Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>What Is The Acronym Music Theory In Education


Music Theory
What Is The Acronym Music Theory In Education
Published: January 31, 2024
Learn the meaning of the acronym "music theory" in education and explore its importance in understanding the principles and elements of music. Gain valuable insights into the world of music theory.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Music Theory
- Music Theory in Education
- Importance of Music Theory in Education
- Curriculum and Content of Music Theory in Education
- Benefits of Incorporating Music Theory in Education
- Challenges and Limitations of Music Theory in Education
- Integrating Music Theory with Practical Music Learning
- Conclusion
Introduction
Music theory is the foundation upon which all musical knowledge and understanding are built. It provides musicians with the tools to analyze, understand, and create music. In the realm of education, music theory plays a crucial role in shaping the musical development of students.
Music theory, in its most basic form, can be defined as the study of the principles and practices of music. It encompasses a wide range of topics, including harmony, melody, rhythm, notation, and structure. By understanding these elements, musicians are able to communicate and express their musical ideas effectively.
In the field of education, music theory is integrated into the curriculum of music programs at various levels, from elementary school to university. It serves as a backbone for learning and performing music, providing students with a solid foundation for musical exploration and expression.
The incorporation of music theory in education is essential for several reasons. First and foremost, it helps students develop a deep understanding of the music they are learning and performing. By studying the structure and inner workings of music, students can appreciate the complexities and nuances that make each piece unique.
Moreover, music theory cultivates critical thinking skills in students. It encourages them to analyze and interpret musical concepts, allowing them to make informed decisions as performers and composers. This analytical thinking extends beyond the realm of music and can be applied to various other disciplines.
Furthermore, music theory aids in the development of aural skills and music literacy. By studying theory, students become proficient in reading and interpreting musical notation, allowing them to sight-read and perform music with greater accuracy and fluency. This not only enhances their performance abilities but also opens up opportunities for collaboration with other musicians.
In the next sections, we will delve deeper into the importance of music theory in education, exploring its role in the curriculum, the benefits it offers to students, and the challenges and limitations educators may encounter when incorporating music theory into their teaching practices.
Definition of Music Theory
Music theory can be defined as the scholarly study of the principles and practices that underpin music. It encompasses a wide range of concepts, including harmony, melody, rhythm, form, notation, and tonality. Through the study of music theory, musicians gain a deeper understanding of how music is constructed, organized, and interpreted.
At its core, music theory seeks to explain and explore the relationships between sounds and their effect on the listener. It aims to provide a framework for understanding why certain combinations of notes create specific emotional responses or convey particular musical ideas.
Music theory is not limited to any specific genre or style of music. It is applicable to all forms of music, from classical to jazz, rock to electronic, and everything in between. While the application and emphasis may vary depending on the genre, the foundational principles of music theory remain constant.
One key aspect of music theory is the study of musical notation. Notation provides a standardized system for representing musical sounds and rhythms on paper. By understanding and interpreting musical notation, musicians can read and perform music accurately, as well as compose and arrange their own musical ideas.
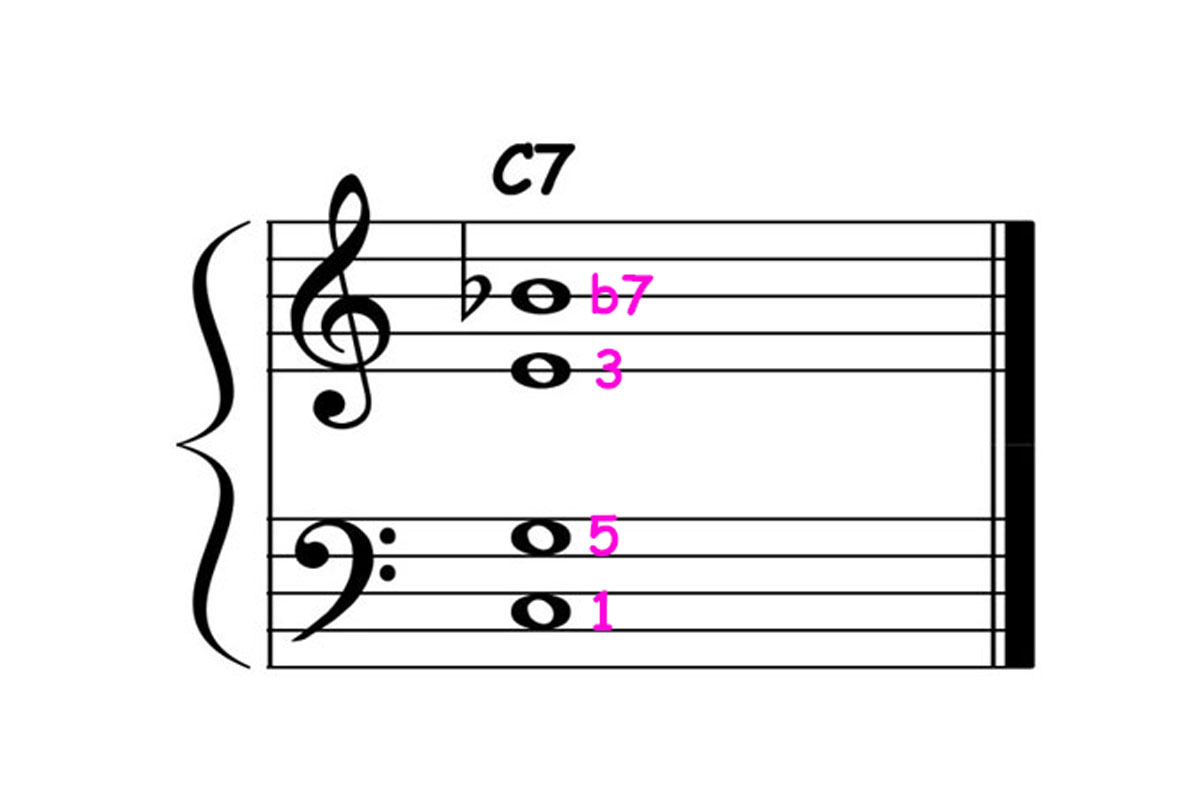
Another important aspect of music theory is the study of harmony. Harmony deals with the simultaneous combination of sounds to create chords and chord progressions. It explores the relationships between notes and the tension and resolution created by different chord progressions.
Melody, rhythm, and form are also integral components of music theory. Melody refers to the sequence of single notes played or sung in a musical piece. Rhythm focuses on the organization and duration of sounds and silences, while form deals with the structure and arrangement of musical ideas within a composition.
Overall, music theory serves as a roadmap for musicians, guiding their understanding and interpretation of music. It provides a vocabulary and conceptual framework for musicians to communicate and collaborate effectively. Whether one is a performer, composer, or music educator, a solid foundation in music theory is essential for a comprehensive understanding and appreciation of music.
Music Theory in Education
Music theory holds a prominent position in music education. It serves as a fundamental component of the curriculum, allowing students to develop a deeper understanding of the music they learn and perform. Music theory is integrated into music education at various levels, from elementary school to university, and plays a vital role in shaping the musical development of students.
In early education, students are introduced to the basics of music theory, such as rhythm, pitch, and notation. They learn to read and interpret musical symbols, understand the concept of beat and meter, and identify basic melodic and harmonic elements. As students progress, they delve deeper into the complexities of music theory, exploring more advanced concepts like chord progressions, scales, modes, and musical analysis.
Music theory is not only taught as a standalone subject but is also integrated into practical music learning. Whether it is through instrumental or vocal instruction, students can apply their knowledge of music theory to enhance their performance abilities. By understanding the underlying structure and patterns in the music they are learning, students can interpret and express the music more effectively.
Furthermore, music theory helps students develop aural skills. Through ear training exercises, students learn to identify and reproduce musical intervals, chords, and melodies. This strengthens their ability to listen critically, which is crucial for accurate pitch recognition and ensemble playing.
Music theory also plays a significant role in music composition and arranging. By understanding the principles of harmony, melody, and form, students can create their own musical compositions and arrangements. They learn to make informed decisions about chord progressions, voicings, and melodic development, resulting in original and compelling musical works.
Moreover, music theory in education fosters critical thinking and analytical skills. Students are encouraged to analyze and interpret music from different periods and genres, identifying patterns, structures, and stylistic elements. This analytical thinking extends beyond music and can be applied to other academic subjects, promoting cognitive development and problem-solving abilities.
Overall, music theory is an essential component of music education. It empowers students to delve deeper into the music they study, providing them with a comprehensive understanding of its structure, form, and expression. By integrating music theory into education, students can develop a stronger musical foundation, enhance their performance abilities, and cultivate a lifelong appreciation for music.
Importance of Music Theory in Education
Music theory holds immense importance in the field of music education. It provides students with the necessary knowledge and skills to understand and interpret music effectively. Here are some key reasons why music theory is essential in education:
- Enhances Musical Understanding: Music theory allows students to delve deeper into the structure and composition of music. By studying concepts such as harmony, melody, rhythm, and form, students gain a comprehensive understanding of how music is created and organized. This understanding enhances their ability to interpret and perform music with greater depth and insight.
- Develops Critical Thinking Skills: The study of music theory encourages students to think analytically and critically. They learn to analyze and interpret musical elements, identify patterns and relationships, and make informed decisions about performance and composition. These critical thinking skills extend beyond music and can be applied to various academic disciplines.
- Builds Aural Skills: Music theory helps in developing students’ aural skills, including their ability to listen, identify, and reproduce musical elements. Through ear training exercises, students become more proficient in recognizing intervals, chords, and melodies, which enhances their performance abilities and overall musicianship.
- Fosters Music Literacy: The study of music theory equips students with the ability to read and interpret musical notation. This literacy in music notation allows them to learn and perform music more efficiently, as well as collaborate with other musicians. It opens up opportunities for engaging with a diverse repertoire of music.
- Encourages Creative Expression: Music theory provides students with the tools and vocabulary to explore their own creative expression. By understanding the principles of harmony, melody, and form, students can compose their own music and arrange existing pieces. This promotes artistic independence and nurtures a lifelong passion for creating music.
- Prepares for Higher-Level Study: For students pursuing higher education or a career in music, a strong foundation in music theory is essential. It provides the groundwork for more advanced studies in music composition, musicology, music theory, and performance. It also prepares students for standardized examinations and auditions.
Overall, music theory plays a crucial role in music education by enhancing students’ musical understanding, developing critical thinking skills, fostering creative expression, and preparing them for further studies and careers in music. It is an integral component of a well-rounded music education curriculum, contributing to the holistic development of students as musicians and individuals.
Curriculum and Content of Music Theory in Education
The curriculum and content of music theory in education vary depending on the level of study and the specific music program. However, there are certain foundational concepts and topics that are typically covered. Here are some key aspects of the curriculum and content of music theory in education:
- Basic Music Foundations: At the elementary level, students are introduced to the fundamental elements of music theory. This includes learning about rhythm, beat, pitch, and basic musical notation. They learn to read and interpret simple melodies and rhythms, as well as understand the concept of major and minor tonality.
- Harmony and Chord Progressions: As students progress, they delve into the study of harmony and chord progressions. They learn about different types of chords, including triads and seventh chords, and how they function within a musical key. Students analyze chord progressions and understand their role in creating musical tension and resolution.
- Scales and Modes: The study of scales and modes forms an important part of music theory education. Students learn major and minor scales, as well as modes such as the Dorian, Phrygian, and Mixolydian modes. They explore the relationship between scales and chords and how they contribute to creating different musical moods and flavors.
- Rhythmic Notation and Meter: Students develop their understanding of rhythmic notation and meter. They learn to read and interpret more complex rhythmic patterns, including syncopation and complex time signatures. They further study concepts such as polyrhythms and metric modulation, expanding their rhythmic vocabulary and abilities.
- Musical Analysis: Analysis is a critical component of music theory. Students learn to analyze musical compositions, identifying formal structures, harmonic progressions, and melodic motifs. They study different musical styles and genres, analyzing the characteristics and techniques used by composers.
- Ear Training: Ear training exercises are an integral part of music theory education. Students develop their aural skills by listening to and identifying intervals, chords, melodies, and rhythmic patterns. They learn to transcribe music by ear, improving their ability to play music accurately and confidently.
- Composition and Arranging: The curriculum often includes opportunities for students to compose and arrange their own music. They apply their understanding of music theory to create original compositions, experimenting with different harmonic progressions, melodic structures, and forms. They also explore arranging existing pieces for various ensembles and instruments.
It is important to note that the depth and progression of these topics may vary based on the educational level and the specific goals of the music program. However, the overarching aim is to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of music theory, enabling them to engage with music more effectively and expressively.
Benefits of Incorporating Music Theory in Education
Incorporating music theory in education offers numerous benefits for students, both in their musical development and overall cognitive growth. Here are some key advantages of integrating music theory into education:
- Enhanced Musical Understanding: By studying music theory, students develop a deeper understanding of the inner workings and structure of music. They learn to recognize patterns, analyze musical compositions, and interpret musical elements, fostering a more profound appreciation for the music they learn and perform.
- Improved Performance Skills: Music theory enhances students’ performance abilities. By understanding the harmonic progressions, melodic contours, and rhythmic patterns in the music they play, students can perform with greater accuracy, expression, and musicality. They develop a stronger sense of phrasing, dynamics, and interpretation.
- Enhanced Aural Skills: Through ear training exercises, students develop their aural skills, including the ability to identify and reproduce musical intervals, chords, and melodies by ear. This improves their ability to listen critically, recognize musical patterns, and play music by ear, contributing to overall musical fluency.
- Promotes Critical Thinking: The study of music theory fosters critical thinking skills in students. They learn to analyze and interpret musical elements, identify patterns and relationships, and make informed decisions about performance and composition. This analytical thinking extends beyond music and can be applied to various academic disciplines.
- Improves Music Literacy: Music theory equips students with the ability to read and interpret musical notation. This literacy in music notation allows them to learn and perform music more efficiently, communicate effectively with other musicians, and broaden their repertoire. It lays the foundation for continued growth in music throughout their lives.
- Encourages Creative Expression: Music theory provides students with the knowledge and tools to explore their creativity in music composition and arrangement. They learn to apply the principles of harmony, melody, and form to create their own musical works, nurturing their individual artistic expression and fostering innovation.
- Connections to Other Disciplines: The study of music theory encompasses various elements of mathematics, physics, and language. Students develop a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships in rhythm and harmony, as well as the physics of sound. Music theory also enhances language skills through the interpretation of musical symbols and terminology.
- Preparation for Higher Musical Studies: For students aspiring to pursue higher-level music studies or careers in music, a strong foundation in music theory is crucial. It provides the necessary groundwork for advanced studies in music theory, composition, musicology, and performance. It also prepares students for standardized examinations and auditions.
Incorporating music theory in education not only cultivates musical skills but also promotes cognitive development, critical thinking, creativity, and a lifelong appreciation of music. It empowers students to engage with music at a deeper level and prepares them for continued growth and success in their musical journeys.
Challenges and Limitations of Music Theory in Education
While the incorporation of music theory in education offers numerous benefits, there are also some challenges and limitations that educators may encounter. It is important to be aware of these factors to ensure effective implementation of music theory in the educational setting:
- Complexity and Abstract Nature: Music theory can be complex and abstract, especially when studying advanced concepts such as advanced harmonic progression or complex rhythmic patterns. This may present a challenge for some students who struggle to grasp these abstract concepts without sufficient guidance and support.
- Perceived Irrelevance: Some students may perceive music theory as disconnected from their actual music-making experiences. They may question the practical relevance of certain theoretical concepts and struggle to see how it applies directly to their performance or composition. Engaging in hands-on and real-life applications of music theory can help address this challenge.
- Balance with Practical Music Learning: Finding the right balance between music theory and practical music learning can be challenging. It is important to ensure that students have ample opportunities to apply their theoretical knowledge to their performance, composition, and improvisation. Integrating theory into practical lessons and activities can help reinforce the connection between theory and practice.
- Time Constraints: The limited amount of time available within the school curriculum may pose a challenge for comprehensive music theory instruction. Teachers may find it difficult to cover all necessary concepts adequately within the constraints of a limited time frame. Integration of music theory into regular music classes and careful selection of essential topics can help address this limitation.
- Varied Learning Paces: Students have different learning paces and levels of prior musical knowledge. Some students may grasp music theory concepts quickly and require more advanced instruction, while others may need more time and support to understand the fundamental principles. Teachers must make efforts to differentiate their instruction to cater to the diverse needs of students.
- Accessibility of Resources: Access to quality music theory resources, textbooks, and technology can be a limitation, particularly for schools with limited budgets or in remote areas. Providing affordable or free resources, leveraging technology, and encouraging collaboration with other institutions or organizations can help overcome this obstacle.
- Perception of Difficulty: Music theory is often perceived as a challenging subject by students who have limited background knowledge or previous exposure. This perception may create a barrier to engagement and motivation. Teachers can employ innovative and interactive teaching techniques, such as gamification or real-world examples, to make the learning process more enjoyable and approachable.
Despite these challenges, it is crucial to overcome the limitations and find creative ways to integrate music theory effectively into music education. By addressing these challenges and adapting instructional approaches, educators can provide a solid foundation of music theory knowledge and skills while ensuring that students see its practical relevance and value in their musical journey.
Integrating Music Theory with Practical Music Learning
Integrating music theory with practical music learning is paramount to ensure a holistic and well-rounded music education. By bridging the gap between theory and practice, students can develop a deeper understanding of music and enhance their performance and composition abilities. Here are some effective strategies for integrating music theory with practical music learning:
- Apply Theory to Performance: Encourage students to apply their theoretical knowledge to their performance repertoire. Analyze the harmonic progressions, identify key modulations, or discuss the formal structure of the pieces they are learning. This deepens their understanding of the music and helps them approach their performance with greater insight.
- Compose and Arrange Music: Engage students in composing and arranging music using the principles they have learned in music theory. This allows them to apply their knowledge of harmony, melody, and form, fostering their creativity and encouraging them to experiment with different musical ideas.
- Improvise with Theory Concepts: Encourage students to improvise using the theoretical concepts they have learned. This can involve creating melodies using specific scales or improvising over chord progressions. It allows students to explore their musicality and develop their improvisational skills while solidifying their understanding of music theory.
- Analysis of Compositions: Analyze and study musical compositions in class, discussing the various elements of music theory present in the piece. This can include examining the chord progressions, identifying melodic motifs, or analyzing the structure of the composition. This analysis develops critical thinking skills and trains students to identify the theoretical components within music.
- Ear Training Exercises: Incorporate ear training exercises into practical lessons. This can involve identifying intervals, chords, or rhythmic patterns by ear. These exercises enhance students’ aural skills, allowing them to recognize and reproduce musical elements accurately, improving their overall musical fluency.
- Collaborative Performances and Composition: Encourage group collaborations where students work together to perform or compose music. This fosters teamwork and communication skills while allowing students to apply their theoretical knowledge in a practical and cooperative setting.
- Real-World Applications: Relate music theory concepts to real-world applications and musical styles that resonate with students. For example, discuss the theory behind popular songs or genres that they enjoy. This helps students see the practical relevance of music theory and sparks their interest and motivation to further explore the subject.
By integrating music theory with practical music learning, teachers can create a dynamic and engaging learning environment. This approach not only enhances students’ understanding of music theory but also strengthens their performance, composition, improvisation, and aural skills. It brings theory to life and demonstrates its practical applications, ultimately deepening students’ musical journey and fostering a lifelong love for music.
Conclusion
Music theory is an integral part of music education, providing students with a deep understanding of the principles and practices that underpin music. By studying music theory, students develop a comprehensive knowledge of harmony, melody, rhythm, form, and notation, enabling them to analyze, interpret, and create music with greater insight and proficiency.
The importance of incorporating music theory in education cannot be understated. It enhances students’ musical understanding, fosters critical thinking skills, improves performance abilities, and promotes creative expression. Furthermore, it prepares students for higher-level musical studies and opens up opportunities for collaboration and musical exploration.
The curriculum and content of music theory in education cover a wide range of topics, from basic music foundations to more advanced concepts such as harmony, scales, and musical analysis. It is vital to strike a balance between theory and practical music learning to create a well-rounded music education experience, where students can apply their theoretical knowledge to their performance, composition, improvisation, and collaborative projects.
However, there are challenges and limitations to consider when integrating music theory into education. These challenges include the complexity and abstract nature of theoretical concepts, time constraints, and varying learning paces among students. It is essential to address these challenges by employing innovative teaching methods, providing accessible resources, and making connections between theory and real-world applications.
In conclusion, incorporating music theory in education has numerous benefits for students. It deepens their musical understanding, develops critical thinking skills, enhances performance abilities, and fosters creative expression. By integrating theory with practical music learning, we create a rich and engaging learning environment that empowers students to become well-rounded musicians with a lifelong appreciation for music.