Home>Production & Technology>Sound>What Is DB In Sound


Sound
What Is DB In Sound
Modified: February 18, 2024
Learn about dB in sound and how it affects your hearing. Understand the science behind sound and its importance in everyday life.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Sound is an integral part of our everyday lives. From the melodic tunes of birds chirping to the rhythmic beats of our favorite tunes, sound surrounds us everywhere we go. Yet, have you ever wondered how sound is measured and quantified? That’s where dB, or decibel, comes into the picture.
In the world of audio and acoustics, dB is a term that represents the intensity or loudness of a sound. It is a unit of measurement used to quantify the power or amplitude of sound waves. Understanding how dB works is essential in various industries, including sound engineering, music production, and even communication systems.
In this article, we will delve into the world of dB in sound, exploring its definition, significance, and applications. We will also explore its impact on our hearing and its role in sound systems and audio engineering.
So, let’s embark on this audio adventure as we unravel the mysteries of decibels in sound!
dB: Definition and Explanation
dB, short for decibel, is a logarithmic unit of measurement used to express the relative intensity or loudness of sound. It was named after Alexander Graham Bell, the inventor of the telephone. The decibel scale quantifies the ratio of two sound intensities, making it a convenient way to describe the wide range of sound levels our ears can perceive.
Unlike linear units of measurement, such as meters or seconds, the decibel scale is logarithmic. This means that each increase of 10 dB represents a tenfold increase in sound intensity. So, a sound that measures 70 dB is ten times more intense than a sound that measures 60 dB.
The threshold of human hearing, or the softest sound that the average human ear can detect, is generally regarded as 0 dB. However, it’s important to note that the decibel scale is relative and often used to compare sound levels to a reference point.
dB is not limited to measuring sound. It can also be used to quantify other phenomena, such as electrical signals, power levels, and even seismic activity. However, in the context of this article, we will primarily focus on its application in sound measurement and analysis.
To better understand how dB works in the context of sound, let’s take a closer look at sound waves and how they are measured.
Understanding Sound Waves
To understand how dB is used to measure sound, we must first grasp the concept of sound waves. Sound waves are vibrations that travel through a medium, such as air or water, and are detected by our ears as sound.
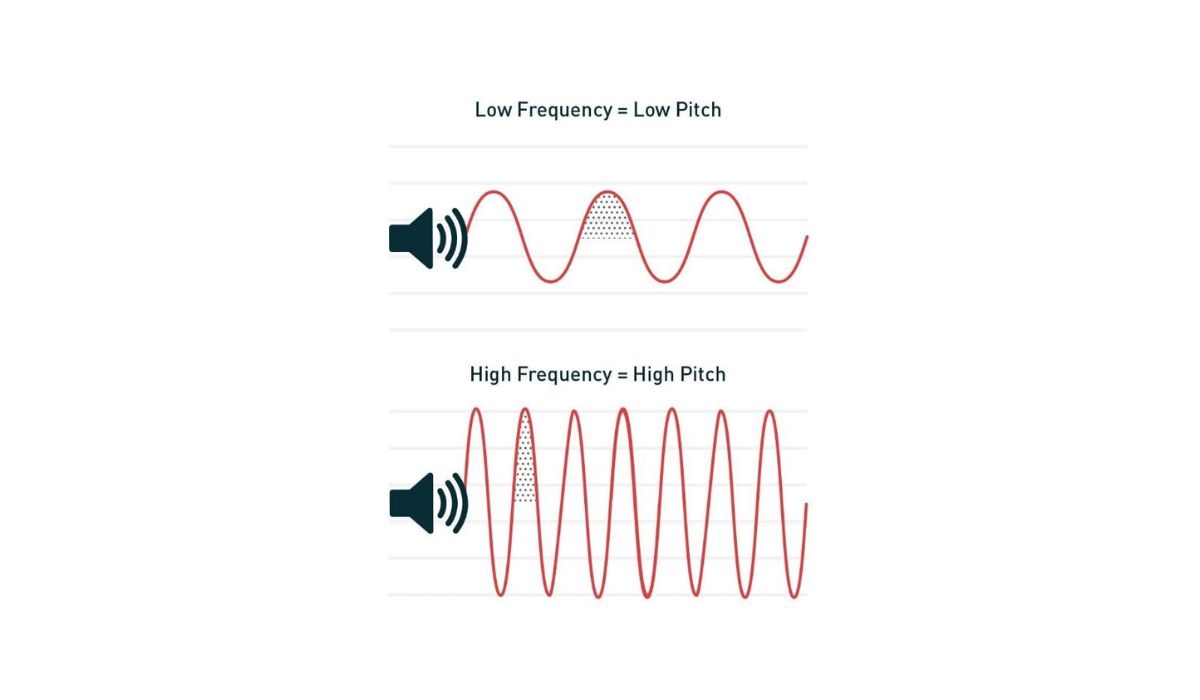
Sound waves are characterized by several properties, including amplitude, frequency, and wavelength. Amplitude refers to the strength or intensity of the sound wave, while frequency refers to the number of cycles or vibrations per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). Wavelength is the distance between two corresponding points on a wave, such as from one peak to the next.
When a sound wave reaches our ears, it causes the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are then transmitted to the inner ear, where they are converted into electrical signals that our brain interprets as sound. Different sound waves with varying frequencies and amplitudes result in different auditory sensations, ranging from soft whispers to thunderous roars.
Measuring sound waves is crucial to understand their properties and potential effects. This is where the decibel scale comes into play, offering a practical way to quantify sound intensity.
Stay tuned as we explore the decibel scale and how it helps measure the intensity of sound in the next section.
Decibel Scale and Measurement
The decibel scale, as mentioned earlier, is a logarithmic scale used to measure the intensity or loudness of sound. It provides a standardized way to express the relative differences in sound levels.
On the decibel scale, 0 dB is often considered the threshold of human hearing. This means that sounds with an intensity below 0 dB are generally too soft for us to perceive. As the intensity of sound increases, the corresponding decibel level also increases.
But how do we measure sound levels in decibels? Sound level meters, or decibel meters, are sophisticated devices used to quantify sound intensity. These meters consist of a microphone that detects sound waves and a circuit that converts the detected signals into dB readings.
When measuring sound levels, it’s important to consider the reference point against which the measurements are made. The most common reference point used in sound measurements is the sound pressure level (SPL) of 20 microPascals (µPa). SPL is a measure of the pressure exerted by the sound wave on a surface and is commonly used as a reference for comparing sound levels.
For example, a typical conversation between two people might measure around 60 dB SPL. A busy street with traffic noise can reach levels of 80 dB SPL. A rock concert or a jet engine can exceed 100 dB SPL. The scale is not linear, so an increase of 10 dB represents a significant change in sound intensity.
It’s important to note that sound perception is subjective, and different individuals may have different sensitivities to sound. Furthermore, the duration of exposure to a certain sound level can also affect its impact on our hearing. This is why sound level regulations and guidelines exist to protect people’s hearing in various environments.
In the next section, we will explore the practical applications of dB in sound and how it impacts our daily lives.
Applications and Uses of dB in Sound
The decibel scale plays a crucial role in various industries and applications related to sound. Let’s explore some of the key uses of dB in sound:
- Sound Engineering and Music Production: In the world of sound engineering and music production, dB is an essential tool. It helps audio engineers and producers measure and control the sound levels during recording, mixing, and mastering processes. dB is also used to adjust the volume levels of individual tracks and instruments to create a balanced and cohesive sound mix.
- Acoustics and Architectural Design: In architectural acoustics, dB is used to evaluate and optimize the sound quality and acoustic performance of buildings, concert halls, auditoriums, and other spaces. By measuring and analyzing sound levels, professionals can make informed decisions regarding the placement of sound-absorbing materials, speaker systems, and room dimensions to enhance the overall sound experience.
- Environmental Noise Monitoring: dB is used to assess and monitor environmental noise in urban areas, industrial zones, and residential neighborhoods. By measuring sound levels, authorities can determine the impact of noise pollution on public health and implement necessary measures to control and mitigate the effects of excessive noise.
- Communication Systems: dB is also utilized in communication systems, such as telecommunication networks and broadcasting. It helps ensure optimal signal-to-noise ratios, which is essential for clear and reliable communication. dB is used to measure and evaluate the performance of antennas, receivers, amplifiers, and other components of communication systems.
- Occupational Noise Exposure: In occupational settings, workers may be exposed to high levels of noise that can potentially damage their hearing. dB measurements are used to assess and monitor noise exposure in workplaces. These measurements help determine if proper hearing protection measures need to be taken to ensure the safety and health of workers.
These are just a few examples of the many applications and uses of dB in the realm of sound. The decibel scale provides a standardized method to quantify sound levels, enabling professionals and researchers to make informed decisions and measurements in various fields.
Next, we will discuss the effect of dB on our hearing and the importance of protecting our ears from excessive noise.
The Effect of dB on Hearing
Exposure to excessive noise levels can have a profound impact on our hearing. The intensity of sound, measured in decibels (dB), plays a crucial role in determining the potential harm to our ears.
Our ears are sensitive, intricate organs that can handle a wide range of sound levels. However, prolonged exposure to high decibel levels can lead to irreversible damage to our hearing. This damage is known as noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL).
The severity of the damage depends on both the intensity of the sound and the duration of exposure. Sounds above 85 dB can become harmful with prolonged exposure. For every 3 dB increase in sound level, the safe exposure time is halved. This means that a sound at 88 dB can be damaging after just 4 hours of exposure, while a sound at 91 dB can be harmful after only 2 hours.
NIHL is cumulative, meaning that repeated exposure to loud sounds over time can result in a gradual loss of hearing. The damage can be permanent, leading to difficulties in communication, reduced quality of life, and an increased risk of developing other health problems.
Protecting our hearing is paramount. The use of hearing protection devices, such as earplugs or earmuffs, is crucial in environments where high sound levels are present, such as construction sites, music venues, or manufacturing facilities. Additionally, following recommended sound limits and taking breaks from noise exposure can help reduce the risk of hearing damage.
By understanding the impact of dB on our hearing, we can take proactive steps to safeguard our auditory health and enjoy a lifetime of good hearing.
Next, let’s explore how dB is utilized in sound systems and the field of audio engineering.
dB in Sound Systems and Audio Engineering
Sound systems and audio engineering heavily rely on the use of decibels (dB) to achieve optimal sound reproduction and balance. Let’s delve into how dB is utilized in these fields.
In sound systems, dB is used to set and control the volume levels of various audio components. This ensures that all elements, such as microphones, instruments, and speakers, work harmoniously together to produce a clear and balanced sound. dB measurements allow audio engineers to accurately assess and adjust the sound levels to achieve the desired impact and fidelity.
Audio mixing and mastering involve meticulous manipulation of sound levels using dB measurements. Engineers carefully sculpt the sound by adjusting the volume levels of individual tracks, applying dynamic range compression, and equalizing the frequency response. dB is used as a reference to achieve a well-balanced mix, with each element occupying its rightful place in the sonic spectrum.
When designing sound systems, dB is crucial in determining the appropriate power amplification and speaker configurations. By understanding the dB sensitivity of speakers, audio engineers can match the power amplifiers to ensure efficient and reliable performance without overloading or distorting the sound.
Additionally, dB is used in audio measurements and analysis. Sound engineers use dB measurements to assess the frequency response of speakers, evaluate the signal-to-noise ratio, and detect potential audio anomalies or problems in recordings.
The decibel scale is also utilized in audio equipment specifications. It indicates the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), dynamic range, and power handling capabilities of audio devices, providing valuable information for audio professionals when selecting and comparing equipment.
Whether it’s live sound reinforcement, studio recording, or mixing for film and television, dB is an indispensable tool in sound systems and audio engineering. It allows for precise control, accurate measurements, and the creation of immersive and captivating sound experiences.
As we conclude this article, we have explored the definition and significance of dB in sound. We discussed its applications, the effect of dB on hearing, and its role in sound systems and audio engineering.
By understanding how dB works and its impact on our auditory world, we can appreciate the importance of sound measurement, protection, and the pursuit of optimal sound quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, decibels (dB) play a vital role in the field of sound and audio. dB is a unit of measurement used to quantify the intensity or loudness of sound waves. It provides a logarithmic scale that allows for the comparison of sound levels over a wide range.
Understanding dB is essential in various industries, such as sound engineering, music production, acoustics, and communication systems. dB measurements help professionals set appropriate volume levels, optimize sound quality, and assess the impact of sound on human hearing.
Excessive exposure to high decibel levels can result in noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). It is imperative to protect our hearing by using proper ear protection and following sound exposure guidelines in different environments.
In sound systems and audio engineering, dB is utilized for volume control, mixing, mastering, and equipment specifications. Audio professionals rely on dB measurements to achieve balanced sound reproduction, evaluate equipment performance, and create immersive sound experiences.
By understanding the concept of dB and its applications, we can appreciate the importance of sound measurement, protection, and the pursuit of optimal sound quality. It enables us to enjoy the beauty of sound while preserving our auditory health.
So next time you listen to your favorite song or attend a live concert, remember that behind the scenes, the world of dB is at work, shaping the way we experience and appreciate the world of sound.