Home>Devices & Equipment>Subwoofer>What Does An Amp Do For A Subwoofer


Subwoofer
What Does An Amp Do For A Subwoofer
Published: January 22, 2024
Discover how an amp enhances your subwoofer's performance and delivers powerful bass. Learn about the benefits of using an amplifier with your subwoofer to achieve optimal sound quality.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of subwoofers, where deep bass and powerful sound reproduction reign supreme. Whether you are a music aficionado, a movie buff, or simply someone who appreciates a well-balanced audio experience, understanding the role of an amplifier in a subwoofer system is essential. In this article, we will explore the components of a subwoofer system and delve into the importance of an amplifier in enhancing the overall performance of a subwoofer.
When it comes to audio systems, a subwoofer is a specialized speaker that is designed to reproduce low-frequency sounds, commonly referred to as bass. While the main speakers in a system can reproduce a wide range of frequencies, subwoofers excel in producing the deepest and most impactful bass notes that can be felt as much as they are heard.
However, for a subwoofer to deliver its full potential, it requires more than just a speaker cone and enclosure. This is where an amplifier comes into play. An amplifier, also known as an amp, is an electronic device that strengthens the audio signal and provides the necessary power to drive the subwoofer. Without an amplifier, the subwoofer would lack the ability to produce the deep bass that we crave.
The role of an amplifier in a subwoofer system is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it provides power to the subwoofer, allowing it to reproduce low-frequency sounds at high volumes without distortion. The amplifier takes the weak audio signal from the source device, such as a stereo receiver or home theater system, and amplifies it to a level suitable for driving the subwoofer.
In addition to power delivery, the amplifier also plays a significant role in controlling and shaping the sound produced by the subwoofer. Many amplifiers feature adjustable settings, such as crossover frequency, phase control, and equalization, which allow you to fine-tune the subwoofer’s performance to suit your preferences and the acoustic characteristics of your listening environment.
Furthermore, an amplifier can enhance the overall dynamic range and clarity of the bass produced by a subwoofer. By providing clean and precise amplification, it ensures that the subwoofer faithfully reproduces the intricate details and nuances of low-frequency content, adding depth and realism to your audio experience.
Now that we have established the importance of an amplifier in a subwoofer system, let us explore the various components that make up a subwoofer setup in more detail. By understanding the different elements involved, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions when it comes to choosing the right amplifier for your subwoofer.
Components of a Subwoofer System
A subwoofer system consists of several key components that work together to deliver deep bass and immersive sound. Understanding these components will enable you to build a well-rounded subwoofer setup that meets your audio needs. Let’s take a closer look at the essential elements of a subwoofer system:
- Subwoofer: The subwoofer itself is the heart of the system. It is a specialized speaker designed to reproduce low-frequency sounds. Subwoofers come in various sizes and designs, including sealed, ported, and bandpass enclosures, each offering different characteristics and sound qualities.
- Amplifier: As mentioned earlier, the amplifier provides power to the subwoofer. It takes the audio signal from the source device and amplifies it, ensuring that the subwoofer receives enough power to produce impactful bass. Matching the amplifier’s power rating with the subwoofer’s power handling capabilities is crucial to achieve optimal performance.
- Enclosure: The subwoofer is housed in an enclosure, which plays a vital role in shaping its sound. Enclosures can be sealed (also known as acoustic suspension), ported (also known as bass reflex), or bandpass. The choice of enclosure type affects factors such as bass response, transient accuracy, and overall efficiency.
- Crossover: A crossover is a circuitry component that ensures the subwoofer only receives the low-frequency portion of the audio signal, filtering out higher frequencies that are better suited for the main speakers. Crossovers can be built-in to subwoofers and amplifiers or external units that allow for more precise control over the crossover frequencies.
- Source Device: The source device is the audio equipment that provides the audio signal to the subwoofer system. It can be a stereo receiver, home theater system, or other audio devices such as a computer or smartphone. The source device sends the audio signal to the amplifier, which then powers the subwoofer.
- Wiring and Cables: Proper wiring and cables are essential for connecting the subwoofer, amplifier, and source device together. High-quality cables with appropriate gauge sizes ensure a clean and reliable signal transfer, minimizing signal loss and interference.
By understanding these components and their roles within a subwoofer system, you can make informed choices when selecting and configuring your setup. Each component plays a crucial role in delivering the deep bass and immersive sound that subwoofers are known for.
What is an Amplifier?
An amplifier is an electronic device that increases the amplitude or power of an audio signal. It takes a low-level signal from a source device, such as a stereo receiver or audio player, and boosts it to a level suitable for driving speakers or subwoofers. Amplifiers come in various forms, including separate stand-alone units and built-in amplification found in some audio equipment.
The primary function of an amplifier is to provide power to the speakers or subwoofers, enabling them to produce sound at adequate volume levels. Amplifiers work by taking the incoming audio signal and applying additional electrical current to it. This current then drives the speaker or subwoofer’s voice coil, which in turn moves the speaker cone or subwoofer diaphragm, producing sound waves.
Amplifiers are designed to faithfully reproduce the audio signal without introducing distortion or noise. The quality of an amplifier’s design, components, and construction can significantly impact the sound performance. Well-designed amplifiers offer improved clarity, accuracy, and dynamics, allowing for a more enjoyable and immersive audio experience.
Amplifiers are classified by the number of channels they have, which determines the number of speakers or subwoofers they can power. For example, a stereo amplifier has two channels, typically used for powering a pair of speakers, while a mono or monoblock amplifier has a single channel, ideal for driving a subwoofer. Multi-channel amplifiers, such as a 5.1 or 7.1 amplifier, have multiple channels to accommodate surround sound setups.
In addition to power output and channel configuration, amplifiers often offer various features and controls. These can include tone controls, equalizers, adjustable crossover frequencies, and advanced signal processing options. These features allow users to customize and fine-tune the audio reproduction, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility with other audio equipment in the system.
Amplifiers can be classified into different classes, such as Class A, Class AB, and Class D, each with its own advantages and characteristics in terms of efficiency, heat generation, and audio fidelity. Class D amplifiers, for example, are known for their high efficiency and compact size, making them popular for powering subwoofers in car audio systems.
Overall, amplifiers are essential components in audio systems, including subwoofers. They provide the necessary energy to drive speakers and subwoofers, allowing them to produce clear, powerful, and precise sound. Choosing the right amplifier with the appropriate power rating and features is crucial for achieving optimal performance in your subwoofer system.
How Does an Amplifier Enhance a Subwoofer?
An amplifier plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of a subwoofer. It provides several key benefits that significantly improve the overall sound reproduction and impact of the subwoofer. Here are some ways in which an amplifier enhances a subwoofer:
Power Delivery: One of the primary functions of an amplifier is to provide sufficient power to the subwoofer. Subwoofers require more power compared to other speakers due to the lower frequencies they reproduce. By supplying the subwoofer with ample power, the amplifier allows it to produce deep, punchy bass with authority. This ensures that the subwoofer can accurately reproduce low-frequency content without distortion or strain.
Improved Control: Amplifiers provide additional control over the performance of the subwoofer. Many amplifiers feature adjustable settings such as crossover frequency, phase control, and equalization. Crossover frequency settings allow you to determine the frequency at which the subwoofer starts playing, ensuring that it only reproduces the low-frequency content. Phase control helps align the subwoofer’s output with the main speakers, minimizing phase cancellation and optimizing overall sound coherence. Equalization enables you to fine-tune the subwoofer’s frequency response, compensating for room acoustics or personal preferences.
Dynamic Range: Amplifiers with high dynamic range capability can significantly enhance the impact and realism of the subwoofer. Dynamic range refers to the difference between the quietest and loudest sounds in an audio signal. A high-quality amplifier preserves the dynamic range, allowing the subwoofer to accurately reproduce subtle details and powerful bass transients. This results in a more engaging and immersive listening experience, especially when watching movies or listening to music with intricate bass lines.
Signal Clarity: Amplifiers with low distortion levels ensure that the audio signal remains clean and transparent. Distortion can degrade the quality of the sound and introduce unwanted artifacts. A good amplifier minimizes distortion, allowing the subwoofer to faithfully reproduce the original audio signal without any unwanted coloration or degradation in sound quality. This leads to a more accurate and enjoyable listening experience, with punchy and well-defined bass response.
Bass Extension: An amplifier with sufficient power and control capabilities can extend the lower frequency response of a subwoofer. This means that the subwoofer can reproduce deeper bass notes, capturing the full depth and impact of the audio content. This enhanced bass extension adds depth and realism to movie soundtracks and music recordings, creating a more immersive and engaging listening experience.
Overall, an amplifier enhances a subwoofer by providing power, control, and improved sound quality. It ensures that the subwoofer operates optimally, delivering deep, powerful bass that adds a new dimension to your audio experience. Choosing a high-quality amplifier that is compatible with your subwoofer is essential for unlocking its full potential and achieving outstanding bass performance.
Powering the Subwoofer
Properly powering a subwoofer is crucial for achieving optimal performance and ensuring that it can deliver deep, impactful bass. The power requirements of a subwoofer depend on its design, sensitivity rating, and the desired volume levels. Here are some important considerations when it comes to powering a subwoofer:
Power Rating: Subwoofers have different power handling capabilities, which are typically specified in watts (W) or root mean square (RMS) power. This rating indicates the maximum power the subwoofer can handle without getting damaged. It is essential to match the power rating of the subwoofer with the power output of the amplifier to avoid underpowering or overpowering the subwoofer.
Impedance: Subwoofers have impedance ratings, typically 4 ohms or 8 ohms. The amplifier should be able to handle the impedance of the subwoofer. Matching the impedance ensures proper power transfer and avoids potential overloading or distortion. Some amplifiers may offer different impedance settings or multiple outputs to accommodate subwoofers with various impedance ratings.
Power Distribution: If you have a multi-channel amplifier powering both the main speakers and the subwoofer, it’s important to ensure proper power distribution. Most amplifiers provide separate channels for the main speakers and the subwoofer, allowing you to allocate the appropriate power to each component. Adjusting the gain controls or settings on the amplifier can help balance the power distribution and achieve the desired bass level relative to the main speakers.
Amplifier Class: Different amplifier classes have varying power efficiency and heat generation characteristics. Class AB and Class D amplifiers are commonly used for subwoofers. Class AB amplifiers offer a good balance of sound quality and efficiency, while Class D amplifiers are highly efficient and generate less heat. Consider the size of your space, heat dissipation requirements, and energy efficiency when selecting an amplifier class for your subwoofer.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio: A subwoofer amplifier with a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) ensures clean and low-level signal amplification. SNR represents the ratio of the audio signal to background noise and indicates the amplifier’s ability to reproduce the audio signal accurately without introducing unwanted noise or interference.
Wiring and Cable Quality: Using high-quality wiring and cables is crucial for efficient power delivery to the subwoofer. Subpar cables can cause voltage drops and signal loss, resulting in reduced power and degraded audio performance. It is recommended to use cables with appropriate gauge sizes and quality connectors to ensure optimal power transfer and minimal signal degradation.
Properly powering a subwoofer ensures that it operates within its designed capabilities, delivering accurate and powerful bass reproduction. It is important to consider the power rating, impedance, amplifier class, and wiring quality to achieve the best performance and longevity for your subwoofer. Consulting the specifications and recommendations provided by the subwoofer and amplifier manufacturers is essential when setting up and powering your subwoofer system.
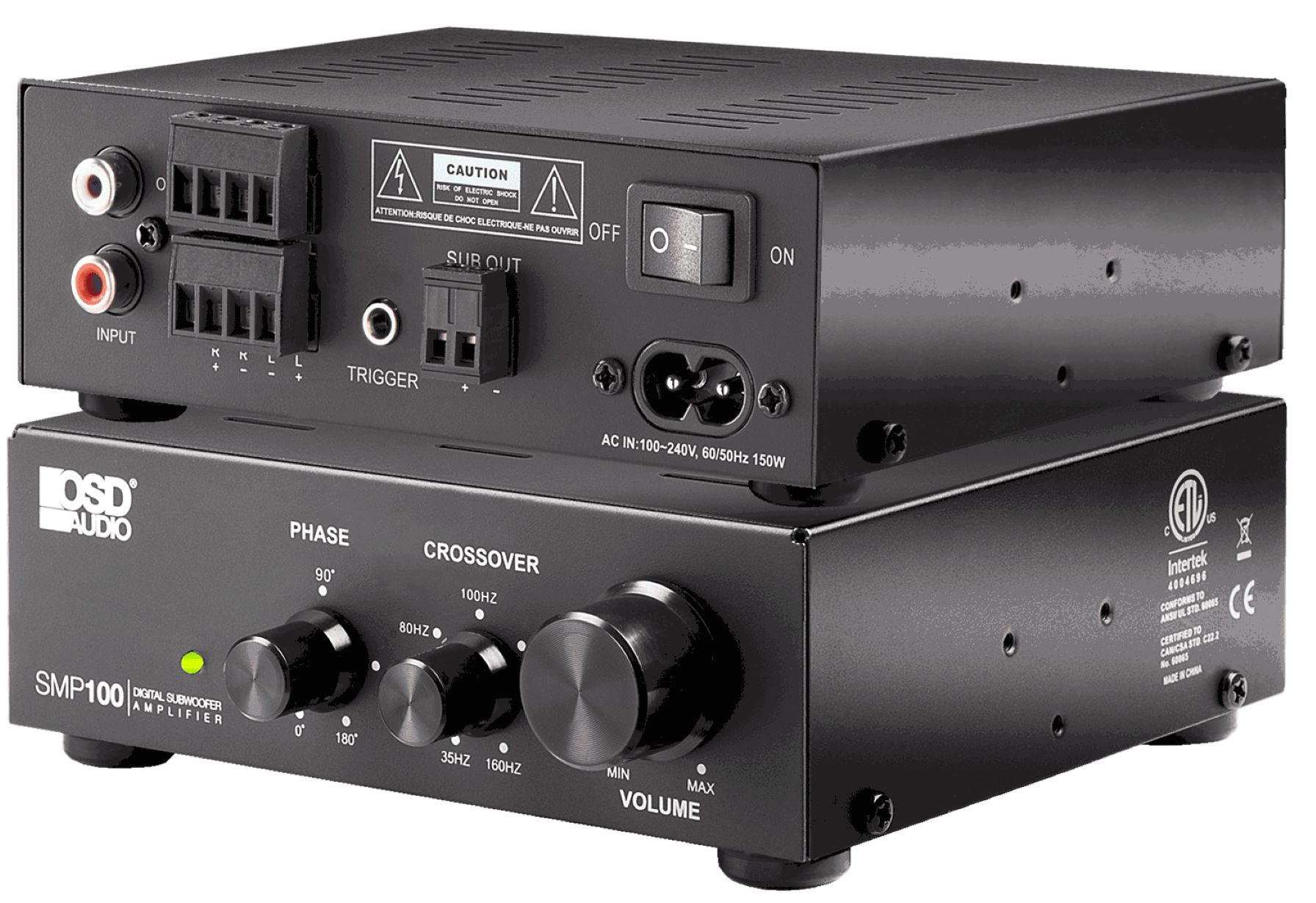
Amplifier Settings for Subwoofers
The settings on your amplifier play a crucial role in optimizing the performance of your subwoofer. Properly configuring the amplifier settings ensures that the subwoofer integrates seamlessly with the rest of your audio system and delivers the deep, impactful bass you desire. Here are some important amplifier settings to consider for your subwoofer:
Crossover Frequency: The crossover frequency setting determines the point at which the subwoofer starts playing and the main speakers take over. This setting is crucial for achieving a smooth transition between the subwoofer and the main speakers, ensuring that each component reproduces its designated frequency range. The crossover frequency can be adjusted on the amplifier or a dedicated crossover unit. Experimenting with different crossover frequencies helps find the optimal balance for your specific audio setup.
Phase Control: The phase control setting determines the alignment of the subwoofer’s sound waves with those of the main speakers. It helps eliminate phase cancellation, which can occur when sound waves from the subwoofer and the main speakers interfere destructively. Adjusting the phase control helps achieve better synchronization between the subwoofer and the main speakers, resulting in improved bass performance and a more seamless audio experience.
Gain Control: The gain control, also known as the volume or level control, adjusts the output level of the subwoofer. It allows you to match the subwoofer’s volume with that of the main speakers, ensuring a balanced and cohesive sound. Start by setting the gain control to a comfortable level and make fine adjustments as needed to achieve the desired bass balance and integration with the rest of the audio system.
Equalization (EQ) Settings: Some amplifiers offer built-in equalization features or provide options for connecting external equalizers. These EQ settings allow you to fine-tune the frequency response of the subwoofer. You can adjust the EQ to compensate for room acoustics, bass anomalies, or personal preferences. Experimentation with the EQ settings can help you achieve the desired bass performance, ensuring that the subwoofer complements the overall sound reproduction of your audio system.
Low-Pass Filter: The low-pass filter is a function that limits the upper frequency range that the subwoofer reproduces. It ensures that the subwoofer only plays the low-frequency content, filtering out higher frequencies that are better suited for the main speakers. Adjusting the low-pass filter helps prevent the subwoofer from reproducing frequencies that it cannot accurately reproduce, optimizing its performance and efficiency.
Bass Boost: Some amplifiers offer a bass boost feature, which amplifies specific bass frequencies. While it may be tempting to use this feature to enhance the bass impact, it is important to use it judiciously. Excessive bass boosting can result in an unbalanced and boomy sound, causing distortion and potentially damaging the subwoofer. It is recommended to use the bass boost sparingly, if at all, and focus on achieving a balanced and natural bass response through proper setup and calibration.
Properly configuring the amplifier settings for your subwoofer ensures that it integrates seamlessly with the rest of your audio system, delivering the deep, impactful bass you desire. Experimenting with different settings, taking into account room acoustics and personal preferences, allows you to achieve the optimal performance and sonic balance for your specific setup.
Choosing the Right Amplifier for Your Subwoofer
Choosing the right amplifier for your subwoofer is crucial to achieving optimal performance and enjoying immersive bass reproduction. The amplifier serves as the powerhouse behind your subwoofer, providing the necessary power and control to unleash deep, impactful bass. Here are some important factors to consider when selecting the right amplifier for your subwoofer:
Power Output: The power output of the amplifier should be matched to the power handling capabilities of your subwoofer. Ensuring that the amplifier provides sufficient power allows the subwoofer to reproduce bass accurately without distortion. It’s important to consider both the RMS power rating and the peak power handling of the subwoofer when selecting the amplifier. The amplifier should be able to deliver enough power to support the subwoofer’s capabilities and provide headroom for dynamic bass passages.
Impedance Matching: It is essential to ensure that the impedance of the amplifier matches the impedance of the subwoofer. Mismatched impedance can result in less power transfer, reduced performance, and potential damage to the amplifier or subwoofer. Check the specifications of both the amplifier and subwoofer to ensure compatibility in terms of impedance. Some amplifiers offer adjustable impedance settings or multiple outputs to accommodate different impedance requirements.
Amplifier Class: Amplifiers come in various classes, such as Class A, Class AB, and Class D, each with its own characteristics in terms of sound quality, efficiency, and heat generation. Class AB amplifiers offer a good balance of sound quality and efficiency, while Class D amplifiers are highly efficient and generate less heat. Consider your priorities in terms of sound quality, power efficiency, and available space when choosing the amplifier class for your subwoofer.
Features and Controls: Evaluate the features and controls offered by the amplifier, such as adjustable crossover frequency, phase control, and equalization options. These features allow you to fine-tune the performance of the subwoofer according to your preferences and the characteristics of your listening environment. Additionally, consider the availability of input and output options, as well as any compatibility requirements with your audio system.
Budget: Set a realistic budget for your amplifier purchase. Amplifiers range in price, and it’s important to find a balance between budget and quality. Consider amplifiers from reputable brands that offer good performance within your budget range. It’s also worth investing in a high-quality amplifier that complements the capabilities of your subwoofer, as this can greatly enhance your overall audio experience.
Reviews and Recommendations: Research and read reviews from audio enthusiasts and experts to gain insights into different amplifier options. Pay attention to feedback regarding reliability, sound quality, and compatibility with subwoofers. Additionally, seek recommendations from professionals or fellow audio enthusiasts who have experience with subwoofer amplification.
By carefully considering the factors mentioned above and taking into account your specific subwoofer’s requirements, you can choose the right amplifier that delivers the power, control, and sonic performance needed to make your subwoofer shine. A well-matched amplifier will enable your subwoofer to produce deep, accurate bass that enhances your music and movie enjoyment.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Using an Amplifier with a Subwoofer
Using an amplifier with a subwoofer can greatly enhance your audio experience, but it’s important to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder performance or potentially damage your equipment. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using an amplifier with a subwoofer:
Inadequate Power: One of the most common mistakes is using an amplifier that does not provide enough power for the subwoofer. Underpowering the subwoofer can result in reduced bass response and distortion, as the amplifier may struggle to drive the subwoofer at higher volume levels. Be sure to match the power rating of the amplifier to the power handling capabilities of your subwoofer to ensure optimal performance.
Incorrect Gain Settings: The gain control on the amplifier determines the output level of the subwoofer. Incorrect gain settings can lead to imbalanced audio or cause the subwoofer to overpower the main speakers. It’s important to properly set the gain level, taking into consideration the desired bass level relative to the main speakers. Making gradual adjustments and using your ears as a guide is crucial for achieving the right balance.
Improper Phase Alignment: Incorrect phase alignment between the subwoofer and the main speakers can result in phase cancellation, leading to weakened bass response. Phase alignment ensures that the sound waves from the subwoofer and the main speakers reinforce each other instead of canceling each other out. Take the time to properly adjust the phase control on your amplifier to achieve optimal alignment and maximize bass impact.
Over-Boosting Bass: While it may be tempting to crank up the bass boost on the amplifier, excessive bass boosting can distort the sound and potentially damage the subwoofer. It’s important to use bass boost sparingly, if at all, and focus on achieving a balanced and natural bass response through proper setup, calibration, and room acoustics adjustments.
Inadequate Wiring and Cables: Using poor-quality wiring or cables can result in signal loss, increased interference, and reduced power delivery to the subwoofer. Ensure that you use high-quality cables with appropriate gauge sizes and connectors to minimize signal degradation and maximize power transfer. Properly connect and secure the cables to prevent any loose connections, which can lead to audio dropouts or noise issues.
Ignoring Room Acoustics: The acoustic properties of your listening room can significantly impact the performance of your subwoofer. Ignoring room acoustics can result in uneven bass response and resonances. Consider using room treatment options such as bass traps or acoustic panels to minimize reflections and standing waves. Additionally, make use of room correction software or equalization settings on your amplifier to compensate for room acoustics and achieve a more accurate and balanced bass response.
Not Following Manufacturer Recommendations: Each amplifier and subwoofer manufacturer may have specific recommendations and guidelines for optimal performance and setup. It’s important to read and follow these instructions to ensure that you use the equipment correctly and avoid any potential issues. Ignoring manufacturer recommendations can lead to subpar performance or even damage to your equipment.
By avoiding these common mistakes and taking the time to properly set up and configure your amplifier with your subwoofer, you can maximize the performance and longevity of your audio system. Paying attention to power, gain settings, phase alignment, and room acoustics will help you achieve the best possible bass reproduction and enjoy a satisfying audio experience.
Conclusion
When it comes to subwoofers, an amplifier is a crucial component for bringing out the best in your audio system. The amplifier provides the necessary power and control to drive the subwoofer, ensuring deep, impactful, and immersive bass reproduction. By properly selecting and configuring the amplifier for your subwoofer, you can enhance your audio experience and enjoy a more balanced and dynamic sound.
Understanding the components of a subwoofer system, such as the subwoofer itself, amplifier, enclosure, crossover, source device, and wiring, is essential for creating a well-rounded setup that delivers impressive bass performance. Taking into account factors like power output, impedance matching, amplifier class, and budget helps you choose the right amplifier for your specific subwoofer requirements.
Properly setting up the amplifier, including adjusting the crossover frequency, phase control, gain, and equalization settings, allows for precise customization and integration with the rest of your audio system. Avoiding common mistakes, such as underpowering the subwoofer, incorrect gain settings, improper phase alignment, over-boosting bass, inadequate wiring, neglecting room acoustics, and ignoring manufacturer recommendations, ensures optimal performance and safeguards your equipment.
By following these guidelines and taking the time to fine-tune your amplifier settings, you can enjoy rich, deep bass that adds a new dimension to your music, movies, and overall audio experience. The right amplifier paired with a quality subwoofer creates a powerful combination that elevates the enjoyment of your favorite media, and leaves a lasting impact with its impressive low-frequency reproduction.
Remember, the subwoofer and amplifier are two pieces of a larger audio puzzle, and when properly chosen and configured, they work in harmony to deliver the immersive and captivating bass that makes the audio experience truly memorable.