Home>Devices & Equipment>Radio>What Is Single Side Band Radio
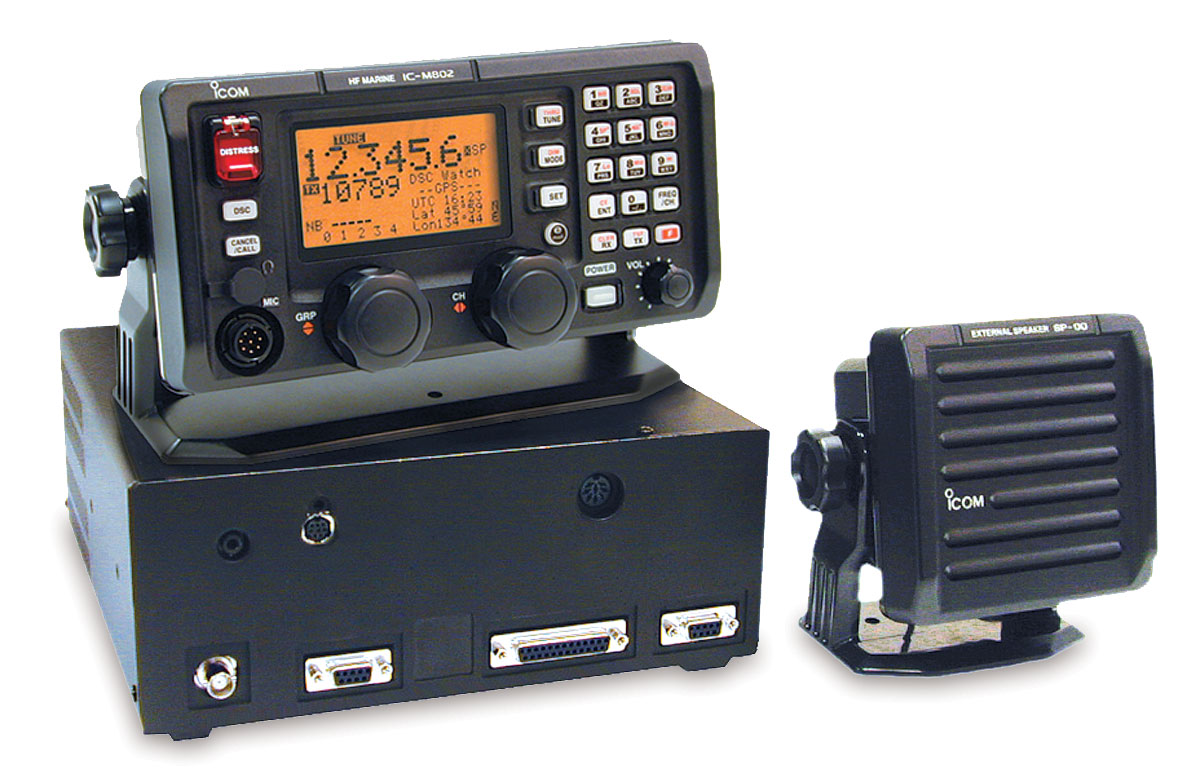


Radio
What Is Single Side Band Radio
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn about single side band radio and its benefits. Explore how this type of radio technology works and how it can enhance your radio communication experience.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Radio has been a vital communication medium for decades, allowing people to stay informed, entertained, and connected across vast distances. One of the key advancements in radio technology is the development of Single Side Band (SSB) radio. This innovative technology has revolutionized long-range communication, particularly in the maritime and aviation industries.
Single Side Band radio, also known as SSB radio, is a modulation technique that allows for efficient transmission of audio signals over long distances. Unlike the traditional Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM) radios, SSB radio eliminates the redundant carrier wave and transmits only the necessary sidebands. This eliminates the need for a wide bandwidth and significantly enhances the range and clarity of communication.
SSB radio has gained popularity and is widely used in various sectors including amateur radio operators, emergency communication services, and long-haul trucking. The simplicity, efficiency, and robustness of SSB technology make it a favored choice for professionals and radio enthusiasts alike.
In this article, we will explore the definition and working principles of Single Side Band radio. We will also discuss its advantages over traditional AM/FM radios, applications in different industries, and the limitations and challenges it presents. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of Single Side Band radio and discover how it has transformed long-range wireless communication.
Definition of Single Side Band (SSB) Radio
Single Side Band (SSB) radio is a modulation technique that allows for efficient transmission of audio signals over long distances. It is a type of radio transmission in which only one sideband of the carrier wave is transmitted, while the other sideband and the carrier itself are suppressed. This results in a more efficient use of bandwidth and improved signal strength.
In traditional Amplitude Modulation (AM) radio, both sidebands (upper and lower) of the carrier wave, as well as the carrier wave itself, are transmitted. This requires a wide bandwidth, making it less efficient for long-range communication. Additionally, the transmission of both sidebands and the carrier wave can result in interference and reduced signal clarity.
On the other hand, SSB radio eliminates the redundant carrier wave and transmits only one sideband, either the upper or lower sideband, depending on the specific mode used. This significantly reduces the necessary bandwidth while maintaining the integrity of the audio signal. The receiver at the other end uses a process called “synthesis” to reconstruct the missing carrier wave and the opposite sideband, resulting in the complete audio signal being received.
It is important to note that SSB radio requires both the transmitter and the receiver to be in synchrony regarding the carrier frequency and the sideband being transmitted. This synchronization is achieved using techniques like phase-locked loops or frequency synthesis methods.
The implementation of SSB radio technology has revolutionized long-range communication, particularly in scenarios where bandwidth efficiency and signal clarity are crucial. This modulation technique has found widespread use in various industries, including maritime communication, aviation, amateur radio, and military applications.
Next, let’s explore how Single Side Band radio works and the principles behind its operation.
How Single Side Band Radio Works
Single Side Band (SSB) radio works by suppressing the carrier wave and one of the sidebands, transmitting only the necessary sideband and allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth. This is achieved through a process called modulation, which involves manipulating the audio signal before transmitting it over the radio waves.
The modulation technique used in SSB radio is called “Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier Modulation” or “SSB-SC.” In this technique, the audio signal is mixed with a high-frequency carrier wave, resulting in a modulated signal. This modulated signal contains the original audio signal encoded as variations in amplitude or frequency, depending on the specific modulation method used.
The crucial step in SSB-SC modulation is the elimination of the carrier wave and one of the sidebands. This is accomplished using a device called a “sideband filter” or “balanced modulator.” The sideband filter allows only one sideband to pass through while suppressing the carrier wave and the other sideband. The selected sideband can be either the upper sideband (USB) or the lower sideband (LSB), depending on the frequency range being used and the specific mode of transmission.
At the receiving end, the SSB signal is demodulated by mixing it with a local oscillator signal of the same frequency. The mixing process removes the carrier wave and the suppressed sideband, leaving only the original audio signal. The reconstructed audio signal is then amplified and played back through a speaker or can be further processed for various applications.
It is worth noting that although SSB radio eliminates the need to transmit the carrier wave and one sideband, it places a higher demand on receiver equipment. The receiver must be capable of accurately synthesizing the missing carrier wave and suppressed sideband in order to reconstruct the complete audio signal. This is achieved using complex mixers, filters, and frequency synthesis techniques that are designed to match the transmitter’s modulation parameters.
Overall, the operation of Single Side Band radio revolves around the efficient modulation and demodulation of the audio signal, eliminating unnecessary components and maximizing bandwidth utilization. This results in increased range, improved signal clarity, and enhanced communication capabilities.
Next, we will explore the advantages of using Single Side Band radio over traditional AM/FM radios.
Advantages of Single Side Band Radio
Single Side Band (SSB) radio offers several advantages over traditional AM/FM radios, making it a preferred choice for long-range communication in various industries. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of using SSB radio:
- Improved Range: SSB radio has a significantly greater range compared to AM/FM radios. By eliminating the carrier wave and one sideband, SSB radio allows for more efficient use of bandwidth. This results in stronger and clearer signals that can travel longer distances, making it ideal for long-range communication, especially in remote or challenging environments.
- Better Signal Clarity: The elimination of the carrier wave and one sideband in SSB radio helps reduce interference and improve signal clarity. This results in a cleaner, distortion-free audio signal, even in situations with weak or noisy reception. It allows for better intelligibility of voice transmissions and enhanced reception of weak signals.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: SSB radio uses a narrower bandwidth compared to AM/FM radios, allowing for more efficient use of available frequency spectrum. This is particularly important in situations where multiple channels need to coexist within a limited frequency range, such as in crowded radio frequency environments or during emergency situations.
- Enhanced Battery Efficiency: SSB radio typically operates at lower power levels compared to AM/FM radios while still maintaining acceptable signal strength. This translates into significant power savings, making it more battery-friendly, especially in portable or mobile applications where power conservation is crucial.
- Cost-effectiveness: SSB radio equipment tends to be more affordable compared to complex and sophisticated AM/FM radios. This makes it an attractive option for individuals, organizations, and industries that require reliable long-range communication on a constrained budget.
These advantages make Single Side Band radio a valuable tool in various industries and applications, including maritime communication, aviation, emergency services, long-haul trucking, amateur radio, and military operations. The efficiency, extended range, and improved signal clarity of SSB radio make it an indispensable technology for reliable long-range communication.
Next, we will explore the diverse applications of Single Side Band radio in different industries.
Applications of Single Side Band Radio
Single Side Band (SSB) radio has found widespread applications in various industries and sectors. Its unique advantages, such as extended range, improved signal clarity, and bandwidth efficiency, make it a valuable tool for reliable long-range communication. Let’s explore some of the key applications of SSB radio:
- Maritime Communication: SSB radio is extensively used in maritime communication, especially for long-distance communication between ships and shore stations. It enables reliable communication over vast stretches of water, allowing for crucial maritime safety and coordination.
- Aviation: SSB radio is widely utilized in aviation, particularly in long-range aircraft communication. It enables pilots and air traffic controllers to maintain clear and reliable communication during extended flights, even over remote or oceanic areas where other forms of communication may be limited.
- Emergency Services: SSB radio plays a vital role in emergency communication services, such as search and rescue operations and disaster response. Its extended range and superior signal clarity make it suitable for effective communication in remote or disaster-stricken areas where other means of communication may be unreliable or unavailable.
- Long-Haul Trucking: SSB radio is commonly used by long-haul truckers to stay connected and informed during their journeys. It allows truck drivers to communicate with each other, coordinate logistics, and obtain real-time information on road conditions and potential hazards.
- Amateur Radio: SSB radio is a popular choice among amateur radio enthusiasts. It provides the opportunity for long-range communication and allows operators to connect with fellow enthusiasts across vast distances, engaging in worldwide conversations and exploring the limits of radio propagation.
- Military Applications: SSB radio has been widely adopted by the military for its long-range and secure communication capabilities. It is utilized in various military operations, including remote deployments, reconnaissance missions, and coordination between ground forces and aircraft.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of Single Side Band radio. Its flexibility, reliability, and efficiency make it suitable for diverse industries and scenarios where long-range communication is essential.
Next, we will compare Single Side Band radio with traditional AM/FM radios to understand their differences and advantages.
Comparison between Single Side Band Radio and AM/FM Radios
Single Side Band (SSB) radio and AM/FM radios are two different technologies used for wireless communication, each with its own characteristics and advantages. Let’s compare these two radio systems:
- Bandwidth Efficiency: SSB radio offers superior bandwidth efficiency compared to AM/FM radios. By transmitting only one sideband and eliminating the carrier wave, SSB radio utilizes a narrower bandwidth, allowing for more efficient use of the available frequency spectrum.
- Range and Signal Clarity: SSB radio generally provides a longer range and better signal clarity compared to AM/FM radios. The elimination of the carrier wave and one sideband results in stronger and clearer signals, reducing interference and improving reception, especially in challenging environments or over long distances.
- Interference and Noise: SSB radio is less susceptible to interference and noise compared to AM/FM radios. The elimination of one sideband and the carrier wave helps reduce unwanted noise and makes the communication channel less prone to external disturbances, resulting in improved signal quality.
- Equipment Complexity: SSB radio equipment is generally simpler and more compact compared to AM/FM radios. This makes it more cost-effective and easier to use, especially in portable or mobile applications where space and simplicity are essential.
- Power Consumption: SSB radios typically consume less power compared to AM/FM radios while maintaining acceptable signal strength. This makes them more energy-efficient, prolonging battery life and making them suitable for remote or off-grid communication needs.
While SSB radio offers several advantages over AM/FM radios, it is important to note that AM/FM radios still have their own strengths and are widely used in various applications. AM/FM radios are generally simpler to operate and more readily available, making them suitable for everyday communication needs in local or regional areas where long-range capabilities may not be required.
Both SSB radio and AM/FM radios have their place in different industries and scenarios, and the choice between them depends on factors such as the required range, signal quality, bandwidth efficiency, and equipment cost.
Next, let’s discuss the limitations and challenges associated with Single Side Band radio.
Limitations and Challenges of Single Side Band Radio
While Single Side Band (SSB) radio offers numerous benefits, it also has its limitations and challenges. Let’s take a closer look at some of these:
- Synchronization: SSB radio requires precise synchronization between the transmitter and receiver regarding the carrier frequency and the sideband being transmitted. Any deviation can result in distorted or unintelligible audio signals, making synchronization a critical factor for successful communication.
- Complex Receiver Design: SSB radio relies on complex receiver designs that are capable of accurately synthesizing the missing carrier wave and suppressed sideband. These receiver designs can be more sophisticated and costly compared to traditional AM/FM receivers, which may pose challenges in terms of availability and affordability.
- Learning Curve: Operating SSB radio may require some learning and familiarity with the modulation technique and the specific equipment being used. Individuals who are not familiar with SSB radio may need to invest time and effort into understanding its operation and optimizing their communication setup.
- Compatibility: SSB radio is not directly compatible with AM/FM radios due to the differences in modulation techniques and bandwidth utilization. This can limit its interoperability with existing radio systems, especially in scenarios where compatibility and integration are essential.
- Noise and Interference: While SSB radio does reduce interference and noise compared to AM/FM radios, it is not entirely immune to external disturbances. In certain situations, such as in crowded radio frequency environments or during adverse weather conditions, noise and interference can still affect SSB radio signals, impacting signal quality and reliability.
Despite these limitations and challenges, the benefits of SSB radio, including extended range, improved signal clarity, and bandwidth efficiency, make it a valuable technology for many industries and applications. With proper knowledge, equipment, and setup, these challenges can be effectively addressed and managed, ensuring reliable long-range communication.
Now, let’s conclude our exploration of Single Side Band radio.
Conclusion
Single Side Band (SSB) radio has revolutionized long-range wireless communication, offering numerous advantages over traditional AM/FM radios. By eliminating the carrier wave and transmitting only one sideband, SSB radio provides extended range, improved signal clarity, and efficient bandwidth utilization.
SSB radio finds applications in various industries, including maritime communication, aviation, emergency services, long-haul trucking, amateur radio, and military operations. Its reliability, robustness, and ability to overcome challenges make it a preferred choice for professionals and radio enthusiasts alike.
Despite its advantages, SSB radio does come with limitations and challenges. Synchronization, complex receiver design, a learning curve, compatibility issues, and vulnerability to noise and interference are factors to consider. However, with the right knowledge, equipment, and setup, these challenges can be overcome to ensure effective and reliable long-range communication.
In conclusion, Single Side Band radio offers a powerful and efficient solution for long-range wireless communication needs. Its range, signal clarity, bandwidth efficiency, and cost-effectiveness make it a valuable tool in various industries where reliable and long-distance communication is essential.
As technology continues to evolve, SSB radio is expected to further improve and adapt to the changing communication landscape. Whether used in maritime operations, aviation, emergency services, or amateur radio, SSB radio continues to play a vital role in connecting individuals and organizations across vast distances.
So, embrace the fascinating world of Single Side Band radio and explore the endless possibilities it offers for seamless and efficient long-range communication.