Home>Production & Technology>Sheet Music>How To Read Tab Sheet Music


Sheet Music
How To Read Tab Sheet Music
Modified: February 14, 2024
Learn how to read sheet music with our step-by-step guide. Mastering the art of reading tab sheet music has never been easier. Start playing your favorite songs today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Sheet music is an essential tool for musicians, serving as a guide for reading and playing music. While traditional sheet music uses standard notation to represent musical elements such as pitch and rhythm, there is another popular form of notation called tab sheet music that specifically caters to fretted instruments like the guitar, bass, and ukulele.
Tab sheet music, also known as tablature or tabs, provides a simplified visual representation of the instrument’s fingerboard. It uses numbers and symbols to indicate which strings to play and which frets to press down. This makes it easier for beginners to quickly learn to play their favorite songs without having to decipher complex traditional notation.
Understanding how to read tab sheet music opens up a world of possibilities for aspiring musicians. It allows you to learn and play a wide variety of songs, from popular rock and pop tunes to classical compositions and everything in between.
In this article, we will explore the basics of reading tab sheet music, including the symbols, notation, and techniques you need to know. Whether you’re a beginner or have some experience with traditional notation, this guide will help you navigate the world of tab sheet music and enhance your musical journey.
What is Tab Sheet Music?
Tab sheet music, also known simply as “tab” or “tablature,” is a form of notation specifically designed for fretted instruments like the guitar, bass, and ukulele. Unlike traditional sheet music, which uses standard notation to represent musical elements such as pitch, rhythm, and dynamics, tab sheet music provides a simplified visual representation of the instrument’s fingerboard.
Tab sheet music uses numbers to indicate which frets on which strings should be played. Each string is represented by a horizontal line, and the numbers are placed on the line to indicate the fret to be played. This allows musicians to easily identify the finger placements required to play a specific melody, riff, or chord progression.
The simplicity and ease of understanding make tab sheet music a popular choice for beginners learning to play the guitar or other fretted instruments. It eliminates the need to learn to read traditional sheet music, which can be time-consuming and challenging for some musicians.
Tab sheet music is versatile and can be used to notate various playing techniques, including single notes, chords, slides, bends, and vibrato. It can also include symbols and annotations to provide additional instructions or indications for specific musical elements.
While tablature is primarily used for fretted instruments, it is not limited to just the guitar, bass, or ukulele. There are variations of tablature specifically designed for instruments like the banjo, mandolin, and even the piano.
As with any form of notation, tab sheet music has its limitations. It may not accurately convey all the nuances and subtleties that standard notation provides, such as precise rhythm or dynamics. Additionally, it is not commonly used in classical music or complex compositions that require intricate arrangements.
However, tab sheet music serves as an excellent learning tool for beginners and casual players who want to quickly pick up their favorite songs and play them on their chosen instrument. It enables musicians to learn and share music in an accessible and straightforward way, making it a valuable resource for players of all skill levels.
Understanding Tabs and Symbols
When diving into the world of tab sheet music, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the various symbols and conventions used. These symbols provide crucial information about how to play the notes, chords, and techniques indicated in the tab. Here are some common symbols you may encounter:
- Numbers: The numbers in the tab indicate which fret to press down on a particular string. For example, if you see the number 3 on the top line, it means you should press down the third fret on the highest-pitched string of your instrument.
- Lines: Each line in the tab corresponds to a specific string on your instrument. The bottom line represents the lowest-pitched string, while the top line represents the highest-pitched string.
- Zero (0): A zero in the tab indicates that you play the open string, meaning you don’t press down any frets and let the string ring out.
- X: An “X” symbol typically indicates a muted or deadened string. You lightly touch the string without pressing it down on any fret to create a muted sound.
- Hammer-Ons and Pull-Offs: These techniques are indicated by a curved line connecting two or more numbers. A hammer-on is when you play a note by “hammering” your finger onto a higher fret without picking it again. A pull-off is when you “pull” your finger off a higher fret to play a lower note.
- Slides: Slides are denoted by a diagonal line connecting two numbers. It indicates that you smoothly transition from one fret to another without lifting your finger off the string.
- Bends: Bends are shown by an upward curved arrow or the letter “b” above a number. Bending a string means stretching it to raise the pitch and create a expressive effect.
- Vibrato: Vibrato is indicated by a wavy line above a note. It instructs you to slightly fluctuate the pitch of the note by bending the string back and forth.
- Palm Muting: Palm muting is denoted by placing a “P.M.” (palm mute) above the tab. It signifies that you should lightly rest the palm of your picking hand on the strings near the bridge to dampen the sound.
These are just a few of the many symbols and techniques you may encounter while reading tab sheet music. It’s essential to refer to a legend or key at the beginning of the tab to understand any specific symbols or markings used.
By familiarizing yourself with these symbols, you can decipher tab sheet music with ease and accurately reproduce the melodies, chords, and techniques indicated in the tabs. Practice reading tabs and playing the songs or exercises will help you become more comfortable and proficient in using this notation system.
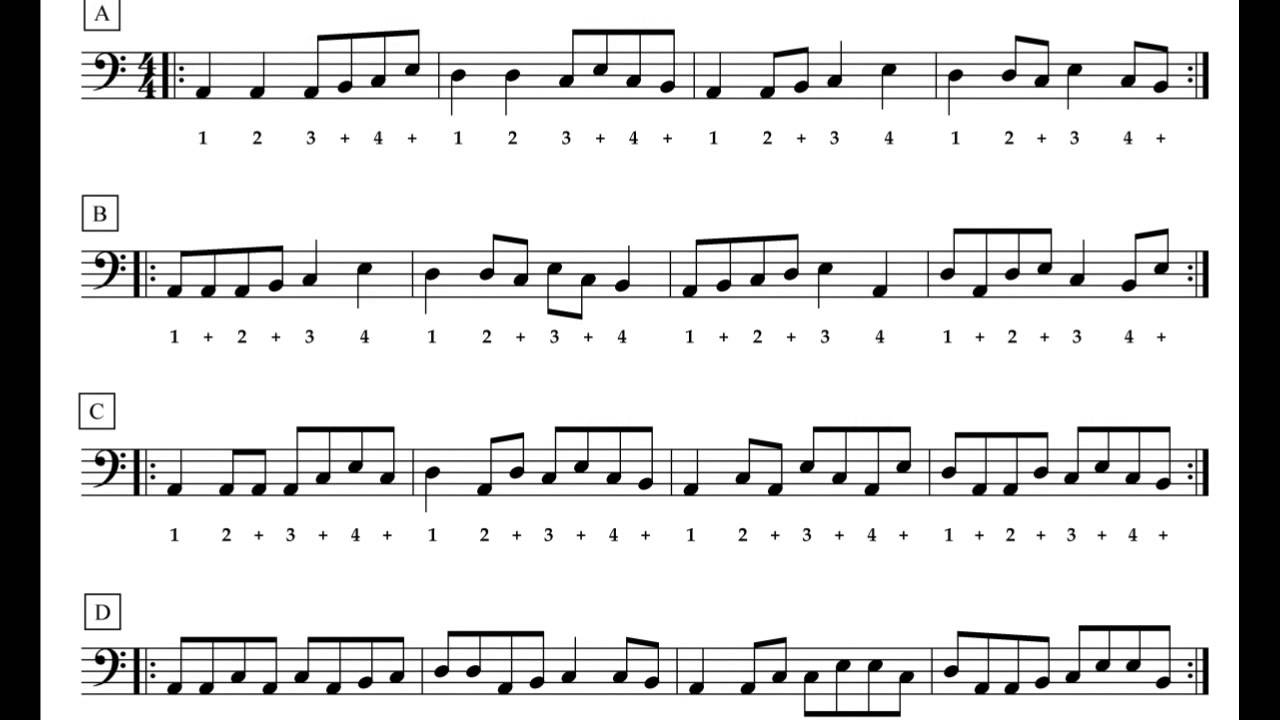
Basic Tablature Notation
Tablature notation, commonly referred to as “tab,” provides a straightforward visual representation of the instrument’s fingerboard. Before delving into more complex tablature notations, it’s crucial to grasp the basics.
The basic tablature notation consists of six horizontal lines, each representing the six strings of the guitar. Starting from the bottom, the lines correspond to the strings in the following order: E, A, D, G, B, and high E. The top line represents the highest-pitched string.
To indicate which fret to press on a particular string, numbers are placed on the lines. A number on the bottom line represents the first fret, while a number on the top line denotes the highest available fret on that string. The numbers increase as you move up the fretboard, with higher numbers representing higher frets.
For example, if you see the number 3 on the second line (A string), it means you should press down the third fret on the A string. If you come across the number 0, it represents an open string, where the string is played without pressing down any frets.
It’s important to note that tablature notation does not indicate the duration of the notes or the rhythm. To gain a complete understanding of the piece’s timing, it’s advisable to refer to the song itself or listen to a recording.
Furthermore, tablature notation can also indicate chord diagrams to depict the finger positions for a specific chord. These diagrams consist of vertical lines representing the strings and numbers or X’s placed on the strings to indicate where the fingers should be placed.
By understanding these basic tablature notations, you can follow along with tab sheet music and correctly position your fingers on the fretboard. With regular practice, you will become more comfortable with tab notation and be able to play a wide range of songs on your instrument.
Reading Notes on the Tab
One of the essential skills in reading tab sheet music is understanding how to read the notes represented by the numbers on the lines. Each number corresponds to a specific fret on a particular string, indicating where to place your fingers to produce the desired pitch.
Let’s break down how to read notes on the tab:
- Identify the string: Each line of the tab represents a specific string on your instrument, with the bottom line representing the lowest-pitched string and the top line representing the highest-pitched string.
- Locate the number: The number placed on a particular line indicates which fret to play on that string. For example, if you see the number 3 on the second line (A string), it means you should press down the third fret on the A string.
- Understand the timing: Tablature notation does not indicate the note’s duration, so it’s important to refer to the song or recording to understand its timing. This means you’ll need to rely on your ear or refer to the sheet music for the rhythm and timing of the notes.
- Coordinate fingers and strings: As you read the tab, coordinate your fingers with the numbers indicated on the lines to produce the desired pitch. This involves pressing down the appropriate string and fret with the designated finger.
Reading notes on the tab requires practice and familiarity with your instrument’s fingerboard. Start with simple songs or exercises and gradually progress to more complex pieces as you gain confidence in reading the notes on the tab.
It’s important to note that tab sheet music may not indicate specific fingerings or hand positions, particularly for more intricate melodies. In such cases, it’s beneficial to experiment with different fingerings and find what works best for you.
Remember, tab sheet music provides a simplified representation of the music, primarily focusing on the pitch and finger placement. To fully bring the music to life, you may need to rely on your ear, musical intuition, and additional resources to incorporate dynamics, phrasing, and musical expression.
Practice regularly, listen to the song, and observe other players to refine your interpretation and bring your unique musicality to the tab sheet music you’re reading.
Playing Techniques and Indications
Tab sheet music not only represents the notes and finger placements but also includes specific indications and symbols for various playing techniques. Understanding and interpreting these playing techniques are crucial for accurately reproducing the intended sound and style of a piece. Here are some common playing techniques and their indications in tab sheet music:
- Hammer-Ons and Pull-Offs: A hammer-on is indicated by a curved line connecting two or more numbers. It instructs you to play a note by “hammering” your finger onto a higher fret without picking it again. A pull-off, on the other hand, is represented by a curved line indicating that you should “pull” your finger off a higher fret to play a lower note.
- Slides: Slides are denoted by a diagonal line connecting two numbers. It indicates that you smoothly transition from one fret to another without lifting your finger off the string. Slides can add a smooth and seamless quality to your playing.
- Bends: Bends are shown by an upward curved arrow or the letter “b” above a number. Bending a string means stretching it to raise the pitch and create an expressive effect. The arrow or “b” symbol indicates the direction and degree of the bend.
- Vibrato: Vibrato is indicated by a wavy line above a note. It instructs you to slightly fluctuate the pitch of the note by bending the string back and forth. Vibrato adds an expressive and dynamic element to your playing.
- Palm Muting: Palm muting is denoted by placing a “P.M.” (palm mute) above the tab. It signifies that you should lightly rest the palm of your picking hand on the strings near the bridge to dampen the sound. Palm muting is commonly used in rock, metal, and punk genres to create a muted, percussive effect.
- Tapping: Tapping is indicated by a “T” or the letter “P” above the tab. It involves using your fretting hand to tap on the fretboard to produce notes. Tapping is a popular technique in rock and metal guitar playing for fast and intricate passages.
These are just a few examples of the playing techniques and indications you may encounter in tab sheet music. It’s important to refer to a legend or key at the beginning of the tab for any specific symbols or markings used.
By familiarizing yourself with these playing techniques and practicing them, you can add depth, expressiveness, and stylistic nuances to your playing. Experiment with different techniques, explore various musical genres, and observe professional players to refine your skills and develop your unique musical voice.
Common Tablature Symbols and Abbreviations
Tab sheet music utilizes various symbols and abbreviations to provide additional information and instructions to the musician. These symbols and abbreviations help clarify specific techniques, repetitions, and other musical elements. Here are some of the most common tablature symbols and abbreviations:
- / or : These symbols indicate a slide up (/) or a slide down () from one note to another. They are typically used in conjunction with a number to signify the starting and ending fret positions for the slide.
- h: The “h” symbol stands for a hammer-on. It indicates that you should play a note on a lower fret, then “hammer” your finger onto a higher fret without picking the string again.
- p: The “p” symbol represents a pull-off. It instructs you to play a note on a higher fret, then “pull” your finger off the string to produce a lower note without picking the string again.
- b or bend: The “b” symbol instructs you to perform a bend on the string, raising its pitch. This can be indicated by an upward curved arrow (↑) or the word “bend.” The strength and direction of the bend can vary, so it’s important to listen to the song or follow any additional instructions provided.
- r: The symbol “r” represents a release or return from a bend. It indicates that you should gradually release the string from its bent position back to its original pitch.
- t: The “t” symbol denotes a tap. Tapping involves using your fretting hand to “tap” the string onto a specific fret, often while simultaneously picking or strumming with the other hand.
- ~: The tilde (~) symbol indicates vibrato. It instructs you to rapidly and subtly fluctuate the pitch of the note by alternately bending the string slightly upward and releasing it back to its original position.
- PM: The abbreviation “PM” stands for palm mute. It suggests that you should place the palm of your picking hand lightly on the strings near the bridge to dampen the sound and create a muted effect.
- : or ||: These symbols indicate a repetition or repeat. A single colon (:) often signifies that the section before it should be repeated, while a double vertical bar (||) denotes the end of the repetition or the entire piece.
These are just a few examples of the common tablature symbols and abbreviations you may encounter while reading tab sheet music. It’s important to consult a legend or key if you come across any unfamiliar symbols or markings.
By understanding and implementing these symbols and abbreviations in your playing, you can accurately reproduce the desired musical effects and articulations indicated in the tab. Pay close attention to the dynamics, techniques, and expressions indicated to bring the music to life.
Tips for Efficiently Reading Tab Sheet Music
Reading tab sheet music efficiently requires practice and a good understanding of the notation system. Here are some tips to help you read tab sheet music more effectively:
- Start with simple songs: Begin by practicing with easy songs or exercises that incorporate basic techniques. This will allow you to gradually build your skills and confidence in reading tab.
- Pay attention to string and fret numbers: Always double-check the string and fret numbers in the tab to ensure you’re playing the correct notes. Inaccurate placements can lead to wrong pitches and confusion.
- Refer to the rhythm and timing: While tab provides the note placements, it does not indicate the rhythm or timing. Listen to the song or refer to the sheet music for the rhythm, and incorporate it into your playing.
- Utilize additional resources: Use backing tracks, recordings, or tutorial videos to enhance your understanding of the songs you’re learning. These resources can provide valuable guidance on timing, phrasing, and expression.
- Learn to read intervals: As you become more familiar with tab, try to visualize the intervals between consecutive frets. This will help you anticipate finger placements and navigate the fretboard more efficiently.
- Master common chord shapes and patterns: Familiarize yourself with common chord shapes and patterns, as they often appear in tab sheet music. This will allow you to recognize and play chords effortlessly.
- Experiment with fingerings: While tab may not always provide specific fingerings, feel free to experiment with different finger placements to find what works best for you. This can help you achieve smoother transitions and improve your overall technique.
- Practice regularly: Like any skill, reading tab sheet music requires practice. Set aside dedicated practice time and work on progressively challenging pieces to improve your reading proficiency.
- Follow the dynamics and expressions: Pay attention to any dynamics (soft, loud) and expressions (legato, staccato) indicated in the tab. This will help you add musicality and interpret the piece more accurately.
- Ask for help when needed: If you come across a challenging section or have difficulty understanding a specific notation, don’t hesitate to seek assistance. Utilize online forums, instructional books, or consult with a music teacher to clarify any confusion.
By implementing these tips and diligently practicing, you will gradually improve your ability to read tab sheet music fluently. Remember, reading tab is a valuable skill that can open up a vast repertoire of songs and allow you to express yourself musically on your chosen instrument.
Exercises and Practice Tips
To enhance your proficiency in reading tab sheet music and improve your overall playing skills, practicing regularly is crucial. Here are some exercises and practice tips to help you develop your abilities:
- Start with simple melodies: Begin by practicing simple melodies or single-note exercises from songs you enjoy. This will help you get comfortable with reading tab and coordination between your fingers.
- Focus on accuracy over speed: When practicing, prioritize accuracy and precision in your playing rather than speed. Gradually increase the tempo as you build confidence, ensuring that every note is clear and clean.
- Break challenging sections into smaller parts: If you encounter a challenging section in a song, break it down into smaller segments and practice each part separately. Once you’ve mastered each segment, gradually piece them together.
- Use a metronome: Incorporate a metronome into your practice routine to develop a sense of timing and improve your ability to play in-sync with a beat. Start at a slow tempo and gradually increase it as you become more comfortable.
- Focus on technique: Pay attention to your technique while practicing. Ensure that your fingers are pressing down the strings cleanly and that your hand and arm positions are comfortable and relaxed.
- Practice scales and exercises: Dedicate some time to practice scales, arpeggios, and technical exercises tailored to your instrument. They will strengthen your fingers, improve your fingerboard knowledge, and enhance your overall dexterity and coordination.
- Transcribe songs by ear: Challenge yourself by transcribing songs you love by ear. This exercise helps you develop your listening skills, musical memory, and the ability to recognize patterns and melodies on your instrument.
- Experiment with different genres and styles: Explore various genres and styles of music to expand your musical horizons and improve your versatility. The more diverse your repertoire, the more comfortable you’ll become in reading different types of tab sheet music.
- Record and analyze your playing: Record yourself playing and listen back to identify areas for improvement. Pay attention to timing, dynamics, and clarity of notes. Analyzing your playing will help you identify strengths and weaknesses, guiding your practice sessions more effectively.
- Consistency is key: Consistent practice is essential for progress. Aim for regular, focused practice sessions rather than sporadic, lengthy practices. Even short daily practice sessions can yield significant results over time.
Remember, progress takes time, patience, and dedication. Celebrate your achievements, no matter how small, and enjoy the process of learning and growing as a musician. With consistent practice and a positive mindset, you will continue to improve your reading skills and musical capabilities.
Conclusion
Learning to read tab sheet music opens up a world of possibilities for musicians who play fretted instruments like the guitar, bass, or ukulele. It provides a simplified and accessible way to learn and play a wide range of songs without the need for extensive knowledge of traditional notation.
In this article, we explored the fundamentals of reading tab sheet music, including understanding symbols, finger placements, and common techniques. By familiarizing yourself with these elements and practicing regularly, you can develop your ability to read tab and accurately reproduce songs on your instrument.
Remember, reading tab sheet music is a skill that requires time, patience, and practice to master. Start with simple songs and exercises, gradually progress to more complex pieces, and experiment with different styles and genres. Use additional resources and seek guidance when needed to further enhance your understanding and technique.
By honing your reading skills and incorporating musical expression and dynamics into your playing, you can bring tab sheet music to life and make the music uniquely yours.
So, take your instrument, grab some tab sheet music, and start exploring the vast world of songs that await you. Enjoy the journey, embrace the challenges, and let the tabs guide you on your musical adventure.