Home>Instruments>Percussion Instruments>Which One Of These Percussion Instruments Is Not Part Of A Standard Drum Set Drum Kit Apex


Percussion Instruments
Which One Of These Percussion Instruments Is Not Part Of A Standard Drum Set Drum Kit Apex
Modified: February 9, 2024
Discover which percussion instrument is not typically found in a standard drum set. Explore the Apex selection of drum kits and find the perfect set for your musical needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
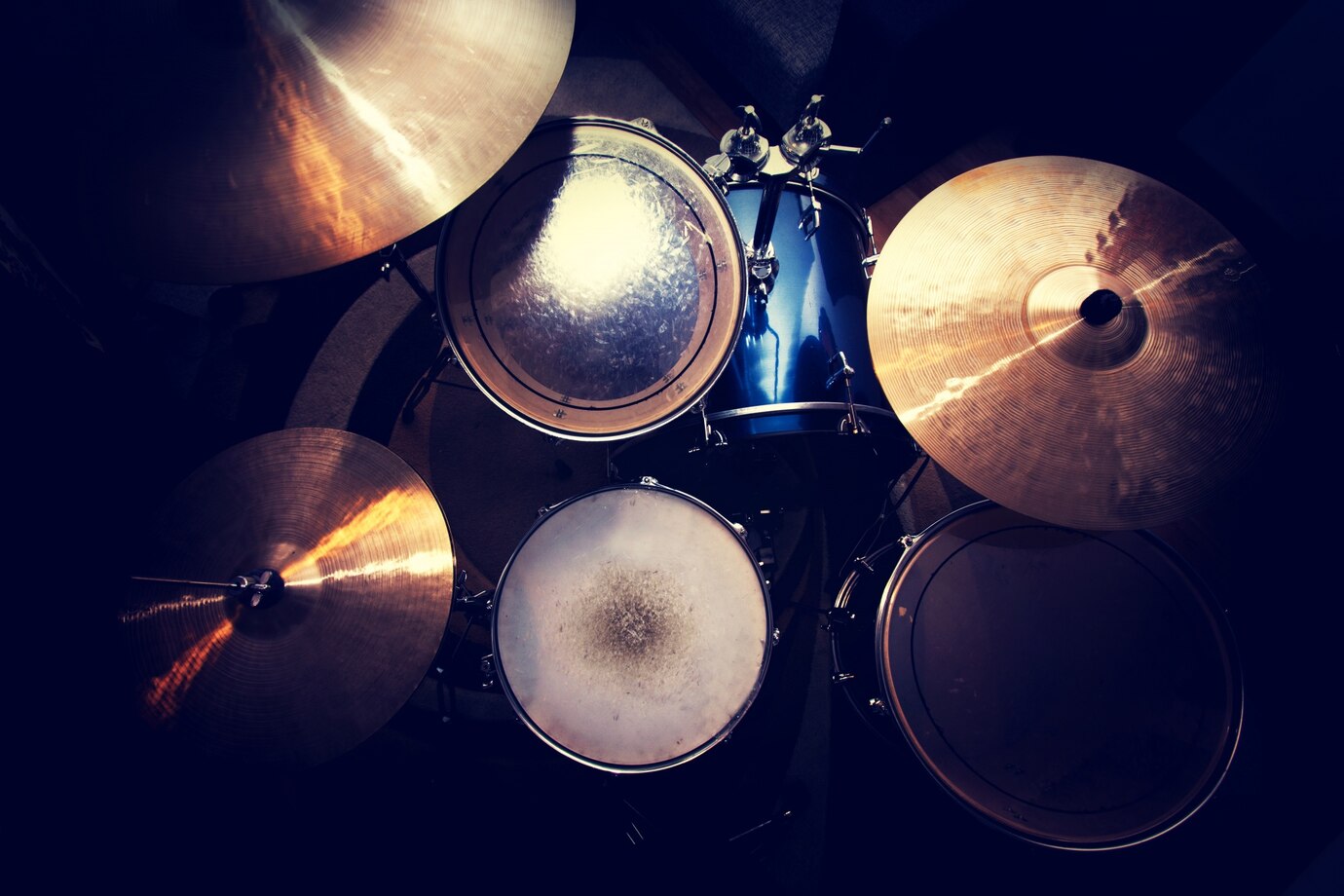
When it comes to creating rhythmic and melodic texture, percussion instruments play a vital role. Among the wide array of percussive instruments available, the drum set, also known as a drum kit, stands out as one of the most popular and versatile options. A standard drum set consists of various components that work together to produce a rich and dynamic sound.
In this article, we will explore the different percussion instruments that make up a standard drum set and delve into their individual characteristics. From the deep thump of the bass drum to the crisp crack of the snare drum, each instrument plays a distinct role in creating the groove and driving the music forward.
We will discuss the components that are commonly found in a drum kit, including the bass drum, snare drum, tom-toms, hi-hat, ride cymbal, crash cymbal, and floor tom. These instruments come together in harmony, allowing drummers to express their creativity and provide the backbone for a wide range of musical genres, from rock and pop to jazz and funk.
Additionally, we will identify the percussion instrument that is not part of a standard drum set. While drum kits are versatile and diverse, there is one instrument that stands alone in its distinctive sound and purpose.
So let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of percussion instruments and the important role they play in creating rhythm and groove in music.
Percussion Instruments in a Standard Drum Set
A standard drum set consists of several percussion instruments that work together to create the distinct sound and rhythm that we associate with drums. Each instrument has its own unique characteristics and purpose, allowing drummers to express themselves and enhance the overall musical experience.
The main percussion instruments commonly found in a standard drum set are:
- Bass Drum
- Snare Drum
- Tom-Toms
- Hi-Hat
- Ride Cymbal
- Crash Cymbal
- Floor Tom
Let’s explore each of these instruments in more detail:
Bass Drum
The bass drum, also known as the kick drum, is the largest drum in the drum set. It is played using a foot pedal and produces a deep, low-pitched sound. The bass drum provides the foundation and pulse of the music, creating a solid rhythm that drives the music forward.
Snare Drum
The snare drum is a versatile and essential part of the drum kit. It is characterized by its distinctive snappy sound, which is produced by a set of metal wires called “snares” that vibrate against the drumhead when it is struck. The snare drum adds a sharp and crisp attack to the overall sound and is often used to accentuate certain beats or create intricate rhythms.
Tom-Toms
The tom-toms are cylindrical drums of varying sizes that are mounted on the drum set. They produce a melodic and resonant tone when struck with drumsticks. The tom-toms are used to create fills, rolls, and dynamic variations, adding texture and depth to the music.
Hi-Hat
The hi-hat is a pair of cymbals mounted on a stand and operated by a foot pedal. By pressing the foot pedal, the cymbals can be brought together or separated to create open or closed sounds. The hi-hat is played with drumsticks, brushes, or even by using the foot pedal alone. It provides a steady rhythmic pattern and is often used to create a driving groove.
Ride Cymbal
The ride cymbal is a large, suspended cymbal that produces a clear and ringing sound when struck with a drumstick or brushes. It is used to create a constant ride pattern or to accentuate specific beats or musical phrases. The ride cymbal adds a shimmering and sustained tone to the music.
Crash Cymbal
The crash cymbal is a large, thin cymbal that produces a loud and explosive sound when struck. It is used to create dramatic accents, fill sections, or mark transitions in the music. The crash cymbal adds a powerful and impactful element to the drum set.
Floor Tom
The floor tom is a larger version of the tom-tom that is placed on the floor using tripod legs. It produces a deep and booming sound when struck and is often used to add a powerful low-end to the drum pattern.
These percussion instruments work together in harmony, allowing drummers to create a wide range of sounds and rhythms. They provide the backbone of the music, establishing the groove and driving the energy of the performance.
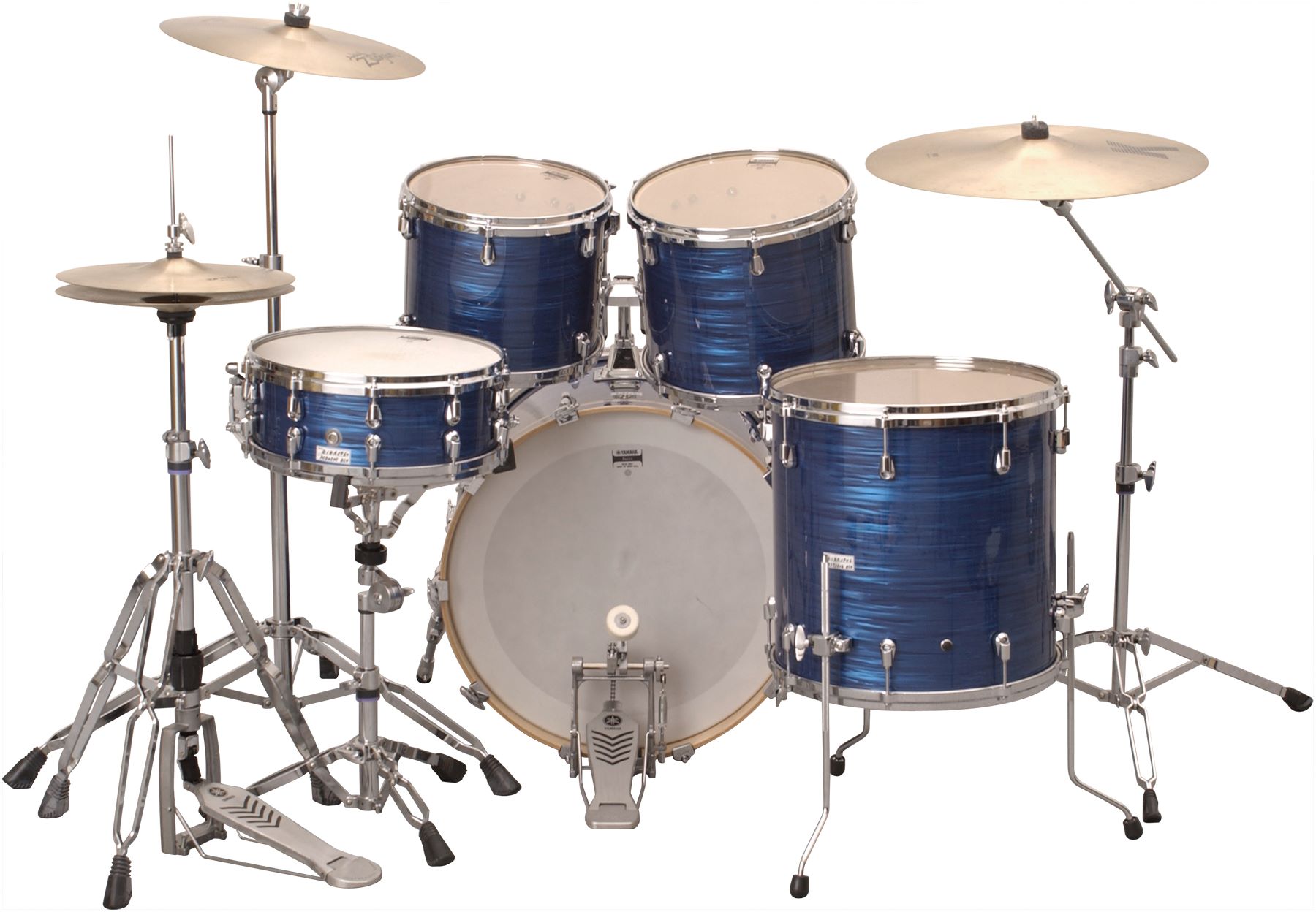
Common Components of a Drum Kit
A drum kit, also known as a drum set, is a collection of percussion instruments that are arranged to be played simultaneously by a single drummer. While the specific arrangements and configurations of drum kits can vary, there are several common components that can be found in most setups.
Let’s take a closer look at the common components of a drum kit:
- Bass Drum: The bass drum is typically the largest drum in a drum kit. It is played using a foot pedal and produces a deep and resonant sound. The bass drum provides the foundation and pulse of the music, creating a solid rhythmic backbone.
- Snare Drum: The snare drum is an essential part of the drum kit. It is often positioned between the drummer’s legs and has a set of wires called snares stretched across the bottom drumhead. When the top drumhead is struck, the snares vibrate, creating a distinct snappy sound. The snare drum is versatile and can produce a wide range of tones, making it a vital component for accenting beats and adding dynamics to the music.
- Tom-Toms: Tom-toms are cylindrical drums that come in different sizes and are positioned above the bass drum and to the right of the snare drum. They are played with drumsticks and produce a melodic tone. Drummers use the tom-toms to create fills, rolls, and expressive patterns that add texture and variation to their playing.
- Hi-Hat: The hi-hat consists of a pair of cymbals mounted on a stand and operated by a foot pedal. By pressing the foot pedal, the cymbals can be brought together or separated to create open or closed sounds. The hi-hat is a fundamental component for establishing a steady rhythm and is often played with drumsticks, brushes, or even just the foot pedal alone.
- Ride Cymbal: The ride cymbal is a large, suspended cymbal that produces a clear and sustained tone. It is typically positioned on the right side of the drum set and is played with a drumstick or brushes. The ride cymbal is used to create a steady pattern or to accent beats and phrases, providing a shimmering and rhythmic texture to the music.
- Crash Cymbal: The crash cymbal is a larger, thin cymbal that produces a loud and dramatic sound when struck. It is often positioned above the drum kit and is used to add power, emphasis, and excitement to the music. Drummers use the crash cymbal to punctuate important moments, transitions, or to create dynamic fills.
- Floor Tom: The floor tom is a larger version of the tom-tom, placed on the floor using tripod legs. It produces a deep and booming sound, adding a powerful low-end element to the drum kit. Drummers often use the floor tom to create dramatic accents and to add weight to the overall sound.
These common components of a drum kit are carefully arranged to provide a versatile and expressive platform for drummers to showcase their skills and creativity. By mastering the coordination and technique required to play these instruments, drummers can create dynamic rhythms and contribute to the overall sound and feel of a musical performance.
The Bass Drum
The bass drum, also known as the kick drum, is a fundamental component of a standard drum set. It is the largest drum in the kit and is typically placed on the floor and played with a foot pedal. The bass drum produces a deep and resonant sound that provides the foundation and pulse of the music.
Characterized by its low-pitched thump, the bass drum is responsible for creating a solid rhythmic backbone in various musical genres. Its booming sound adds power and impact to the overall drumming performance.
Drummers use a foot pedal attached to the bass drum to strike the drumhead. By stepping on the pedal, a beater attached to it hits the drumhead, creating the desired sound. The technique and control required to play the bass drum effectively is crucial for drummers to maintain a steady beat and drive the music forward.
The bass drum is commonly played on the downbeat, providing a strong emphasis and drive to the rhythm. However, drummers can also incorporate techniques such as double bass drumming, where both feet are used to play fast and intricate patterns, adding speed and complexity to their playing. This technique is often utilized in genres like rock, metal, and fusion.
In addition to providing rhythm, the bass drum is also used for dynamic expression. By varying the intensity of the strike and the damping of the drumhead, drummers can create a range of tonal variations. They can achieve a booming and full-bodied sound by allowing the drumhead to resonate or produce a shorter and punchier tone by quickly dampening the drumhead with a mallet or their foot.
Furthermore, the bass drum can be creatively combined with other drum kit components to create unique patterns and textures. Drummers often synchronize their bass drum hits with accents played on the cymbals or use it to punctuate specific musical phrases and transitions.
Overall, the bass drum is an essential element of a drum set, providing the solid foundation and rhythmic drive that is crucial for any musical performance. From providing a steady beat to adding power and impact, the bass drum is a versatile instrument that plays a vital role in shaping the sound and feel of a drummer’s performance.
The Snare Drum
The snare drum is a central and iconic component of a standard drum set. Positioned between a drummer’s legs, the snare drum is easily distinguishable by its distinctive snares – a set of metal wires that are stretched across the bottom drumhead.
Known for its sharp and snappy sound, the snare drum adds a unique character to the overall drum kit. When the top drumhead is struck, the snares vibrate against the bottom drumhead, creating a distinct buzzing sound that is instantly recognizable.
The versatility of the snare drum is one of its defining features. It is capable of producing a wide range of tones, from a crisp crack to a deep, resonant thud, depending on how it is played and tuned.
Drummers can vary their technique to achieve different sounds from the snare drum. Traditional playing involves striking the drumhead with a drumstick, creating a sharp and focused attack. Brushes can be used for a softer and more delicate sound, perfect for jazz and ballads. Rimshots, where the drumstick strikes both the drumhead and the rim simultaneously, produce a loud and explosive sound that cuts through the mix.
The snare drum also plays a critical role in accenting beats and adding dynamics to the music. Drummers often use the snare drum to create accents, fills, and rolls, injecting excitement and energy into their playing. Its sharp sound cuts through the mix and helps to drive the rhythm and pulse of the music.
Tuning is an important aspect of snare drum performance. By adjusting the tension of the drumhead, drummers can achieve different sounds and characteristics. Higher tension produces a brighter and more focused sound, ideal for crisp and articulate snare hits. Lower tensions create a deeper and more resonant tone, perfect for creating a warm and fat snare sound.
Overall, the snare drum is a versatile and essential tool for drummers. Its distinctive sound and ability to add accents, dynamics, and texture make it a vital component of any drum set. The snare drum’s presence and impact ensure that it stands out in any musical performance, whether it’s driving a rock anthem or providing subtle embellishments in a jazz composition.
The Tom-Toms
The tom-toms are an integral part of a standard drum set, adding depth and variety to the overall sound. These cylindrical drums come in various sizes and are positioned above the bass drum and to the right of the snare drum.
Tom-toms are played using drumsticks, and their distinct sound provides drummers with the opportunity to create melodic and rhythmic patterns, adding complexity and texture to their playing.
Depending on the number of tom-toms in a drum kit, they can be categorized as rack toms (smaller and mounted on the drum set) or floor toms (larger and placed on the floor using tripod legs).
Drummers utilize the tom-toms to produce fills, rolls, and dynamic variations within a piece of music. They can vary the pitch and tonality by striking different parts of the drumhead or using different playing techniques.
The high tom-toms produce a brighter and higher-pitched sound, while the low tom-toms produce a deeper and more resonant tone. By combining different tom-toms and playing patterns across them, drummers can create intricate and captivating drum fills.
Tom-toms also provide drummers with the opportunity for creative expression and improvisation. They can experiment with different rhythms and patterns, syncing them with other components of the drum kit to enhance the overall groove and feel of the music.
Furthermore, drummers may tune their tom-toms to achieve the desired sound. Higher tension results in a brighter and more focused tone, while lower tension produces a warmer and more resonant sound. Tuning the tom-toms appropriately allows drummers to blend and balance the overall sound of the drum kit.
In addition to their rhythmic and melodic functions, the tom-toms can be used for accentuating specific musical phrases and creating dramatic moments in a drum performance. Drummers often execute powerful, repeated strikes on the tom-toms, creating a climactic buildup or adding impact to a musical transition.
Overall, the tom-toms play a vital role in creating depth, movement, and expression in a drum set. With their wide range of tonal possibilities and versatility, these drums allow drummers to showcase their creativity and add a captivating element to their playing.
The Hi-Hat
The hi-hat is a crucial component of a standard drum set, providing a versatile and dynamic sound that enhances the overall rhythm and groove. It consists of a pair of cymbals mounted on a stand and operated by a foot pedal.
The hi-hat cymbals are typically made of metal and have a diameter ranging from 12 to 15 inches. They can be brought together or separated by pressing and releasing the foot pedal, creating a range of sound textures and expressions.
The hi-hat’s primary function is to establish and maintain the beat and rhythm of a song. Its characteristic sound is achieved by closing the cymbals tightly, resulting in a crisp and defined ‘chick’ sound when struck with drumsticks or brushes. The closed position produces a short and muted sound, which is useful for accenting specific beats or creating a tight rhythmic pattern.
By partially opening the hi-hat cymbals with the foot pedal, drummers can produce a ‘half-open’ sound that adds a sense of airiness and depth to the play. This technique creates a sustained and more resonant tone, perfect for creating a groove or providing a steady rhythmic pattern.
Opening the hi-hat cymbals fully results in a ‘crash’ sound, similar to that of a crash cymbal. This technique is often used for dramatic accents or to mark transitions in a song. The crash sound adds intensity and impact to a drum performance, just like a punctuation mark in a sentence.
The hi-hat cymbals are played not only with the foot pedal but also with drumsticks or brushes. Drummers can create a variety of intricate rhythmic patterns by alternating between the hi-hat and other drum kit components, such as the snare drum or tom-toms. The hi-hat can be played in conjunction with other cymbals or independently to add complexity and depth to a drumming performance.
Furthermore, drummers can employ various playing techniques on the hi-hat to expand their creative options. They can incorporate foot splashes, where the foot pedal is pressed momentarily to produce a quick and accentuated sound. They can also execute ‘chick’ sounds while simultaneously striking the hi-hat with drumsticks, adding further complexity and texture to their rhythm.
The hi-hat’s ability to produce a wide range of sounds and its essential role in establishing the beat and groove make it an indispensable instrument in drumming. From providing a steady rhythm to creating dynamic accents and textures, the hi-hat adds depth and character to any drum set.
The Ride Cymbal
The ride cymbal is a key component of a standard drum set, providing a distinct and versatile sound that enhances the overall rhythm and musicality. It is a large suspended cymbal, typically positioned on the right side of the drum set.
Characterized by its clear and sustained tone, the ride cymbal is a fundamental part of creating the groove and texture in a drumming performance. It is played with a drumstick or brushes, producing a shimmering sound that adds depth and complexity to the music.
The primary function of the ride cymbal is to maintain a steady pattern or rhythm throughout a piece of music. It is commonly played in a consistent motion, creating a constant ride pattern that serves as a foundation for the other drum kit components.
Drummers can vary their playing technique to achieve different sounds and dynamics from the ride cymbal. Playing closer to the cymbal’s bell produces a more defined and focused tone, while playing towards the outer edge results in a fuller and more resonant sound.
The ride cymbal is not limited to providing a rhythmic foundation. Its unique sound allows drummers to accentuate specific beats or musical phrases, adding dynamic accents and nuances to their playing. By strategically incorporating ride cymbal accents, drummers can highlight musical transitions or create suspense and intensity within a drumming performance.
In addition to its role in creating rhythm and accents, the ride cymbal can also be used for improvisation and expression. Drummers can execute intricate and complex patterns on the ride cymbal, utilizing different sticking techniques and rhythms to add flair and personality to their playing.
Another technique often employed on the ride cymbal is the “ride bell.” By striking the small rounded portion in the center of the cymbal, drummers can produce a distinct and piercing sound that cuts through the mix and adds emphasis to specific musical moments or sections. This technique is commonly used for climactic buildups or dramatic endings in drum performances.
In summary, the ride cymbal is a versatile and essential component of a drum set, offering a clear and sustained tone that helps to establish the groove and texture of the music. Its ability to provide a steady pattern, add dynamic accents, and facilitate improvisation makes it a valuable instrument for drummers to express their creativity and contribute to the overall musical experience.
The Crash Cymbal
The crash cymbal is a vital component of a standard drum set, adding power, impact, and excitement to drumming performances. It is a large and thin cymbal that produces a loud and explosive sound when struck.
Positioned above the drum set, the crash cymbal serves as a sonic punctuation mark, marking important moments, transitions, and accents in a musical piece. It is often used to create dramatic emphasis, fill sections, or add dynamic flair to a drumming performance.
When struck with a drumstick, the crash cymbal resonates with a powerful and sustained crash sound that cuts through the mix. The sound produced can vary depending on where the cymbal is struck – hitting closer to the edge results in a brighter and more shimmering sound, while striking near the center produces a darker and more explosive tone.
Drummers can utilize different techniques to produce a variety of effects and sounds from the crash cymbal. For example, a choked or quick stop on the cymbal immediately mutes the sound, creating a sudden and dramatic silence. This technique is often employed to create tension or to add a dynamic contrast to a drumming performance.
In addition to its primary role as an accentuating instrument, the crash cymbal can also be used to create musical textures and effects. By scraping a drumstick or another object along the surface of the cymbal, drummers can produce a haunting and eerie sound that adds a distinctive character to their playing.
It is worth noting that crash cymbals come in a range of sizes, each producing a slightly different sound. Smaller crashes offer a quick and focused attack, while larger crashes produce a deeper and more sustained resonance. Drummers often select crash cymbals based on the desired sound characteristics and how they blend with the other components of the drum set.
The crash cymbal can be used alongside other drum kit components to enhance the overall impact and energy of a performance. Drummers often coordinate crash hits with bass drum strokes or use them to punctuate specific musical phrases, creating a cohesive and dynamic sound.
Overall, the crash cymbal is a vital instrument in a drum set, providing dramatic accents, dynamic contrasts, and powerful punctuation to drumming performances. Its explosive sound and ability to add impact and excitement make it an essential tool for drummers to express their musicality and elevate the energy of a musical piece.
The Floor Tom
The floor tom is an important component of a standard drum set, adding depth and resonance to the overall sound. It is a larger version of the tom-tom, placed on the floor using tripod legs.
Positioned to the right side of the drummer, the floor tom produces a deep and booming sound when struck. Its low-pitched tone adds a powerful and impactful element to the drum set, enhancing the overall rhythm and groove of the music.
Drummers play the floor tom with drumsticks, striking the drumhead to produce the desired sound. By varying the velocity and angle of the strikes, drummers can create a range of tonal variations and dynamics.
The floor tom is often used to add weight and depth to a drum pattern. It provides a solid and resonant foundation, reinforcing the rhythm set by the bass drum and providing a rich low-end presence.
In addition to its role in providing a steady beat, the floor tom can also be used for creative expression. Drummers can perform fills, rolls, and patterns on the floor tom, adding complexity and variation to their playing. The deep and thunderous sound of the floor tom adds a dramatic element, enhancing musical phrases and transitions.
Like other drums in a drum set, the floor tom can be tuned to achieve different pitch and tonality. Adjusting the tension of the drumhead affects the resonance and depth of the sound produced. Higher tension results in a brighter and more focused tone, while lower tension produces a fuller and more boomy sound.
The placement of the floor tom within the drum set arrangement also influences its sound and accessibility. Drummers can position the floor tom at different heights and angles to suit their playing style and comfort, allowing for seamless integration into their drumming technique.
The floor tom can be expertly combined with other components of the drum set to create dynamic and engaging rhythms. Drummers often coordinate their floor tom strikes with other drum hits, cymbal crashes, or accentuated beats, adding depth and complexity to the drumming performance.
In summary, the floor tom is a significant and impactful element of a drum set. Its deep and resonant sound contributes to the overall rhythm and groove of the music, providing a solid foundation and adding dramatic flair to drumming performances.
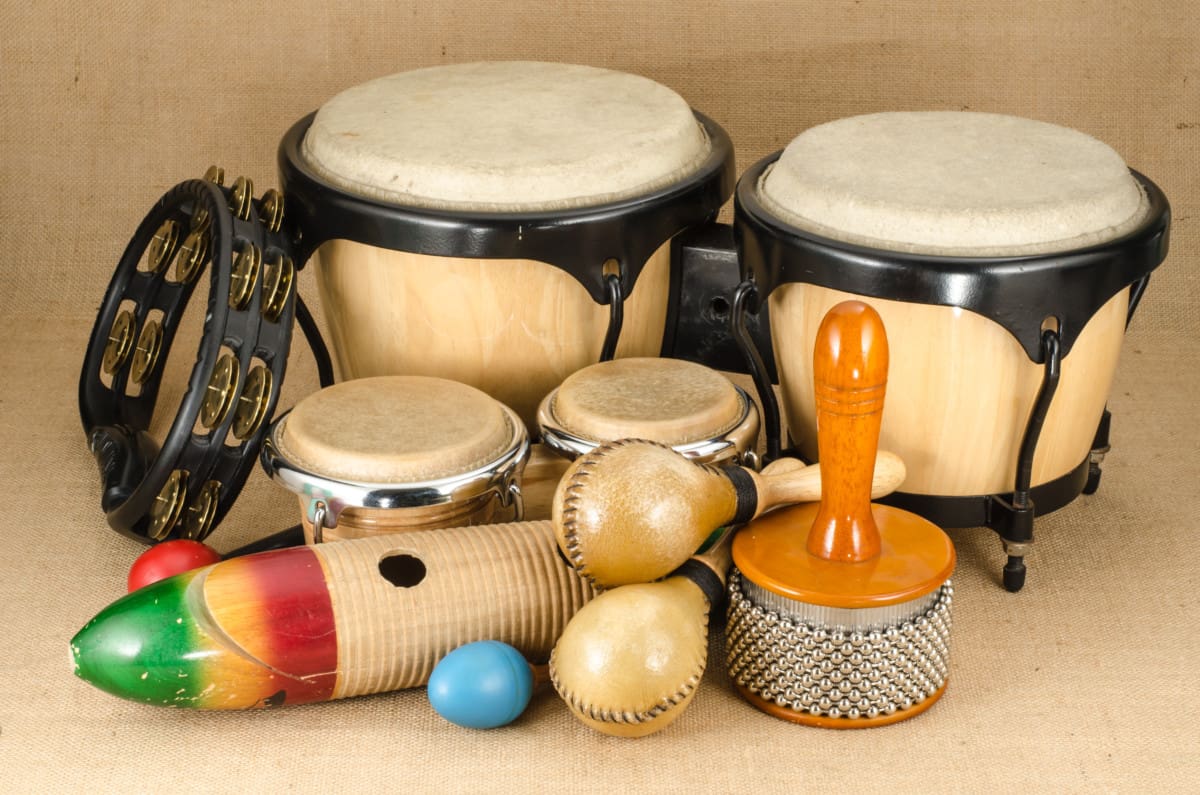
The Percussion Instrument That Is Not Part of a Standard Drum Set
While a standard drum set consists of various percussion instruments that work harmoniously together, there is one percussion instrument that typically stands alone and is not part of the traditional drum kit: the tambourine.
The tambourine is a handheld percussion instrument that consists of a circular frame with small metal jingles, or zils, attached to it. It is played by striking the drumhead with the hand or shaking it to create a jingling sound.
The tambourine adds a bright and shimmering texture to music and is often used in a wide range of genres, including folk, rock, pop, and world music. Drummers and percussionists use the tambourine to provide accents, fill sections, and add a tinge of percussive color to their performances.
Unlike the components of a standard drum set, the tambourine does not have a designated position or mount on the drum set. Instead, it is held in the hand and played independently or alongside other percussion instruments.
With its versatile and portable nature, the tambourine allows drummers and percussionists to incorporate it into their performances in various ways. They can play the tambourine using their free hand while keeping the beat on the drum set, or they can use it as a standalone instrument to create rhythmic patterns and textures.
Drummers often utilize the tambourine in sections of a song where an extra layer of movement and rhythmic embellishment is desired. Its jingly sound can provide a vibrant backdrop to a chorus or add a touch of excitement to a musical break.
Furthermore, the tambourine’s versatile playing techniques allow for creativity and improvisation. Drummers can experiment with different striking and shaking patterns, incorporating the tambourine into their drumming style to add a unique and expressive element to their performances.
While not a standard component of a drum set, the tambourine’s distinct sound and versatility make it a valuable addition to any percussionist’s toolkit. Its ability to enhance the musical experience with its jingling accents and rhythmic ornamentation showcases the wide range and diversity of percussion instruments beyond the traditional drum set.
Conclusion
Percussion instruments are the driving force behind rhythmic expression and musicality. In the realm of percussion instruments, the drum set, or drum kit, stands out as a versatile and dynamic ensemble of instruments. From the deep thump of the bass drum to the sharp crack of the snare drum, each component plays a vital role in shaping the overall sound and feel of a drumming performance.
In this article, we have explored the various percussion instruments that make up a standard drum set, including the bass drum, snare drum, tom-toms, hi-hat, ride cymbal, crash cymbal, and floor tom. These instruments work together in harmony, creating a wide range of sounds and textures that allow drummers to express their creativity and drive the music forward.
Additionally, we have highlighted the tambourine as a percussion instrument that stands alone and is not typically part of a standard drum set. The tambourine adds a distinct jingling sound and serves as a colorful accompaniment to the drum kit, enhancing the rhythm and texture of a musical performance.
Whether it’s the powerful thump of the bass drum, the snappy attack of the snare drum, or the shimmering resonance of the cymbals, each instrument in a standard drum set contributes to the overall musical experience. Drummers use their technical skills, creativity, and musical intuition to bring these instruments to life, creating captivating rhythms and providing the foundation for various genres of music.
In conclusion, percussion instruments, especially those found in a standard drum set, are essential in shaping the rhythm, groove, and energy of a musical composition. Through their intricate interplay and the drummer’s artistry, these instruments ignite the primal instinct to move, groove, and connect with the power of rhythm.