Home>Instruments>Bass>How To Read Bass Tabs

Bass
How To Read Bass Tabs
Modified: January 28, 2024
Learn how to read bass tabs and master the art of playing bass guitar. Unlock the secrets of playing your favorite bass lines and grooves with ease.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of bass tabs, where you can unlock the secret language of bass guitarists everywhere. If you’re a beginner or aspiring bassist, understanding how to read bass tabs is essential to your musical journey. While standard music notation can be overwhelming for beginners, bass tabs offer a simplified way to learn your favorite songs without the need for extensive music theory knowledge.
In this article, we will guide you through the basics of bass tabs, including how to read and interpret them. Whether you’re learning to play your favorite songs or creating your own basslines, mastering bass tabs will give you the confidence and skills to take your bass playing to the next level.
Unlike traditional sheet music, bass tabs utilize a system of numbers and symbols that represent the strings, frets, and techniques used to play specific notes. This makes it much easier for beginners to learn songs quickly and effectively. By understanding this unique language, you’ll be able to follow along with bass tabs and recreate the basslines of your favorite tunes.
Throughout this article, we will cover the fundamental elements of bass tabs, including string and fret numbers, common techniques and symbols, and helpful practice tips. By the end, you’ll have a solid foundation in reading bass tabs and will be able to apply your newfound knowledge to enhance your bass playing skills.
So, let’s dive into the world of bass tabs and unravel the mysteries that lie within the six strings of the mighty bass guitar.
Understanding Bass Tabs
Before we dive into how to read bass tabs, it’s important to have a clear understanding of what they actually represent. Bass tabs consist of horizontal lines, also known as the staff, which represent the strings of the bass guitar. Each line corresponds to a specific string, with the lowest string typically appearing at the bottom of the staff. The numbers and symbols written on these lines indicate the frets and techniques used to produce the desired notes.
Unlike standard music notation, which indicates the pitch and duration of the notes, bass tabs primarily focus on the placement of the fingers on the fretboard. This allows bassists to quickly and easily recreate basslines without needing extensive music theory knowledge.
While bass tabs don’t provide exact timing or rhythm information, they give you a visual roadmap of the notes you need to play. It’s up to you to listen to the song and develop a sense of timing and rhythm that matches the original recording.
It’s also worth mentioning that bass tabs can vary in complexity. Some tabs may only consist of the basic notes and techniques, while others may include additional symbols and notations to capture the specific nuances of a song. As you gain more experience and proficiency, you’ll be able to tackle more complex bass tabs.
Now that we have a basic understanding of what bass tabs represent, let’s delve into the process of reading and deciphering them.
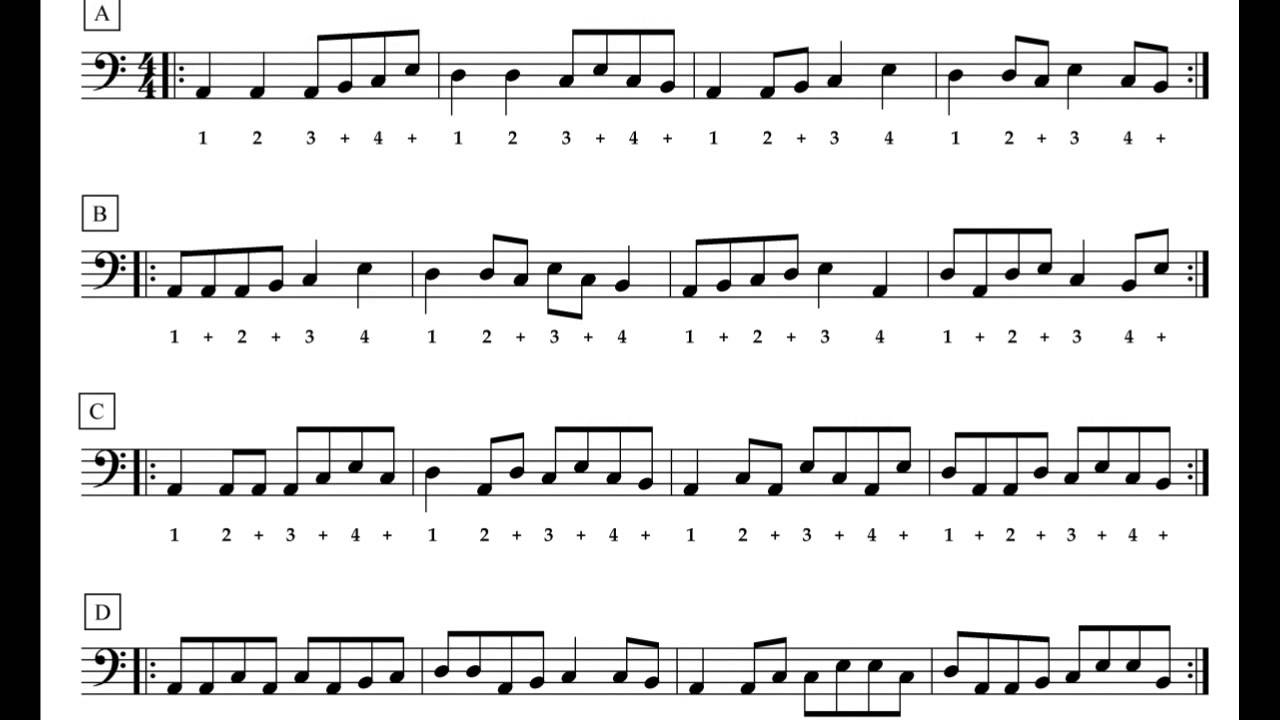
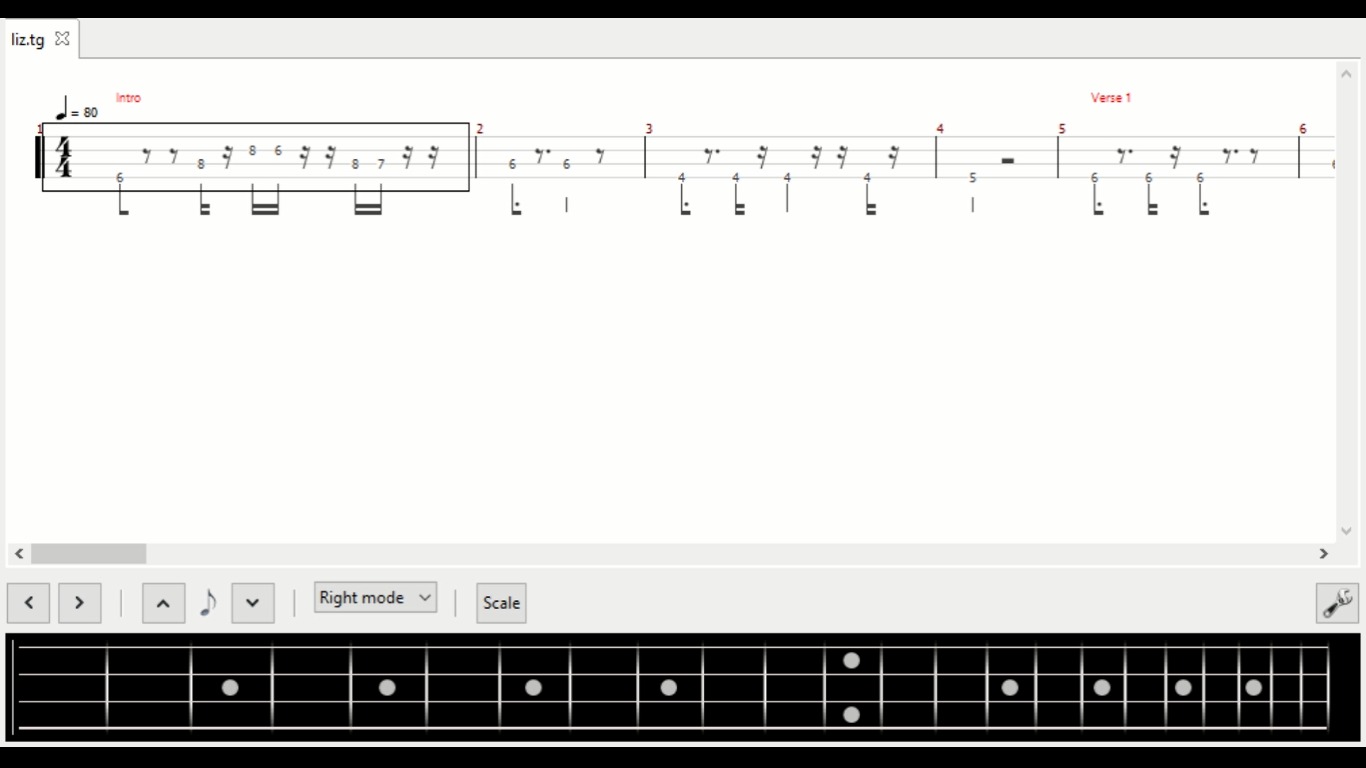
Reading the Tablature
Reading bass tablature, or tabs for short, is a simple and intuitive process once you understand the basic structure. Let’s break it down step by step:
- Staff Lines: The staff consists of horizontal lines that represent the strings of the bass guitar. The bottom line represents the lowest string (typically the E string), and the top line represents the highest string (usually the G string).
- String Numbers: Each line on the staff is numbered from the thickest string (usually the E string) to the thinnest string (typically the G string). These numbers indicate the strings on which you should play the notes.
- Fret Numbers: On the staff lines, you will see numbers placed vertically. These numbers represent the frets on the bass guitar’s neck where you should place your fingers to play the corresponding notes.
- Note Duration: While tabs don’t provide precise timing, you can still get an idea of note duration by paying attention to how long a number or symbol is held. Shorter notes are typically represented by a single number or symbol, while longer notes may span multiple numbers or be connected by stems or ties.
- Slurs, Bends, and Hammer-ons/Pull-offs: To add more expression and technique to bass lines, tabs may include symbols like slurs (marked with a curved line), bends (marked with an upward arrow), and hammer-ons/pull-offs (indicated by an “H” or “P” between two notes). These techniques allow you to create smoother transitions and add variation to your playing.
Remember that while tabs provide a simplified way to learn and play basslines, they don’t convey all the subtleties of timing and rhythm. It’s essential to listen to the song and develop a sense of timing and groove to accurately recreate the original bassline.
Now that you have a grasp of the basic structure of tabs, let’s explore the common notations and techniques you’ll encounter in bass tabs.
Basic Notations in Bass Tabs
When reading bass tabs, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the common notations and symbols used. These notations provide additional information and instructions to help you accurately play the desired notes and techniques. Here are some of the basic notations you’ll encounter:
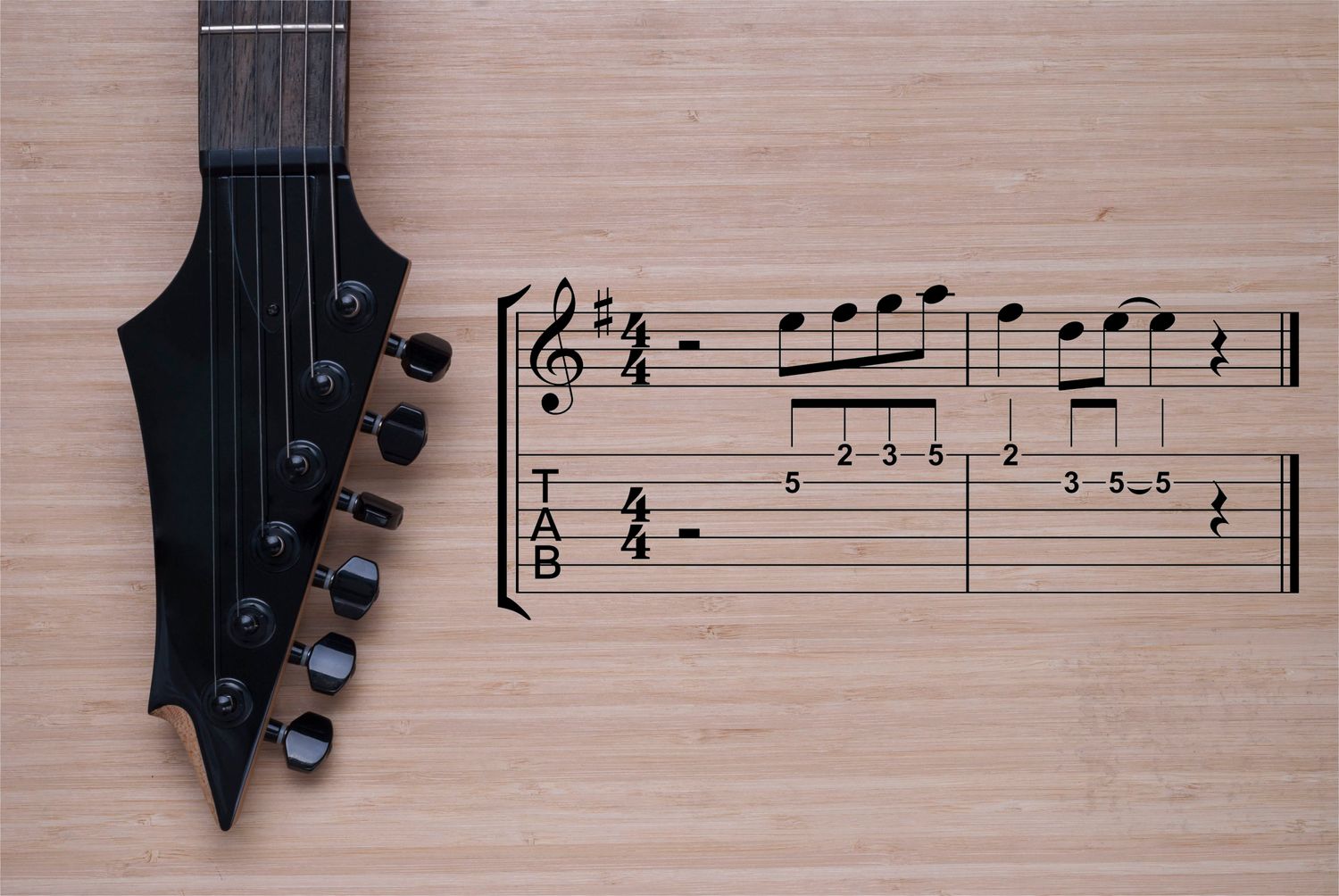
- Numbers: The numbers on the lines of the staff indicate the fret numbers you should play on the corresponding strings. For example, if you see the number 3 on the bottom line, you would press down the third fret on the lowest string.
- Open String: Occasionally, you may come across a number 0 on a line. This represents an open string, where you need to play the string without pressing down any frets.
- Slides: Slides are indicated by a diagonal line connecting two numbers. It means you should slide your finger along the string from the starting fret to the ending fret without picking the string again. Upward-slanting lines indicate slides from lower to higher frets, while downward-slanting lines represent slides from higher to lower frets.
- Vibrato: The vibrato technique adds a slight fluctuation in pitch to a sustained note. It is represented by a squiggly line above or below the number, indicating that you should rapidly shake or vibrate the finger on the fretted note while it is being played.
- Palm Muting: Palm muting is a technique where you lightly rest the side of your hand (palm) on the strings near the bridge to produce a muted or dampened sound. It is shown by the letters “PM” above the corresponding notes.
- Damping: Damping is a technique that involves using your fretting hand to lightly touch the strings after playing a note or chord, resulting in a muted or choked sound. It is indicated by the letter “X” above the specific strings to be damped.
By familiarizing yourself with these basic notations, you’ll be well-equipped to interpret and play bass tabs more effectively. As you progress, you may come across additional symbols and techniques, but with a solid understanding of the fundamentals, you’ll be able to adapt and tackle more complex bass tabs.
Next, let’s explore how string and fret numbers are represented in bass tabs for accurate playing.
String and Fret Numbers
String and fret numbers play a crucial role in bass tabs, as they indicate where you should place your fingers on the fretboard to produce the desired notes. Understanding how string and fret numbers are represented will greatly assist you in accurately playing bass tabs.
String numbers are typically shown on the left-hand side of the staff, ranging from the lowest string (usually the E string) to the highest string (usually the G string). These numbers help to identify which string to play for each note indicated in the tab. For example, if you see the number 4 on the left-hand side of the tab, it means you should play the note on the fourth string of your bass, counting from the thickest string.
On the other hand, fret numbers are placed on the corresponding string line to indicate where you should press down on the fretboard. The fret numbers represent the spaces between the metal bars (frets) on your bass guitar. For instance, if you see the number 5 on the fourth string line, it means you should press down on the fifth fret of that string to produce the desired note.
It’s important to note that sometimes you may come across a “0” instead of a fret number. This represents an open string, indicating that you should play that string without pressing down any frets. It produces a natural, ringing sound.
As you progress with bass tabs, you’ll encounter more complex fingerings, including chords, double stops, and harmonics. These can be represented by multiple numbers on different strings, indicating which frets and strings should be played simultaneously.
Having a solid understanding of string and fret numbers allows you to accurately navigate the fretboard and play bass tabs with confidence. As you practice reading tabs and playing songs, you’ll develop muscle memory and familiarity with different fret positions, enabling you to quickly find the right notes on your bass.
Now that we have covered the basics of string and fret numbers, let’s explore the common techniques and symbols used in bass tabs.
Common Techniques and Symbols
When reading bass tabs, you’ll often come across various symbols and notations that represent different playing techniques. These symbols provide valuable information on how to execute specific techniques and add expressive elements to your bass playing. Let’s take a look at some of the most common techniques and symbols found in bass tabs:
- Slides: Slides are indicated by a diagonal line connecting two numbers. They represent a smooth transition from one note to another without picking the string again. Upward-slanting lines indicate slides from lower to higher frets, while downward-slanting lines represent slides from higher to lower frets.
- Hammer-ons and Pull-offs: Hammer-ons (H) and pull-offs (P) are techniques used to create smooth and fluid transitions between notes. A hammer-on is indicated by an “H” between two numbers. It means you should strike the first note and then use a finger to “hammer” down on the higher fret without re-picking the string. A pull-off is represented by a “P” between two notes, indicating that you should pluck the first note and then “pull” the finger off to sound the second note.
- Bends: Bends are used to raise the pitch of a note by pushing or pulling the string behind a fret. They are often represented by an upward arrow (^) above the number or a “B” followed by the desired pitch. The number of arrows or the pitch indication determines the extent of the bend.
- Artificial Harmonics: Artificial harmonics produce a bell-like sound by lightly touching the string with your fretting hand while plucking it with your other hand. They are indicated by diamond-shaped or triangular symbols above the note, along with a number indicating the fret where you should touch the string.
- Vibrato: Vibrato adds a subtle wavering effect to a sustained note. It is represented by a squiggly line (~) above or below the number, indicating that you should rapidly shake or vibrate the finger on the fretted note while it is being played.
- Palm Muting: Palm muting involves dampening the sound of the strings by resting the side of your hand (palm) lightly on the strings near the bridge. It produces a muted or percussive sound and is indicated by the letters “PM” above the specific notes or a solid line across the strings to be muted.
These are just a few examples of the techniques and symbols commonly used in bass tabs. As you encounter more diverse and complex music, you may come across additional symbols that represent specific techniques or accents. Learning and understanding these symbols will greatly enhance your ability to interpret and play bass tabs accurately.
Now that we’ve covered the essential techniques and symbols, let’s explore some tips for effectively reading and practicing with bass tabs.
Tips for Reading and Practicing with Bass Tabs
Reading and practicing with bass tabs can greatly enhance your bass playing skills. Here are some tips and techniques to help you make the most of your learning experience:
- Start with Simple Songs: Beginners should begin by tackling easy songs with straightforward basslines. This will help you get accustomed to reading tabs and develop finger coordination without feeling overwhelmed. Gradually work your way up to more complex songs as you gain confidence and skill.
- Listen to the Song: While bass tabs provide the notes, it’s crucial to listen to the song as well. Pay attention to the rhythm, timing, and nuances in the bassline. This will improve your understanding of how the notes fit into the context of the music.
- Focus on Accuracy: While it’s tempting to play through a song quickly, prioritize accuracy over speed. Take the time to learn each section correctly, paying attention to proper finger placement and technique. This will build a solid foundation for your playing.
- Use a Metronome: Practicing with a metronome will help you develop a sense of timing and improve your rhythmic accuracy. Start slow and gradually increase the tempo as you become more comfortable with the bassline.
- Break It Down: If a part of the song is particularly challenging, break it down into smaller sections. Practice each section individually and then slowly piece them together. This approach will help you master difficult passages more effectively.
- Experiment with Dynamics and Expressiveness: While bass tabs may not indicate dynamics, experiment with your playing to add expression. Vary your attack, volume, and tone to bring life to the bassline. This will make your playing sound more dynamic and engaging.
- Record and Assess: Record yourself practicing or playing along with a song. Listen back and assess your performance to identify areas for improvement. This will help you fine-tune your technique and become a better bassist.
- Explore Different Genres and Styles: Don’t limit yourself to a single genre or style of music. Explore different genres and styles to broaden your playing skills and musical knowledge. This will make you a versatile and well-rounded bassist.
- Join a Community: Joining a bass playing community, whether in-person or online, can provide valuable support, feedback, and inspiration. Interacting with fellow bassists can motivate you to practice more and push your playing to new heights.
Remember, practice is key when it comes to mastering bass tabs. Dedicate regular time to practice, stay patient, and enjoy the journey. With consistent effort and a passion for bass playing, you’ll steadily improve and become a confident and skilled bassist.
Now, armed with these tips and techniques, you’re ready to dive into the world of bass tabs and unleash your musical potential.
Conclusion
Congratulations on learning the ins and outs of reading bass tabs! By mastering this essential skill, you have unlocked a world of musical possibilities on the bass guitar. Whether you’re jamming along to your favorite songs or creating your own basslines, the ability to read and interpret bass tabs is a valuable asset in your musical journey.
Remember, understanding the structure of bass tabs, including string numbers, fret numbers, and common techniques and symbols, is fundamental to accurately playing the desired notes and executing various playing techniques. Building your foundation by starting with simple songs and gradually progressing to more complex basslines will help you develop your skills and confidence as a bassist.
Don’t forget to listen to the songs you’re playing, as this will help you understand the timing, groove, and nuances of the bassline. Experiment with dynamics, expression, and different playing styles to add your personal touch to the music.
Keep in mind that practice is crucial to refining your skills. Take advantage of tools such as metronomes and recordings to enhance your timing and assess your progress. And don’t hesitate to join a community of bassists to connect with fellow musicians, seek guidance, and share your musical journey.
With consistent practice, patience, and a passion for the bass guitar, you will continue to grow as a musician. So pick up your bass, dive into the world of bass tabs, and let your creativity and rhythm shine. Happy playing!











