Home>Events & Info>Music History>During Which Period In Music History Did George Frideric Handel Contribute?


Music History
During Which Period In Music History Did George Frideric Handel Contribute?
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the musical contributions of George Frideric Handel during the captivating period of Music History. Uncover the profound impact Handel had on the evolution of music during his era.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
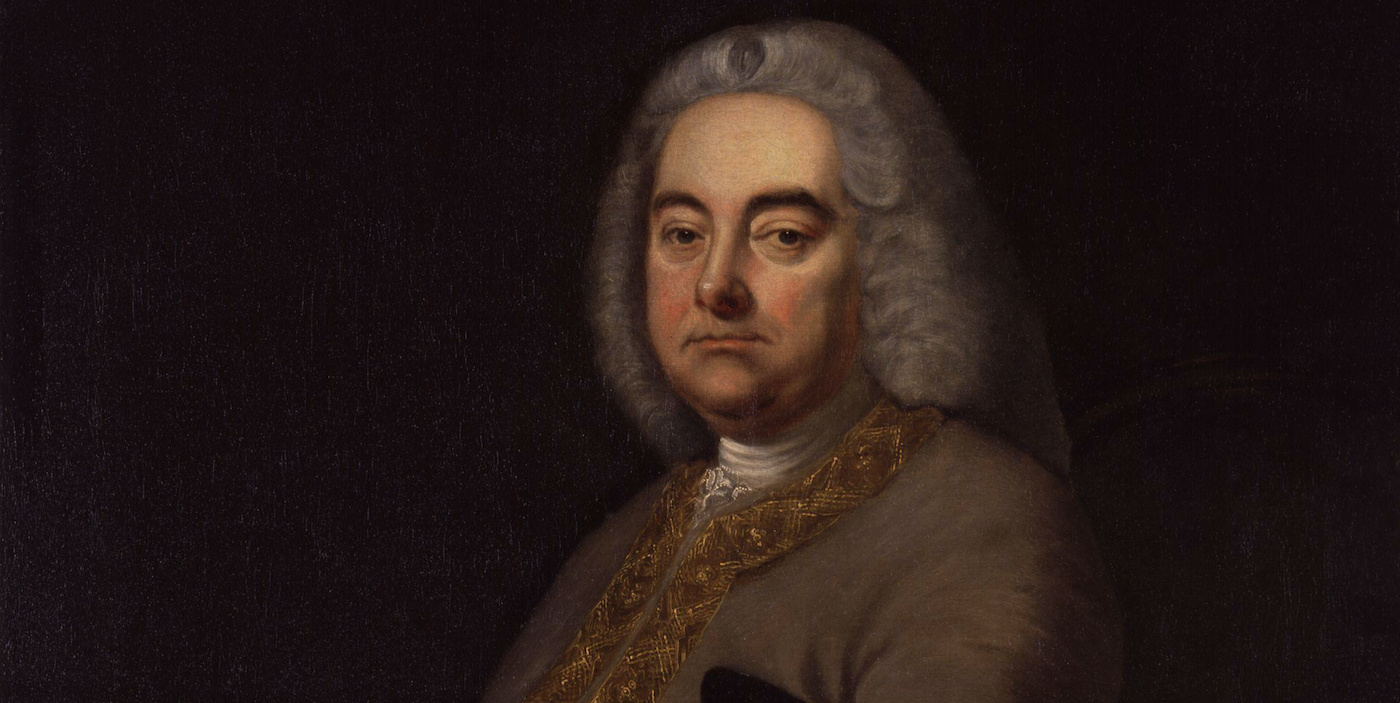
George Frideric Handel is undoubtedly one of the most influential figures in music history. Born in Germany in 1685, Handel contributed significantly to the Baroque period, a time of great artistic innovation and grandeur. His remarkable musical talent and creative genius allowed him to compose a vast array of works, including operas, oratorios, concertos, and chamber music.
Handel’s impact on music history can be seen through his unique contributions to various genres and his ability to captivate audiences with his emotional and expressive compositions. His music continues to be celebrated and performed worldwide, highlighting the enduring power of his artistic legacy.
In this article, we will explore the period in music history during which Handel made his significant contributions. We will delve into his early life and career, his influences, and his journey to becoming one of the most renowned composers of his time. Join us as we unravel the fascinating story behind Handel’s musical achievements and his lasting impact on the world of classical music.
Baroque Period
The Baroque period, spanning from the early 17th century to the mid-18th century, was a time of great artistic and musical development. Characterized by extravagant and elaborate compositions, the Baroque era gave rise to a new style of music that emphasized intricate melodies, ornate ornamentation, and contrasting dynamics.
During the Baroque period, music became more complex and expressive, reflecting the cultural and intellectual shifts of the time. Composers sought to evoke intense emotions and highlight the grandeur of their compositions through distinctive harmonies and rhythmic patterns.
Handel emerged as a prominent figure in the Baroque period, contributing significantly to its musical landscape. His compositions captured the essence of the era, combining elements of drama, virtuosity, and technical brilliance. He played a crucial role in shaping the development of various musical forms, particularly opera and oratorio, leaving a lasting impact on the genre.
Handel’s works during the Baroque period showcase his mastery in crafting intricate melodic lines and utilizing a rich harmonic language. His compositions are known for their grandeur and depth, captivating audiences with their emotional intensity and evocative themes. Handel’s unique blending of musical elements from different cultures and traditions created a distinct musical language that set him apart from his contemporaries.
As we explore Handel’s contributions during the Baroque period, it becomes evident that his music embodies the spirit and artistic essence of the era. His compositions continue to be celebrated for their technical brilliance, emotional depth, and enduring appeal, cementing his status as a true titan of the Baroque period.
Early Life and Career
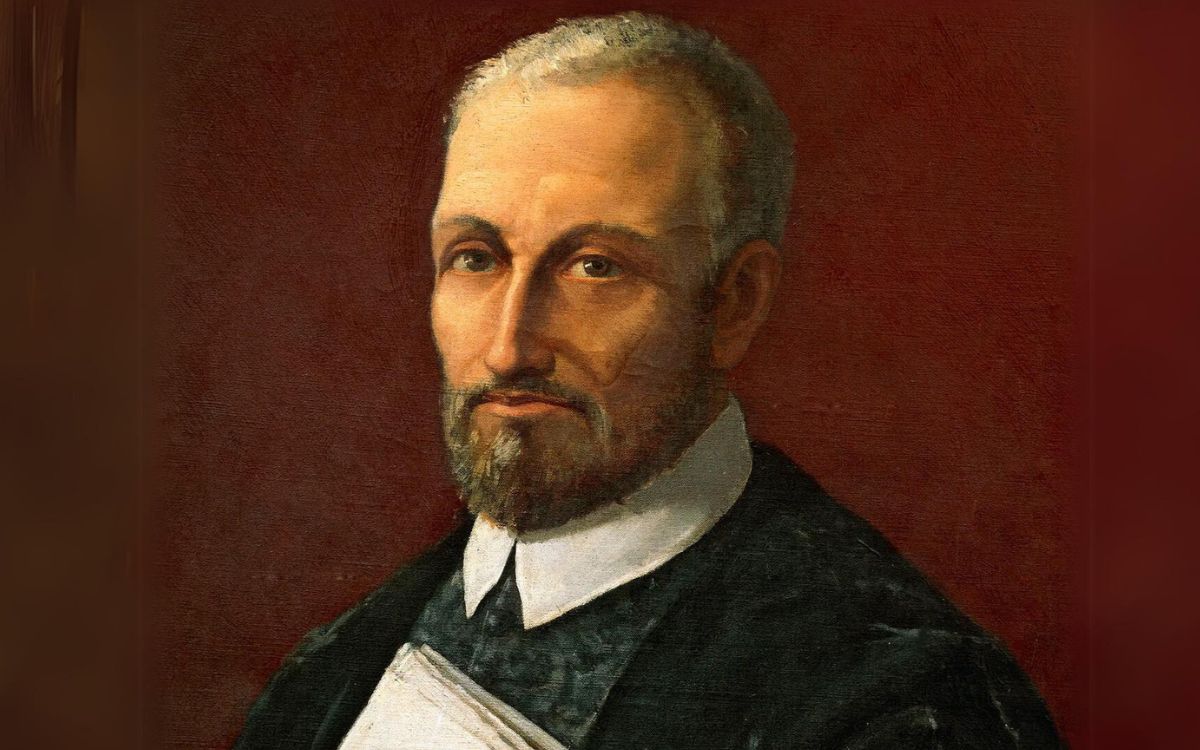
George Frideric Handel was born on February 23, 1685, in Halle, Germany. He displayed prodigious musical talent from a young age, receiving early training in keyboard and composition. Despite his father’s disapproval, Handel pursued his passion for music and eventually moved to Hamburg in 1703 to further his career.
In Hamburg, Handel immersed himself in the vibrant musical scene of the city. He joined the opera house as a violinist and soon began composing his own works. Handel’s early compositions showcased his talent and ingenuity, allowing him to establish a name for himself as a composer of operas and cantatas.
A turning point in Handel’s career came in 1707 when he moved to Italy. This period proved instrumental in shaping his artistic style and solidifying his position as a renowned composer. In Italy, Handel was exposed to the works of great composers such as Vivaldi and Corelli, which had a profound influence on his music.
During his time in Italy, Handel composed numerous operatic works that showcased his mastery of the Italian style. These operas, characterized by their lyrical melodies, expressive vocal writing, and dramatic flair, earned Handel considerable acclaim and brought him recognition as a leading composer.
Handel’s success in Italy laid the foundation for his future career and paved the way for his eventual move to London. His compositions during this period demonstrated his ability to adapt to various musical traditions and incorporate different styles into his own unique musical language.
As Handel ventured into the London music scene, he quickly established himself as a prominent figure. His first opera premiered in 1711, marking the beginning of his prolific career in the English capital. Handel’s ability to compose music that resonated with English audiences, combined with his exceptional skill as a conductor and performer, propelled him to great heights of success.
Handel’s early life and career set the stage for his future achievements and laid the groundwork for his immense contributions to music history. His passion for music, coupled with his unwavering determination and exceptional talent, propelled him towards becoming one of the most revered composers of his time.
Italian Influence
George Frideric Handel’s time in Italy had a profound impact on his musical development and compositional style. During his stay in the country from 1706 to 1710, Handel absorbed the Italian musical tradition and incorporated its influence into his own compositions.
Italy was renowned for its vibrant and sophisticated music scene during the Baroque era, making it an ideal environment for Handel to refine his craft. He immersed himself in the works of Italian composers such as Alessandro Scarlatti and Arcangelo Corelli, whose styles would greatly shape his musical language.
Handel’s exposure to the Italian operatic tradition profoundly influenced his approach to composition. Italian operas were characterized by their lyrical melodies, dramatic storytelling, and elaborate vocal ornamentation. Handel incorporated these elements into his own operatic works, infusing them with emotional depth and expressive virtuosity.
Handel’s time in Italy also allowed him to explore the world of Italian cantatas and oratorios. He composed a significant number of both during his stay, further honing his skills in vocal writing and showcasing his ability to convey deep emotions through music.
One of Handel’s notable Italian works is the opera “Agrippina,” composed during his time in Venice in 1709. It exemplifies his assimilation of the Italian style, with its intricate vocal lines, dramatic plot, and sophisticated orchestration.
Handel’s Italian influence extended beyond his compositional style. He also became well-versed in the intricacies of Italian opera production, serving as a conductor and performer in several operatic productions. This experience provided him with valuable insights into the dramatic and theatrical aspects of opera, which he would later apply to his English operas in London.
Handel’s exposure to the Italian musical tradition had a profound and lasting impact on his development as a composer. The richness and expressiveness of the Italian style infused his music with a distinct sense of passion and emotion, solidifying his place as one of the greatest composers of the Baroque era.
Arrival in London
George Frideric Handel’s arrival in London in 1712 marked a significant turning point in his career and cemented his status as one of the most celebrated composers of his time. Drawn by the thriving music scene and the patronage of the British royal family, Handel made London his home and established a lasting legacy in the city.
Upon his arrival in London, Handel wasted no time in making his mark on the music scene. His first opera, “Rinaldo,” premiered at the Queen’s Theatre in 1711 to great acclaim. The opera’s success served as a launching pad for Handel’s career in the city, solidifying his reputation as a composer of remarkable skill and creativity.
Handel’s compositions during his early years in London demonstrated his ability to adapt to the tastes and preferences of the English audience. He combined elements of the Italian operatic tradition with English musical sensibilities, creating a unique and compelling style that resonated with both aristocratic patrons and the wider public.
Handel’s exceptional talent as a conductor and keyboard player further contributed to his success in London. He established his own opera company, the Royal Academy of Music, and took on the role of music director. His impressive performances and unwavering dedication to his craft earned him the respect and admiration of his peers and audiences alike.
Handel’s influence in London extended beyond the opera house. He also composed numerous instrumental works, including concertos and orchestral suites, which showcased his virtuosity as a composer and performer. These compositions, characterized by their technical brilliance and expressive melodies, further solidified Handel’s reputation as a musical genius.
Furthermore, Handel’s association with the British royal family played a significant role in his success. He became the court composer to Queen Anne in 1714 and later gained the patronage of King George I. These connections provided Handel with substantial financial support and elevated his status as a composer of royal standing.
Handel’s arrival in London marked the beginning of a prolific and transformative period in his career. The city became the backdrop for some of his most celebrated works, including the esteemed oratorio “Messiah.” Handel’s lasting impact on the London music scene solidifies his status as a legendary composer and an integral part of the city’s rich musical heritage.
Operatic Success
George Frideric Handel’s operatic compositions played a pivotal role in his career, garnering him widespread acclaim and establishing his reputation as a leading composer of the Baroque era. His innovative approach to opera, characterized by rich orchestration, expressive vocal writing, and dramatic storytelling, propelled him to great heights of success.
During his time in London, Handel composed a staggering number of operas, mesmerizing audiences with his captivating melodies and dramatic flair. His operas showcased a wide range of styles and themes, from mythological tales to historical dramas.
One of Handel’s greatest operatic successes was “Giulio Cesare” (Julius Caesar), composed in 1724. It remains one of his most beloved and frequently performed operas. “Giulio Cesare” exhibits Handel’s deep understanding of vocal writing and his ability to infuse dramatic emotion into his music.
Handel’s operas were not only renowned for their musical brilliance but also for their theatricality. He incorporated elaborate stage designs, stunning costumes, and inventive choreography to enhance the visual impact of his productions. Handel understood that opera was a collaborative art form, and he worked closely with singers, dancers, and set designers to create truly immersive experiences for his audience.
Despite his success, Handel faced stiff competition from rival opera companies in London. The city was filled with talented composers and performers vying for the spotlight. However, Handel’s ability to craft compelling and memorable melodies, combined with his exceptional skills as an orchestrator, set him apart from his peers.
Handel’s opera productions were grand affairs, attracting aristocrats, intellectuals, and the general public alike. His ability to capture the essence of human emotion through his music and his keen understanding of dramatic pacing made his operas unforgettable experiences for audiences.
However, by the 1730s, Handel faced a decline in interest in Italian opera in London. Sensing the changing tastes of the audience, he shifted his focus to the composition of oratorios, a decision that would eventually lead to his greatest triumph.
Handel’s operatic successes showcased his exceptional talent as a composer and his ability to captivate audiences with his powerful and emotive music. Even today, his operas continue to be celebrated for their beauty, complexity, and enduring allure, cementing Handel’s legacy as one of the greatest composers in the history of opera.
Oratorios and Sacred Music
While George Frideric Handel achieved great success as an opera composer, it is his contributions to the genre of oratorios and sacred music that truly solidified his place in music history. Handel’s oratorios, in particular, stand as monumental works that combine powerful choral writing with emotionally charged solo performances.
During Handel’s time in London, a shift in public interest from opera to religious and sacred music prompted him to explore new avenues of composition. Inspired by the large-scale choral works of his contemporaries, Handel began composing oratorios, which are elaborate musical narratives set to religious, biblical, or historical texts.
One of Handel’s most iconic oratorios is “Messiah.” Composed in just a few weeks in 1741, this masterpiece has become synonymous with Handel’s name and is regarded as one of the greatest works of Western classical music. “Messiah” features stunning choruses, poignant arias, and powerful recitatives that convey the story of the birth, life, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ.
The enduring popularity of “Messiah” and Handel’s other oratorios lies in their ability to deeply resonate with audiences. Handel skillfully combines the grandeur of choral writing with intimate and introspective solo passages, creating a rich tapestry of emotions that capture the essence of the text.
In addition to oratorios, Handel also composed a significant amount of sacred music, including anthems, hymns, and instrumental works for religious services. One of his notable pieces in this genre is the “Coronation Anthems,” composed for the coronation of King George II in 1727. These anthems exemplify his mastery in creating majestic and celebratory music that perfectly complements the grandeur of royal occasions.
Handel’s sacred compositions are known for their expressive harmonies, rich orchestrations, and powerful vocal writing. He seamlessly weaves together the text and music to convey the intended religious message, creating a transcendent musical experience that resonates with listeners of all backgrounds.
Handel’s oratorios and sacred music display his exceptional ability to communicate profound emotions through music. Their enduring popularity and continued performances to this day are a testament to the lasting impact of Handel’s compositions in the realm of religious and sacred music.
Later Years and Legacy
In his later years, George Frideric Handel continued to compose prolifically, leaving an indelible mark on the world of music. Despite facing various challenges and setbacks, Handel’s unwavering passion for his craft and remarkable resilience ensured that his musical legacy would endure for generations to come.
As the popularity of Italian opera waned in London, Handel shifted his focus to the composition of oratorios, which brought him immense success and critical acclaim. His oratorio “Samson,” composed in 1741, showcased his ability to create compelling narrative structures while weaving together melodies that evoked a broad range of emotions.
Another significant work from Handel’s later years is “Israel in Egypt.” This powerful oratorio, composed in 1739, features stunning choruses and vivid musical depictions of Biblical stories, leaving a lasting impact on both audiences and fellow composers.
Handel’s financial struggles in later life led him to establish the tradition of benefit concerts, where the proceeds went to charity. These events not only helped him financially but also solidified his reputation as a generous and philanthropic figure within the music community.
Handel’s later years were marked by declining health, including the loss of his eyesight. Despite this immense challenge, he continued to compose music and even performed in public. His determination and resilience in the face of adversity serve as a testament to his artistic dedication.
George Frideric Handel passed away on April 14, 1759, leaving behind a rich and varied musical legacy. His compositions spanned a wide range of genres, including opera, oratorio, instrumental music, and sacred works. His ability to captivate audiences with his powerful melodies, intricate harmonies, and emotional depth solidifies his place as one of the greatest composers in history.
Handel’s influence on subsequent composers cannot be overstated. His works served as inspiration for composers such as Mozart, Beethoven, and Mendelssohn, who admired his mastery of compositional technique and his ability to evoke profound emotions through music. Handel’s impact also extends beyond the realm of classical music, with his iconic masterpiece, “Messiah,” becoming a beloved part of the holiday tradition.
Today, Handel’s music continues to be performed and cherished worldwide, a testament to its enduring beauty and timeless appeal. His legacy as a trailblazer in the world of music, his dedication to his craft, and his remarkable musical contributions ensure that he will forever be remembered as one of the greatest composers in history.
Conclusion
George Frideric Handel’s contributions to music history are immeasurable. Born during the Baroque period, Handel’s remarkable talent and musical genius allowed him to make significant contributions during a time of artistic innovation and grandeur. His works, spanning various genres including opera, oratorio, and sacred music, continue to captivate audiences worldwide.
Handel’s journey from his early life and career in Germany to his arrival in London marked a transformative period in his musical development. Influenced by the Italian musical tradition, Handel synthesized various styles and techniques to create his own unique musical language.
His operas showcased his ability to infuse dramatic storytelling with beautiful melodies and emotional depth, captivating audiences with their grandeur and innovation. Handel’s later focus on oratorios and sacred music demonstrated his mastery in crafting powerful choral works that remain beloved classics to this day.
Handel’s legacy reaches far beyond his own time. His compositions have left an indelible mark on music history, influencing countless composers who followed in his footsteps. His ability to evoke profound emotions through his music and his unwavering dedication to his craft ensure that his works continue to resonate with listeners of all generations.
Today, performances of Handel’s works, such as “Messiah” and “Water Music,” are cherished events, bringing joy, awe, and inspiration to audiences around the world. Handel’s enduring impact on the music world serves as a testament to his status as one of the greatest composers in history.
As we reflect on Handel’s contributions to music history, we are reminded of the power of music to transcend time and unite people across cultures and generations. His melodies continue to resonate, his harmonies continue to inspire, and his passion for music continues to ignite the hearts of performers and listeners alike.
George Frideric Handel, with his profound musical talents and his ability to shape the course of music history, remains an everlasting figure in the annals of classical music. His enduring legacy is a testament to the remarkable power of music to transcend time and touch the deepest corners of our souls.