Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>What Is A Note In Music Theory


Music Theory
What Is A Note In Music Theory
Published: January 31, 2024
Discover the meaning and importance of notes in music theory. Enhance your understanding of music theory and its fundamental concepts.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Music theory is the foundation that supports the composition, performance, and understanding of music. At its core, it is a system of rules and principles that govern how musical elements like rhythm, melody, and harmony interact. One fundamental element of music theory is the concept of notes.
Notes are the building blocks of music. They are the individual sounds that make up melodies, harmonies, and chords. Understanding the concept of a note is crucial in developing a solid foundation in music theory.
In this article, we will explore the definition of a note, its pitch and duration, the various notations used to represent notes, the different types of notes, and the importance of notes in music theory.
Whether you’re a music student, a musician, or simply curious about the inner workings of music, understanding notes and their role in music theory is essential. So, let’s dive into the world of notes and explore their significance in the realm of music theory.
Definition of a Note
In music theory, a note is defined as a single sound with a specific pitch and duration. It is the fundamental unit of musical composition and performance. A note represents a specific frequency or pitch on the musical scale, and it has a defined duration, which determines how long the sound is held or played.
Notes can be represented by symbols or notations, which allow musicians to read and perform musical compositions. These symbols or notations provide information about the pitch, duration, and other musical elements like dynamics and articulation.
Notes serve as the language of music. They allow composers to express their ideas and emotions and enable musicians to bring those compositions to life through performance. Without notes, the world of music would be devoid of melody, harmony, and rhythm.
It is important to note that a note is not just a single sound but a musical gesture with expressive qualities. Each note carries its own unique characteristics, such as intensity, tone color, and articulation, which contribute to the overall musical interpretation and expression.
Understanding the concept of a note lays the foundation for exploring the intricacies of music theory. By grasping the fundamental nature of a note, musicians and music enthusiasts can begin to decipher the complexities of melodies, harmonies, and musical structures.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what a note is, let’s delve deeper into its pitch and duration, as these two aspects play a crucial role in shaping the musical landscape.
Pitch of a Note
The pitch of a note refers to its perceived highness or lowness of sound. It is determined by the frequency of the vibrations that produce the sound. A higher frequency creates a higher pitch, while a lower frequency produces a lower pitch.
In music theory, pitch is often organized into a system called the musical scale. The most commonly used scale is the Western chromatic scale, which consists of twelve notes. These notes are represented by letter names, starting from A and going up to G, with the inclusion of sharps (#) and flats (b) to indicate higher or lower pitches.
Notes within a musical scale are further divided into octaves. An octave is the distance between one note and another with twice or half the frequency. For example, the note A4 has a frequency of 440 Hz, while the note A5 has a frequency of 880 Hz, which is exactly twice the frequency of A4.
It’s important to note that the pitch of a note is also affected by other factors, such as the instrument producing the sound and the technique of the musician. Different instruments have different ranges and capabilities, which can influence the perceived pitch quality of a note.
Additionally, musicians can manipulate the pitch of a note through techniques like bending (commonly used in string instruments) or altering the embouchure (in wind instruments), adding expressiveness and nuances to their performance.
Understanding the concept of pitch in music theory allows musicians to interpret and perform music accurately. It enables them to distinguish between different notes, melodies, and harmonies, contributing to the richness and depth of musical compositions.
Now that we have explored the pitch of a note, let’s move on to the next aspect: the duration or length of a note, which plays a vital role in shaping the rhythm of music.
Duration of a Note
The duration of a note refers to the length of time the sound is played or held. It determines the rhythmic value of a note and plays a crucial role in shaping the overall rhythm of a musical composition.
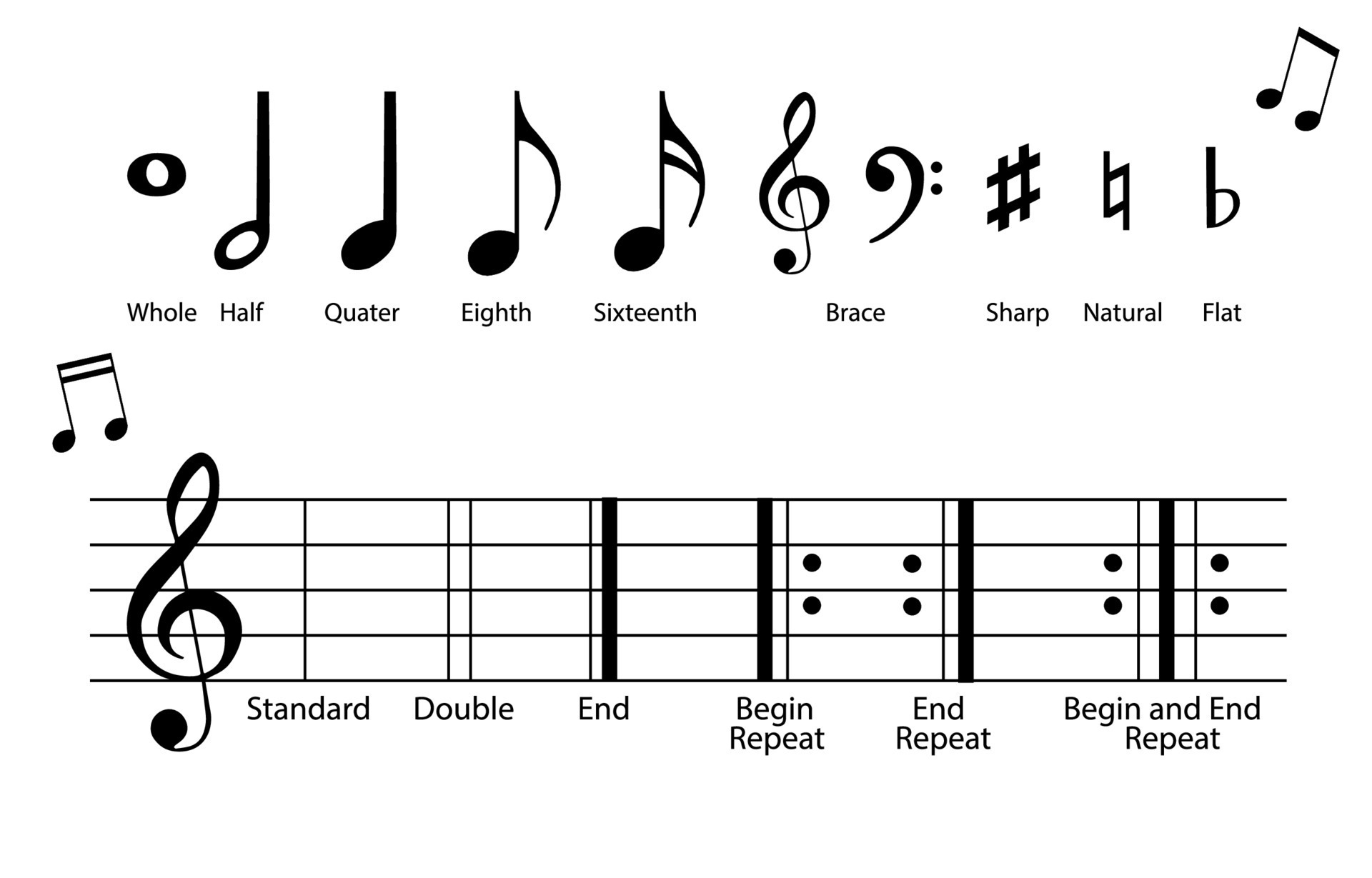
In music notation, the duration of a note is represented by different types of note symbols, each indicating a specific length of time. The most common note values include whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, eighth notes, and sixteenth notes. These note values are divided into smaller fractions to further specify the duration, such as triplets or dotted notes.
The duration of a note is relative to the tempo of the music. Tempo refers to the speed at which the music is played, and it is usually indicated at the beginning of a musical piece or section using descriptive terms like “adagio” (slow) or “allegro” (fast). A note with a specific duration will remain the same length regardless of the tempo, but the overall speed at which the notes are played will affect the perceived rhythm.
Rhythmic patterns are created by combining notes with different durations. The relationship between shorter and longer note values produces a sense of musical pulse and rhythmic structure. Understanding the duration of notes is crucial for musicians to accurately interpret and perform rhythmically complex music.
Rests are also an essential aspect of note duration. A rest is a symbol that represents a silence or pause in the music. Rests have the same durations as notes and are written in music notation to indicate specified moments of silence.
The precise and accurate execution of note durations is vital in ensemble playing, as it ensures that all musicians are synchronized and playing together. It also allows for the proper execution of musical phrasing and dynamics.
By understanding the concept of note duration in music theory, musicians can bring life and precision to a composition’s rhythmic structure, contributing to the overall musical expression and impact.
Now that we have explored the pitch and duration of notes, let’s move on to the next section, which focuses on the various notations used to represent notes in music.
Notation of Notes
In music theory, the notation of notes refers to the symbols and markings used to represent musical sounds and their characteristics, such as pitch, duration, dynamics, and articulation. These notations provide a standardized system for musicians to read and perform musical compositions accurately.
The most common form of notation used for notes is the musical staff. The staff consists of horizontal lines and spaces that represent different pitches. Notes are placed on the staff to indicate the specific pitch and duration of the sound to be played.
The pitch of a note is indicated by the vertical placement of the note on the staff. Higher pitch notes are placed on higher lines or spaces, while lower pitch notes are placed on lower lines or spaces. Ledger lines are used to extend the staff when notes fall above or below the standard nine lines and spaces.
The duration of a note is represented by the shape and presence of additional symbols or flags attached to the note. Whole notes are represented by an unfilled oval shape, while half notes are an unfilled oval with a stem. Quarter notes have a filled-in oval shape with a stem, and eighth notes have the same oval shape with a stem and one flag attached. These symbols can be further modified with dots or additional flags to indicate variations in duration.
Other notations used for notes include accidentals, such as sharps (#), flats (b), and naturals (♮), which alter the pitch of a note. Dynamics markings, such as piano (soft) and forte (loud), indicate the volume at which a note should be played. Articulation markings, such as staccato (short and detached) or legato (smooth and connected), indicate how a note is played in terms of its attack and release.
Modern music notation has evolved over centuries and continues to be refined and expanded. There are also alternative notations and tablatures used for specific instruments or genres, such as guitar tablature or drum notations.
Learning and understanding the notation of notes is essential for musicians, as it allows them to read and interpret sheet music accurately. It enables them to translate the written music into actual sound, enabling them to perform compositions as intended by the composer.
Now that we have explored the notation of notes, let’s move on to the different types of notes in music theory.
Types of Notes
In music theory, there are various types of notes that represent different durations and rhythmic values. These notes play a significant role in shaping the rhythm and overall musical structure. Let’s explore some of the most common types of notes:
- Whole Note: A whole note is a note with the longest duration. It is represented by an unfilled oval shape and has no flags or stems attached. A whole note typically lasts for four beats in common time.
- Half Note: A half note is half the duration of a whole note. It is represented by an unfilled oval shape with a stem. A half note typically lasts for two beats in common time.
- Quarter Note: A quarter note is half the duration of a half note. It is represented by a filled-in oval shape with a stem. A quarter note typically lasts for one beat in common time.
- Eighth Note: An eighth note is half the duration of a quarter note. It is represented by a filled-in oval shape with a stem and one flag attached. An eighth note typically lasts for half a beat in common time.
- Sixteenth Note: A sixteenth note is half the duration of an eighth note. It is represented by a filled-in oval shape with a stem and two flags attached. A sixteenth note typically lasts for one-fourth of a beat in common time.
In addition to these basic note types, there are also note variations that further divide the beat and add rhythmic complexity. Examples include triplets, which divide the beat into three equal parts, and dotted notes, which extend the duration of a note by half. These variations add musical variety and interest to compositions.
Furthermore, rests are also considered types of notes in music theory, representing moments of silence or pauses. Rests have corresponding durations that match their note counterparts and are essential for maintaining the rhythmic structure of a piece.
By understanding the different types of notes, musicians can accurately interpret and perform the rhythm of a musical composition. Composers can use these note types creatively to craft rhythmic patterns and express their musical ideas effectively.
Now that we have explored the various types of notes, let’s move on to the importance of notes in music theory.
Importance of Notes in Music Theory
Notes play a crucial role in music theory and are of utmost importance in the understanding, composition, and performance of music. Let’s explore the significance of notes in music theory:
1. Melody and Harmony: Notes form the foundation of melodies and harmonies. Melodies are created by organizing a sequence of notes with specific pitches. These melodies give a composition its recognizable tune and emotional character. Harmonies consist of notes played simultaneously, creating chords and chord progressions that provide depth and richness to the music.
2. Rhythm and Timing: Notes, with their various durations, determine the rhythm and timing of a piece. The arrangement of different note durations creates intricate rhythmic patterns and establishes the tempo and pulse of the music.
3. Communication and Interpretation: Notes serve as a universal language in music. Composers notate their musical ideas using notes, allowing them to communicate their intentions to performers and listeners. Musicians then rely on notes as a guide to interpret and perform the music accurately, ensuring consistency and cohesion among ensemble members.
4. Structure and Form: The organization of notes within a composition contributes to its formal structure. Sections of music are delineated by the arrangement and repetition of specific note patterns, creating verses, choruses, bridges, and other structural components. Notes help shape the overall form and flow of a piece.
5. Expressiveness and Emotion: Notes, with their specific pitches, durations, and nuances, allow musicians to express a wide range of emotions and convey musical ideas. Notes bring life to a composition, enabling performers to infuse their personal interpretations and dynamics, evoking different moods and feelings in the listener.
6. Improvisation and Creativity: Understanding notes gives musicians the freedom to improvise and create their own melodies, harmonies, and solos. Notes serve as a starting point for improvisation, allowing musicians to explore and experiment within the boundaries of the given musical context.
7. Analysis and Study: Notes form the basis for analyzing and studying music. Examining the patterns, relations, and progressions of notes in compositions offers insights into the structure, harmonic progressions, and stylistic elements employed by composers.
8. Musical Literacy: Developing a strong understanding of notes is essential for becoming musically literate. It enables musicians to read sheet music, communicate with other musicians, and collaborate effectively in ensemble settings.
Overall, notes are the fundamental elements of music theory, connecting composers, performers, and listeners. By understanding notes and their significance, musicians can unlock the full potential of their musical abilities, delve into the intricacies of musical compositions, and communicate their artistic vision.
Now that we have explored the importance of notes in music theory, let’s conclude our journey.
Conclusion
In the realm of music theory, notes serve as the building blocks that give life and structure to musical compositions. They represent the pitch, duration, and expressive qualities of sound, allowing musicians to communicate and interpret music effectively. Understanding notes is essential for composers, performers, and music enthusiasts alike.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of a note and its primary components, including pitch and duration. We have also delved into the various notations used to represent notes in sheet music, as well as the different types of notes that form the rhythmic landscape of music.
Notes play a fundamental role in the creation of melody, harmony, and rhythm. They provide the means for communicating musical ideas, expressing emotions, and crafting structured compositions. From the creation of melodies to the development of harmonies, notes enable musicians to express themselves and connect with listeners on a deep level.
Furthermore, notes facilitate the study and analysis of music, allowing for exploration and understanding of musical structures, patterns, and styles. They provide the foundation for musical literacy and enable musicians to engage in improvisation and creative expression.
Therefore, it is crucial for musicians, both aspiring and experienced, to develop a deep understanding of notes and their role in music theory. By doing so, they can enhance their musical abilities, appreciate the intricacies of compositions, and effectively communicate and perform music with depth and expression.
So, whether you’re learning an instrument, studying music theory, or simply an appreciator of music, the concept of notes is central to your musical journey. Embrace the power of notes, and let them guide you through the vast and awe-inspiring world of music.