checking Power Source
When your amp shuts off when the bass hits, one of the first troubleshooting steps you should take is to check the power source. Inadequate or unstable power supply can often be the culprit behind this issue. Here are some steps to follow when checking the power source:
- Ensure proper power outlet: Verify that the power outlet you are using is functioning correctly. Plug in another device or use a voltage tester to confirm that the outlet is providing power.
- Use a dedicated circuit: If possible, connect your amplifier to a dedicated circuit. Sharing a circuit with other high-power devices like refrigerators or air conditioners can lead to power fluctuations and interruptions, causing the amp to shut off.
- Check power cable: Inspect the power cable connecting the amplifier to the power source. Ensure that it is not damaged and securely plugged into both the amplifier and the power outlet.
- Consider a power conditioner: A power conditioner can help stabilize the power supply, filtering out any electrical noise or fluctuations that could affect the amplifier. It is especially useful in environments with poor electrical wiring or high interference.
- Verify power ratings: Make sure that the power supply matches the amplifier’s requirements. Check the voltage rating to ensure compatibility. Using a power supply with lower capacity than required can result in insufficient power delivery and cause the amp to shut off when the bass hits.
- Check the power cable length: If the power cable connecting the amplifier to the power outlet is excessively long, it can cause a drop in voltage and power loss. Consider using a cable of appropriate length to ensure efficient power delivery.
- Clean power contacts: Over time, dust and debris can accumulate on the power contacts, leading to poor electrical connections. Use a clean cloth or electrical contact cleaner to gently clean the contacts on both the power plug and the power outlet.
By performing these checks on the power source, you can ensure that your amplifier is receiving a stable and adequate power supply. If the issue persists even after verifying the power source, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further diagnose and address the problem.
Inspecting Speaker Connections
When your amp shuts off when the bass hits, it’s essential to inspect the speaker connections as they can play a significant role in causing interruptions and shutdowns. Loose or damaged speaker wires can disrupt the flow of electrical signals, triggering the amplifier’s protective mechanisms. Here are some steps to follow when inspecting speaker connections:
- Check for loose connections: Start by ensuring that all speaker connections are secure. Verify that each speaker wire is tightly connected to both the amplifier and the corresponding speaker terminal. Any loose connections can cause intermittent interruptions and lead to the amp shutting off.
- Look for damaged wires: Thoroughly examine the speaker wires for any signs of damage, such as cuts, fraying, or exposed conductors. Damaged wires can result in short circuits or signal loss, causing the amp to shut down when the bass hits.
- Use the correct wire gauge: Check that you are using the appropriate wire gauge for your speakers. The wire gauge affects the resistance and power transmission capabilities. Using a wire that is too thin for the power demands can lead to power loss and trigger the amp’s protection mechanisms.
- Avoid long wire lengths: Keep the speaker wire lengths as short as possible. Long wires can introduce resistance and signal degradation, leading to fluctuations in power delivery and potential shutdowns.
- Consider using banana plugs or spade connectors: Using banana plugs or spade connectors can provide a more secure and reliable connection between the amplifier and the speakers. These connectors eliminate the risk of loose wires and ensure a consistent signal flow.
- Separate speaker wires: Keep the speaker wires separated from other cables or power cords to minimize the chances of interference. Electrical interference can cause distortions and interruptions when the bass hits, potentially leading to the amp shutting off.
- Check for polarity: Make sure the speaker wires are connected with the correct polarity—positive to positive and negative to negative. Reversed polarity can affect the sound quality and potentially cause issues with the amplifier’s protection circuitry.
By inspecting and ensuring the integrity of your speaker connections, you can minimize the chances of interruptions and shutdowns when the bass hits. These steps will help maintain a reliable and consistent signal flow, allowing your amplifier to perform optimally without encountering connection-related issues.
Verifying Grounding Issues
One of the potential causes of an amp shutting off when the bass hits is poor grounding. Grounding issues can introduce electrical noise or interference into the amplifier’s circuitry, disrupting its performance and potentially triggering a shutdown. Here are some steps to follow when verifying grounding issues:
- Check grounding connections: Inspect the grounding connections for both the amplifier and the speakers. Ensure that all grounding wires are securely connected to their respective terminals and free from any corrosion or damage.
- Verify ground loop: Ground loops occur when there are multiple grounding paths that create a loop, leading to electrical interference. If you suspect a ground loop, try disconnecting audio sources or other devices connected to the amplifier one by one to identify the source of the interference.
- Separate audio and power cables: Keep audio cables and power cables separate to minimize the chances of electrical interference. Running audio and power cables parallel to each other can induce noise and disrupt the amplifier’s performance.
- Consider using a ground loop isolator: A ground loop isolator can help eliminate ground loop interference by interrupting the loop and preventing noise from traveling along the signal path. This device can be placed between the audio source and the amplifier to isolate the ground loop.
- Utilize star grounding: Implementing star grounding involves connecting all ground wires to a central point, such as a grounding bar or a single grounding point on the amplifier. This method reduces the chances of ground loops and ensures a centralized and clean ground reference.
- Inspect grounding wires: Examine the grounding wires for any breaks or loose fittings. Ensure that the wires are properly connected to both the ground terminals on the amplifier and the grounding points in your electrical system.
- Consider using a power conditioner: Power conditioners not only stabilize power supply but can also help reduce electrical noise and interference. They often include built-in grounding capabilities and provide a cleaner electrical environment for your amplifier.
Verifying and addressing grounding issues can significantly enhance the performance of your amplifier and reduce the chances of it shutting off when the bass hits. By ensuring proper grounding, you create a stable and noise-free electrical environment for your audio setup.
Examining Amplifier Settings
When your amp shuts off when the bass hits, it’s important to examine the settings on your amplifier. Incorrectly adjusted settings can cause distortion, clipping, or overload, triggering a shutdown to protect the amplifier and speakers. Here are some steps to follow when examining amplifier settings:
- Check bass levels: Evaluate the bass levels on your amplifier. If the bass is set too high, it can put excessive strain on the amplifier and lead to distortion or clipping. Adjust the bass levels to a suitable and balanced setting.
- Review equalizer (EQ) settings: Examine the EQ settings on your amplifier. Ensure that the frequency response is properly adjusted to avoid boosting specific frequencies too much, which can result in distorted sound and potentially trigger the amplifier’s protection circuitry.
- Monitor gain control: The gain control on your amplifier regulates the input sensitivity. If it is set too high, it can cause the amplifier to overload and shut off when the bass hits. Adjust the gain control to an appropriate level that matches your audio source.
- Verify input and output connections: Check that the input and output connections on the amplifier are secure and properly matched. Loose or incorrect connections can lead to signal loss or distortion, potentially triggering a shutdown.
- Reset factory settings: If you have made extensive changes to your amplifier settings, consider resetting it to the factory defaults. This can help eliminate any unintentional adjustments or configurations that may be causing the amp to shut off.
- Update firmware (if applicable): Some amplifiers have firmware that can be updated to improve performance and address potential bugs or issues. Check the manufacturer’s website for any available firmware updates and follow the instructions to update your amplifier.
- Refer to the user manual: If you are uncertain about specific settings or their impact on the amplifier’s performance, consult the user manual provided by the manufacturer. It contains valuable information and guidance on optimal settings for your amplifier model.
By carefully examining and adjusting the settings on your amplifier, you can optimize its performance and minimize the likelihood of a shutdown when the bass hits. Keep in mind that finding the right balance may require some trial and error, so be patient and trust your ears to guide you towards the ideal settings for your audio setup.
Assessing Speaker Specifications
When your amp shuts off when the bass hits, it’s crucial to assess the compatibility between your amplifier and the speakers. Mismatched speaker specifications can lead to excessive current flow, overloading the amplifier and triggering a shutdown. Here are some steps to follow when assessing speaker specifications:
- Power handling capability: Check the power handling capability of your speakers. Ensure that the amplifier’s output power falls within the recommended range provided by the speaker manufacturer. Using an amplifier that exceeds the speaker’s power handling capabilities can cause distortion, overheating, or shutdowns.
- Impedance matching: Verify that the impedance of the speakers matches the rated impedance of your amplifier. Impedance mismatch can lead to unstable power delivery and potentially trigger the amplifier’s protection circuitry, resulting in shutdowns. Ensure that the impedance values are compatible.
- Speaker sensitivity: Speaker sensitivity refers to how efficiently a speaker converts electrical power into sound. Higher sensitivity speakers require less power to reach the same volume level. Ensure that the sensitivity of your speakers is suitable for your amplifier’s power output, avoiding the need for excessive amplification that could strain the amplifier.
- Number of speakers: Consider the number of speakers connected to your amplifier. Adding additional speakers beyond the amplifier’s capacity can overload the system and cause shutdowns. Ensure that the amplifier can handle the load of all connected speakers.
- Speaker placement: Improper speaker placement can impact the bass response and lead to overload or shutdowns. Ensure that the speakers are positioned correctly, allowing them to operate optimally without straining the amplifier to deliver bass frequencies.
- Consider using an external crossover: If you’re using multiple speakers, using an external crossover can help distribute the bass frequencies more effectively. This reduces the demand on the amplifier and prevents overload or shutdowns.
- Consult manufacturer documentation: If you’re unsure about the compatibility between your amplifier and speakers, refer to the documentation provided by the respective manufacturers. They often provide guidance on recommended speaker specifications and amplifier compatibility to ensure optimal performance and avoid issues like shutdowns.
By assessing and ensuring the compatibility of your amplifier and speakers, you can prevent potential overload, distortion, and shutdown issues. Understanding the specifications and making appropriate adjustments will lead to a harmonious and balanced audio setup.
Evaluating Speaker Impedance
When your amp shuts off when the bass hits, it’s important to evaluate the speaker impedance. Impedance mismatch between the speakers and the amplifier can result in excessive current flow, leading to overheating and eventual shutdown. Here are some steps to follow when evaluating speaker impedance:
- Check the speaker impedance rating: Verify the impedance rating specified by the speaker manufacturer. It is usually indicated in ohms and can be found on the back of the speaker or in the product documentation. Common impedance ratings for speakers range from 4 ohms to 8 ohms.
- Verify the amplifier’s impedance compatibility: Review the specifications of your amplifier to determine its impedance compatibility range. It is essential to ensure that the amplifier can handle the impedance of the connected speakers.
- Avoid impedance mismatches: Match the speaker impedance as closely as possible to the amplifier’s rated impedance. Impedance mismatches can result in excessive current draw, potentially overheating the amplifier and triggering shutdowns.
- Consider series or parallel connections: If you need to connect speakers with different impedance ratings to a single amplifier, you can use series or parallel connections to achieve an overall impedance that matches the amplifier’s requirements. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional assistance to ensure proper wiring configurations.
- Be cautious with low-impedance speakers: Some speakers, particularly subwoofers, may have lower impedance ratings such as 2 ohms. Using low-impedance speakers requires an amplifier specifically designed to handle such loads. Ensure that your amplifier is capable of driving the lower impedance speakers without overloading or causing shutdowns.
- Seek professional advice: If you are unsure about the impedance requirements or how to properly configure your speakers and amplifier, consider consulting a professional audio technician. They can provide guidance and make recommendations specific to your setup, helping you achieve optimal performance and avoid any impedance-related issues.
By evaluating and ensuring proper speaker impedance matching, you can prevent excessive current flow, maintain a stable electrical environment for your amplifier, and prevent shutdowns when the bass hits. Take the time to understand the specifications of your speakers and amplifier to create a seamless and compatible audio system.
Analyzing Bass Boost Settings
When troubleshooting an amp that shuts off when the bass hits, it’s important to analyze the bass boost settings on your amplifier. While bass boosts can enhance low-frequency response, excessive bass boost levels can strain the amplifier and cause it to overload or shut off. Here are some steps to follow when analyzing bass boost settings:
- Review the bass boost control: Locate the bass boost control on your amplifier and assess its settings. This control allows you to increase or decrease the bass level in your audio signal.
- Avoid extreme bass boost levels: Excessive bass boost levels can significantly increase the power demand on the amplifier. If set too high, the amplifier may struggle to deliver the amplified bass signal, causing distortion, clipping, or even triggering the protection circuitry and shutting off.
- Adjust the bass boost level: Experiment with different bass boost settings to find a balanced and pleasing bass response without pushing the amplifier to its limits. Set the bass boost level to a moderate setting that enhances the low frequencies while still maintaining clarity and avoiding distortion.
- Consider utilizing other tone controls: Instead of relying solely on the bass boost control, explore other tone controls on your amplifier, such as the equalizer (EQ), to shape the bass response. Adjusting the EQ settings can help achieve balanced bass levels without excessively relying on the bass boost feature.
- Know your speaker and amplifier limitations: Be mindful of the power handling capabilities and frequency response limits of your speakers and amplifier. Pushing them beyond their capabilities, especially with extreme bass boosts, can lead to overheating, distortion, and shutdowns.
- Monitor distortion and clipping: Keep an ear out for any signs of distortion or clipping when testing different bass boost settings. If you notice distortion or the sound becomes distorted when the bass hits, reduce the bass boost level or consider using other tone controls to achieve a cleaner sound.
- Consider using an external bass processor: If you find it challenging to achieve the desired bass response with the built-in bass boost controls on your amplifier, consider using an external bass processor. These devices provide more precise control over the bass frequencies and allow for a more tailored and nuanced bass enhancement.
By carefully analyzing and adjusting the bass boost settings on your amplifier, you can enhance the low-frequency response while avoiding excessive strain on the amplifier and potential shutdowns. Finding the right balance and understanding the limitations of your equipment will help you achieve a satisfying and distortion-free bass experience.
Preventive Measures
Experiencing an amp shutting off when the bass hits can be frustrating, but there are several preventive measures you can take to avoid encountering this issue in the future. By implementing these measures, you can ensure the optimal performance of your amplifier and speakers. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Proper ventilation: Ensure that your amplifier has sufficient ventilation to dissipate heat effectively. Avoid placing it in enclosed spaces or stacking it with other equipment that could obstruct airflow. Adequate ventilation helps prevent overheating, which can result in shutdowns.
- Choose high-quality cables: Invest in high-quality speaker cables and interconnects to minimize signal loss and interference. Poor quality cables can introduce noise or affect signal transmission, potentially leading to shutdowns or degraded sound quality.
- Regular maintenance: Periodically inspect and clean your amplifier and speakers. Remove any dust or debris that may accumulate on the components or in the ventilation openings. Dust can impair heat dissipation and increase the risk of overheating and shutdowns.
- Ensure stable power supply: Use a stable power source or consider using a power conditioner to protect your amplifier from voltage fluctuations or electrical noise. A stable power supply minimizes the risk of shutdowns caused by inadequate power delivery.
- Proper speaker placement: Position your speakers correctly to optimize bass response and airflow. Avoid placing them too close to walls or corners, as this can result in exaggerated bass or boomy sound, potentially overworking the amplifier and triggering shutdowns.
- Monitor volume levels: Avoid excessively high volume levels that can strain the amplifier and speakers. Prolonged exposure to high volume can lead to overheating and potentially cause the amp to shut off.
- Read user manuals: Familiarize yourself with the user manuals and documentation provided by the manufacturers. Understand the recommended operating guidelines, limitations, and maintenance requirements specific to your amplifier and speaker models.
- Regularly update firmware: If your amplifier has firmware, check for regular updates from the manufacturer. Firmware updates can address bugs and improve performance, ensuring the stability and reliability of your amplifier.
- Consult professional assistance: If you encounter persistent issues with your amplifier or experience frequent shutdowns, consider seeking professional assistance from an audio technician. They can diagnose the problem accurately and provide tailored solutions to prevent future shutdowns.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can minimize the chances of your amplifier shutting off when the bass hits. Taking proactive steps to maintain and properly operate your audio equipment promotes longevity, reliability, and enhanced performance.
Conclusion
Experiencing an amp shutting off when the bass hits can be a frustrating obstacle that disrupts your music enjoyment. However, by understanding the causes and implementing the appropriate troubleshooting steps, you can work towards resolving the issue and preventing it from recurring in the future.
In this article, we explored some common causes behind an amp shutting off, including power overload, overheating, short circuits, impedance mismatch, grounding issues, and built-in safety features. We discussed the importance of checking the power source, inspecting speaker connections, verifying grounding issues, examining amplifier settings, assessing speaker specifications, analyzing bass boost settings, and implementing preventive measures.
Remember, troubleshooting and resolving the issue may require a combination of these steps and potentially seeking professional assistance. Each audio setup is unique, and it’s important to consider the specific characteristics of your amplifier and speakers.
By following the preventive measures outlined in this article, you can reduce the chances of experiencing an amp shutdown when the bass hits. Proper ventilation, high-quality cables, regular maintenance, stable power supply, appropriate speaker placement, monitoring volume levels, and keeping up with firmware updates are all crucial aspects of maintaining a reliable and robust audio system.
If the issue persists or you need further guidance, don’t hesitate to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or reach out to an audio technician for expert assistance.
By taking a proactive approach and implementing the appropriate measures, you can ensure that your amplifier and speakers deliver the best possible audio experience, free from unexpected shutdowns and interruptions when the bass hits.