Home>Production & Technology>Producer>Do I Need To Know How To Play An Instrument To Be A Music Producer


Producer
Do I Need To Know How To Play An Instrument To Be A Music Producer
Published: March 5, 2024
Learn whether playing an instrument is essential for becoming a successful music producer. Discover the skills and knowledge needed to excel in the role of a music producer.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to the world of music production, there's often a lingering question that arises in the minds of aspiring producers: "Do I need to know how to play an instrument to be a successful music producer?" This query is not uncommon, as many individuals are drawn to the art of music production due to their passion for creating and shaping sounds rather than their proficiency in playing traditional instruments.
The role of a music producer is multifaceted, encompassing a diverse range of skills and knowledge. While the ability to play an instrument can undoubtedly be beneficial in this field, it's not necessarily a prerequisite for success. In fact, the landscape of music production has evolved significantly in recent years, with technological advancements enabling individuals to create music using digital audio workstations (DAWs) and software instruments, without the need for traditional instrumental proficiency.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of knowing how to play an instrument in the realm of music production. We'll explore the role of music producers, the importance of understanding music theory, the benefits of possessing instrumental skills, and alternative approaches to music production. By the end of this journey, you'll gain valuable insights into the relationship between instrumental proficiency and music production, empowering you to make informed decisions about your own creative path in the world of music.
The Role of Music Producers
Music producers play a pivotal role in the creation and development of music. They serve as the architects behind the sonic landscapes that captivate audiences and shape the musical experiences of listeners. The responsibilities of a music producer extend far beyond simply playing instruments; they are the masterminds who oversee the entire production process, from conceptualization to the final mix.
One of the primary functions of a music producer is to collaborate with artists to actualize their creative vision. This involves understanding the artist's unique style, musical preferences, and desired emotional impact of the music. By establishing a deep connection with the artist, the producer can effectively guide the recording and arrangement process, ensuring that the final product authentically reflects the artist's intentions.
In addition to artist collaboration, music producers are adept at utilizing various recording techniques, mixing technologies, and sound manipulation tools to achieve the desired sonic quality. They possess a keen ear for detail, enabling them to identify and rectify any sonic imperfections while enhancing the overall audio aesthetics.
Furthermore, music producers are often involved in the selection and arrangement of musical elements, such as instrumentation, vocal performances, and sonic textures. Their expertise in music theory and arrangement allows them to make informed decisions regarding song structure, chord progressions, and harmonic content, thereby elevating the musical composition to new heights.
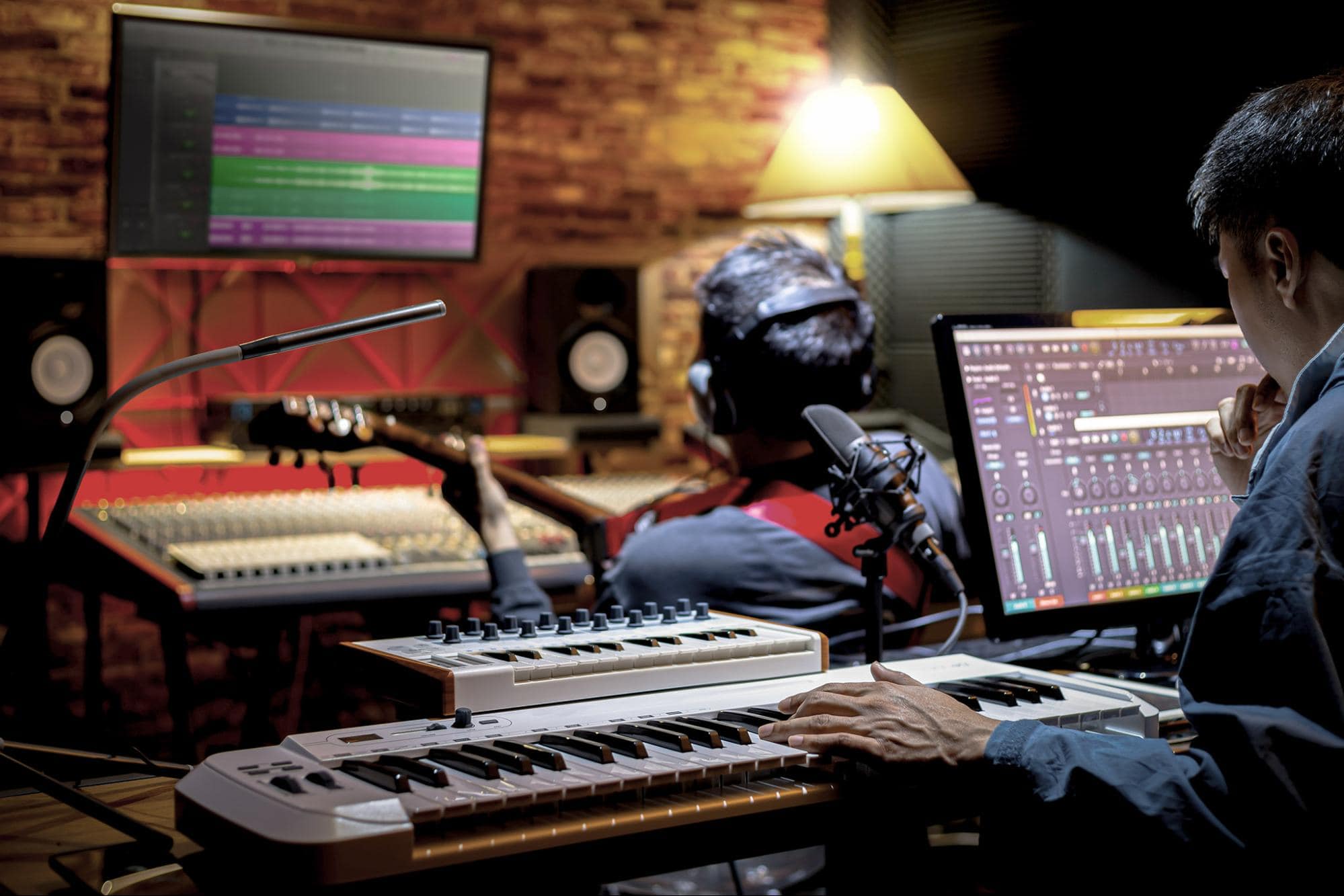
Beyond the creative aspects, music producers also assume managerial and technical roles. They oversee the logistical aspects of the recording process, including scheduling studio sessions, coordinating with session musicians, and managing the budget for the project. Additionally, they are proficient in utilizing state-of-the-art recording equipment and software, ensuring a seamless and efficient production workflow.
Ultimately, the role of a music producer is multifaceted, encompassing artistic, technical, and managerial competencies. They are the driving force behind the transformation of musical ideas into tangible, emotive experiences, and their contributions are integral to the success of any musical endeavor. While instrumental proficiency can be advantageous for a music producer, it is not the sole determinant of their effectiveness in fulfilling this diverse and dynamic role.
Aspiring music producers should recognize that while instrumental skills can enhance their capabilities, the essence of their craft lies in their ability to conceptualize, collaborate, and innovate within the ever-evolving landscape of music production.
Understanding Music Theory
Understanding music theory is a fundamental aspect of music production that transcends the need for instrumental proficiency. Music theory serves as the cornerstone of musical composition, providing producers with a comprehensive framework for understanding the intricacies of melody, harmony, rhythm, and structure. While the ability to play an instrument can certainly facilitate a deeper comprehension of music theory, it is not a prerequisite for acquiring this essential knowledge.
Music theory equips producers with a nuanced understanding of musical elements, enabling them to make informed creative decisions during the production process. By grasping concepts such as chord progressions, scales, and tonal relationships, producers can craft compositions that resonate with listeners on a profound emotional level. Moreover, a solid foundation in music theory empowers producers to experiment with unconventional musical ideas, push creative boundaries, and infuse their productions with a distinctive artistic flair.
In the realm of music production, a strong grasp of music theory fosters effective communication and collaboration with musicians and artists. Producers who understand music theory can articulate their creative vision with clarity, facilitating productive interactions with instrumentalists, vocalists, and arrangers. This shared understanding of musical concepts cultivates a harmonious working environment, where all collaborators are aligned in their pursuit of sonic excellence.
Furthermore, music theory serves as a catalyst for innovation within the production process. Producers who are well-versed in music theory can deconstruct and reinterpret established musical conventions, leading to the creation of groundbreaking and genre-defying compositions. This ability to transcend traditional paradigms and harness the expressive potential of music theory is a hallmark of visionary producers, irrespective of their instrumental proficiency.
In essence, understanding music theory empowers music producers to navigate the intricate tapestry of musical expression with confidence and insight. While the ability to play an instrument can undoubtedly enrich one's understanding of music theory, it is the application of this theoretical knowledge within the context of music production that truly distinguishes exceptional producers. By embracing the principles of music theory, producers can unleash their creative potential, shape compelling musical narratives, and leave an indelible imprint on the fabric of contemporary music.
Benefits of Knowing How to Play an Instrument
The benefits of possessing instrumental proficiency extend far beyond the act of playing a musical instrument; they permeate every facet of the music production journey, enriching the creative process and yielding multifaceted advantages for producers.
First and foremost, instrumental proficiency imbues producers with a profound understanding of musical expression. By intimately engaging with an instrument, producers develop a tactile and intuitive connection to the essence of music, honing their ability to convey emotions and ideas through sound. This heightened musical sensitivity empowers producers to craft compositions that resonate with authenticity and depth, transcending technical prowess to evoke genuine emotional responses from listeners.
Moreover, instrumental proficiency fosters a holistic comprehension of musical arrangements and performance dynamics. Producers who are adept instrumentalists possess an innate grasp of instrumental interplay, dynamics, and tonal nuances, allowing them to orchestrate intricate musical dialogues within their productions. This innate understanding of instrumental intricacies enables producers to guide and collaborate with session musicians effectively, facilitating cohesive and compelling performances that elevate the sonic tapestry of their compositions.
Additionally, instrumental proficiency engenders a versatile and adaptive approach to music production. Producers who can proficiently play an instrument possess the agility to experiment with diverse musical styles, genres, and sonic palettes, seamlessly integrating live instrumentation into their productions. This versatility extends to the realm of arrangement and composition, as instrumental proficiency equips producers with the dexterity to spontaneously explore musical ideas and translate them into captivating compositions in real-time.
Furthermore, instrumental proficiency cultivates a deeper appreciation for the technical and sonic nuances of music production. Producers who are proficient instrumentalists possess an acute awareness of sound articulation, timbre, and performance subtleties, enabling them to meticulously sculpt and refine the sonic characteristics of their productions. This heightened sonic acumen empowers producers to imbue their compositions with a rich and expressive sonic identity, elevating their artistic vision to new heights.
In essence, the benefits of knowing how to play an instrument extend beyond technical proficiency; they encompass a profound enrichment of the creative process, fostering emotional depth, collaborative synergy, artistic versatility, and sonic refinement. While instrumental proficiency is not a prerequisite for success in music production, it undeniably bestows producers with a multifaceted toolkit for crafting evocative, immersive, and timeless musical experiences.
Alternative Approaches to Music Production
In the contemporary landscape of music production, alternative approaches have emerged, redefining the traditional paradigms and expanding the horizons of creative expression. These innovative methodologies embrace technology, unconventional techniques, and diverse sources of inspiration, offering aspiring producers a myriad of pathways to manifest their musical visions.
One prominent alternative approach to music production revolves around the utilization of digital audio workstations (DAWs) and software instruments. These powerful tools empower producers to craft intricate compositions, manipulate sonic textures, and engineer polished mixes entirely within the digital realm. By leveraging the capabilities of DAWs and software instruments, producers can transcend the limitations of physical instrumentation, accessing a vast array of virtual sounds and effects to sculpt their sonic landscapes with precision and ingenuity.
Furthermore, the advent of sampling and sound design has revolutionized the creative possibilities within music production. Producers adept in the art of sampling can extract sonic elements from diverse sources, such as field recordings, vintage vinyl records, and archival audio, repurposing these sonic fragments to construct captivating musical collages. This approach fosters a fusion of disparate sonic textures, genres, and cultural influences, yielding compositions that resonate with eclectic and immersive sonic tapestries.
Another alternative approach to music production involves collaborative experimentation and interdisciplinary fusion. Producers are increasingly exploring interdisciplinary collaborations with visual artists, choreographers, and multimedia creators, integrating sonic elements into immersive multimedia experiences. This convergence of artistic disciplines engenders a symbiotic relationship between sound and visual expression, culminating in multi-sensory productions that transcend conventional artistic boundaries, captivating audiences on a profound and immersive level.
Moreover, the rise of algorithmic composition and generative music systems has ushered in a new era of creative exploration within music production. Producers are harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and algorithmic tools to generate dynamic and evolving musical sequences, blurring the lines between human creativity and computational artistry. This avant-garde approach enables producers to delve into uncharted sonic territories, embracing the serendipitous interplay between human intuition and algorithmic innovation.
In essence, alternative approaches to music production epitomize the boundless creativity and innovation permeating the modern music landscape. By embracing these alternative methodologies, aspiring producers can embark on transformative creative journeys, transcending conventional norms and forging distinctive artistic identities within the ever-evolving tapestry of contemporary music production.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether one needs to know how to play an instrument to be a successful music producer encapsulates a nuanced and multifaceted discourse within the realm of music production. While instrumental proficiency undoubtedly bestows producers with a myriad of advantages, it is not the sole determinant of their creative prowess or potential for success. The role of a music producer transcends instrumental proficiency, encompassing a diverse array of skills, knowledge, and creative acumen that collectively shape the sonic landscapes of contemporary music.
Understanding music theory emerges as a pivotal cornerstone that bridges the gap between instrumental proficiency and music production. A profound grasp of music theory empowers producers to navigate the intricacies of musical composition, harnessing a comprehensive framework for creative expression and innovation. This foundational knowledge serves as a catalyst for collaborative synergy, artistic versatility, and sonic refinement, enabling producers to sculpt compositions that resonate with authenticity and depth.
Furthermore, the benefits of possessing instrumental proficiency extend beyond technical adeptness, permeating every facet of the music production journey. Instrumental proficiency fosters a holistic understanding of musical expression, orchestration, and performance dynamics, enriching the creative process and yielding multifaceted advantages for producers. It imbues producers with a tactile and intuitive connection to the essence of music, enabling them to craft compositions that resonate with genuine emotional depth and authenticity.
Moreover, alternative approaches to music production have redefined traditional paradigms, offering aspiring producers a myriad of pathways to manifest their musical visions. From the utilization of digital audio workstations and sampling techniques to interdisciplinary collaborations and algorithmic innovation, these alternative methodologies epitomize the boundless creativity and innovation permeating the modern music landscape. By embracing these alternative approaches, aspiring producers can embark on transformative creative journeys, transcending conventional norms and forging distinctive artistic identities within the ever-evolving tapestry of contemporary music production.
Ultimately, while instrumental proficiency can undoubtedly enhance the capabilities of a music producer, it is not a prerequisite for success. The essence of music production lies in the ability to conceptualize, collaborate, and innovate within the ever-evolving landscape of music, transcending traditional boundaries and forging new pathways of creative expression. Aspiring music producers are encouraged to embrace a holistic approach to their craft, drawing inspiration from diverse sources, honing their technical and artistic skills, and cultivating a deep understanding of the profound emotional impact of music. In doing so, they can navigate the dynamic terrain of music production with confidence, creativity, and a relentless passion for sonic innovation.