Home>Production & Technology>Composer>Early Romantic Music Was Influenced By Which Composer?


Composer
Early Romantic Music Was Influenced By Which Composer?
Published: December 6, 2023
Discover which composer influenced early romantic music and shaped the movement with his innovative compositions. Uncover the musical genius behind this influential era.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to the evolution of classical music, the Romantic era holds a special place. This period, which spanned roughly from the late 18th to the early 19th century, witnessed a profound shift in musical expression and aesthetics. The music of this era is characterized by heightened emotions, evocative melodies, and a departure from the formal structures of the preceding Classical period.
One of the key factors that shaped Early Romantic music was the influence of composers who thrived during this period. While multiple composers contributed to the development of the Romantic style, one composer stands out as a seminal figure whose impact reverberated throughout the musical landscape.
In this article, we will delve into the background of Early Romantic music, explore the influences that shaped this genre, and examine the profound impact of one particular composer on its development.
So, what made Early Romantic music so distinctive? Let’s explore this captivating era and discover the composer who left an indelible mark on its evolution.
Background of Early Romantic Music
The Early Romantic period emerged as a reaction to the order and restraint of the Classical era. Composers sought to break free from the rules and structures that had defined music for centuries and instead focus on expressing powerful emotions and personal experiences.
During this time, there was a growing fascination with nature, the supernatural, and the inner workings of the human mind. Composers aimed to capture these themes through their music, creating works that were often characterized by dramatic contrasts, intense emotions, and a sense of individualism.
While the Classical period was marked by meticulous craftsmanship and adherence to established forms, Early Romantic composers aimed to bring a more personal and subjective approach to their music. They experimented with new musical forms, expanded orchestras, and incorporated innovative techniques to evoke specific emotions and narratives.
The Early Romantic period also witnessed a change in the way music was consumed. With the Industrial Revolution and the rise of the middle class, there was an increase in the number of public concerts and a growing demand for music outside of the aristocratic court. This shift allowed composers to reach a wider audience and receive recognition and support from patrons and music lovers.
Furthermore, technological advancements, such as the invention of the piano and improvements in music printing, enabled composers to explore new possibilities in composition and share their works more widely.
It is important to note that while the term “Early Romantic” is used to describe the period as a whole, there were distinct regional differences in style and approach. For example, German composers, such as Ludwig van Beethoven and Franz Schubert, emphasized individual expression and the power of the human spirit. In contrast, French composers like Hector Berlioz and Frédéric Chopin focused on poetic and atmospheric elements in their compositions.
With this broader understanding of the background of Early Romantic music, we can now explore the influences that shaped this genre and paved the way for its development.
Influences on Early Romantic Music
Early Romantic music was greatly influenced by a variety of factors and artistic movements that shaped the musical landscape of the time. These influences helped to drive the creative exploration and innovation that defined the era.
One notable influence on Early Romantic music was the literary movement known as Romanticism. Romantic writers and poets, such as William Wordsworth, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, and Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, emphasized individual expression, emotional intensity, and a deep connection to nature. Composers took inspiration from these literary works, infusing their music with a similar sense of passion, imagination, and freedom.
In addition to literature, the visual arts also played a significant role in shaping Early Romantic music. The art movements of the time, such as Romantic painting and the Gothic revival, emphasized the sublime, the mysterious, and the supernatural. Composers sought to capture these visual elements in their music, creating pieces that were often characterized by rich harmonies, dynamic contrasts, and evocative imagery.
Furthermore, the political and social changes of the era had a profound impact on Early Romantic music. The French Revolution and the subsequent Napoleonic Wars disrupted the established order and led to a sense of upheaval and a desire for freedom. This spirit of revolution and nationalism found its way into the music of composers such as Ludwig van Beethoven, who used his music to express his political and social ideals.
Another significant influence on Early Romantic music was the exploration of exotic cultures and musical traditions. Composers often drew inspiration from folk music, incorporating elements of regional and national styles into their compositions. This infusion of diverse musical influences added depth and richness to the evolving Romantic repertoire.
Lastly, the advancements in music technology during the Early Romantic period played a pivotal role in shaping the music of the time. The development of new instruments, such as the piano and the valve system for wind instruments, expanded the range and expressive capabilities of the orchestra. Composers eagerly embraced these innovations, pushing the boundaries of what was musically possible.
These various influences converged to create a vibrant and diverse musical landscape during the Early Romantic era. Composers were inspired by literature, painting, social changes, cultural exploration, and technological advancements, all of which contributed to the unique and transformative music of this period.
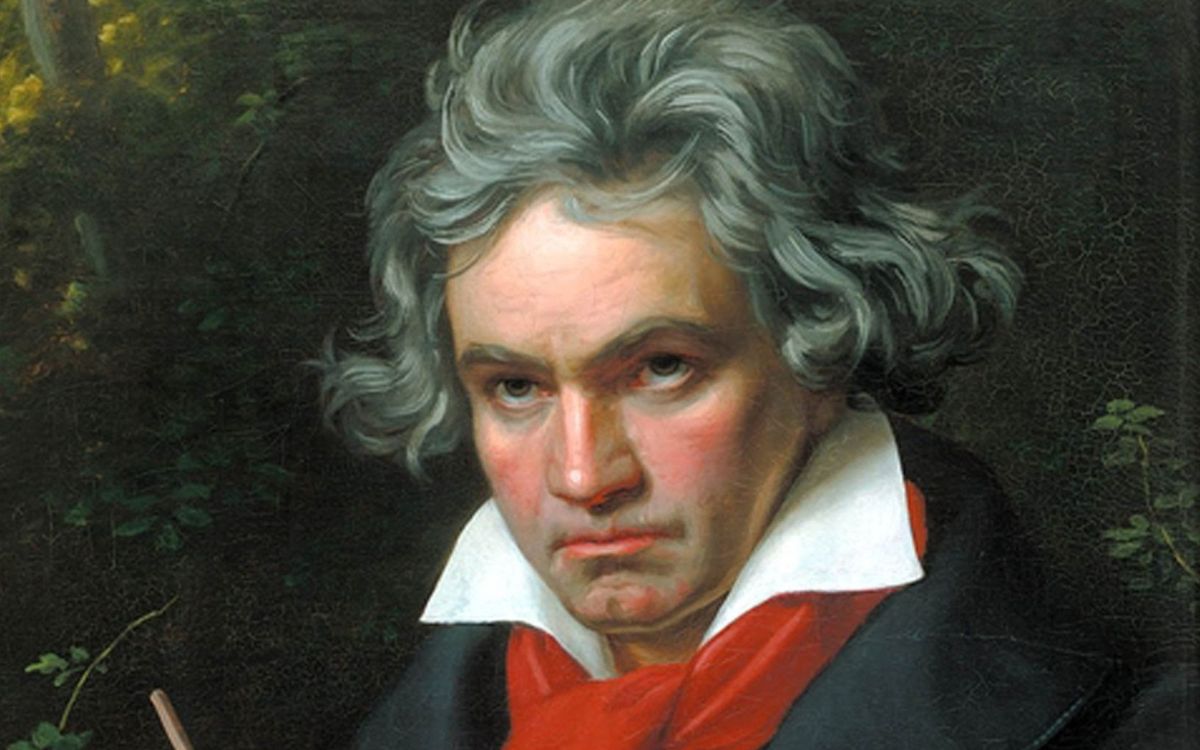
The Impact of Ludwig van Beethoven on Early Romantic Music
When discussing the impact of a key composer on Early Romantic music, it is impossible to overlook the profound influence of Ludwig van Beethoven. Beethoven’s innovative compositions and adventurous spirit not only encapsulated the spirit of the Romantic era but also set the stage for the development of music in the years to come.
Beethoven’s music heralded a new era of individualism and emotional depth. He bridged the gap between the Classical and Romantic periods, pushing the boundaries of musical expression and forever changing the trajectory of Western music.
One of Beethoven’s most revolutionary contributions was his expansion of musical forms. In his symphonies, sonatas, and concertos, Beethoven introduced bold and dramatic contrasts, unexpected harmonic shifts, and powerful emotional journeys. He transformed the traditional structures of the Classical period, infusing them with a heightened sense of drama and intensity.
Moreover, Beethoven’s music was deeply personal. He used his compositions as a means of expressing his own struggles, triumphs, and inner turmoil. Through his music, he conveyed a sense of raw emotion and authenticity that resonated with audiences then and continues to do so today.
Beethoven’s impact on the orchestral landscape cannot be overstated. He expanded the size and scope of the orchestra, introducing new instruments and demanding a higher level of virtuosity from performers. His symphonies, such as the iconic Ninth Symphony, showcased a grandeur and power that was previously unparalleled.
Furthermore, Beethoven’s approach to music had a profound influence on subsequent composers. His relentless pursuit of artistic vision and uncompromising dedication to his craft inspired generations of musicians to push artistic boundaries and explore new realms of musical expression.
Beethoven’s impact extended beyond his compositions. His unwavering commitment to his ideals and his ability to navigate the challenges of his personal life showcased the power of art and music as a transformative force. He was seen as a symbol of struggle, resilience, and triumph, inspiring countless musicians and artists to view their craft as a vehicle for personal and societal change.
Beethoven’s legacy in the realm of Early Romantic music is immeasurable. His groundbreaking compositions, innovative spirit, and unwavering dedication to his artistic vision set the stage for the development of the Romantic era. His impact continues to be felt in the music of composers who came after him, shaping the course of Western classical music for centuries to come.
Conclusion
The Early Romantic era in music was a transformative period marked by a departure from the structures and conventions of the Classical era and a focus on individual expression, emotional depth, and artistic exploration. Influenced by the literary and visual arts movements of the time, as well as the political and social changes, Early Romantic composers sought to create music that captured the essence of human emotions, nature, and the supernatural.
Within this diverse musical landscape, one composer stood out as a key figure whose impact on Early Romantic music was unparalleled: Ludwig van Beethoven. Beethoven’s innovative compositions and pioneering spirit revolutionized the musical landscape, pushing the boundaries of form, expression, and orchestration.
Beethoven’s music epitomized the transition from the Classical to the Romantic era, bridging the gap with his dynamic and emotionally charged compositions. His expansion of musical forms, emphasis on personal expression, and relentless pursuit of artistic vision set the stage for the development of music in the years to come.
Furthermore, Beethoven’s influence extended beyond his compositions, serving as a symbol of struggle, resilience, and triumph. His unwavering dedication to his art became an inspiration for generations of musicians, propelling them to explore new realms of musical expression and to view music as a powerful force for societal change.
The impact of Beethoven on Early Romantic music cannot be overstated. His legacy continues to shape the course of Western classical music, with countless composers drawing inspiration from his groundbreaking compositions and his unwavering commitment to his artistic ideals.
In conclusion, the Early Romantic era was a time of artistic exploration and innovation in which composers sought to break free from the constraints of the past. The influences that shaped this era, from literary and visual arts movements to political and social changes, converged to create a rich and diverse musical landscape.
Through their bold and emotionally charged compositions, Early Romantic composers captured the essence of the era, pushing the boundaries of musical expression and paving the way for future generations of musicians. And at the forefront of this movement stood Ludwig van Beethoven, whose impact on Early Romantic music remains indelible, forever shaping the course of music history.